Important Points
The group of molecules is called matter. Matter is made up of small particles. Matter is in three states, Solid, liquid and gas. The other two states are known as Plasma and Bose, Einstein condensate. The physical state of the matter changes by changing temperature. The physical properties of a subtance are changed by changing its physical state but the chemical properties do not change, sometimes the rate of chemical reaction changes by changing the physical state. During the chemical calculation, it is most essential to have the information about the physical state of substances (reactant or product) and hence it is essential to study the physical state of matter, factors affecting and related some important laws. The deciding factors of the physical state of matter are intermolecular forces, molecular interaction and the effect of thermal energy on the motion of particles.
The Dutch scientist van der Waals suggested that the weak forces of attraction exist between the molecules, which cannot be explained by any other chemical attraction is known as van der Waals attractive forces. This force is universal. This force of attraction is exerted upto 4.5 0Adistance in substance. van der Waals forces depend upon the shape of molecules, number of electrons present in molecules, contact surface of molecules and average intermoleculer distance. The van der Waals forces of attraction are different like (i) Dispersion forces or London forces. (2) Dipole-dipole forces and (3) Dipole-induced dipole forces.
Dispersion forces of attraction was first of all proposed by the German scientist Fritz London so it is known as London forces. This type of force of attraction is observed in atoms or molecules, there is a temporary dispersion in electron density that affect the electron density of nearby atom or molecule so the force of attraction is developed and so such effect is called dispersion force. The dipole-dipole forces are observed in permantently dipolar olecules. Such dipolar molecules also have interactive London forces so the cummulative effect of both forces are observed. The dipole-dipole force is stronger than London forces. The dipole-induced dipole forces are observed when dipolar molecules come near to nonpolar molecules. This type of molecules also have London forces and hence the cumulative effect of both forces are observed. The hydrogen bonding is an important intermolecular force. The first elements of groups 5, 6 and 7 due to their high electronegativity combine with hydrogen to form hydride compounds, in which hydrogen bond is observed. There also exists an intermoleculer repulsive forces; and based on that the effect of pressure on solid, liquid and gaseous state explained very easily. The most important factor which decides the physical, state of matter is the effect of thermal energy, on motion of molecules due to this motion of molecules or atoms the energy produced is called thermal energy to keep the molecules near to each other while the thermal energy has tendency to keep the molecules away from each other. By balancing combination of the two opposite factors, the physical state of matter as solid, liquid or gas is ecided. Due to weak forces of attraction between molecules of gaseous state have some characteristics. The behaviour of gas is described by the quantitative relation between mass, volume, temperature and pressure and these relations are discovered by experimental observations and such relations are called laws of gases. The relation between pressure and volume of a gas was studied and it is known as Boyle’s law. At constant temperature for a fixed amount gas, pressure (P) varies inversely with its volume (V). Mathematically the Boyle’s law is written as PV = K or P1V1 = P2V2. The equation d/P = K devised from Boyle’s law where d is the density. The Kelvin temparature is accepted as an SI unit. The relation T = (t + 273.15) K is obtained. On the basis of experimental observations a relation between absolute temperature and volume is obtained, which is known charles' law. Mathematically it is written as
V/T= K or V1/T2=V1/T2 . The relation between pressure and absoulte temperature (T) is obtained on the basis of experimental orbservations by scientist Gay Lussac and is known as Gay Lussac’s law. Mathematically it is written as P/T= K or P1/T2=P1/T2 . The relation between volume of a gas and number of molecules was given by Avogadro, which is known as Avogadro’s law. The mathematical form of it is V = K . n. The 00C or 273 K temperature and 1 bar pressure is accepted as a standared value by SI system and hence these values are known as standard temperature and pressure (STP). 1 mole of gas at STP is having volume 22.4 litre and number of molecules equal to 6.022 × 1023 known as molar volume and Avogadro’s number respectively. Combining Boyle’s law and Charles’ law, the relation obtainged PV/T=K or P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 is known as combined gas equation. The ideal gas equation, PV = nRT is also known as equation of state and R is called universal gas constant which has different values in different units. The real gas behaves as ideal gas at high temperature and low pressure and are called ideal gases. The behaviour of real gas is deviated from ideal gas and its study came from the study of effect of pressure and temperature and so the ideal gas equation is written as.
M.C.Q.
1. What is value of Boyle’s temperature of ethane gas when a= 5.489 dm6 atm mol-2 and b = 0.0638 dm3 atm mol-1
(a) 1048K (b) 104.8K (c) 209.6K (d)290.6K
2. The value of universal gas constant R depends upon the
(a) Temperature of the gas (b) Volume of the gas
(c) Number moles of the gas (d) none of these
3. The Boyle’s temperature for the ideal gases is given by
(a) a/R (b) a/bR (c) 2a/bR (d) none of these
4. The ratio of van der Waals’ constants a and b has the dimensions of
(a) atm mole-1 (b) L mole-1 (c) atm . L mole-1 (d) atm mole-2
5. A gas expanse through a porons plug and exhibits cooling if its temperature is
(a) More than inversion temperature (b) Less than inversion temperature
(c) Less than critical temperature (d) Less than Boyle’s temperature
6. A gas behaves like an ideal gas at
(a) High pressure and low temperature (b) High pressure and high temperature
(c) At low pressure and increasing in volume (d) Decreasing velocity by lowering temperature


22. 4.0 gm ideal gas is filled in a bulb having volme 10 dm3 at a constant temperature T & constant pressure P. If 0.8 gm gas is removed from the bulb to maintain the original pressure at (T + 125)K temperature, what would be the value of T for a gas having molar mass 40 gm mole-1.
(a) 500K (b) 500°C (c) 773K (d) 773°C
23. What would be vlaue of ratio for RMS and average speed of gaseous molecules at a constant temperature ?
(a) 1.086 : 1 (b) 1 : 1.086 (c) 2 : 1.086 (d) 1.086 : 2
30. Helium gas is compressed to half of the volume at 303 K. It should be heated to which temperature for its volume to increase to double of its original volume ?
(a) 303K (b) 606K (c) 1212K (d) 30°C
31. When a gas is heated from 298K to 323K at a constant pressure of 1 atm its volume is
(a) Increases from V to 1.8 V (b) Increases from V to 1.08 V
(c) Increases from V to 1.5 V (d) Increases from V to 2 V
53. The vapour density of pure ozone would be
(a) 48 (b) 32 (c) 24 (d) 16
54. Equal masses of CH4 and H2 are mixed in an empty container at 25°C. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by H2 is
(a) 1/2 (b) 8/9 (c) 1/9 (d) 16/17
55. The ratio between the root mean square (rms) vlocity of H2 at 50L that of at 800 K is ?
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 1 (d) 1/4
56. A real gas behave more ideally at
(a) Low temperature and low presure (b) Low temperature and high presure
(c) high temperature and low presure (d) high temperature and high presure
57. According to the kinetic theory of gases
(a) The pressure exerted by a gas is proportional to mean square velocity of the molecules.
(b) The pressure exerted by the gas is proportional to the root mean square velocity of the molenles.
(c) The root mean square velocity is invesly proportional to the temperature
(d) The mean transtational K.E of molecule is direlty propostional to the alsolute temperature
58. The value of vander waals constant a for gses O2, N2, NH3 and CH4 are 1.36, 1.39, 4.37 and 2.253 L2 atm mol-1 respectively the gas which can liquefied most easily will be
(a) O2 (b) N2 (c) NH3 (d) CH4
59. A certain sample of a gas volume 0.24Liter measared at 1.0 atm pressure and 273°C its volume will be
(a) 0.4L (b) 0.8L (c) 27.8L (d) 55.6L
60. If a volume containg gas is compressed to half, how many moles of gas remained in the vessel
(a) Just double (b) just half (c) same (d) more than double
61. At constant Volume for a fixed number of a moles of a gas, the pressure of the gas increases with the rise in tempreture due to
(a) Increase in average molecules speed (b) Increase rate of collisions amongst
(c) Increase in molecular attraction (d) Increase in mean free path
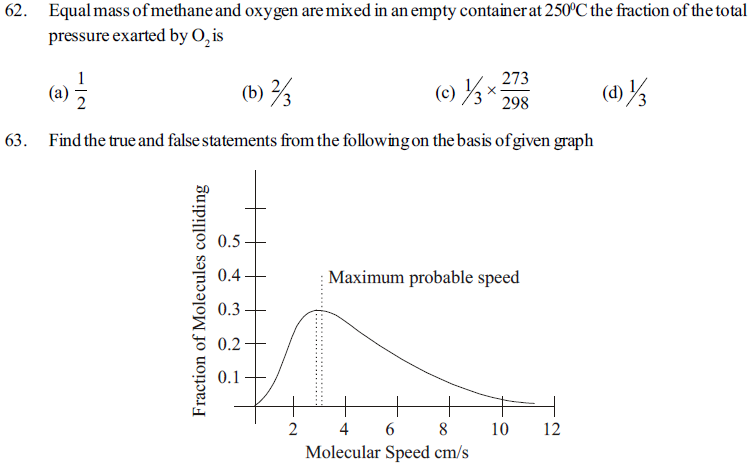
1. Maxwell and Boltz mann had studied the distribution of molecules between different possiblespeeds
2. This graph is known as maxwell’s distribution curve in which kinetic energy and molecular speed of gas is studdied.
3. The fraction molecues with very high or very low speed is very high
4. Inecresing the speed fraction also increasing Which becomes maximum and then deereases.
5. The top portion of curve indicates maximum fraction of molewles and the speed of molecules is called most probable speed which is indicated byµ
6. On increasing temperature the collison of molecules increases and speed of molecules decreases
(a) TTFTTF (b) TFTTFT (c) FTTFFT (d) TTTTFF
64. When a real gas behaves as an ideal gas ?
(a) Inter molecular attraction among molecules are negligible then
(b) At very low pressure and high temperature then
(c) When molecular size is very very small and negligible to the volume of container then
(d) In all the above condition

71. For an ideal gas if pressure is (P), temperature (T) and gas constant is (R) then how many moles of gas will be available in its 10 litre volume ?



85. Which factor is the deciding factor of physical state of matter ?
(a) inter molecular forces (b) molecular interaction
(c) effect of thermal energy on the motion of partcles (d) Given all.
86. Whichphysical state is accuired by water in between temperature above than 273 K and below 373 K?
(a) plasma (b) liquid (c) solid (d) Gas
87. Which physical state of water is more compressable applying pressure at constant temperature ?
(a) Ice (b) water (c) Vapour (d) Plasma
88 Which sabstance can be easily poored form one container into the other at room temperature ?
(a) Kerosene (b) Ice (c) salt (d) all
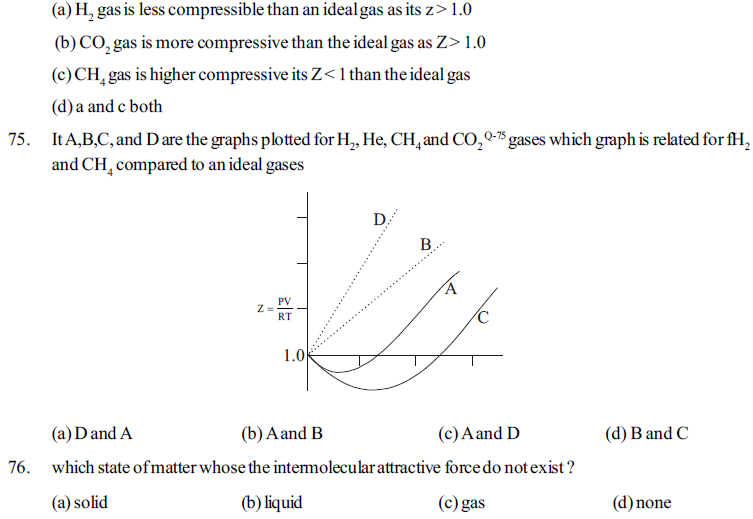
89. Match column I with column II
Column I Column II
i) Gas (a) Easily povred form one container to the other
ii) Liquid (b) difinite shape and fixed volume like a container is acquired
iii) Solid (c) stats to melt at a definite temperature
(d) At constant pressure the increasing in temperature raises Volume effectively
(A) i) - b, ii) - a, iii) - c (B) i) - a, ii) - b, iii) - c
(C) i) - d, ii) - c, iii) - b (D) i) - a, ii) - c, iii) - b
90. Observation on physical state of water at 273K up to 373K are given as below, find the Correct option.
(A) changing the temperature of water above 273K upto 373K, composition of water is changing gradnally.
(B) When temp is changed to rise from 273K on ward the physical state of water changes fom solid - liquid to vapour state.
(C) Heating water at 373K temperture, propotion of hydrogen with oxygen is changed
(D) Molar mass of water decreases with changing its physical states solid - liquid gaseous an raising the temperature
91. What is meant by Bose Einstein condensate ?
[A] It is the specific state of matter
[B] Showing relation E = MC2 for the matter
[C] It is an electronic device developed by Bose and Einstein
[D] It is an energy of radiation
92. Which pheno menon will occur when temperature of the matter is changed ?
[A] Physical state of matter changes.
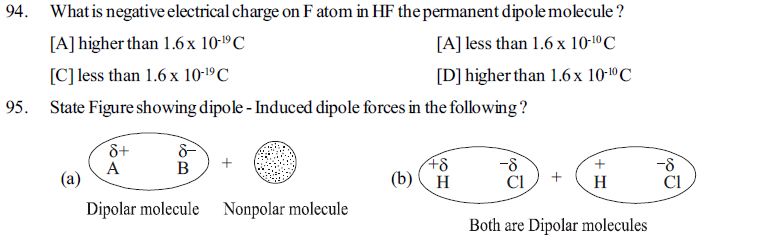
[B] Specific arrangement of molecules in a matter changes
[C] Chemical properties are not chaging but density is changing
[D] Given all
93. Physical state of matter depend on ___
[A] Inter molecular forces which keeps moleules near to eachother
[B] Thermal energy of kinetic molecules which keeps molecules away from eachother
[C] By balncing of combination of two opposite factors is intermolecular forces and thermal energy decide the physical state of matter
[D] Given all
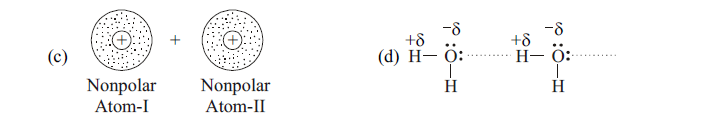
96. HCl polar molecule comes closer to He molecule, which effect of vander waals forces will be created ?
[A] Dipole - induced dipole forces [B] Dipole induced dipole forces with London forces
[C] London forces [D] dipole - dipole forces with London forces
97. Melting point of Rhomic Salphar is higher than phosphorus because ____state
[A] size and number of electrons in Rhombic sulphur is more compared to phosphorus
[B] sulphur S8 has metallic properties while P4 is nonmetal
[C] Inter attratcion forces are lower compared to thermal energy in sulphur than that of in phosphorus
[D] Given all
98. Statement (A) : In liquid state molecules are arranged little for form each other compared to its solid state. hence the effect of pressure is observed in liquid.
Statement (R) : At 293 K temperature and 1000 bar pressure applied on water than the volume reduced by 4%
[A] statement (A) and (R) both correct, statement (R) is the explanation to statement (A)
[B] statement (A) and (R) both correct, statement (R) is not the explanation to statement (A)
[C] statement (A) is correct, statement (R) is wrong
[D] statement (A) is wrong, statement (R) is correct
99. Common physical states and other two physical states of matter are____
[A] plasma, liquid, Gas are common but solid state and Bose Einstein conden sate are spcial.
[B] Bose Einistein condensate and plasma are the other. rtwo states than common physical states gas, liquid and solid.
[C] solid, liquid and Gas states are the only physical states : no other state is included.
[D] Bose Einistein condensate and plasma are the main rules to decided the common physical states solid, liquid and Gas
100. Which statement is correct in the following.
[A] Matter is existing as a individual single moleule
[B] A group of matter is called molecule
[C] a group of moleules is called matter
[D] combination of group of different moleules form the same type of matter
101. Which of the following statements is false
[A] Matter is made of small particles always exist in solid state
[C] matter is solid state possess fixed volume with definite shape
[B] matter of the same substance in liquid state has more volume compared to its solid state
[D] Beyond solid, liquid and gaseous state, two other physical states are also known as plasma and Bose Einistein condensate.
108. 50 ml of a gas A diffuse throught a membrane in the same time as for this diffiusion of 40 ml of a gas B under identical pressure temperature conditions . If the molecular weight of A = 64, that of B would be
(a) 100 (b) 250 (c) 200 (d) 80
109. Which of the following statement is false ?
(a) The product of volume pressure of fixed amound of a gas is independent of temperateure
(b) Molecules of differant gases have the same K.E. at a given temperature
(c) The gas equation is not valid at high pressure and low temperature
(d)The gas costant per moleule is known as Boltzmann Constant.
Read the following paragraph carefully and give correct choice to the option for the questions asked related to the paragraph
In the following given figure three glass containers X, Y, and Z are connected by values 1 and 2 having negligible volume at 300K abd 1.0 atmosphere pressure.
When values 1 and 2 are closed, container X contains H2 gas at 8.2 atmosphere pressure in volume 6.0 litre, container Y contains N2 gas at 1.64 atm pressure in 10 litre volume, and container Z is evacurated with pressure Zero atmosphere
external pressure = 1.0 atm, temperature = 300 K
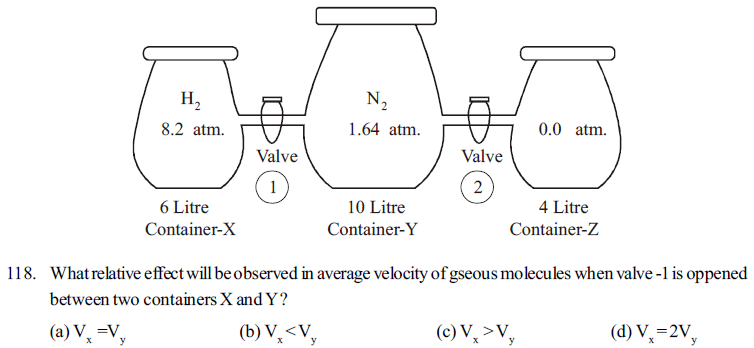
119. What pressure will be exerted in container X when valve -1 is opened
(a) 4.1 atm (b) 8.2 atm (c) 2.05 atm (d) 3.84 atm
120. Keeping valve -1 closed, on opening valve 2 between container Z and Y, on expansion of gas how much work will be done by process ?
(a) 1.0 litre atm (b) 14 - litre atm (c) -14.0 litre atm (d) zero
121. Opening valve 1 and 2 , on connecting all the three X,Y,Z containers with each other, What would be the kineti cenergy of all. gaseous molecules ? (R = 0.082 litre atm /mol.K = 8.314 J/molk)
(a) 6842 J (b) 9974 J (c) 4988 J (d) 3832 J
122. Connecting all the three containers by opening valves 1 and 2, if internal pressure of containers are obtained 1.0 atmosphere by lowering temperature of the system, what would be the contribution of partical pressure of H2 gas and N2 gas respectively ?
(a) 0.85 atm, 0.15 atm (b) 0.15atm, 0.85 atm
(c) 0.75 atm, 0.25 atm (d) 0.25 atm, 0.75 atm
Paragraph - 2
The gases which do not obey general gas equation at all tempratures and pressures are called non ideal or real gases . But such gases show ideal behaviour at low pressure and high temperatures.
According to vander waals, the following are two faulty assumptions in kinetic theroy of gases.
(1) molecules of gas zero consideraed as point masses and the volume occupied by the gas motecules is neglihigible in comparison to the total volume of gas.
(2) It was also assumed that there are no intermolecular attractive forces and the molecules of gas move independently.
Hence the vanderwaals equation for non- ideal (real) gases becomes
Passage
A gas Undergoes dissociation as M4 (q) → M g in a closed rigid container having volume 22.4L at 273K If the initialmoles of M4 taken befor dissoliciation is 1 then.
132. The total pressure (in attm) after 50% completion of the reaction assuning ideal behaviour is
(a) 0.5 (b) 2.5 (c) 2.8 (d) 3.8
133. If the gases are not ideal at the begining total pressure observed is less than 1 atm then
134. If the gases are not ideal and after 100 % dissociation total pressure is greater than 4 atm, then
(a) Compressing of M(q) is easiq then an ideal gas
(b) The compression of M(q) is difficult than an ideal gas
(c) The compression of m(g) is the same as an ideal gas
(d) A gas is non compressible
ANSWER KEY

