Refer to NEET Chemistry Thermodynamics MCQs Set B provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by NEET, NCERT and KVS. Thermodynamics Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Chemistry and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Thermodynamics in Full Syllabus.
Thermodynamics MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: In thermodynamics a process is called reversible when
- a) System and surrounding change into each other
- b) There is no boundary between system and surrounding
- c) The surroundings are always in equilibrium with the system
- d) The system changes into the surroundings spontaneously
Answer: The surroundings are always in equilibrium with the system
Question: The molar heat capacity of water at constant pressur e P is 75 J K–1 mol–1. When 1.0 kJ of heat is supplied to 1000 g of water, which is free to expand, the increase in temperature of water is
- a) 1.2 K
- b) 2.4 K
- c) 4.8 K
- d) 0.24 K
Answer: 0.24 K
Question: 16 kg oxygen gas expands at STP (1 atm) isobarically to occupy double of its original volume. The work done during the process is nearly
- a) 260 kcal
- b) 180 kcal
- c) 130 kcal
- d) 271 kcal
Answer: 271 kcal
Question: The enthalpy and entropy change for a chemical reaction are –2.5 × 103 cal and 7.4 cal K–1 respectively. Predict the nature of reaction at 298 K is
- a) Spontaneous
- b) Reversible
- c) Irreversible
- d) Non-spontaneous
Answer: Spontaneous
Question: The temperature at which the given reaction is at equilibrium
- a) 462.12 K
- b) 362.12 K
- c) 262.12 K
- d) 562.12 K
Answer: 462.12 K
Question: One mole of a non ideal gas undergoes a change of state (2.0 atm, 3.0 L, 95 K) → (4.0 atm, 5.0 L, 245 K) with a change in internal energy ΔU = 30.0 L atm. The change in enthalpy of the process in L atm is
- a) 40.0
- b) 42.3
- c) 44.0
- d) 56.0
Answer: 44.0
Question: In an insulated container water is stirred with a rod to increase the temperature. Which of the following is true?
- a) ΔU = W ≠0, q = 0
- b) ΔU = W = q ≠ 0
- c) ΔU = 0, W = q ≠ 0
- d) W = 0, ΔU = q ≠0
Answer: ΔU = W ≠0, q = 0
Question: Two atoms of hydrogen combine to form a molecule of hydrogen gas the energy of the H2 molecule is
- a) Greater than that of separate atoms
- b) Equal to that of separate atoms
- c) Lower than that of separate atoms
- d) Sometimes lower and sometimes higher
Answer: Lower than that of separate atoms
Question: The temperature of 15 ml of a strong acid increases by 2°C when 15 ml of a strong base is added to it. If 5 ml of each are mixed, temperature should increase by
- a) 0.6°C
- b) 0.3°C
- c) 2°C
- d) 6°C
Answer: 2°C
Question: The standard heat of formation of NO2(g) and N2O4(g) are 8.0 and 4.0 kcal mol–1 respectively. The heat of dimerisation of NO2 in kcal is
- a) –12 kcal
- b) 12 kcal
- c) 4 kcal
- d) 16 kcal
Answer: –12 kcal
Question: If 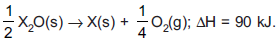 Then heat change during reaction of metal X with one mole of O2 to form oxide to maximum extent is
Then heat change during reaction of metal X with one mole of O2 to form oxide to maximum extent is
- a) 360 kJ
- b) –360 kJ
- c) –180 kJ
- d) +180 kJ
Answer: –360 kJ
Question: For a gaseous reaction :
ΔE is 17 kcal at 27°C. Assuming R = 2 cal K–1 mol–1 the value of ΔH for the above reaction will be
- a) 15.8 kcal
- b) 16.4 kcal
- c) 18.2 kcal
- d) 20.0 kcal
Answer: 18.2 kcal
Question: A mixture of 2 mole of CO and 1 mol of O2 is ignited. Correct relationship is
- a) ΔH = ΔU
- b) ΔH > ΔU
- c) ΔH < ΔU
- d) The relationship depends upon the capacity of vessel
Answer: ΔH < ΔU
Question: Bond dissociation energy of XY, X2 and Y2(all diatomic molecules) are in the ratio of 1 : 1 : 0.5 and ΔHf of XY is –200 kJ mol–1. The bond dissociation energy of X2 will be
- a) 800 kJ mol–1
- b) 200 kJ mol–1
- c) 300 kJ mol–1
- d) 400 kJ mol–1
Answer: 800 kJ mol–1
Question: Vapour density of a gas is 8. Its molecular mass will be
- a) 8
- b) 16
- c) 32
- d) 64
Answer: 16
More Questions...........................................
Question: If x mole of ideal gas at 27°C expands isothermally and reversibly from a volume of y to 10y, then the work done is
- a) w = x R 300 ln y
- b)
- c) w = – 300x R ln 10
- d)
Answer: w = – 300x R ln 10
Question: Enthalpy of formation of NH3 is – X kJ and ΔHH–H, ΔHN–H are respectively Y kJ mol–1 and ΔZ kJ mol–1. The value of ΔHN ≡ N is
- a)
- b) – 3Y + 6Z – 2X
- c) 3Y + 6Z + X
- d) Y + 6X + Z
Answer: – 3Y + 6Z – 2X
Question: A system X undergoes following changes
The overall process may be called as
- a) Reversible process
- b) Cyclic process
- c) Cyclic reversible process
- d) Isochoric process
Answer: Cyclic process
Question: The heat of neutralisation for strong acid and strong base forming 2 moles of water is
- a) – 2 × 57.1 kJ
- b) – 57.1 kJ
- c)
- d) Strong acid and strong base will not undergo neutralisation
Answer: – 2 × 57.1 kJ
Question: The value of ΔH° in kJ for the reaction will be
- a) x + 4y – z – 2r
- b) r + z + 4y – x
- c) 2r + z + 4y + x
- d) x + 4y + z – 2r
Answer: x + 4y + z – 2r
Question: The heat liberated on complete combustion of 1 mole of CH4 gas to CO2 (g) and H2O(l) is 890 kJ. Calculate the heat evolved by 2.4 L of CH4 on complete combustion.
- a) 95.3 kJ
- b) 8900 kJ
- c) 890 kJ
- d) 8.9 kJ
Answer: 95.3 kJ
Question: The work done in an open vessel at 300 K, when 112 g iron reacts with dil HCl to give FeCl2 , is nearly
- a) 1.1 kcal
- b) 0.6 kcal
- c) 0.3 kcal
- d) 0.2 kcal
Answer: 1.1 kcal
Question: Which statement is correct?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) All of these
Answer:
Question: A schematic representation of enthalpy changes for the 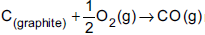 reaction, is given below.
reaction, is given below.
The missing value is
- a) + 10.5 kJ
- b) – 11.05 kJ
- c) – 110.5 kJ
- d) – 10.5 J
Answer: – 110.5 kJ
Question: Which of the following equations represent standard heat of formation of CH4?
- a) C(diamond)+ 2H2(g) → CH4(g)
- b) C(graphite)+ 2H2(g) → CH4(g)
- c) C(diamond)+ 4H(g) → CH4(g)
- d) C(graphite)+ 4H(g) → CH4(g)
Answer: C(graphite)+ 2H2(g) → CH4(g)
Question: Different types of systems are given below
The A and B systems respectively are
- a) Open system, Closed system
- b) Isolated system, Closed system
- c) Adiabatic system, Isolated system
- d) Closed system, Isolated system
Answer: Closed system, Isolated system
Question: Set of intensive properties is shown by
- a) Mole fraction, standard electrode potential, heat capacity
- b) Viscosity, refractive index, specific heat
- c) Density, Gibbs free energy, internal energy
- d) Number of moles, molarity, electrode potential
Answer: Viscosity, refractive index, specific heat
Question: For the expansion occurring from initial to final stage in finite time, which is incorrect?
- a) Equilibrium exist in initial and final stage
- b) Work obtained is maximum
- c) Driving force is much greater than the opposing force
- d) Both (1) & (2)
Answer: Work obtained is maximum
Question: The enthalpy of fusion of water is 1.435 kcal/mol. The molar entropy change for the melting of ice at 0°C is
- a) 5.260 cal/(mol K)
- b) 0.526 cal/(mol K)
- c) 10.52 cal/(mol K)
- d) 21.04 cal/(mol K)
Answer: 5.260 cal/(mol K)
Question: Three moles of an ideal gas expanded spontaneously into vacuum. The work done will be
- a) Infinite
- b) 3 Joules
- c) 9 Joules
- d) Zero
Answer: Zero
Question: Which of the following are not state functions ? (I) q + w (II) q (III) w (IV) H-TS
- a) (II) and (III)
- b) (I) and (IV)
- c) (II), (III) and (IV)
- d) (I), (II) and (III)
Answer: (II) and (III)
Question: Given that bond energies of H–H and Cl – Cl are 430 kJ/mol and 240 kJ/mol respectively and ΔfH of HCl is –90kJ/mol. Bond enthalpy of HCl is
- a) 245 kJ mol–1
- b) 2909 kJ mol–1
- c) 380 kJ mol–1
- d) 425 kJ mol–1
Answer: 425 kJ mol–1
Question: Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction ?
- a) Exothermic and decreasing disorder
- b) Endothermic and increasing disorder
- c) Exothermic and increasing disorder
- d) Endothermic and decreasing disorder
Answer: Exothermic and increasing disorder
Question: Identify the correct statement regarding entropy
- a) At absolute zero of temperature, the entropy of all crystalline substances is taken to be zero
- b) At absolute zero of temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is +ve
- c) At absolute zero of temperature, entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero
- d) At 0°C, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero
Answer: At absolute zero of temperature, entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero
Question: One mole of an ideal gas at 300 K is expanded isothermally from an initial volume of 1 litre to 10 litres. The ΔE for this process is (R = 2 cal. Mol–1K–1)
- a) 1381.1 cal
- b) Zero
- c) 163.7 cal
- d) 9 L atm
Answer: Zero
Question: At 27°C latent heat of fusion of a compound is 2930 J/mol. Entropy change is
- a) 9.77 J/mol·K
- b) 10.77 J/mol·K
- c) 9.07 J/mol·K
- d) 0.977 J/mol·K
Answer: 9.77 J/mol·K
Question: When 1 mol of gas is heated at constant volume temperature is raised from 298 to 308 K. Heat supplied to the gas is 500 J. Then which statement is correct?
- a) q = ΔU = –500 J, w = 0
- b) q = ΔU = 500 J, w = 0
- c) q = w = 500 J, ΔU = 0
- d) ΔU = 0, q = w = –500 J
Answer: q = ΔU = 500 J, w = 0
Question: Enthalpy of 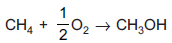 is negative. If enthalpy of combustion of CH4 and CH3OH are x and y respectively. Then which relation is correct?
is negative. If enthalpy of combustion of CH4 and CH3OH are x and y respectively. Then which relation is correct?
- a) x > y
- b) x < y
- c) x = y
- d) x ≥ y
Answer: x > y
Question: Unit of entropy is
- a) JK–1 mol–1
- b) J mol–1
- c) J–1 K–1 mol–1
- d) JK mol–1
Answer: JK–1 mol–1
Question: In a closed insulated container a liquid is stirred with a paddle to increase the temperature which of the following is true?
- a) ΔE = W ≠ 0, q = 0
- b) ΔE = W = q ≠ 0
- c) ΔE = 0, W = q ≠0
- d) W = 0, ΔE = q ≠0
Answer: ΔE = W ≠ 0, q = 0
Question: 2 mole of ideal gas at 27°C temperature is expanded reversibly from 2 lit. to 20 lit. Find entropy change (R =2 cal/mol K)
- a) 92.1
- b) 0
- c) 4
- d) 9.2
Answer: 9.2
Question: What is the entropy change (in JK–1 mol–1) when one mole of ice is converted into water at 0°C? (The enthalpy change for the conversion of ice to liquid water is 6.0 kJ mol–1 at 0°C)
- a) 20.13
- b) 2.013
- c) 2.198
- d) 21.98
Answer: 21.98
Question: The molar heat capacity of water at constant pressure, C, is 75 J K–1 mol–1. When 1.0 kJ of heat is supplied to 100 g of water which is free to expand, the increase in temperature of water is
- a) 1.2 K
- b) 2.4 K
- c) 4.8 K
- d) 6.6 K
Answer: 2.4 K
Question: The work done during the expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atm is (1 L atm = 101.32 J)
- a) –6 J
- b) –608 J
- c) +304 J
- d) –304 J
Answer: –608 J
Question: Three moles of an ideal gas expanded spontaneously into vacuum. The work done will be
- a) Infinite
- b) 3 Joules
- c) 9 Joules
- d) Zero
Answer: Zero
Question: The enthalpy of fusion of water is 1.435 kcal/mol. The molar entropy change for the melting of ice at 0°C is
- a) 5.260 cal/(mol K)
- b) 0.526 cal/(mol K)
- c) 10.52 cal/(mol K)
- d) 21.04 cal/(mol K)
Answer: 5.260 cal/(mol K)
Question: The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is –119.5 kJ mol–1. If resonance energy of benzene is –150.4 kJ mol–1, its enthalpy of hydrogenation would be
- a) –358.5 kJ mol–1
- b) –508.9 kJ mol–1
- c) –208.1 kJ mol–1
- d) –269.9 kJ mol–1
Answer: –208.1 kJ mol–1
Question: The work done during the expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atm is (1 L atm = 101.32 J)
- a) –6 J
- b) –608 J
- c) +304 J
- d) –304 J
Answer: –608 J
Question: The molar heat capacity of water at constant pressure, C, is 75 J K–1 mol–1. When 1.0 kJ of heat is supplied to 100 g of water which is free to expand, the increase in temperature of water is
- a) 1.2 K
- b) 2.4 K
- c) 4.8 K
- d) 6.6 K
Answer: 2.4 K
Question: What is the entropy change (in JK–1 mol–1) when one mole of ice is converted into water at 0°C? (The enthalpy change for the conversion of ice to liquid water is 6.0 kJ mol–1 at 0°C)
- a) 20.13
- b) 2.013
- c) 2.198
- d) 21.98
Answer: 21.98
Question: Heat of combustion for C(s), H2(g) and CH4(g) are –94, –68 and –213 kcal/mol, then ΔH forC(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4(g) is
- a) –17 kcal
- b) –111 kcal
- c) –170 kcal
- d) –85 kcal
Answer: –17 kcal
Question: 2 mole of ideal gas at 27°C temperature is expanded reversibly from 2 lit. to 20 lit. Find entropy change (R =2 cal/mol K)
- a) 92.1
- b) 0
- c) 4
- d) 9.2
Answer: 9.2
Question: For the reaction
,which one is true?
- a) ΔH = ΔE – RT
- b) ΔH = ΔE + RT
- c) ΔH = ΔE + 2RT
- d) ΔH = ΔE – 2RT
Answer: ΔH = ΔE – RT
Question: In the reaction : S + 3/2 O2→ SO3+ 2x kcal and SO2+ 1/2 O2→SO3+ y kcal, the heat of formation of SO2 is
- a) (2x + y)
- b) (x – y)
- c) (x + y)
- d) (y – 2x)
Answer: (y – 2x)
Question:
What is heat of formation of CO?
- a)
- b) 2x – y
- c) y – 2x
- d)
Answer:
Question: For a reaction to occur spontaneously
- a) ΔH must be negative
- b) ΔS must be negative
- c) (ΔH – TΔS) must be negative
- d) (ΔH + TΔS) must be negative
Answer: (ΔH – TΔS) must be negative
Question: Which reaction, with the following values of ΔH, ΔS, at 400 K is spontaneous and endothermic?
- a) ΔH = –48 kJ; ΔS = + 135 J/K
- b) ΔH = –48 kJ; ΔS = – 135 J/K
- c) ΔH = +48 kJ; ΔS = + 135 J/K
- d) ΔH = +48 kJ; ΔS = – 135 J/K
Answer: ΔH = +48 kJ; ΔS = + 135 J/K
Question: Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction ?
- a) Exothermic and decreasing disorder
- b) Endothermic and increasing disorder
- c) Exothermic and increasing disorder
- d) Endothermic and decreasing disorder
Answer: Exothermic and increasing disorder
Question: Three moles of an ideal gas expanded spontaneously into vacuum. The work done will be
- a) Infinite
- b) 3 Joules
- c) 9 Joules
- d) Zero
Answer: Zero
Question: For the gas phase reaction,
which of the following conditions is correct ?
- a) ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
- b) ΔH = 0 and ΔS < 0
- c) ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
- d) ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
Answer: ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
MCQs for Thermodynamics Chemistry Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Chemistry to develop the Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Chemistry will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the NEET MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by NEET for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Thermodynamics MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics

