Refer to NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by NEET, NCERT and KVS. Surface Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Chemistry and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Surface Chemistry
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Surface Chemistry in Full Syllabus.
Surface Chemistry MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: Which one of the following is a property of physisorption?
- a) Non-specific nature
- b) High specificity
- c) Irreversibility
- d) Single layer adsorption
Answer: Non-specific nature
Question: Which of the following is not a characteristic of chemisorption?
- a) Irreversible nature
- b) ΔH is of the order of 500 J
- c) Specific in nature
- d) Increases with increase of surface area
Answer: ΔH is of the order of 500 J
Question: Freundlich adsorption isotherm gives a straight line on plotting
- a) x/m versus P
- b) log x/m versus P
- c) log x/m versus log P
- d) x/m versus 1/P
Answer: log x/m versus log P
Question: Which can adsorb larger volume of hydrogen gas?
- a) Colloidal solution of palladium
- b) Finely divided nickel
- c) Finely divided platinum
- d) Colloidal Fe(OH)3
Answer: Colloidal solution of palladium
Question: The process of froth floatation and chromatography are based on
- a) Emulsification
- b) Adsorption
- c) Absorption
- d) Both (2) & (3)
Answer: Adsorption
Question: The graph plotted against adsorption versus pressure P at constant temperature, the Freundlich equation at points A, B, C respectively are (if n > 1)
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The intercept on Y-axis in the graph of 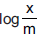 versus log P gives
versus log P gives
- a)
- b) k
- c) log k
- d) Temperature
Answer: log k
Question: Which of the following is correct about the adsorption of N2 over Iron?
- a) It is always physically adsorbed
- b) Extent of adsorption over iron decreases with the increase in temperature first and then increases
- c) It is always chemically adsorbed
- d) N2 is never adsorbed over iron
Answer: Extent of adsorption over iron decreases with the increase in temperature first and then increases
Question: By plotting log x/m on y-axis and log P on x-axis, we should get
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: In adsorption from solution phase, the Freundlich adsorption isotherm is modified as
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Which is not a colloidal solution?
- a) Smoke
- b) Ink
- c) Air
- d) Blood
Answer: Air
Question: Lyophobic colloids are
- a) Reversible colloids
- b) Irreversible colloids
- c) Protective colloids
- d) Gum, proteins
Answer: Irreversible colloids
Question: Size of colloidal particle ranges between
- a) 1 nm to 100 nm
- b) 1 nm to 1000 nm
- c) 10 nm to 1000 nm
- d) 100 nm to 1000 nm
Answer: 1 nm to 1000 nm
Question: Which of the following processes best describes the purification of muddy water by addition of alum?
- a) Absorption
- b) Coagulation
- c) Dialysis
- d) Electrodialysis
Answer: Coagulation
More Questions........................................................
Question: Colloidal solution commonly used in treatment of eye disease is
- a) Colloidal sulphur
- b) Colloidal silver
- c) Colloidal gold
- d) Colloidal antimony
Answer: Colloidal silver
Question: Micelles formation takes place
- a) At CMC and at kraft temperature
- b) At CMC and at above kraft temperature
- c) At above CMC and at kraft temperature
- d) Above CMC and above kraft temperature
Answer: Above CMC and above kraft temperature
Question: Colloids can be purified by
- a) Tyndall effect
- b) Coagulation
- c) Peptization
- d) Ultrafiltration
Answer: Ultrafiltration
Question: Which of the following has minimum protecting power?
- a) Gelatin (Gold no. = 0.01)
- b) Dextrin (Gold no. = 15)
- c) Potato starch (Gold no. = 25)
- d) Albumin (Gold no. = 0.25)
Answer: Potato starch (Gold no. = 25)
Question: Which of the following is positively charged colloidal particle?
- a) As2S3
- b) Al2O3.xH2O
- c) Au
- d) Pt
Answer: Al2O3.xH2O
Question: Movement of colloidal particles under the influence of electric field is called
- a) Electrophoresis
- b) Dialysis
- c) Ionisation
- d) Electrodialysis
Answer: Electrophoresis
Question: Emulsifier is an agent which
- a) Accelerates the dispersion
- b) Stabilises the emulsion
- c) Homogenizes the emulsion
- d) Dissociate emulsions
Answer: Stabilises the emulsion
Question: Gelatin is often used as an ingredient in the manufacture of ice-cream. The reason for this is
- a) To prevent the formation of a colloid
- b) To stabilize the colloid and prevent crystal growth
- c) To cause the mixture to solidify
- d) To improve the flavour
Answer: To stabilize the colloid and prevent crystal growth
Question: Milk can be preserved by adding a few drops of
- a) Formic acid solution
- b) Formaldehyde solution
- c) Acetic acid solution
- d) Acetaldehyde solution
Answer: Formaldehyde solution
Question: When a river enters the sea, a delta is formed. Formation of delta is due to
- a) Peptization
- b) Coagulation
- c) Emulsification
- d) Dialysis
Answer: Coagulation
Question: Which statement is incorrect?
- a) Higher the gold number of lyophilic sol better is its protective action
- b) Lower the gold number of a lyophilic sol better is its protective action
- c) The Bredig's arc method is usually suitable for preparing sols of inert metals
- d) The osmotic pressure method gives the average molar mass of a polymer
Answer: Higher the gold number of lyophilic sol better is its protective action
Question: The potential difference between the fixed charged layer and the diffused layer having opposite charge is called
- a) Zeta potential
- b) Streaming potential
- c) Dorn potential
- d) Colloidal potential
Answer: Zeta potential
Question: When dilute aqueous solution of AgNO3 (excess) is added to KI solution, positively charged sol particles of AgI are formed due to adsorption of ion
- a) K+
- b) Ag+
- c) I–
- d) NO3–
Answer: Ag+
Question: In the preparation of AgI sol, AgNO3 is added to excess of potassium iodide solution. The particles of the sol will acquire
- a) Negative charge
- b) Positive charge
- c) No charge
- d) Unpredictable
Answer: Negative charge
Question: Which of the following method is not employed for the purification of colloids?
- a) Electrodialysis
- b) Dialysis
- c) Ultracentrifugation
- d) Peptisation
Answer: Peptisation
Question: During purification of colloidal sol by ultracentrifugation which of the following is observed?
- a) Colloidal particles are settled at the bottom of ultracentrifuge tube
- b) Impurities are settled at the bottom of the ultracentrifuge tube
- c) Impurities are removed through ultrafilters
- d) It’s rate can be increased by applying pressure
Answer: Colloidal particles are settled at the bottom of ultracentrifuge tube
Question: A positive colloid will be formed when
- a) NH4OH is added dropwise in dilute solution of FeCl3
- b) H2S is passed in dilute AsCl3 solution
- c) Dilute AgNO3 solution is added to saturated AgI solution
- d) Gelatin is dissolved in water
Answer: Dilute AgNO3 solution is added to saturated AgI solution
Question: Which of the following is with highest and lowest flocculation value among Al+3, Na+, Mg+2, Ba+2?
- a) Al+3, Na+
- b) Na+, Al+3
- c) Ba+2, Al+3
- d) They have same flocculation value
Answer: Na+, Al+3
Question: Most effective coagulant for a colloidal solution of arsenic sulphide in water is
- a) 0.1 M sodium phosphate
- b) 0.1 M zinc sulphate
- c) 0.1 M zinc nitrate
- d) 0.1 M aluminium chloride
Answer: 0.1 M aluminium chloride
Question: Flocculation value is expressed in terms of
- a) Millimoles of electrolyte per litre of solution
- b) Moles of electrolyte per litre of solution
- c) Gram of electrolyte per litre of solution
- d) Millimoles of electrolyte per millilitre of solution
Answer: Millimoles of electrolyte per litre of solution
Question: Colloidal particles in soap sol carry
- a) Negative charge
- b) Positive charge
- c) No charge
- d) Either positive or negative charge
Answer: Negative charge
Question: Which of the following metallic sols cannot be prepared by Breding’s arc method?
- a) Gold
- b) Silver
- c) Platinum
- d) Sodium
Answer: Sodium
Question: The stabilization of the dispersed phase in a lyophobic sol is due to
- a) The viscosity of the medium
- b) The surface tension of the medium
- c) Affinity for the medium
- d) The formation of an electrical double layer between the two phases
Answer: The formation of an electrical double layer between the two phases
Question: When SO2 gas is bubbled into H2S gas
- a) Lyophillic sol of sulphur is formed
- b) Lyophobic sol of sulphur is formed
- c) Suspension of water and sulphur is formed
- d) A true solution of sulphur in water is formed
Answer: Lyophobic sol of sulphur is formed
Question: When FeCl3 solution is added to NaOH a negatively charged sol is obtained. It is due to the
- a) Presence of basic group
- b) Preferential adsorption of OH– ions
- c) Self dissociation
- d) Electron capture by sol particles
Answer: Electron capture by sol particles
Question: The example of homogeneous catalysis is
- a) Formation of NH3 in Haber's process
- b) Formation of NO in Ostwald's process
- c) Formation of SO3 in Lead chamber process
- d) Formation of SO3 in Contact process
Answer: Formation of SO3 in Lead chamber process
Question: Which property of colloidal solution is independent of charge on the colloidal particles?
- a) Tyndall effect
- b) Coagulation
- c) Electrophoresis
- d) Electro-osmosis
Answer: Tyndall effect
Question: Which property of colloids is not dependent on the charge on colloidal particles?
- a) Coagulation
- b) Electrophoresis
- c) Electro-osmosis
- d) Tyndall effect
Answer: Tyndall effect
Question: Which one of the following statement is incorrect about enzyme catalysis?
- a) Enzymes are denaturated by ultraviolet rays and at high temperature
- b) Enzymes are least reactive at optimum temperature
- c) Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature
- d) Enzyme action is specific
Answer: Enzymes are least reactive at optimum temperature
Question: In Freundlich Adsorption isotherm, the value of 1/n is
- a) 1 in case of physical adsorption
- b) 1 in case of chemisorption
- c) Between 0 and 1 in all cases
- d) Between 2 and 4 in all cases
Answer: Between 0 and 1 in all cases
Question: Which of the following statements is correct for the spontaneous adsorption of a gas?
- a) ΔS is negative and, therefore, ΔH should be highly positive
- b) ΔS is negative and therefore, ΔH should be highly negative
- c) ΔS is positive and, therefore, ΔH should be negative
- d) ΔS is positive and, therefore, ΔH should also be highly positive
Answer: ΔS is negative and therefore, ΔH should be highly negative
Question: The protecting power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of
- a) Critical miscelle concentration
- b) Oxidation number
- c) Coagulation value
- d) Gold number
Answer: Gold number
Question: If x is amount of adsorbate and m is amount of adsorbent, which of the following relations is not related to adsorption process?
- a)
- b) x/m = f(p) at constant T
- c) x/m = f(T) at constant P
- d) p = f(T) at constant (x/m)
Answer:
Question: The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption
- a) The adsorbed molecules interact with each other
- b) The adsorption takes place in multilayers
- c) The adsorption sites are equivalent in their ability to adsorb the particles
- d) The heat of adsorption varies with coverage
Answer: The adsorption sites are equivalent in their ability to adsorb the particles
Question: A plot of log x/m versus log p for the adsorption of a gas on a solid gives a straight line with slope equal to
- a) – log k
- b) n
- c) 1/n
- d) log k
Answer: 1/n
Question: Which one of the following forms micelles in aqueous solution above certain concentration?
- a) Urea
- b) Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride
- c) Pyridinium chloride
- d) Glucose
Answer: Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride
Question: When a few typical solutes are separated by a particular selective membrane such as protein particles, blood corpuscles, this process is called
- a) Transpiration
- b) Endosmosis
- c) Dialysis
- d) Diffusion
Answer: Dialysis
Question: The ability of anion, to bring about coagulation of a given colloid, depends upon
- a) Magnitude of the charge
- b) Both magnitude and sign of charge
- c) Its charge only
- d) Sign of the charge alone
Answer: Both magnitude and sign of charge
Question: A colloidal system has particles of which of the following size?
- a) 10–9 m to 10–12 m
- b) 10–6 m to 10–9 m
- c) 10–4 m to 10–10 m
- d) 10–5 m to 10–7 m
Answer: 10–6 m to 10–9 m
Question: At the critical micelle concentration (CMC) the surfactant molecules
- a) Associate
- b) Dissociate
- c) Decompose
- d) Become completely soluble
Answer: Associate
Question: Which one of the following method is commonly used method for destruction of colloid?
- a) Dialysis
- b) Condensation
- c) Filteration by animal membrane
- d) By adding electrolyte
Answer: By adding electrolyte
Question: Pure water can be obtained from sea water by
- a) Centrifugation
- b) Plasmolysis
- c) Reverse osmosis
- d) Sedimentation
Answer: Reverse osmosis
Question: Which is not correct regarding the adsorption of a gas on surface of a solid?
- a) On increasing temperature adsorption increases continuously
- b) Enthalpy and entropy change is negative
- c) Adsorption is more for some specific substance
- d) It is a reversible reaction
Answer: On increasing temperature adsorption increases continuously
Question: Position of non polar and polar part in micelle
- a) Polar at outer surface but non polar at inner surface
- b) Polar at inner surface non polar at outer surface
- c) Distributed over all the surface
- d) Are present in the surface only
Answer: Polar at outer surface but non polar at inner surface
Question: According to the adsorption theory of catalysis, the speed of the reaction increases because
- a) The concentration of reactant molecules at the active centres of the catalyst becomes high due to adsorption
- b) In the process of adsorption, the activation energy of the molecules becomes large
- c) Adsorption produces heat which increases the speed of the reaction
- d) Adsorption lowers the activation energy of the reaction
Answer: Adsorption lowers the activation energy of the reaction
Question: Which of the following forms cationic micelles above certain concentration?
- a) Sodium dodecyl sulphate
- b) Sodium acetate
- c) Urea
- d) Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
Answer: Sodium dodecyl sulphate
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
MCQs for Surface Chemistry Chemistry Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Chemistry to develop the Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Chemistry will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the NEET MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Surface Chemistry for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by NEET for Full Syllabus Chemistry Surface Chemistry have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Surface Chemistry MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Surface Chemistry

