Refer to NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by NEET, NCERT and KVS. Electrochemistry Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Chemistry and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Electrochemistry in Full Syllabus.
Electrochemistry MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: Purpose of hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell is to
- a) Generate heat
- b) Create potential difference
- c) Produce high purity water
- d) Remove adsorbed oxygen from electrode surface
Answer: Create potential difference
Question: Fluorine is the best oxidising agent because it has
- a) Highest electron affinity
- b)
- c)
- d) Lowest electron affinity
Answer:
Question:
In the above chemical reaction
- a) Water is oxidised
- b) Silver is oxidised
- c) Silver is reduced
- d) Hydrogen is reduced
Answer: Silver is reduced
Question: Which of the following is not a strong electrolytes?
- a) NaCl
- b) KNO3
- c) NH4OH
- d) FeSO4
Answer: NH4OH
Question: The molar conductivity of strong electrolyte
- a) Increases on dilution slightly
- b) Does not change on dilution
- c) Decreases on dilution
- d) Depends on density of electrolyte itself
Answer: Decreases on dilution
Question: The amount of electricity that can deposit 108 g of silver from silver nitrate solution is
- a) 1 ampere
- b) 1 coulomb
- c) 1 faraday
- d) 2 ampere
Answer: 1 faraday
Question: The electrochemical cell stops working after sometime because
- a) The reaction reverse its direction
- b) One of the electrode completely vanishes
- c) Electrode potential of both the electrodes equalise
- d) Electrode potential of both the electrodes becomes zero
Answer: Electrode potential of both the electrodes equalise
Question: The conduction of electricity through the electrolyte solution is due to
- a) Movement of molecules of electrolyte
- b) Movement of ions of electolyte
- c) Movement of separate atoms
- d) Movement of particles of the solvent
Answer: Movement of ions of electolyte
Question: In which of the following cell the energy of combustion of the reaction is directly converted into electricity?
- a) Lechlanche cell
- b) Concentration cell
- c) Fuel cell
- d) Lead storage battery
Answer: Fuel cell
Question: Corrosion is basically
- a) Altered reaction in presence of H2O
- b) Electrochemical phenomenon
- c) Union between two light metals and a heavy metal
- d) Self oxidation and reduction
Answer: Electrochemical phenomenon
Question: The equilibrium constant for a feasible cell reaction
- a) < 1
- b) 0
- c) = 0
- d) > 1
Answer: > 1
Question: In the galvanic cell, true statement
- a) Current flows from anode to cathode
- b) Anode is +ve terminal
- c) If Ecell< 0, it is a spontaneous reaction
- d) Cathode is +ve terminal
Answer: Cathode is +ve terminal
More Questions..............................................
Question: Which of the following is not correct?
- a) Molar conductance of a solution increases with dilution
- b) Equivalent conductance increases with dilution
- c) Specific conductance increases with dilution
- d) At infinite dilution each ion (cation or anion) plays a definite role towards electrical conductance
Answer: Specific conductance increases with dilution
Question: As the dilution of an electrolyte increases
- a) Specific conductance decreases
- b) Molar conductance decreases
- c) Resistance decreases
- d) No change takes place in conductance
Answer: Specific conductance decreases
Question: Equivalent conductance of a weak electrolyte increases on dilution because of
- a) Increase in number of ions per unit volume
- b) Increase in molecular attraction
- c) Increase in degree of association
- d) Increase in degree of ionisation of the substance
Answer: Increase in degree of ionisation of the substance
Question: The variation of equivalent conductance of strong electrolyte with concentration is correctly shown in which figure?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A 0.1M solution of monobasic acid at specific resistance of r ohms-cm, its molar conductivity is
- a) 10/r
- b) 10r
- c) 104/r
- d) 104r
Answer: 104/r
Question: The number of Faradays required to deposit 1 g equivalent of aluminium (At.wt. 27) from a solution of AlCl3
- a) 1
- b) 2
- c) 3
- d) 4
Answer: 1
Question: Electrochemical equivalent of Cu in the reaction 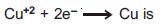
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: When dil. HNO3 is electrolysed
- a) H2(g) is formed at anode
- b) O2 gas is formed at anode
- c) NO2 is formed at anode
- d) N2 is formed at anode
Answer: O2 gas is formed at anode
Question: The specific conductivity of 0.5N solution is 0.01287 ohm–1 cm–1. What would be its equivalent conductance?
- a) 257.4
- b) 2.574
- c) 25.74
- d) 0.2574 ohm–1 cm2 (g. eq)–1
Answer: 25.74
Question: The specific conductance of saturated solution of CaF2 is 3.86 × 10–5 mho cm–1 and that of water used for solution is 0.15 × 10–5. The specific conductance of CaF2 alone is
- a) 3.71 × 10–5
- b) 4.01 × 10–5
- c) 3.7 × 10–4
- d) 3.86 × 10–4
Answer: 3.71 × 10–5
Question: What will be the molar conductance ‘Λ’, if resistivity is ‘x’ for 0.1 N H2SO4 solution?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The conductivities at infinite dilution of NH4Cl, NaOH and NaCl are 130, 218, 120 ohm–1cm2 eq–1. If equivalent conductance of N/100 solution of NH4OH is 10, then degree of dissociation of NH4OH at this dilution is
- a) 0.005
- b) 0.043
- c) 0.01
- d) 0.02
Answer: 0.043
Question: The resistance of a N/10 KCl aqueous solution is 245Ω. If the electrodes in the cell are 4 cm apart and area having 7 cm2 each, the molar conductance of the solution will be
- a) 233
- b) 2.33
- c) 23.32
- d) 0.233
Answer: 23.32
Question: For strong electrolytes the values of molar conductivities at infinite dilution are given below :
The molar conductance at infinite dilution for Ba(OH)2 is
- a) 523 × 10–4 Sm2 mol–1
- b) 52.3 × 10–4 Sm2 mol–1
- c) 5.23 × 10–4 Sm2 mol–1
- d) 6.23 × 10–4 Sm2 mol–1
Answer: 523 × 10–4 Sm2 mol–1
Question: Three faraday of electricity is passed through three electrolytic cells connected in series containing Ag+, Ca2+ and Al+3 ions respectively. The molar ratio in which the three metal ions are liberated at the electrodes is
- a) 1 : 2 : 3
- b) 3 : 2 : 1
- c) 6 : 3 : 2
- d) 3 : 4 : 2
Answer: 6 : 3 : 2
Question: Deduced from the following E° values of half cells, what combination of two half cells would result in a cell with the largest potential?
- a) (i) and (iii)
- b) (i) and (ii)
- c) (ii) and (iv)
- d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (i) and (ii)
Question: E° values of Mg2+|Mg, Zn2+|Zn and Fe2+|Fe are –2.37 V, –0.76 V and –0.44 V respectively. Which of the following is correct ?
- a) Mg2+ oxidises Fe
- b) Zn oxidises Fe2+
- c) Zn reduces Mg2+
- d) Zn reduces Fe2+
Answer: Zn reduces Fe2+
Question: The standard reduction potential value of three metallic cations X, Y and Z are 0.52, –3.303 and –1.18 V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is
- a) Y > Z > X
- b) X > Y > Z
- c) Z > Y > X
- d) Z > X > Y
Answer: Y > Z > X
Question: The maximum current can be drawn from which of the following cells?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) All of these
Answer:
Question: The standard reduction potential of Pb and Zn electrodes are –0.126 and –0.763 volts respectively. The e.m.f. of the cell
Zn | Zn2+ (0.1 M) || Pb2+ (1 M) | Pb is
- a) 0.637 V
- b) < 0.637 V
- c) > 0.637 V
- d) 0.889
Answer: > 0.637 V
Question: For given half cell; 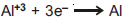 ; on increasing [Al+3], the electrode potential
; on increasing [Al+3], the electrode potential
- a) Increases
- b) Decreases
- c) No change
- d) First increases then decreases
Answer: Increases
Question: During electrolysis of aqueous solution of a salt pH in the space near one of the electrodes is increased. Which of the following salt solution was electrolysed?
- a) KCl
- b) CuCl2
- c) Cu(NO3)2
- d) CuSO4
Answer: KCl
Question: Calculate EMF of the cell
- a) 0.30 V
- b) 1.21 V
- c) 0.26 V
- d) 0.80 V
Answer: 0.26 V
Question: If ΔG for the reaction is A+ + B– → A2+ + B2– is x, the ΔG for the reaction is
- a) x/2
- b) 2x
- c) x2
- d) √x
Answer: x/2
Question: Consider the following equations for a cell
Then
- a) x = y, K1= K2
- b) x = 2y, K12 = K2
- c) x = y, K12 = K2
- d) x2 = y, K12 = K2
Answer: x = y, K12 = K2
Question: The EMF of a chemical cell is positive when free energy change of reaction
- a) > 0
- b) < 0
- c) = 0
- d) No relationship of free energy change and e.m.f.
Answer: < 0
Question: Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- a) Electrons enter through cathode in an electrolytic cell
- b) Electrons leave through anode in an electrolytic cell
- c) Cations in the electrolytic cell move towards cathode and anions towards anode
- d) Cations are reduced at anode and anions are oxidised at cathode in an electrolytic cell
Answer: Cations are reduced at anode and anions are oxidised at cathode in an electrolytic cell
Question: The mass of Cl2 produced when 1A current is passed through NaCl solution for 30 minute is
- a) 0.33 g
- b) 0.66 g
- c) 0.33 mol
- d) 0.66 mol
Answer: 0.66 g
Question: The ionic mobility of alkali metal ions in aqueous solution is maximum for
- a) Na+
- b) K+
- c) Rb+
- d) Li+
Answer: Rb+
Question: A current of 9.65 A flowing for 10 minutes, deposits 3.0 g of a metal. The equivalent weight of the metal is
- a) 10
- b) 30
- c) 50
- d) 96.5
Answer: 50
Question: Hydrazene can be used in fuel cell  If ΔG° for this reaction is –600 kJ, what will be the E° for the cell?
If ΔG° for this reaction is –600 kJ, what will be the E° for the cell?
- a) 1.25 V
- b) 1.50 V
- c) 1.57 V
- d) 1.75 V
Answer: 1.57 V
Question: Which of the following solution will have highest specific conductance?
- a) 0.01 M CH3COOH
- b) 0.01 M NH4OH
- c) 0.01M NaCl
- d) 0.01M K2SO4
Answer: 0.01M K2SO4
Question: Saturated solution of KNO3 is used to make salt bridge because
- a) Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO3-
- b) Velocity of NO3- is greater than that of K+
- c) Velocity of K+ and NO3- are nearly same
- d) KNO3 is highly soluble in water
Answer: Velocity of K+ and NO3- are nearly same
Question: The equivalent conductivity of 1M H2SO4 solution would be if specific conductance is 26 × 10–2S cm–1.
- a) 1.3 × 102 S cm2 sq–1
- b) 1.6 × 102 S cm–1
- c) 13 S cm2 mol–1
- d) 1.3 × 103 S cm2 mol–1
Answer: 1.3 × 102 S cm2 sq–1
Question: The main factors which affect corroision are
- a) Position of metal in electrochemical series
- b) Presence of CO2 in water
- c) Presence of impurities in metals
- d) All of these
Answer: All of these
Question: If 9 g of H2O is electrolyzed completely with 50% current efficiency
- a) 1 F of electricity will be needed
- b) 3 F of electricity is needed
- c) 5.6 L of O2 at STP will be formed
- d) 11.2 L of O2 at STP will be formed
Answer: 5.6 L of O2 at STP will be formed
Question: During the recharging of lead acid storage cell the reaction at anode is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Which of the following cannot envolve H2 from dil acid?
- a) Pt
- b) Zn
- c) Mg
- d) Pb
Answer: Pt
Question: If the density of copper is 8.94 g/cm3, the number of Faradays required to plate an area (10cm × 10cm) of thickness of 10–2 cm using CuSO4 solution as electrolyte is
- a) 0.1 F
- b) 0.28 F
- c) 0.4 F
- d) 0.5 F
Answer: 0.28 F
Question: An electrolytic cell is composed of Cu and Zn. A current of 9.65 A is drawn from a cell for 1 hour. Then the loss in mass at anode and gain in mass at cathode, respectively could be
- a) 11.77 g, 11.43 g
- b) 11.77 g, 10 g
- c) 22.86 g, 23.54 g
- d) 23.54 g, 22.86 g
Answer: 11.77 g, 11.43 g
Question: Volume of gases evolved when dil. H2SO4 is electrolysed using 2F at STP
- a) 22.4 L
- b) 11.2 L
- c) 33.6 L
- d) 44.8 L
Answer: 33.6 L
Question: 2.5 faraday of electricity is passes through a solution of CuSO4 . The number of gram eqivalents of copper deposited on the cathode will be
- a) 1
- b) 2
- c) 2.5
- d) 1.25
Answer: 2.5
Question: The specific conductivity of N/10 KCl solution at 20°C is 0.0212 ohm–1 cm–1 and the resistance of the cell containing this solution at 20°C is 55 ohm. The cell constant is
- a) 4.616 cm–1
- b) 1.166 cm–1
- c) 2.173 cm–1
- d) 3.324 cm–1
Answer: 1.166 cm–1
Question: Which of the following is a strong electrocyte?
- a) Ca(NO3)2
- b) HCN
- c) H2SO3
- d) NH4OH
Answer: Ca(NO3)2
Question: If equal quantities of electricity are passed through three voltameter containing FeSO4, Fe2(SO4)3 and Fe(NO3)3, then which of the following is not true?
- a) Amount of iron deposited in FeSO4 and Fe2(SO4)3 is equal
- b) Amount of iron deposited in Fe(NO3)3 is 2/3 of the amount of iron deposited in FeSO4
- c) Amount of iron deposited in Fe2(SO4)3 and Fe(NO3)3 are equal
- d) Same gas will evolve in all three cases at anode
Answer: Amount of iron deposited in FeSO4 and Fe2(SO4)3 is equal
Question: A solution is 1 molar in each of NaCl, CdCl2, ZnCl2 and PbCl2 . To this Sn metal is added, which of the following is true?
- a) Sn can reduce Na+ to Na
- b) Sn can reduce Zn2+ to Zn
- c) Sn can reduce Cd2+ to Cd
- d) Sn can reduce Pb2+ to Pb
Answer: Sn can reduce Pb2+ to Pb
Question: Equivalent conductance of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa at infinite dilution are 126.45, 425.16 and 91ohm–1 cm2 respectively. The equivalent conductance of CH3COOH at infinite dilution would be
- a) 101.38 ohm–1 cm2
- b) 253.62 ohm–1 cm2
- c) 389.71 ohm–1 cm2
- d) 678.90 ohm–1 cm2
Answer: 389.71 ohm–1 cm2
Question: An electrochemical cell has two half cell reactions as,
The cell voltage will be
- a) 2.71 V
- b) 2.03 V
- c) –2.71 V
- d) –2.03 V
Answer: 2.71 V
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
MCQs for Electrochemistry Chemistry Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Chemistry to develop the Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Chemistry will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the NEET MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by NEET for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Electrochemistry MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry

