When two or more than two substance mix and from a uniform or homogeneous mixture, Such a mixture is called solution.
The solutions can be found in three states; Solid, Liquid and Gas. The solute and solvent can also be in three states. The physical state of the resulting solution can be decided on the basis of physical state of solute and solvent.
M.C.Q.
1. Which of the following possesses physical state of solute and solvent are liquid and solid respectively ?
(a) solution of sugar in water (b) zinc amalgam
(c) solution of Naphthelene in benzene (d) brass
2. Which of the following alternative is correct for physical state of solute and solvent for a solution of camphor in N2 gas ?
(a) solid, gas (b) solid, liquid (c) gas, solid (d) gas, gas
3. Which of the following is an example of solid solution ?
(a) interstitial compound of hydrogen and Pd (b) WC
(c) Zn / Hg (d) Given all
4. Which of the following pair of solution having same physical state of solute ?
(a) homogenous mixture of chloroform in N2 gas, solution of CO2 in water
(b) brass, sodium amalgam
(c) homogenous mixture of camphor in N2 gas, solution of H2 gas in Pd metal
(d) moist air, solution of ethanol in water
5. Which of the following pair of solution having same physical state of solvent ?
(a) homogenous mixture of chloroform in N2 gas, solution of CO2 in water
(b) brass, solution of salt in water
(c) homogenous mixture of camphor in N2 gas, moist air
(d) solution of H2 gas in Pd metal, solution of ethanol in water
6. Which of the following pair of solution having different physical state of solute ?
(a) homogenous mixture of chloroform in N2 gas, solution of CO2 in water
(b) brass, homogenous mixture of camphor in N2 gas
(c) sodium amalgam, moist air
(d) solution of H2 gas in Pd metal mixture of N2 and O2
7. Which of the following pair of solution having different physical state of solvent ?
(a) homogenous mixture of N2 gas in chloroform, mixture of N2 and O2
(b) brass, solution of H2 gas in Pd metal
(c) sodium amalgam, solution of urea in water
(d) solution of CO2 in water, solution of Naphthelene in benzene
8. Which of the following compound possesses maximum solubility in water ?
(a) pentan – 1 - ol (b) Pentane – 2, 3 – diol
(c) pentane – 1, 2, 3 – triol (d) Pentane – 1, 2, 3, 4 – tetraol
9. Which of the following given compound is least soluble in water ?
(a) Hexan – 1 – ol (b) glycerol
(c) Propane – 1, 3 – diol (d) ethylene glycol
10. To convert molarity into which of the following unit of concentration, does not require density of the solution ?
(a) molality (b) normality (c) mole-fraction (d) % w/w
11. To convert molality into which of the following unit of concentration require density of the solution ?
(a) percentage weight by weight (b) percentage by volume
(c) mole-fraction (d) given all
12. Which of the following unit of concentration does not depend on temperature ?
(a) formality (b) molarity (c) molality (d) normality
13. Which of the following unit of concentration depends on temperature ?
(a) molality (b) normality (c) mole-fraction (d) given all
14. What would be the formality of solution prepared by dissolving 9.48 gm. Potash-alum dissolved in 5 litre water ? [M.W of Potash-alum = 948 gm/mole]
(a) 0.04 F (b) 0.02 F (c) 0.002 F (d) 0.004 F
15. What quantity of potash-alum is required to prepare 500ml solution having strength 1.5 F
(a) 711gm (b) 355.5 gm (c) 35.55 gm (d) 71.1 gm
16. What would be the concentration in % w/v of aqueous solution in which 80 ml ethanol is dissolved in 4 lt. Solution ?
(a) 4% v/v (b) 10% v/v (c) 2% v/v (d) 8% v/v
17. What would be the volume of acetone required to prepare 10% v/v acetone solution in 5 lt. Solution ?
(a) 50 ml (b) 5 ml (c) 100 ml (d) 500 ml
18. 15 % w/v solution of sugar is prepared by dissolving 1200 gm sugar in water, then, what would be the volume of the solution ?
(a) 8000 ml (b) 4 lt (c) 800 ml (d) 5000 ml
19. 0.004 gm O2 is dissolved in an aqueous solution of 50 litre, then, what would be the ppm of solution by weight-volume ?
(a) 0.04 (b) 0.008 (c) 0.004 (d) 0.08
20. The concentration of Ca2+ion in a sample of water is 0.0002 M then what would be the concentration of Ca2+ in ppm by weight-volume ? (Atomic wt. of ca = 40 gm/mole)
(a) 4 (b) 8 (c) 0.08 (d) 0.4
21. The concentration of F-ion in a sample of water is 10 ppm; then, concentration of F-ion in a solution in % w/v is
(a) 10-3 (b) 10-2 (c) 10 (d) 10-4
22. What would be the weight of O2 gas in gram dissolved in an aqueons solution of 500ml having strength 5 ppm ?
(a) 0.025 (b) 2.5 × 10-4 (c) 2.8 × 10-3 (d) 2.8 × 10-5
23. What would be the molarity of solution prepared by taking a mixture of 1400 ml 0.3 M, 700 ml 0.4 M and 500 ml 1.2 M aqueous solutions ?
(a) 0.5 M (b) 0.8 M (c) 0.6 M (d) 0.7 M
24. What quantity of KOH is required to prepare 10 % w/w KOH solution having weight 1000 gm ?
(a) 50 gm (b) 25 gm (c) 100 gm (d) 150 gm
25. What amount of water is added in an aqueous solution of 5000 ml having concentration 1.5 M to prepare 0.5 M solution ?
(a) 15 litre (b) 5 litre (c) 10 litre (d) 20 litre
26. On Which factors, the solubility of gaseous solute in liquid depends ?
(a) temperature (b) Pressure of the gas
(c) Nature of gaseous solute and solvent (d) Given all
27. At 293 K temperature, if partial pressure of all given gases are same, then, which of the following gas possesses maximum solubility in water ?
(a) He (b) N2 (c) H2 (d) O2
28. At 298 K temperature, if partial pressure of all given gases are same, then, which of the following gas possesses least solubility in water ?
(a) carbon dioxide (b) formaldehyde (c) methane (d) vinyl chloride
69. At constant temperature, binary ideal solution is formed by two liquids A and B. At equilibrium,mole-fraction of liquid A is 0.7 and in vapour state mole-fraction of A is 0.4 Poa + Pob =90 mm then at the same temperature, what will be the vapour pressure of pure liquid A and B ?
(a) 40 mm, 50 mm (b) 30 mm, 60 mm (c) 50 mm, 40 mm (d) 20 mm, 70 mm
70. At constant temperature, binary ideal solution is formed by two liquids A and B. At equilibrium,mole-fraction of liquid B is 0.4 and vapour state mole-fraction of B is 0.25. PoB=40 mm, then at the same temperature, what will be the vapour pressure of pure liquid ‘A’ ?
(a) 80 mm (b) 60 mm (c) 40 mm (d)50 mm
71. Choose correct alternative for True and False statements for given diagram. (For correct statement T and for wrong statement F) (Assume that ionic solid substances completely dissociates in the solution) (For Correct- Stutement T and for Wrory worry Srut ment F)
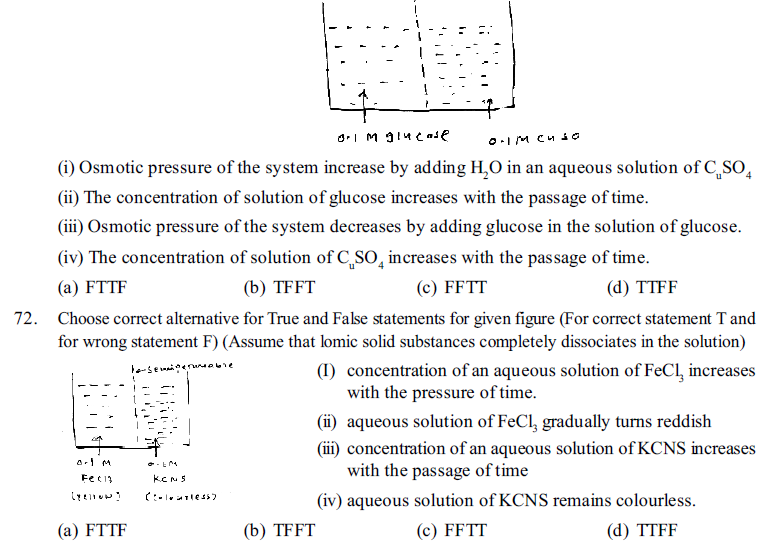

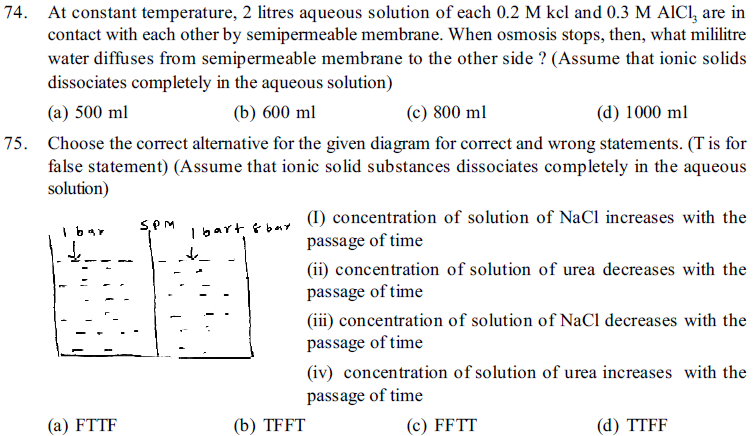
76. Which of the following solution is hypotonic with fluids in RBC ?(Assume that ionic solid substances completely dissociates in the solution)
(a) 0.2 M NaCl (b) 0.1 M NaCl (c) 0.18 M NaCl (d) given all
77. At constant temperature, Which of the following solution is hypotonic in the comparison with fluids in RBC ? (Assume that ionic solid substances completely dissociates in the solution)
(a) 0.17 M NaCl (b) 0.12 M NaCl (c) 0.1 M NaCl (d) given all
78. X M NaCl is isotonic with fluids present in RBC (Red Blood Corpusceles), then what would be the value of x ? (M.w. Of NaCl =58.5 gm/mole) (Assume that ionic solid substances completely dissociates in the solution)
(a) 0.15 (b) 0.05 (c) 0.18 (d) 0.78
79. Which of the following solution is hypotonic in comparison with the solution of 0.4 M glucose?
(a) 0.1 M CaCl2 (b) 0.2 M NaCl (c) 0.15 M FeCl3 (d) 0.3 M urea
80. Which of the following solution is hypotonic in comparison with 0.15 M kCl solution ?(Assume that ionic solid substances completely dissociates in the solution)
(a) 0.1 M CaCl2 (b) 0.08 M FeCl3 (c) 0.2 M urea (d) 0.12 BaCl2
81. Which of the following solution is isotonic with fluid of RBC ? (For NaCl, i=2)
(a) 5.6% w/v glucose (b) 2.8% w/v glucose
(c) 1.5% w/v urea (d) 0.91% w/v urea
82. Which of the following solution is isotonic with fluid of RBC ? (For NaCl, 2=2)
(a) 2.02 % w/v glucose (b) 4.02% w/v glucose
(c) 8.0% w/v urea (d) both b and c
83. In Which of the following solution, RBC get burst ? (Molecular wt, CaCl2=111, FeCl3=162.5, glucose=180 and urea=60 gm/mole) (Assume that ionic solid completely dissociates in aqueous solution)
(a) 1.2% w/v urea (b) 0.2 MkCl (c) 0.09% M FeCl3 (d) 6.0% w/v glucose
84. In Which of the following solution, RBC get shrinks ? (Molecular wt, CaCl2=111, FeCl3=162.5, glucose=180 and urea=60 gm/mole) (Assume that ionic solid completely dissociates in aqueous solution)
(a) 0.1% w/v CaCl2 (b) 2% w/v urea (c) 1.0% w/v FeCl3 (d) 5.0% w/v glucose
85. FeCl3 ionizes 80% in their aqueous solution, then what will be the value of Vant ‘Hoff factor i ?
(a) 4 (b) 2.7 (c) 3.4 (d) 3.1
86. CaCl2 ionices 80% in their aqueons solution of 0.2 m CaCl2, then, molality of solution is -
(a) 0.48 m (b) 0.52 m (c) 0.6 m (d) 2.6 m
87. A substances associates in their solution as dimer (or bimolecule), then what will be the value of Van’t hoff factor i ?
(a) 0.2 (b) 0.4 (c) 0.6 (d) given all
88. A substance associates as trimer in their solution; then, what would be the value of Van’t Hoff factor i ?
(a) 0.4 (b) 0.3 (c) 0.2 (d) 0.25
89. A substance associates as bimolecule in their solution; then what would be the value of Van’t Hoff factor i ?
(a) 0.4 d” i < 1 (b) 0.5 d” i < 1 (c) 0 < i < 1 (d) 0.6 d” i < 1

91. Which of the following ratio is irrelevant formula mass and experimental molecular weight obtained from colligative properties of solution of ionic solid of AB type ?
(a) 3 : 2 (b) 5 : 3 (c) 4 : 3 (d) 5 : 2
92. Which of the following ratio of correct molecular wt (formula weight) and experimental molecular weight obtained from colligative properties of solution of ionic solid of AB type is possible ?
(a) 5 : 3 (b) 4 : 1 (c) 7 : 3 (d) 5 : 2
93. A substance associates as trimer in their solution, then which of the following ratio is irrelevant for real molecular weight and experimental molecular weight obtained from colligative properties of solution ?
(a) 2 : 3 (b) 2 : 5 (c) 1 : 4 (d) 1 : 2

101. Choose the correct option for true and false statement. (For true statement ‘T’ and for false statement ‘F’ is used)
(i) solubility of gas in liquid increases with increase in partial pressure of the gas.
(ii) solubility of gas in liquid increases with increase in temperature
(iii) solubility of gas in liquid isKH is less
(iv) solubility of gas in liquid increases, as partial pressure of gas decreases and temperature increases.
(a) TTFF (b) FTTT (c) TFFF (d) FFTT
102. Boiling point of an aqueous solution of 0.05m FeCl3 is 100.087 °C; then, what will be the value of Van’t Hoff factor i ? (Kb = 0.513 °C – kg - mole-1)
(a) 4 (b) 3.4 (c) 2.5 (d) 2.8
103. Difference of boiling point and freezing point of an aqueous solution of glucose is 104 oC at 1 bar pressure; then what will be the molality of the solution ? (Kb = 0.513°C and K+” = 1.86 oC – kg - mole-1)
(a) 2.373 m (b) 1.05 m (c) 2.151 m (d) 1.68 m
104. Difference of boiling point and freezing point of 0.2 m acetic acid prepared in benzene is 75.7 oC ; then, state the value of Van’t Hoff factor i ? (For benzene, Kb = 2.65 °C – kg – mol–1, Kf = 5.12 oC – kg – mol– 1, Tb = 80 oC, Tf = 5.5 oC)
(a) 1.44 (b) 0.64 (c) 0.83 (d) 0.77
105. Difference in boiling point and freezing point of 10 kg aqueous solution of urea is 100.2372 °C;then what quantity of urea dissolved in the solution ? (Kb = 0.513o and K+” = 1.86 oC – kg - mole-1)
(a) 59.64 (b) 38.946 (c) 51.65 (d) 40.5
106. 500 ml solution of HCl is prepared by dissolving 14.6 gm HCl in water. What will be the molarity of HCl in the solution ? (Molecular weight of HCl = 36.5 gm/mole )
(a) 0.4 M (b) 0.3 M (c) 0.8 M (d) 0.3 M
107. What would be the molality of the solution prepared by dissolving 60 gm NaOH in 1.5 kg water ? (Moleculea weight of NaOH = 40 gm/mole)
(a) 0.5 m (b) 1.0 m (c) 0.8 m (d) 0.4m
108. What would be the molarity of 3.0 N H2SO4 solution ?
(a) 6 M (b) 1.5 M (c) 3 M (d) 1 M
109. What quantity of NaOH is needed to prepare 1.2 m, 800 ml NaOH solution ?
(a) 3.84 (b) 60 (c) 42 (d) 38.4
110. What would be the molarity and normality of solution prepared by dissolving 19.6 gm H2SO4 in dissolved water to prepare 800 ml solution ? (Molecular weight of H2SO4 is 98 gm/mole)
(a) 0.5 M, 0.25 N (b) 0.25 M, 0.125 N
(c) 0,25 M, 0.5 N (d) 0.125 M, 0.25 N
111. What amount of H2SO4 required to prepare 2 litre of 0.5 N H2SO4solution ? (Molecular weight of H2SO4 is 98 gm/mole)
(a) 98 gm (b) 24.5 gm (c) 49 gm (d) 73.5 gm
112. What will be the concentration of solution prepared by dissolving 50 gm glucose in 200 gm water ?
(a) 25 % w/w (b) 20 % w/w (c) 35 % w/w (d) 15 % w/w
113. What quantity of urea required to prepare 20 % w/w solution having weight 150 gm ?
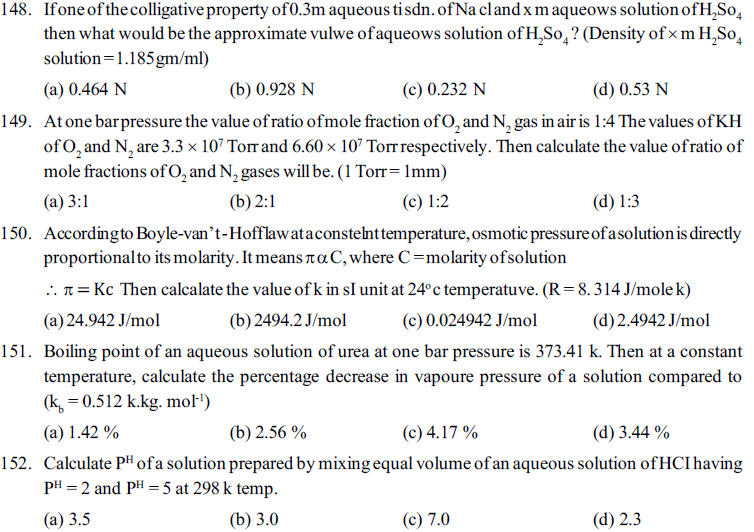
(a) 20 gm (b) 40 gm (c) 10 gm (d) 30 gm
114. What is the normality of an aqueous solution of 0.5 Al2(SO4)3 ?
(a) 3 N (b) 1 N (c) 1.5 N (d) 2.5 N
115. What will be the mole-fraction of ethanol in solution, prepared by dissolving 9.2 gm ethanol in 900 gm water ? (Molecular weight of water and ethanol are 18 and 48 gm/mole respectively)
(a) 0.04 (b) 0.004 (c) 0.4 (d) 0.0004
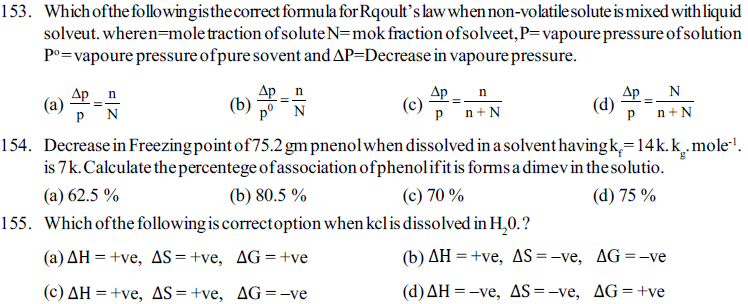
116. What will be the mole-fraction of water and NaOH respectively, when 260 gm NaOH dissolved in 1.8 kg water ? (M.W of watll Naoh = 18440)
(a) 0.96, 0.4 (b) 0.0962, 0.38 (c) 0.0962, .038 (d) 0.962, 0.0038
117. What would be the mole-fraction of solute in an aqueous solution of a substances heaving strength 4.5 m ?
(a) 0.75 (b) 0.075 (c) 0.45 (d) 0.045
118. The density of 98% w/w H2SO4 solution is 1.8 gm/mole then, molarity of the solution is -
(a) 20 M (b) 10 M (c) 18 M (d) None of these
119. Molarity and molality of an aqueous solution of H2SO4 are 1.56 (M) and 1.8 (M) respectively; then, waqht will be the density of the solution ?
(a) 1.835 gm/ml (b) 1.55 gm/ml (c) 1.02 gm/ml (d) 1.725 gm/ml
120. A solution is preparesd from A, B, C and D mole-fraction of A, B and C are 0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 respectively then, mole-fraction of D is -
(a) 0.2 (b) 0.1 (c) 0.3 (d) 0.4
121. The density of 4 M H2SO4 solution is 1.992 gm/ml then, what will be the molality of the solution ? (Molecular weight of H2SO4 is 98 gm/mole)
(a) 3 M (b) 3.5 M (c) 1.2 M (d) 0.4 M
122. Molarity of 1.2 N aqueous solution of AlCl3 is -
(a) 3.6 m (b) 2.4 m (c) 1.2 m (d) 0.4 m
123. What will be the molality of the solution prpared using 500 gm of 25 % w/w NaOH and 500 gm of 15 % w/w NaOH solution ? (Molecular weight of NaOH = 40 gm/mole)
(a) 12.74 m (b) 6.25 m (c) 9 m (d) 5 m
124. What wiil be the molality of solution prepared by taking 25 % w/w NaOH and 15 % w/w NaOH solution ? (Molecular weight of NaOH = 40 gm/mole)
(a) 12.74 m (b) 5.5 m (c) 9 m (d) 4 m
125. The density of 2.5 M NaOH solution is 1.15 gm/ml; then, which of the following alternative is correct for molarity and molality ?
(a) M > m (b) M < m (c) M = m (d) can ’t be predicted
126. Which of the following is correct for an ideal solution ?
(a) “H = 0, “V = 0, “S = 0 (b) “H `” 0, “V = 0, “S = 0
(c) “H = 0, “V = 0, “S `” 0 (d) “H = 0, “V `” 0, “S = 0
127. Boiling point of Aqueous solutions of 0.05 m ABC and 0.02 m X2Y3 are same at 1 bar pressure; then, what will be the values of Van’t Hoff factor (i) for solute in both the solutions ?
(a) 1.04, 5.1 (b) 1.9, 4.75 (c) 1.2, 3.4 (d) 1.5, 3.7
128. Which of the following substances having concentration of aqueous solution 1% w/w, possesses higher boiling point ? (Molecular weight of Kcl, BaCl2, glucose and Al2(SO4)3 are 74.5, 208, 342 gm’mole respectively) (Assume that inonic solids dissociates completely in their aqueous solution)
(a) KCl (b) BaCl2 (c) glucose (d) Al2(SO4)3
129. Molecular weight of biomolecules such as protein can be determined by ______ method.
(a) osmotic pressure measurement (b) Depression in freezing point measurement
(c) Elevation in boiling point measurement (d) Vapour pressure measurement
131. What will be the elevation in boiling point of an aqueous solution of 0.5 m NaCl ? ( i = 1.8)
(a)2.04, 5.1 (b) 1.9, 4.57 (c) 1.2, 3.4 (d) 1.4, 3.7
132. When 2 gm phenol id dissolve in 100gm benzene; then depression in freezing point is 0.69 K.
If its association is dimeric, then calculate its degree of association (X). Molal depression constant for solvent is 5.12 K - kg - mole-1.
(a) 0.0734 (b) 0.374 (c) 0.00734 (d) 0.734
133. At 353 K temperature, the Vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B are 600mm and 800 mm respectively. If mixture of liquids A and B boils at 353 K and 1 bar pressure, then mole proportion of B in percent is -
(a) 80% (b) 60% (c) 20% (d) 40%

138. What amount of urea dissolved in 1 kg water at constant temperature, so that vapour pressure of the solution reduced by 2% ? ( M.W of urea = 60 gm/mole)
(a) 68 gm (b) 60 gm (c) 50 gm (d) 75 gm
139. What would be tne volume of 15% w/v and 5% w/v NaOH solution required to prepare 1 litre aqueous solution of 2M NaOH ? (M.w of Naoh = 40 gram/mole)
(a) 300 ml, 700ml (b) 250 ml, 750ml (c) 400 ml, 600ml (d) 280 ml, 720ml
140. At constant temperature, vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of 1.5 kg glucose decreases to 0.98% in comparision with vapour pressure of pure water then, what quantity of glucose in gram dissolved in the solution ? (Molecular weight of glucose = 180 gm/mole)
(a) 148.5 gm (b) 14.85 gm (c) 125 gm (d) 135 gm
141. At constant pressure, 0.5 m NaCl aqueous solution is diluted by adding water in it. Which of the following statement is correct in this reference ?
(a) Van’t Hoff factor (i) and boiling point of the solution both decreases
(b) Van’t Hoff factor (i) and boiling point of the solution both increases
(c) Van’t Hoff factor (i) decreases while boiling point of the solution both increases
(d) Van’t Hoff factor (i) increases while boiling point of the solution both decreases
142. Boiling point of an aqueous solution of 0.5 m ionic solid substance is 100.5°C; then state the value of i ? (Kb = 0.512oC -kg – mole-1)
(a) 1.95 (b) 1.85 (c) 1.25 (d) 0.85
143. Aqueous solution of substance boils at 100.5oC at 1 bar pressure; then at what temperature it freezes ? (Kb = 0.512oC -kg - mole-1, Kf = 1.86oC - kg – mole-1)
(a) 11.2oC (b) 29.84oF (c) 271.8oK (d) -1.2oC
144. 1.4 m aqueous solution of a weak electrolyte AB2 ionizes 20%, then, state boiling point and freezing point of the solution respectively.
(a) 100.86oC, -3.12oC (b) 101oC, -3.65oC
(c) 274oC, -3.65oC (d) 374oC, -3.65oC
145. Solute substance in a 1.4 m aqueous solution associates by 25%, then, find the boiling point and freezing point of solution; where, solute exists as trimer in the solution; thus, n = 3. (Kb =0.512oC • kg • mole-1, Kf = 1.86oC • kg • mole-1)
(a) 100.448oC, -2.28oC (b) 373.58oK, -3.65oC
(c) 100.59oC, 2.17oC (d) 213oF, 270.83ok
146. Molecular mass of a weak acid HA is 60gm/mo1 Ifs experimental molecular mass in its 0.7 M aqueous solution obtained from colligative properties is 50gm/mo1. Then calculate ionistion consteint of weak acid HA.
(a) 0.023 (b) 0.0085 (c) 0.035 (d) 0.085
147. At constant temperature, the total pressure of a homogeneous mixture of gas-A and gas-B in a closed container collected on water is 2.0 bar. Their ratio of mole frachion is 1.6 If the values of their KH are 2.4 ×10+4 bur and 4.8 ×104 bar respectively then calcwate its ration of mole fraction when dissolhed in H2O.
(a) 1:2 (b) 2:1 (c) 3:1 (d) 1:3
156. Naphthalene is soluble in ether or benzene because. ?
(a) dipole-dipole attraction is equal (b) London forces are equal
(c) Hydrogen bond (d) Ionic attraction
157. Four Liauids are given.
(i) Water : more polar and capacity to torm H-bond.
(ii) Hexanol : moderatly pdar and partial capacity to form H-bond.
(iii) Chloro form : moderatly polar and does not capable to form H-bond.
(iv) Octane : non polar and does not capable to form H-bond.
which of the following pair of liquids mixed with each other in very less proportion.
(a) I, IV (b) I, II (c) II, III (d) III, IV
158. Which of the following is applicable for the solubility of gases in liquid.
(a) Increases with increase in temperature and pressure.
(b) decreases with increase in temp and pressure.
(c) Increases with decrease in temp and increase in pressure.
(d) Decreases with decrease in temp and increase in pressure.

