Refer to NEET Chemistry Thermodynamics MCQs Set A provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by NEET, NCERT and KVS. Thermodynamics Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Chemistry and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Thermodynamics in Full Syllabus.
Thermodynamics MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: Tea placed in thermos flask is an example of
- a) Open system
- b) Close system
- c) Isolated system
- d) It can't act as system
Answer: Isolated system
Question: Gaseous system is placed with pressure P1, volume V1 and temperature T1 , it has undergone thermodynamic changes where temperature is remaining constant, it is
- a) Adiabatic process
- b) Isothermal process
- c) Isobaric process
- d) Isochoric process
Answer: Isothermal process
Question: The respective examples of extensive and intensive properties are
- a) Enthalpy, Entropy
- b) Entropy, Enthalpy
- c) Entropy, Temperature
- d) Temperature, Entropy
Answer: Entropy, Temperature
Question: A thermally isolated, gaseous system can exchange energy with the surroundings. The mode of energy may be
- a) Heat
- b) Work
- c) Heat and radiation
- d) Internal energy
Answer: Work
Question: Which of the following is a state function?
- a) q
- b) w
- c) q + w
- d) All of these
Answer: q + w
Question: For the reaction 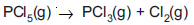
- a) ΔH = ΔE
- b) ΔH >ΔE
- c) ΔH < ΔE
- d) Can’t predicted
Answer: ΔH >ΔE
Question: If ‘r’ is the work done on the system and ‘s’ is heat evolved by the system then,
- a) ΔE = r + s
- b) ΔE = r – s
- c) ΔE = r
- d) ΔE = s
Answer: ΔE = r – s
Question: For the reaction,
Then
- a) ΔH – ΔE = (b – d) RT
- b) ΔH – ΔE = (c – b) RT
- c) ΔH – ΔE = (a + b) – (c + d) RT
- d) ΔH –ΔE = (a – d) RT
Answer: ΔH – ΔE = (c – b) RT
Question: A system absorbs 10 kJ of heat and does 4 kJ of work. The internal energy of the system
- a) Decreases by 6 kJ
- b) Increases by 6 kJ
- c) Decreases by 14 kJ
- d) Increases by 14 kJ
Answer: Increases by 6 kJ
Question: In a reaction, all reactant and products are liquid, then
- a) ΔH > ΔE
- b) ΔH < ΔE
- c) ΔH = ΔE
- d) Can't predicted
Answer: ΔH = ΔE
Question: Regarding the internal energy of the molecule, which of the following statement is correct?
- a) Its absolute value can be successfully calculated
- b) Its absolute value cannot be determined
- c) It is the sum of vibrational and rotational energies
- d) Both (1) & (3)
Answer: Its absolute value cannot be determined
Question: Consider the following reaction :
What is the heat of transition of graphite into diamond?
- a) x1+ x2
- b) x2– x1
- c) x1– x2
- d) x1x2
Answer: x2– x1
Question: For the given reactions,  Steps involved are
Steps involved are
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The heats of combustion of yellow P and red P are –9.91kJ and –8.78kJ respectively. The heat of transition of yellow to red phosphorus is
- a) –18.69 kJ
- b) +1.13 kJ
- c) +18.69 kJ
- d) –1.13 kJ
Answer: –1.13 kJ
Question: If the heat of formation of NO2 is ‘x’
- a) 2x + z = y
- b) 2y + z = x
- c) 2x – z = y
- d) 2z + x = y
Answer: 2x – z = y
Question: In the reactions
- a) x = y
- b) x = 2y
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: ΔHfC2H4= 12.5 kcal
Heat of atomisation of C = 171 kcal
Bond energy of H2= 104.3 kcal
Bond energy C – H = 99.3 kcal
What is C = C bond energy?
- a) 140.7 kcal
- b) 49 kcal
- c) 40 kcal
- d) 76 kcal
Answer: 140.7 kcal
Question: The difference between ΔH and ΔE for the reaction
2C6H6(l) +15O2(g) → 12CO2(g) + 6H2O (l) at 25°C in kJ is
- a) –7.43 kJ
- b) +3.72 kJ
- c) –3.72 kJ
- d) +7.43 kJ
Answer: –7.43 kJ
Question:
The above data can predict that
- a) Rhombic sulphur is yellow in colour
- b) Monoclinic sulphur has metallic lustre
- c) Monoclinic sulphur is more stable
- d) ΔH(Transition) of S(R) to S(M) is endothermic process
Answer: ΔH(Transition)of S(R) to S(M) is endothermic process
Question:
then the enthalpy of formation of H2SO4 at 298 K is
- a) –814.4 kJ
- b) –650.3 kJ
- c) –320.5 kJ
- d) –433.5 kJ
Answer: –814.4 kJ
Question: The volume of a gas expands by 0.25 m3 at a constant pressure of 103N m–2. The work done is equal to
- a) 2.5 erg
- b) 250 J
- c) 250 watt
- d) 250 newton
Answer: 250 J
Question: When 1 g of anhydrous oxalic acid is burnt at 25°C, the amount of heat liberated is 2.835 kJ. ΔH combustion is (oxalic acid : C2H2O4)
- a) –255.15 kJ
- b) –445.65 kJ
- c) –295.24 kJ
- d) –155.16 kJ
Answer: –255.15 kJ
Question: The heat of neutralization of LiOH and HCl at 25°C is 34.868 kJ mol–1. The heat of ionisation of LiOH will be
- a) 44.674 kJ
- b) 22.232 kJ
- c) 32.684 kJ
- d) 96.464 kJ
Answer: 22.232 kJ
Question: Which compound will absorb the maximum amount of heat when dissolved in the same amount of water?(Integral heats of solution at 25°C in kcal/mol of each solute are given in brackets)
- a) HCl (ΔH = –17.74)
- b) HNO3(ΔH = –7.85)
- c) NH4NO3(ΔH = +16.08)
- d) NaCl (ΔH = +1.02)
Answer: NH4NO3(ΔH = +16.08)
Question:
The enthalpy of dissociation of HA is
- a) (q1+ q2)
- b) (q1– q2)
- c) (q2– q1)
- d) –(q1+ q2)
Answer: (q2– q1)
Question: An athlete takes 100 g of glucose of energy equivalent to 1560 kJ. How much amount of energy is uptaken by 1 g molecule of glucose?
- a) 15.6 kJ
- b) 2808 kJ
- c) 1560 kJ
- d) 28.08 kJ
Answer: 2808 kJ
Question:
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: For strong acid strong base neutralisation energy for 1 mole H2O formation is –57.1 kJ. If 0.25 mole of strong monoprotic acid is reacted with 0.5 mole of strong base then enthalpy of neutralisation is
- a) –(0.25 × 57.1)
- b) 0.5 × 57.1
- c) 57.1
- d) –(0.5 × 57.1)
Answer: –(0.25 × 57.1)
Question: The heat of combustion of solid benzoic acid at constant volume is –321.3 kJ at 27°C. The heat of combustion at constant pressure is
- a) –321.3 – 300R
- b) –321.30 + 300R
- c) –321.3 – 150R
- d) –321.3 + 900R
Answer: –321.3 – 150R
Question:
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A cylinder contains either ethylene or propylene. 12 ml of gas required 54 ml of oxygen for complete combustion. The gas is
- a) Ethylene
- b) Propylene
- c) 1 : 1 mixture of two gases
- d) 1 : 2 mixture
Answer: Propylene
Question: The specific heat of a gas is found to be 0.075 calories at constant volume and its formula wt is 40. The atomicity of the gas would be
- a) One
- b) Two
- c) Three
- d) Four
Answer: One
Question:
for this reaction is
- a) Heat of formation of O – H
- b) Bond energy of O – H
- c) Heat of combustion of H2
- d) Zero at all temperatures
Answer: Bond energy of O – H
Question: Energy required to dissociate 4 g of gaseous H2 into free gaseous atoms is 872 kJ at 25°C. The bond energy of H-H bond will be
- a) 8.72 kJ
- b) 4.36 kJ
- c) 436 kJ
- d) 43.6 kJ
Answer: 436 kJ
Question: The dissociation energy of CH4(g) is 360 kcal mol–1 and that of C2H6(g) is 620 kcal mol–1. The C – C bond energy
- a) 260 kcal mol–1
- b) 180 kcal mol–1
- c) 130 kcal mol–1
- d) 80 kcal mol–1
Answer: 80 kcal mol–1
Question: The enthalpy of reaction,
2HC≡CH + 5O2→ 4CO2+ 2H2O
If the bond energies of C–H, C≡C, O=O, C=O and O–H bonds are p, q, r, s, t respectively
- a) [8s + 4t] – [4p + q + 5r]
- b) [4p + 2q + 5r] – [8s + 4t]
- c) [4p + 2q + 5r + 8s + 4t]
- d) [2p + q + 5r] – [8s + 4t]
Answer: [4p + 2q + 5r] – [8s + 4t]
Question: Using bond energy data, calculate heat of formation of isoprene
Given C–H, H–H, C–C, C = C and C(s) → C(g) respectively as 98.8 kcal, 104 kcal, 83 kcal, 147 kcal, 171 kcal
- a) – 21 kcal
- b) 21 kcal
- c) 40 kcal
- d) 50 kcal
Answer: 21 kcal
Question: In a flask colourless N2O4 is in equilibrium with brown coloured NO2. At equilibrium when the flask is heated at 100°, the brown colour deepens and on cooling it becomes less coloured. The change in enthalpy, ΔH for formation of NO2 is
- a) Negative
- b) Positive
- c) Zero
- d) Undefined
Answer: Positive
Question: For which of these reactions will there be ΔS positive?
- a) H2O(g) →H2O(l)
- b) H2(g) + I2(g) →2HI(g)
- c) CaCO3(s)→ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
- d) N2(g) + 3H2(g)→2NH3(g)
Answer: CaCO3(s)→ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Question: For stretched rubber, Entropy
- a) Increases
- b) First increases then decreases
- c) Decreases
- d) First decreases then increases
Answer: Decreases
Question: The least random state of H2O is
- a) Ice
- b) Liquid water
- c) Steam
- d) Randomness is same in all
Answer: Ice
Question: ΔS for the reaction: MgCO3(s) → MgO(s) + CO2(g)
- a) Zero
- b) –ve
- c) +ve
- d) ∞
Answer: +ve
Question: The standard entropies of N2(g), H2(g) and NH3(g) are 191.5, 130.5, 192.6 JK–1 mol–1. The value of ΔSº of formation of ammonia is
- a) –98.9 JK–1 mol–1
- b) Zero
- c) +129.4 JK–1 mol–1
- d) –29.4 JK–1 mol–1
Answer: –98.9 JK–1 mol–1
Question: What is the increase in entropy when 11.2 L of O2 are mixed with 11.2 L of H2 at STP?
- a) 0.576 J/K
- b) 5.76 J/K
- c) 7.56 J/K
- d) 2.76 J/K
Answer: 5.76 J/K
Question:
- a) +25 J
- b) –125 J
- c) 135 J
- d) 315 J
Answer: –125 J
Question: For the melting of NaCl heat required is 7.26 kcal mol–1 and ΔS increases by 6.73 cal mol–1k–1. The melting point of the salt is
- a) 805.75°C
- b) 500 K
- c) 1.77 K
- d) 1.77°C
Answer: 805.75°C
Question: The ΔS for the reaction
- a) –318.4JK–1mol–1
- b) 318.4JK–1mol–1
- c) 31.84 JK–1mol–1
- d) 3.184 JK–1mol–1
Answer: –318.4JK–1mol–1
Question: Which of the following is correct?
- a)
ΔH ΔS Nature of reaction
(–) (+) Spontaneous only at high temperature
- b)
ΔH ΔS Nature of reaction
(+) (–) Nonspontaneous regardless of temperature
- c)
ΔH ΔS Nature of reaction
(+) (+) Spontaneous only at low temperature
- d)
ΔH ΔS Nature of reaction
(–) (–) Spontaneous at all temperatures
Answer:
ΔH ΔS Nature of reaction
(+) (–) Nonspontaneous regardless of temperature
Question: Entropy of vaporisation of water at 100°C, if molar heat of vaporisation is 9710 cal mol–1 will be
- a) 20 cal mol–1 K–1
- b) 26.0 cal mol–1 K–1
- c) 24 cal mol–1 K–1
- d) 28.0 cal mol–1 K–1
Answer: 26.0 cal mol–1 K–1
Question: A particular reaction at 27°C for which ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0 is found to be non-spontaneous. The reaction may proceed spontaneously if
- a) The temperature is decreased
- b) The temperature is increased
- c) The temperature is kept constant
- d) It is carried in open vessel at 27°C
Answer: The temperature is increased
Question: It is impossible for a reaction to take place if
- a) ΔH is +ve and ΔS is +ve
- b) ΔH is –ve and ΔS is +ve
- c) ΔH is +ve and ΔS is –ve
- d) ΔH is –ve and ΔS is –ve
Answer: ΔH is +ve and ΔS is –ve
Question: The standard free energy change ΔG° is related to K (equilibrium constant) as
- a) ΔG° = –2.303 RT logK
- b) ΔG° = 2.303 RT logK
- c) ΔG° = RT logK
- d) ΔG° = –RT logK
Answer: ΔG° = –2.303 RT logK
Question: For an endothermic reaction to be spontaneous
- a) ΔG = 0
- b) ΔG > 0
- c) ΔG < 0
- d) ΔG may be +ve or –ve
Answer: ΔG < 0
Question: The sole criterion for the spontaneity of a process is
- a) Tendency to acquire minimum energy
- b) Tendency to acquire maximum randomness
- c) Tendency to acquire minimum energy and maximum randomness
- d) Tendency to acquire maximum stability
Answer: Tendency to acquire maximum stability
Question: At 27°C the reaction,
proceeds spontaneously because the magnitude of
- a) ΔH = TΔS
- b) ΔH > TΔS
- c) ΔH < TΔS
- d) ΔH > 0 and TΔS < 0
Answer: ΔH > TΔS
Question: For two mole of an ideal gas
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: When an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically and reversibly, the final temperature is
- a) Higher than the initial temperature
- b) Lower than the initial temperature
- c) The same as the initial temperature
- d) Dependent on the rate of compression
Answer: Higher than the initial temperature
Question: ΔS° will be highest for the reaction
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: In an irreversible process, the value of
- a) +ve
- b) –ve
- c) Zero
- d) All of these
Answer: +ve
Question: A closed flask contains a substance in all its three states, solids, liquids and vapour at its triple point. In this situation the average KE of the water molecule will be
- a) Maximum in vapour state
- b) Maximum in solid state
- c) Greater in the liquid than in vapour state
- d) Same in all the three states
Answer: Same in all the three states
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
MCQs for Thermodynamics Chemistry Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Chemistry to develop the Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Chemistry will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the NEET MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by NEET for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Thermodynamics MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Thermodynamics

