Refer to NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by NEET, NCERT and KVS. Electrochemistry Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Chemistry and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Electrochemistry in Full Syllabus.
Electrochemistry MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: If
will be
- a) 3x2– 2x1
- b) x2– x1
- c) x2+ x1
- d) 2x1+ 3x2
Answer: 3x2– 2x1
Question: In lead storage battery, the anode reaction is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Which of the following is cathodic reaction?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Electrode potential data are given below
Based on the above data which statement(s) is incorrect?
- a) Fe2+ is stronger reducing agent than Br–
- b) Fe2+ is stronger oxidising agent than Al
- c) Al is stronger reducing agent than Fe2+
- d) Br– is stronger reducing agent than Alg
Answer: Br– is stronger reducing agent than Alg
Question: The coulombic charge on one mole electron is
- a) 1.6 × 10–19 C
- b) 96500 C
- c) 6.02 × 10–23 C
- d) 1.6 × 10–23 C
Answer: 96500 C
Question: The resistance of 0.0025 M solution of K2SO4 is 326 ohm. The specific conductance of the solution, if cell constant is 4.
- a) 4.997 × 10–4
- b) 5.997 × 10–7
- c) 6.997 × 10–4
- d) 1.20 × 10–2
Answer: 1.20 × 10–2
Question: The conductivity of four electrolytes P, Q, R, S in ohm–1 cm–1 are as follows P(5 × 10–5), Q(1× 10–10), R(7 × 10–8);S(9.2 ×10–3). The one which offers highest resistance to the passage of electric current is
- a) P
- b) S
- c) R
- d) Q
Answer: Q
Question: Zn rod is placed in 100 mL of 1M CuSO4 solution so that molarity of Cu2+ changes to 0.7 M. The molarity of SO4– – at this stage will be
- a) 0.8 M
- b) 1 M
- c) 0.7 M
- d) 1.8 M
Answer: 1 M
Question: A direct current deposits 54 g of silver (atomic mass = 108) during the electrolysis. The same quantity of electricity would deposit aluminium (atomic mass = 27) from aluminium chloride in molten state equal to
- a) 4.5 g
- b) 5.4 g
- c) 54 g
- d) 27 g
Answer: 4.5 g
Question: The time taken by the galvanic cell which operates almost ideally under reversible conditions at a current of 10–16A to deliver 1 mole of electron is
- a) 19.30 × 1020 s
- b) 4.825 × 1020 s
- c) 9.65 × 1020 s
- d) 3.4 × 1011 s
Answer: 9.65 × 1020 s
More Questions.................................
Question: During the electrolysis of water 4 mol of electrons were transferred from anode to cathode. The total volume of gases produced at STP will be approximately
- a) 67.2 L
- b) 22.4 L
- c) 44.8 L
- d) 89.4 L
Answer: 67.2 L
Question: Which of the following can oxidise fluoride ions?
- a) O3
- b) Cl2
- c) Br2
- d) No chemical substance
Answer: No chemical substance
Question: In SHE, the pH of the acid solution should be
- a) 7
- b) 14
- c) 0
- d) 4
Answer: 0
Question: Electrolysis of H2SO4(conc.) gives the following at anode
- a) H2
- b) O2
- c) H2S2O3
- d) H2S2O8
Answer: H2S2O8
Question: If the standard reduction potential E° for four divalent elements X, Y, Z, W are –1.46 V, –0.36V, 0.15 V and –1.24 V respectively then
- a) X will replace Z2+ from aqueous solution
- b) Y will replace Z2+ from aqueous solution
- c) W will replace Z2+ from aqueous solution
- d) All statements are corret
Answer: All statements are corret
Question: E.M.F. of Ni(s)|Ni2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq)|Cu(s) cell can be increased by
- a) Adding NH3 in the right half-cell
- b) Increasing the conc. of Ni2+ ions
- c) Adding dimethyl glyoxime into the left half-cell
- d) Changing the electrolyte present in salt bridge
Answer: Adding dimethyl glyoxime into the left half-cell
Question: For given cell; 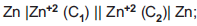 ΔG is negative if
ΔG is negative if
- a) C1= C2
- b) C1> C2
- c) C2> C1
- d) Can't predicted
Answer: C2> C1
Question: The emf of the cell, Zn|Zn2+|Ag+|Ag is independent of
- a) The volume of Zn2+ and Ag+ solution
- b) The molarity of Cu2+ ions in solution
- c) The molarity of Ag+ions in solution
- d) Temperature
Answer: The volume of Zn2+ and Ag+ solution
Question: Standard cell voltage for the cell Pb/Pb2+||Sn2+/Sn is –0.01V. If the cell is to exhibit Ecell= 0, the value of log [Sn2+] /[Pb2+] should be
- a) 0.33
- b) 0.5
- c) 1.5
- d) –0.5
Answer: 0.33
Question: The voltage of a cell whose half cell reactions are given below is
- a) –2.03 V
- b) 1.36 V
- c) 2.71 V
- d) 2.03 V
Answer: 2.71 V
Question: The quantity of electricity required to reduce 12.3 g of nitro benzene to aniline assuming 50% current effeciency is
- a) 115800 C
- b) 57900 C
- c) 231600 C
- d) 28950 C
Answer: 115800 C
Question: A 100 watt, 110 volt lamp is connected in series with an electrolytic cell containing CdSO4 solution, the weight of Cd deposited by the current for 10 hrs is (At. wt. Cd = 112.4)
- a) 19.06 g
- b) 38.12 g
- c) 1.906 g
- d) 3.812 g
Answer: 19.06 g
Question: The two platinum electrodes filted in a conductance cell are 1.5 cm apart while the cross sectional area of each electrode is 0.75 cm2. What is the cell constant?
- a) 1.25 cm
- b) 0.5 cm
- c) 2.0 cm–1
- d) 0.2 cm–1
Answer: 2.0 cm–1
Question: A current of 2.0 A is passed for 5 hours through a molten metal salt deposits 22.2 g of metal (At. mass: 177). The oxidation state of the metal in metal salt is
- a) +1
- b) +2
- c) +3
- d) +4
Answer: +3
Question: The following facts are available
Which of the following statement is correct?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) Can’t predict
Answer:
Question: The hydrogen electrode is dipped in a solution of pH = 3 at 25°C. The reduction potential of the electrode would be
- a) 0.177 V
- b) 0.087 V
- c) –0.177 V
- d) 0.059 V
Answer: –0.177 V
Question:
for the cell is 1.10 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is of the order of
- a) 10–37
- b) 1037
- c) 10–17
- d) 1017
Answer: 1037
Question: A current of 0.965 ampere is passed through 500 ml of 0.2 M solution of ZnSO4 for 10 minutes. The molarity of Zn2+ after deposition of zinc is
- a) 0.1 M
- b) 0.5 M
- c) 0.8 M
- d) 0.194 M
Answer: 0.194 M
Question: What will be the emf of the given cell?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Aqueous solution of which of the following compounds is the best conductor of electric current?
- a) Ammonia, NH3
- b) Fructose, C6H12O6
- c) Acetic acid, C2H4O2
- d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
Answer: Hydrochloric acid, HCl
Question: A device that converts energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen and methane, directly into electrical energy is known as
- a) Ni-Cd cell
- b) Fuel cell
- c) Electrolytic cell
- d) Dynamo
Answer: Fuel cell
Question: When 0.1 mol 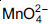 is oxidised the quantity of electricity required to completely oxidise
is oxidised the quantity of electricity required to completely oxidise  is
is
- a) 96500 C
- b) 2 × 96500 C
- c) 9650 C
- d) 96.50 C
Answer: 9650 C
Question: The weight of silver (At. Wt. = 108) displaced by a quantity of electricity which displaces 5600 mL of O2 at STP will be
- a) 5.4 g
- b) 10.8 g
- c) 54.0 g
- d) 108.0 g
Answer: 108.0 g
Question: A button cell used in watches functions as following
The cell potential will be
- a) 0.42 V
- b) 0.84 V
- c) 1.34 V
- d) 1.10 V
Answer: 1.10 V
Question: At 25°C molar conductance of 0.1 molar aqueous solution of ammonium hydroxide is 9.54 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1 and at infinite dilution its molar conductance is 238 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1. The degree of ionisation of ammonium hydroxide at the same concentration and temperature is
- a) 20.800%
- b) 4.008%
- c) 40.800%
- d) 2.080%
Answer: 4.008%
Question: A hydrogen gas electrode is made by dipping platinum wire in a solution of HCl of pH = 10 and by passing hydrogen gas around the platinum wire at one atm pressure. The oxidation potential of electrode would be?
- a) 0.59 V
- b) 0.118 V
- c) 1.18 V
- d) 0.059 V
Answer: 0.59 V
Question: Limiting molar conductivity of 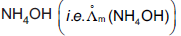 is equal to
is equal to
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Standard reduction potentials of the half reactions are given below
The strongest oxidising and reducing agents respectively are
- a) F2 and I–
- b) Br2 and Cl–
- c) Cl2 and Br–
- d) Cl2 and I2
Answer: F2 and I–
Question: Molar conductivities 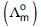 at infinite dilution of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol–1 respectively
at infinite dilution of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol–1 respectively 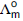 for CH3COOH
for CH3COOH
- a) 425.5 S cm2 mol–1
- b) 180.5 S cm2 mol–1
- c) 290.8 S cm2 mol–1
- d) 390.5 S cm2 mol–1
Answer: 390.5 S cm2 mol–1
Question: The Gibb's energy for the decomposition of Al2O3 at 500°C is as follows
The potential difference needed for the electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) at 500°C is at least
- a) 4.5 V
- b) 3.0 V
- c) 2.5 V
- d) 5.0 V
Answer: 2.5 V
Question: Standard electrode potential for Sn4+ / Sn2+couple is +0.15 V and that for the Cr3+ / Cr couple is –0.74 V. These two couples in their standard state are connected to make a cell. The cell potential will be
- a) + 1.83 V
- b) + 1.19 V
- c) + 0.89 V
- d) + 0.18 V
Answer: + 0.89 V
Question: An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to
- a) Increase in ionic mobility of ions
- b) 100% ionisation of electrolyte at normal dilution
- c) Increase in both i.e. number of ions and ionic mobility of ions
- d) Increase in number of ions
Answer: Increase in ionic mobility of ions
Question: For the reduction of silver ions with copper metal, the standard cell potential was found to be +0.46V at 25°C. The value of standard Gibbs energy, ΔG° will be (F = 96500 C mol–1)
- a) –89.0 kJ
- b) –89.0 J
- c) –44.5 kJ
- d) –98.0 kJ
Answer: –89.0 kJ
Question: Consider the following relations for emf of a electrochemical cell
(a) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Reduction potential of cathode)
(b) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(c) emf of cell = (Reductional potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(d) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation potential of cathode) Which of the above relations are correct?
- a) (c) and (a)
- b) (a) and (b)
- c) (c) and (d)
- d) (b) and (d)
Answer: (b) and (d)
Question: Given
(i) Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu, Eo = 0.337 V
(ii) Cu2+ + e– → Cu+, Eo = 0.153 V
Electrode potential, Eo for the reaction,
Cu+ + e– → Cu, will be
- a) 0.90 V
- b) 0.30 V
- c) 0.38 V
- d) 0.52 V
Answer: 0.52 V
Question: Al2O3 is reduced by electrolysis at low potentials and high currents. If 4.0 × 104 amperes of current is passed through molten Al2O3 for 6 hours, what mass of aluminium is produced? (Assume 100% current efficiency, At.mass of Al = 27 g mol–1)
- a) 8.1 × 104 g
- b) 2.4 × 105 g
- c) 1.3 × 104 g
- d) 9.0 × 103 g
Answer: 8.1 × 104 g
Question: The equivalent conductance of M/32 solution of a weak monobasic acid is 8.0 mhos cm2 and at infinite dilution is 400 mhos cm2. The dissociation constant of this acid is
- a) 1.25 × 10–6
- b) 6.25 × 10–4
- c) 1.25 × 10–4
- d) 1.25 × 10–5
Answer: 1.25 × 10–5
Question: Kohlrausch's law states that at
- a) Infinite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to equivalent conductance of an electrolyte, whatever be the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
- b) Finite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to equivalent conductance of an electrolyte, whatever be the naure of the other ion of the electrolyte
- c) Infinite dilution each ion makes definite contribution to equivalent conductance of an electrolyte depending on the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
- d) Infinite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to conductance of an electrolyte whatever be the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
Answer: Infinite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to equivalent conductance of an electrolyte, whatever be the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
Question: Standard free energies of formation (in kJ/mol) at 298 K are –237.2, –394.4 and –8.2 for H2O (l), CO2(g) andpentane (g) respectively. The value of E°cell for the pentane-oxygen fuel cell is
- a) 0.0968 V
- b) 1.968 V
- c) 2.0968 V
- d) 1.0968 V
Answer: 1.0968 V
Question: On the basis of the following E° values, the strongest oxidizing agent is
- a) [Fe(CN)6]3–
- b) [Fe(CN)6]4–
- c) Fe2+
- d) Fe3+
Answer: Fe3+
Question: The equilibrium constant of the reaction
Cu(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) →Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s) ; E°=0.46V at 298 K is
- a) 4.0 × 1015
- b) 2.4 × 1010
- c) 2.0 × 1010
- d) 4.0 × 1010
Answer: 4.0 × 1015
Question: The efficiency of a fuel cell is given by
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: If 
the standard EMF of the reaction will be
- a) 0.330 V
- b) 1.653 V
- c) 1.212 V
- d) 0.111 V
Answer: 1.212 V
Question: A hypothetical electrochemical cell is shown below A|A+(xM)||B+(yM)|B, the emf measured is +0.20 V. The cell reaction is
- a) A+ + B → A + B+
- b) A+ + e– → A ; B+ + e– → B
- c) The cell reaction cannot be predicted
- d) A + B+ → A+ + B
Answer: A + B+ → A+ + B
Question: 4.5g of aluminium (at. mass 27 amu) is deposited at cathode from Al3+ solution by a certain quantity of electric charge. The volume of hydrogen produced at STP from H+ ions in solution by the same quantity of electric charge will be
- a) 22.4 L
- b) 44.8 L
- c) 5.6 L
- d) 11.2 L
Answer: 5.6 L
Question: A solution contains Fe2+, Fe3+ and I– ions. This solution was treated with iodine at 35°C. E° for Fe3+/Fe2+ is +0.77 V and E° for I2/2I– = 0.536 V. The favourable redox reaction is
- a) I– will be oxidised to I2
- b) Fe2+ will be oxidised to Fe3+
- c) I2 will be reduced to I–
- d) There will be no redox reaction
Answer: I– will be oxidised to I2
Question: Standard reduction potentials at 25°C of Li+ / Li, Ba2+ / Ba, Na+ / Na and Mg2+ / Mg are –3.05, –2.90, –2.71 and –2.37 volt respectively. Which one of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent?
- a) Ba2+
- b) Mg2+
- c) Na+
- d) Li+
Answer: Mg2+
Question: To protect iron against corrosion, the most durable metal plating on it, is
- a) Copper plating
- b) Zinc plating
- c) Nickel plating
- d) Tin plating
Answer: Nickel plating
Question: An electrochemical cell is set up as :
Pt; H2(1 atm) |HCl (0.1 M) || CH3COOH (0.1M) |
H2(1 atm) ; Pt. The e.m.f. of this cell will not be zero, because
- a) Acids used in two compartments are different
- b) e.m.f. depends on molarities of acids used
- c) The temperature is constant
- d) pH of 0.1 M HCl & 0.1 M CH3COOH is not same
Answer: pH of 0.1 M HCl & 0.1 M CH3COOH is not same
Question: Electrode potential for the following half-cell reactions are
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e–; E° = + 0.76 V;
Fe → Fe2+ + 2e–; E° = + 0.44 V
The EMF for the cell reaction Fe2+ + Zn → Zn2+ + Fe will be
- a) – 0.32 V
- b) + 1.20 V
- c) – 1.20 V
- d) + 0.32 V
Answer: + 0.32 V
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
MCQs for Electrochemistry Chemistry Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Chemistry to develop the Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Chemistry will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the NEET MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by NEET for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Electrochemistry MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Electrochemistry

