M.C.Q.
1. The most electronegative element possess the electronic configuration
a) ns2 np2 b) ns2 np4 c) ns2 np5 d) ns2 np3
2. The maximum number of electrons in d– orbital of an element with atomic number 46 is
a) 10 b) 18 c) 20 d) 19
3. The ionisation enthalpy of Cs is 375.6KJmol–1< what is the energy required to convert [at mass of Cs = 133] 2.66mg o f gaseous Cs completely to Cs+
a) 7.512 J b) 7.512 KJ c) 7512.2 J d) 18782 J
4. The atomic num ber of elements M, N, & P are x, x–1, x–3. If P is a halogen atom then the type of bond between N & P is
a) Covalent b) Ionic c) Coordinate d) Metallic
5. In the above question (Question 4) the formula of M & P is
a) MP b) M2P c) MP2 d) M2P3
6. The elem ents X. Y. & Z h ave 2, 3 & 4 electrons in th e o utermo st orb ital respectively.
The element which form most basic oxide is
a) X b) Y c) Z d) None of the above
7. Elements A, B, C & D b elo ng to the 17th gro up . If the atomic numb ers are y , y– x, y + 4x + 4 & y + 2x + 2 (x = 8) > the element which is violet solid is
a) C b) A c) B d) D
8. An element X belongs to Gp16 & 5th period. Its atomic number is
a) 34 b) 50 c) 52 d) 85
9. The position of an element with atomic number 114 is
a) Period 6 gp 14 b) Period 6 gp 16 c) Period 5 gp 18 d) Period 7 gp 14
10. The total no. o f electrons in the outermost o rbital in element A, B, C, D are 2, 1, 4, & 6 respectively. The elements which belongs to chalcogens is
a) B b) C c) D d) A
11. The io nic radii of is oelectron ic sp ecies are fo un d to be 171p m, 136p m & 140pm respectively. The isoelectronic species are __________
a) N3– , O2– , F– b) F– , O2– , N3 – c) O2– , N3– , F– d) N3– , F– , O2 –
12. The size of Mo is very similar to W due to_______
a) Shielding effect b) Actinide contraction
c) Poor Shielding by 4f electrons d) Poor shielding by 4d electrons
13. Choose the correct order ionization energy
a) N > O > F b) F > O > N c) N > O < F d) O > F > N
14. The order of ionization energy of K, Ca, & Ba are
a) K > Ca > Ba b) C a > Ba > K c) Ba > K > Ca d) K > Ba > Ca
15. The element with zero electron gain enthalpy is
a) Argon b) Lithium c) Calcium d) Fluorine



28. Choose the correct statement
a) As shielding effect increases electro negativity decreases
b) As shielding effect increases electro negativity increases
c) As ionization potential increases metallic property increases
d) As +ve charge on species increases ionic radii increases
29. The electronic configuration which contain metals, non metals & metalloid is______
a) ns1 & ns2 b) ns2 , n s2(n–1)d (1– 10)
c) ns2 np6 & ns d) ns2 n p4 & ns2 np 5
30. The group in which all the three physical states (solid ,liquid, gas) are observed is
a) gp 17 b) gp 14 c) gp 18 d) gp 15
31. The element which exhibits highest oxidation number is
a) Mn b) Os c) Fr d) I
32. Fo ur elem en ts A, B, C & D. D is n on reactive gas. C is a highly reactive gas, B is a solid & forms oxide, A is high reactive solid & used to p rep are Lasagne’ s solution.
Choose the correct sequence of possible atomic no. of elements
a) 12, 18, 9, 11 b) 11, 36, 9, 20 c) 20, 36, 11, 9 d) 9, 18, 11, 20
33. The element with highest electronic affinity belongs to
a) Period 1 gp b) Period 3 gp 17 c) Period 2 gp 17 d) Period 2 gp 16
34. The atomic no. of B = atomic of A+18 , Statements A & B to
a) Same pd & same gp b) Same pd but different gp
c) Different pd but same gp d) Different pd and different gp
35. Element B occupies 3rd pd & gp 16
Element C occupies 4 pd & gp 3
The molecular formula of compound formed between B & C is
a) B3C 2 b) C2B3 c) C B2 d) B2C
36. Choose the correct statement w.r.t oxidising property of F
a) It is the strongest oxidising agent because it has highest electron gain enthalpy
b) It is the strongest oxidising agent due to its small size
c) It is the strongest oxidising agent because it has maximum electron negativity
d) It is the strongest oxidising agent due to high lattice enthalpy
37. The name of th e scien tist wh o dis co vered the elem ent Unu & its accep ted IUPAC nameis—
a) Mendeleev &Mendelinium b) Seaborg & Seaborgium
c) Mendeleev &Dubinium d) G.T.Seaborg & Mendelinium
38. Which of the following property does not indicate the periodicity of elements
a) Ionization potential b) Neutron/ proton Ratio
c) Bonding behaviour d) Electron negativity
39. Properties of Li are similar to Mg because
a) The size of Li & Mg are different b) The size by charge ratio is similar
c) The charges are same d) Both are reactive
41. Be shows diagonal relationship with
a) Mg b) Al c) B d) Na
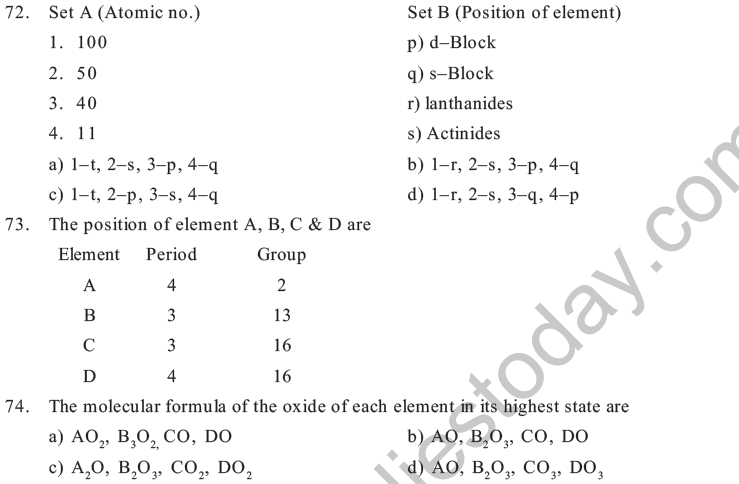
42. Which of the following ions are not isoelectronic with Ar
a) Na+ b) Ca+2 c) Cl– d) K+
43. The ionisation potential of N > O because
a) Ionisation potential increases with decrease in size
b) N posses stable half filled p–orbital
c) The screening effect in N > O
d) O is more electropositive than N
44. The physical properties of chromium is most closely related to
a) Niobium b) Tungsten c) Titanium d) Calcium
45. The electronic configuration of an element of chalcogen family is
a) [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p 1 b) [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p 4
c) [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 n d) [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p 2
46. Choose the incorrect statement
a) An element with high electronegativity always has high electron affinity
b) Electron gain enthalpy is the property of an isolated atom
c) Electronegativity is the property of a bonded atom
d) Both electronegativity & electron affinity are equally proportional to nuclear charge
& inversely proportional to atomic size
47. Choose the ox ide which is most basic CuO, MgO, Al2O3 & K2O
a) K2O b) MgO c) C uO d) Al2O3
48. An element with atomic number 19 will most readily react with the element who seatomic number is
a) 18 b) 21 c) 20 d) 17
49. If graph is drawn between electron enthalpy & atomic num ber from 1 to 60, which of the following statement will be true
a) Alkali metals are at the maxima & noble gases at the minimum
b) Alkali metals are at the minimum & noble gases at the maxima
c) Transition elements at maxima
d) Maxima & minima are not observed
50. In a period with increase in atomic number, the metallic character of an element
a) Decrease across p d & increases in gp
b) increase across pd & decreases in gp
c) increase across pd & increases in gp
d) Decrease across p d & decreases in gp
51. In elem en t P with electron ic configuration [Ar] 4s1 will com bine with an element of ________ configuration to form a highly soluble ionic solid with high melting point
a) [Ar]4s2 b) [Ne]3s2 3p 3 c) [Ne] 3s2 3p 5 d) [Ar] 4s23d 2
52. In group 14 the lower oxidation state becomes more stable down the group. The reason is
a) Inert pair effect b) Decreases in ionisation potential
c) Metallic character increases d) Decrease in electron affinity
53. Choose the correct option. Hint T=true F = False
I. In the second period atomic radii of Be is 90pm, F is 64pm, & that of Ne is 160pm
II. Atomic radii decreases from Li to Ne
III. The increase in size of Ne is due to presen ce of van derwaals force of attractio n & presence of covalent bond
IV. In Ne there is absence of covalent bond therefore the radii is vanderwaals radii
V. The order of radii is Metallic > Covalent > Vanderwaals
a) TTFTF b) TTTFF c) TFFTT d) TFFFT


58. Choose the correct option
I. Transition metals are characterised by variable oxidation state
II. Elements of IB & IIB are transition elements
III. Elements of gp1 exhibit only +1 O.S
IV. Group 17 contains only gases
a) TTFF b) TFTF c) TTTF d) TTTT
59. Choose the correct option
I. The ionisation enthalpy of Be > B
II. d–Block elements are known as representative elements
III. Palladium is the only element of fifth period th at h as no electron in fifth energy level
IV. The second ionisation enthalpy of Al is greater than that of Mg
V. Among Li, Be, B ,C N ; Li has least value of electron gain enthalpy
a) TFTFT b) TFFTT c) TFFFT d) TFTTT
60. Choose the correct option
I. The last electron in case of inner transition elements goes to f–orbital
II. The electron affinity is highest for fluorine
III. Metallic radius is smaller than covalent radii
IV. Ar has lesser ionisation enthalpy than K
a) TFFT b) TFFF c) TTTF d) TTFF
61. Choose the correct option
I. All halogens exhibit variable oxidation state
II. s–Block elements do not exhibit variable oxidation state
III. the most stable oxidation state of Bi is +3
IV. N exhibits –3, +3 & +5 oxidation state
a) TFTT b) TFFT c) FTTT d) FTTF
62. Choose the correct option
I. O.S o f ‘O’ in OF2 is –2
II. Ionisation enthalpy is the minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
III. Screening effect : it is the attraction of electron towards the nuclear
IV. Half filled orbitals are more stable half fully filled orbitals
a) TTTT b) FFFF c) TTFT d) TFFT




75. With reference of above questio n the oxide which is (i) m ost ion ic (ii) ampho teric (iii) highest M.P (iv) reacts most readily acid only
a) AO,BO,AO,AO b) AO,C O,BO,AO
c) BO, AO, AO, DO d) DO, AO, BO, CO
Assertion reason type
75 –85 are assertion reason type for each question select the correct cho ice from the following
a) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true & is correct explanation for statement 1
b) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true but is not correct explanation for statement 1
c) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false
d) Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
75.
1. F atom has lesser electron affinity than atom
2. The size of F is very small therefore electron electron repulsion is high
76.
1. The size of X+,X & O– are id entical
2. The rem oval of electro n decreases th e size while ad ditio n o f e– increases the size.This is primarily due to decreases increases in electronic repulsion

