Refer to NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by NEET, NCERT and KVS. Solutions Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Chemistry and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Solutions
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Solutions in Full Syllabus.
Solutions MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: The normality of 10% (weight/volume) acetic acid is
- a) 1 N
- b) 10 N
- c) 1.7 N
- d) 0.83 N
Answer: 1.7 N
Question: 20 ml of 0.5 M HCl is mixed with 30 ml of 0.3 M HCl the molarity of resulting solution is
- a) 0.8 M
- b) 0.53 M
- c) 0.38 M
- d) 0.83 M
Answer: 0.38 M
Question: 20 ml of 0.2 M Al2(SO4)3 is mixed with 20 ml of 6.6 M BaCl2 , the concentration of Cl– ion in solution is
- a) 0.2 M
- b) 6.6 M
- c) 0.02 M
- d) 0.06 M
Answer: 6.6 M
Question: The expression relating molarity (M) of a solution with its molality (m) is (where d = density, MBmol. wt. of solute)
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: If solubility of any gas in the liquid at 1 bar pressure is 0.05 mol/lit. What will be its solubility at 3 bar pressure, keeping the temperature constant ?
- a)
- b) 0.15 mol/lit
- c) 0.05 mol/lit
- d) 1.0 mol/lit
Answer: 0.15 mol/lit
Question: The boiling points of C6H6, CH3OH, C6H5NH2 and C6H5NO2 are 80oC, 65oC, 184oC and 212oC respectively. Which of the following will have highest vapour pressure at room temperature?
- a) C6H6
- b) CH3OH
- c) C6H5NH2
- d) C6H5NO2
Answer: CH3OH
Question: The highest temperature at which vapour pressure of any liquid can be measured is
- a) Critical temperature
- b) Boyle’s temperature
- c) Boiling point of the liquid
- d) Kraft temperature
Answer: Boiling point of the liquid
Question: If solute and solvent interactions are more than solute - solute and solvent - solvent interactions then
- a) It is ideal solution
- b) It is non-ideal solution with positive deviation
- c) It is non-ideal solution with negative solution
- d) Can't predicted
Answer: It is non-ideal solution with negative solution
Question: Which of the following is correct about a solution showing positive deviation?
- a) Vapour pressure observed will be the less than that calculated from Raoult’s law
- b) Minimum boiling azeotrope will be formed
- c) ΔHmix< 0
- d) ΔVmix< 0
Answer: Minimum boiling azeotrope will be formed
Question: If C2H5OH and H2O solution is example of non-ideal solution then which graphical representation is correct?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: If P0 and P are the vapour pressure of solvent and solution n1 and n2 are the moles of solute and solvent then
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) Pº = P × n1
Answer:
Question: Which of the following statement is true?
- a) Molarity of solution is independent of temperature
- b) Molality of solution is independent of temperature
- c) Mole fraction of solute is dependent on temperature
- d) The unit of molality is mol dm–3
Answer: Molality of solution is independent of temperature
Question: Among the following mixtures, dipole-dipole as the major interaction, is present in
- a) Benzene and CCl4
- b) Benzene and C2H5OH
- c) CH3COCH3 and CH3CN
- d) KCl and water
Answer: CH3COCH3 and CH3CN
Question: For an ideal solution with 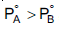 which of the following is true?
which of the following is true?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) No relationship in their mole fraction
Answer:
Question: An azeotropic solution of two liquids has a boiling point lower than either of the boiling points of the two liquids when it
- a) Shows negative deviation
- b) Shows positive deviation
- c) Shows no deviation
- d) Is unsaturated
Answer: Shows positive deviation
More Questions........................................................
Question: The vapour pressure of a solution having 2.0 g of solute X (molar atomic mass = 32 g mol–1) in 100 g of CS2(vapourpressure = 854 torr) is 848.9 torr. The molecular formula of the solute is
- a) X
- b) X2
- c) X4
- d) X8
Answer: X8
Question: Two solutions of a non-electrolyte are mixed in the following manner. 480 mL of 1.5 M first solution + 520 mL of 1.2 M second solution. What is the molarity of the final solution?
- a) 1.344 M
- b) 2.70 M
- c) 1.20 M
- d) 1.50 M
Answer: 1.344 M
Question: A pressure cooker reduces cooking time for food because
- a) Cooking involves chemical changes helped by a rise in temperature
- b) Heat is more evenly distributed in the cooking space
- c) Boiling point of water involved in cooking is increased
- d) The higher pressure inside the cooker crushes the food material
Answer: Boiling point of water involved in cooking is increased
Question: Equal moles of benzene and toluene are mixed the V.P. of benzene and toluene in pure state are 700 and 600 mm Hg respectively. The mole fraction of benzene in vapour state is
- a) 0.7
- b) 0.47
- c) 0.50
- d) 0.54
Answer: 0.54
Question: The vapour pressure of a solvent decreased by 10 mm of Hg when a non-volatile solute was added to the solvent. The mole fraction of solute in solution is 0.2, what would be the mole fraction of solute if decrease in vapour pressure is 20 mm of Hg?
- a) 0.8
- b) 0.6
- c) 0.4
- d) 0.2
Answer: 0.4
Question: Calculate the mole fraction of toluene in the vapour phase which is in equilibrium with a solution of benzene and toluene having a mole fraction of toluene 0.5. (The vapour pressure of pure Benzene is 119 torr and that of toluene is 37 torr at the same temperature)
- a) 0.5
- b) 0.75
- c) 0.625
- d) 0.237
Answer: 0.237
Question: An ideal solution was obtained by mixing methanol and ethanol. If the partial vapour pressure of methanol and ethanol are 2.619 kPa and 4.556 kPa respectively, the composition of vapour (in terms of mole fraction) will be
- a) 0.635 MeOH, 0.365 EtOH
- b) 0.365 MeOH, 0.635 EtOH
- c) 0.574 MeOH, 0.326 EtOH
- d) 0.173 MeOH, 0.827 EtOH
Answer: 0.365 MeOH, 0.635 EtOH
Question: The vapour pressure of a dilute aqueous solution of glucose is 750 mm Hg at 373 K. Calculate the mole fraction of solute. (The vapour pressure of pure water is 760 mm Hg at 373 K)
- a) 0.013
- b) 1.3
- c) 0.13
- d) 1.1
Answer: 0.013
Question: Two liquids having vapour pressures P10 and P20 in pure state in the ratio of 2 : 1 are mixed in the molar ratio of 1 : 2. The ratio of their moles in the vapour state would be
- a) 1 : 1
- b) 1 : 2
- c) 2 : 1
- d) 3 : 2
Answer: 1 : 1
Question: In ideal solution of non volatile solute B in solvent A in 2 : 5 molar ratio has vapour pressure 250 mm. If a another solution in ratio 3 : 4 prepared then vapour pressure above this solution
- a) 200 mm
- b) 250 mm
- c) 350 mm
- d) 400 mm
Answer: 200 mm
Question: In the case of osmosis, solvent molecules move from solution having
- a) Higher vapour pressure to lower vapour pressure
- b) Higher concentration to lower concentration
- c) Lower vapour pressure to higher vapour pressure
- d) Higher osmotic pressure to lower osmotic pressure
Answer: Higher vapour pressure to lower vapour pressure
Question: Equimolar solution of non-electrolyte in the same solvent have
- a) Same boiling point and same freezing point
- b) Different boiling point and different freezing point
- c) Same boiling point but different freezing point
- d) Same freezing point but different boiling point
Answer: Same boiling point and same freezing point
Question: In the phenomenon of osmosis through the semipermeable membrane
- a) Solvent molecules pass from solution to solvent
- b) Solvent molecules pass from solvent to solution
- c) Solute molecules pass from solution to solvent
- d) Solute molecules pass from solvent to solution
Answer: Solvent molecules pass from solvent to solution
Question: The osmotic pressure of 0.1 M sodium chloride solution at 27°C is
- a) 4.0 atm
- b) 2.46 atm
- c) 4.92 atm
- d) 1.23 atm
Answer: 4.92 atm
Question: A solution containing 8.6 g L–1 of urea is isotonic with a 5% solution of unknown solute. The molar mass of the solute will be
- a) 348.9 g mol–1
- b) 174.5 g mol–1
- c) 87.3 g mol–1
- d) 34.89 g mol–1
Answer: 348.9 g mol–1
Question: Which of the following physical properties is used to determine, the molecular mass of a polymer solution?
- a) Relative lowering of vapour pressure
- b) Elevation in boiling point
- c) Depression in freezing point
- d) Osmotic pressure
Answer: Osmotic pressure
Question: In a 0.2 molar aqueous solution of a weak acid HX, the degree of ionization is 0.3. The freezing point of the solution will be nearest to
- a) 0.48°C
- b) –0.48°C
- c) –0.36°C
- d) –0.26°C
Answer: –0.48°C
Question: The boiling point of water at 735 torr is 99.07°C. The mass of NaCl added in 100 g water to make its boiling point 100°C is (kb= 0.51 K kg mol–1)
- a) 10.68 g
- b) 5.34 g
- c) 2.67 g
- d) 26.7 g
Answer: 5.34 g
Question: If van't Hoff factor, i = 1, then
- a) It is dissociation
- b) It is association
- c) Both (1) & (2)
- d) Neither dissociation nor association
Answer: Neither dissociation nor association
Question: Which of the following equimolar solution have highest vapour pressure?
- a) Glucose
- b) NaCl
- c) K2SO4
- d) K4Fe(CN)6
Answer: Glucose
Question: If α is the degree of dissociation of Na2SO4 . The van’t Hoff factor used for the calculation of molecular mass is
- a) 1 + 2α
- b) 1 – 2α
- c) 1 + α
- d) 1 – α
Answer: 1 + 2α
Question: The relationship between the values of osmotic pressure of 0.1M solutions of KNO3(P1) and CH3COOH(P2) is
- a) P1> P2
- b) P2> P1
- c) P1= P2
- d)
Answer: P1> P2
Question: The relationship between osmotic pressure (P) at 273 K when 10 g glucose (P1), 10 g urea (P2) and 10 g sucrose (P3) are dissolved in 250 ml of water is
- a) P1> P2> P3
- b) P2> P1> P3
- c) P2> P3> P1
- d) P3> P2> P1
Answer: P2> P1> P3
Question: What is the molality of C2H5OH in water solution which will freeze at –10oC? [Mol. wt. of C2H5OH = 46, Kf for water = 1.86]
- a) 6.315 m
- b) 63.15 m
- c) 3.540 m
- d) 5.3 m
Answer: 5.3 m
Question: Which of the following pairs of solutions can we expect to be isotonic at the same temperature?
- a) 0.1 M NaCl and 0.1 M Na2SO4
- b) 0.1 M urea and 0.1 M NaCl
- c) 0.1 M urea and 0.2 M MgCl2
- d) 0.1 M Ca(NO3)2and 0.1 M Na2SO4
Answer: 0.1 M Ca(NO3)2and 0.1 M Na2SO4
Question: Which of the following aqueous solution has maximum freezing point?
- a) 0.01 M NaCl
- b) 0.005 M C2H5OH
- c) 0.005 M MgI2
- d) 0.01 M MgSO4
Answer: 0.005 M C2H5OH
Question: 0.1 M aqueous solution of K4[Fe(CN)6] will have the same freezing point as 0.1 M aqueous solution of
- a) Fe(SO4)3
- b) Al2(SO4)3
- c) AlCl3
- d) K3PO4
Answer: Al2(SO4)3
Question: Assuming salts to be 90% dissociated, which of the following will have highest osmotic pressure?
- a) Decimolar Al2(SO4)3
- b) Decimolar BaCl2
- c) Decimolar Na2SO4
- d) A solution obtained by mixing equal volumes of (2) & (3) and filtering
Answer: Decimolar Al2(SO4)3
Question: When CuSO4 is added to a solution of ammonia
- a) Freezing point is lowered
- b) Freezing point is raised
- c) Boiling point is raised
- d) Both (1) & (3)
Answer: Freezing point is raised
Question: An aqueous solution freezes at –0.36°C. Kf and Kb for water are 1.8 and 0.52 respectively then value of boiling point of solution at 1 atm pressure is
- a) 101.04°C
- b) 100.104°C
- c) 0.104°C
- d) 100°C
Answer: 100.104°C
Question: The osmotic pressure of decimolar solution of urea at 27°C is
- a) 2.49 bar
- b) 5.0 bar
- c) 3.4 bar
- d) 1.25 bar
Answer: 2.49 bar
Question: When a saturated solution of KCl is heated it becomes
- a) Unsaturated
- b) Supersaturated
- c) Remains saturated
- d) Attains equilibrium
Answer: Unsaturated
Question: Arrange the following aqueous solutions in the order of their increasing boiling points
(i) 10–4 M NaCl (ii) 10–3 M Urea (iii) 10–3 M MgCl2 (iv) 10–3 M NaCl
- a) (i) < (ii) < (iv) < (iii)
- b) (ii) < (i) = (iii) < (iv)
- c) (i) < (ii) < (iii) < (iv)
- d) (iv) < (iii) < (i) = (ii)
Answer: (i) < (ii) < (iv) < (iii)
Question: Molal elevation constant of a liquid is
- a) The elevation in b.p. which would be produced by dissolving one g of solute in 100 g of solvent
- b) The elevation in b.p. which would be produced by dissolving 1g. solute in 100 g of solvent
- c) Elevation in b.p. which would be produced by dissolving 1 gm of solute in 1000 g of solvent
- d) Elevation in b.p which would be produced by dissolving 1 mole of solute is 1000 g of solvent
Answer: Elevation in b.p which would be produced by dissolving 1 mole of solute is 1000 g of solvent
Question: 100 ml of 1 M NaOH is mixed with 50 ml of 1 N KOH solution. Normality of mixture is
- a) 1 N
- b) 0.5 N
- c) 0.25 N
- d) 2 N
Answer: 1 N
Question: Two solutions marked as A and B are separated through semipermeable membrane as below. The phenomenon undergoing
- a) Na+ moves from solution A to solution B
- b) Both Na+ and Cl– moves from solution (A) to solution (B)
- c) Both Na+ and Cl– moves from solution (B) to (A)
- d) Solvent molecules moves from solution (A) to (B)
Answer: Solvent molecules moves from solution (A) to (B)
Question: Mass of NaCl required to prepare 0.01 m aqueous solution in 1 kg water is
- a) 0.01 g
- b) 0.585 g
- c) 58.8 g
- d) 5.88 g
Answer: 0.585 g
Question: Correct observation
- a) Vapour pressure of solution I is lowest
- b) Relative lowering of vapour pressure is maximum in III
- c) Freezing point is maximum for III
- d) Boiling point is minimum for II
Answer: Relative lowering of vapour pressure is maximum in III
Question: An aqueous solution of sugar is taken in a beaker. At freezing point of solution
- a) Crystals of sugar separated
- b) Crystals of glucose and fructose are separated
- c) Crystals of ice separated
- d) Mixture of ice and some sugar crystals separated
Answer: Crystals of ice separated
Question: 15 g urea and 20 g NaOH dissolved in water. Total mass of solution is 250 g. Mole fraction of NaOH in the mixture
- a) 0.036
- b) 0.62
- c) 0.5
- d) 0.4
Answer: 0.036
Question: Which of the following concentration terms is temperature independent?
I. Molarity II. Molality III. Normality IV. Mole fraction
- a) I & II
- b) I & III
- c) II only
- d) II & IV
Answer: II & IV
Question: A mixture of two liquids A and B having boiling point of A is 70°C, and boiling point of B is 100°C, distills at 101.2°C as single liquid, hence this mixture is
- a) Ideal solution
- b) Non ideal solution showing +ve deviation
- c) Non ideal solution showing –ve deviation
- d) Immiscible solution
Answer: Non ideal solution showing –ve deviation
Question: Vapour phase diagram for a solution is given below if dotted line represents deviation
Correct observation for this solution
- a) ΔHmix :+ve
- b) ΔSmix :+ve
- c) ΔVmix :+ve
- d) All of these
Answer: All of these
Question: The phenomenon taking place
- a) Exo-osmosis
- b) Endo-osmosis
- c) Reverse-osmosis
- d) All of these
Answer: Endo-osmosis
Question: 1 molar aqueous solution is _____ concentrated than 1 m aqueous solution
- a) More
- b) Less
- c) Equally
- d) Very less
Answer: More
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
MCQs for Solutions Chemistry Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Chemistry to develop the Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Chemistry will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the NEET MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Solutions for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by NEET for Full Syllabus Chemistry Solutions have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry Solutions MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Solutions MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Solutions

