Refer to NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by NEET, NCERT and KVS. Chemical Kinetics Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Chemistry and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Chemical Kinetics
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Chemical Kinetics in Full Syllabus.
Chemical Kinetics MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: The unit of rate constant and rate of reaction are same for
- a) First order
- b) Zero order
- c) Second order
- d) Third order
Answer: Zero order
Question: For a reaction of the type  is equal to
is equal to
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: For a gaseous reaction, the rate of reaction may be expressed in the units
- a) atm
- b) atm s
- c) atm/s
- d) atm/s2
Answer: atm/s
Question: A gaseous reaction, 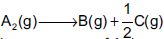 shows increase in pressure from 100 mm to 120 mm in 5 minutes. The rate of disappearance of A2 is
shows increase in pressure from 100 mm to 120 mm in 5 minutes. The rate of disappearance of A2 is
- a) 4 mm min–1
- b) 8 mm min–1
- c) 16 mm min–1
- d) 2 mm min–1
Answer: 8 mm min–1
Question: Which of the following will react at the highest rate?
- a) 1 mol of A and 1 mol of B in a 1 L vessel
- b) 2 mol of A and 2 mol of B in a 2 L vessel
- c) 3 mol of A and 3 mol of B in a 3 L vessel
- d) All would react at the same rate
Answer: All would react at the same rate
Question: Which of the following does not affect the rate of reaction?
- a) Amount of the reactant taken
- b) Physical state of the reactant
- c) ΔH of reaction
- d) Size of vessel
Answer: ΔH of reaction
Question: In a reaction, 2X + Y → X2 Y, the X disappears at
- a) Half the rate as that of disappearance of Y
- b) The same rate as that of disappearance of Y
- c) The same rate as that of appearance of X2Y
- d) Twice the rate as that of appearance of X2Y
Answer: Twice the rate as that of appearance of X2Y
Question: During the course of a chemical reaction, the rate of a reaction
- a) Remains constant throughout
- b) Increases as the reaction proceeds
- c) Decreases as the reaction proceeds
- d) First increases followed by a decrease
Answer: Decreases as the reaction proceeds
Question: A reaction involving two different reactants can never be a
- a) Second order reaction
- b) Biomolecular reaction
- c) Unimolecular reaction
- d) First order reaction
Answer: Unimolecular reaction
Question: For the hypothetical reaction 2A→ 3C, the reaction rate ‘r’ in terms of the rate of change of the concentration is given by
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: In an experiment to study the reaction  at t = 0 was found to be 2.6×10–2 M s–1. What is the value of
at t = 0 was found to be 2.6×10–2 M s–1. What is the value of 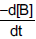 at t = 0 in M s–1 ?
at t = 0 in M s–1 ?
- a) 2.6 × 10–2
- b) 5.2 × 10–2
- c) 1.3 × 10–2
- d) 1.0 × 10–1
Answer: 5.2 × 10–2
Question: For the reaction N2+ 3H2→2NH3 , the rate of change of concentration for hydrogen is –0.3 × 10–4 Ms–1. The rate of change of concentration of ammonia is
- a) –0.2 × 104
- b) 0.2 × 10–4
- c) 0.1 × 10–4
- d) 0.3 × 10–4
Answer: 0.2 × 10–4
Question: The graph plotted between concentration versus time
- a) It gives rate of disappearance of reactant
- b)
- c) Both (1) & (2)
- d) It predicts the order of reaction
Answer: Both (1) & (2)
Question: For reaction, 2B + A→ 2C
Which of the following is correct ?
- a) Rate of disappearance of B is twice that of rate of disappearance of C
- b) Rate of disappearance of A is twice that of rate of disappearance of C
- c) Rate of appearance of C is twice that of rate of disappearance of A
- d) All of these
Answer: Rate of appearance of C is twice that of rate of disappearance of A
Question: For the homogeneous elementary reaction, A + B —→C, the unit of rate constant is
- a) s–1
- b) s–1 mol L–1
- c) s–1 mol–1 L
- d) s
Answer: s–1 mol–1 L
Question: The rate law of a reaction between the substance A and B is given by, rate = k[A]n [B]m. On doubling the concentration of A and making the volume of B half the ratio of new rate to the earlier rate of reaction will be
- a)
- b) m + n
- c) 2n + m
- d) 2n – m
Answer: 2n + m
Question: Consider the reaction, 2A + B —→ C + D. If the rate expression is r = [A]2 [B]0 and if volume is reduced to 1/3 , the rate of reaction will increase
- a) 27 times
- b) 9 times
- c) 8 times
- d) Rate will not get affected
Answer: 9 times
Question: The rate constant is numerically the same for three reaction of first, second and third order respectively. Which one is true for rate of three reaction, if concentration of reactant is greater than 1M?
- a) r1= r2= r3
- b) r1> r2> r3
- c) r1< r2< r3
- d) All of these
Answer: r1< r2< r3
Question: Assuming an elementry reaction H2O2+ 3I– + 2H+ —→ 2H2O + I3–. The effect on the rate of this reaction brought about by doubling the concentration of I– without changing the order
- a) The rate would increase by a factor of 3
- b) The rate would increase by a factor of 8
- c) The rate would decrease by a factor of 1/3
- d) The rate would increase by a factor of 9
Answer: The rate would increase by a factor of 8
Question: For a reaction A + B → products, the rate of reaction was doubled when concentration of A was doubled. When concentration of A and B both was doubled, the rate was again doubled, order of reaction w.r.t. A and B are
- a) 1, 1
- b) 2, 0
- c) 1, 0
- d) 0, 1
Answer: 1, 0
Question: The overall order of reaction between X & Y is 3. Which of the following rate equation must be correct, if on doubling the concentration of X, the rate of reaction gets doubled ?
- a) r = K [X]2 [Y]0
- b) r = K [X]1 [Y]2
- c) r = K [X]1 [Y]3
- d) r = K [X]2 [Y]1
Answer: r = K [X]1 [Y]2
Question: For a zero order reaction, K = 1 × 10–3 mol L–1 s–1. If initial concentration of the reactant is 1.0 mol L–1, the concentration after 10 minutes would be
- a) 1 × 10–2 mol L–1
- b) 0.6 mol L–1
- c) 0.4 mol L–1
- d) 1.0 mol L–1
Answer: 0.4 mol L–1
Question: Which of the following statement is not correct?
- a) Molecularity of a reaction cannot be fractional
- b) Molecularity of a reaction cannot be more than three
- c) Molecularity of a reaction may or may not be equal to the order of reaction
- d) Molecularity of a reaction can be obtained from balanced chemical equation
Answer: Molecularity of a reaction can be obtained from balanced chemical equation
Question: Consider the following in respect of zero order reaction
I. t1/2 is directly proportional to the initial concentration
II. Time taken for the completion of the reaction is twice its t1/2
III. Concentration of the reactant decreases linearly with time
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- a) I & II only
- b) I & III only
- c) II & III only
- d) I, II & III
Answer: I, II & III
Question: If initial concentration is reduced to 1/4th in a zero order reaction, the time taken for half the reaction to complete
- a) Remains same
- b) Becomes 4 times
- c) Becomes one-fourth
- d) Doubles
Answer: Becomes one-fourth
Question: If initial concentration of the reactants is doubled, the time for half reaction is also doubled, the order of the reaction is
- a) Zero
- b) One
- c) Two
- d) Three
Answer: Zero
Question: The inversion of cane sugar represented by C12H22O11+ H2O→ C6H12O6+ C2H12O6 is a _____ reaction.
- a) Unimolecular
- b) Second order
- c) Zero order
- d) First order
Answer: First order
Question: For a Ist order reaction, a straight line is obtained if you plot
- a) Log conc. vs. time
- b) Conc. vs. time
- c) 1/conc. vs. time
- d) Log conc. vs. 1/time
Answer: Log conc. vs. time
Question: Which order reaction obeys the expression 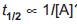 ?
?
- a) First
- b) Second
- c) Third
- d) Zero
Answer: Second
Question: The graph of t½ versus initial concentration ‘a’ is for
- a) First order
- b) Second order
- c) Zero order
- d) Can’t predict
Answer: First order
More Questions.............................
Question: A substance (initial concentration 'a') reacts according to zero order kinetics. The time it takes for the completion of the reaction is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A first order reaction completes 60% in 20 minutes. The time required for the completion of 90% of the reaction is approx...
- a) 30 minutes
- b) 40 minutes
- c) 50 minutes
- d) 60 minutes
Answer: 50 minutes
Question: The half life period of a substance is 50 minutes at a certain initial concentration. When concentration is reduced to one-half, half life is found to 25 minutes. Order of reaction is
- a) Zero
- b) First
- c) Second
- d) Third
Answer: Zero
Question: The half life of a second order process,
2A → products, is
- a) Independent of initial concentration
- b) Directly proportional to initial concentration of A
- c) Inversely proportional to initial concentration of A
- d) Inversely proportional to square of initial concentration
Answer: Inversely proportional to initial concentration of A
Question: The rate constant for the forward and backward reactions of hydrolysis of ester are 1.1×10–2 and 1.5×10–3 min–1 respectively. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is
- a) 7.33
- b) 0.733
- c) 73.3
- d) 733
Answer: 7.33
Question: The rate law for the reaction,
RCl + NaOH(aq) → ROH + NaCl
is given by Rate = k[RCl]. The rate of reaction will be
- a) Doubled on doubling the concentration of NaOH
- b) Halved on reducing the concentration of alkyl halide to one-half
- c) Decreases on increasing the temperature
- d) Unaffected by increasing the temperature
Answer: Halved on reducing the concentration of alkyl halide to one-half
Question: For a reaction, A —→ B, it has been found that the order of the reaction is zero with respect to A. Which of the following expressions correctly describes the reaction?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A sample of a radioactive substance undergoes 80% decomposition in 345 minutes. Its half life is _____ minutes.
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: 99% of a first order reaction, was completed in 32 minute. When will 99.9% of the reaction complete?
- a) 50 minute
- b) 46 minute
- c) 49 minute
- d) 48 minute
Answer: 48 minute
Question: Check, which of the following statements is false?
- a) A catalyst does not differentiate between forward and backward reaction
- b) Large activation energy is associated with low reaction rate
- c) Maxwell's distribution of velocities remains-unaltered under all conditions of temperature and pressure
- d) A catalyst does not affect the equilibrium state of reaction
Answer: Maxwell's distribution of velocities remains-unaltered under all conditions of temperature and pressure
Question: Arrhenius parameter (A) depends on
- a) Steric factor
- b) Collision frequency
- c) Both (1) & (2)
- d) Neither (1) nor (2)
Answer: Both (1) & (2)
Question: The chemical reactions in which the reactants require high amount of activation energy are generally
- a) Slow
- b) Fast
- c) Instantaneous
- d) Spontaneous
Answer: Slow
Question: For an exothermic chemical process occurring in two steps as
(i) A + B → X (slow) ; (ii) X → AB (fast)
The progress of the reaction can be best described by (X is considered as intermediate)
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) None of these
Answer:
Question: A chemical process occurring in two steps, is plotted as
The correct statement is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: For the chemical process energies are plotted in graph.
Which of the following is correct ?
- a) It is the exothermic reaction, ΔH = b – a
- b) Threshold energy, e = a + c
- c) (Ea)f< (Ea)b
- d) All of these
Answer: All of these
Question: The rate of a reaction becomes 2 times for every 10°C rise in temperature. How many times rate of reaction will be increased when temperature is increased from 30°C to 80°C?
- a) 16
- b) 32
- c) 64
- d) 128
Answer: 32
Question: The rate of a reaction increases by 2.5 times when the temperature is raised from 300 K to 310 K. If K is the rate constant at 300 K, then the rate constant at 310 K will be equal to
- a) K
- b) 2K
- c) 2.5K
- d) 3K
Answer: 2.5K
Question: The minimum amount of energy that the reacting molecules must possess at the time of collisions in order to produce effective collision is called
- a) Activation energy
- b) Threshold energy
- c) Internal energy
- d) Free energy
Answer: Threshold energy
Question: The rate constant, the activation energy and Arrhenius parameter of a chemical reaction at 25°C are x, 10xkJ/mol and 2x s–1. Value of rate constant as T → ∞ is
- a) x s–1
- b) 2x s–1
- c) ∞
- d) 10x s–1
Answer: 2x s–1
Question: At particular concentration, the half life of the reaction is 100 minutes. When the concentration of the reactant become double half life becomes, 25 minutes, then what will be the order of the reaction?
- a) 1
- b) 2
- c) 0
- d) 3
Answer: 3
Question: Consider the data below for a reaction A →B
From the above data the order of reaction is
- a) Zero
- b) 1
- c) 2
- d) 3
Answer: Zero
Question: The graph between the log K versus 1/T is a straight line. The slope of the line is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The temperature coefficient for most of the reaction lies between
- a) 1 & 3
- b) 2 & 3
- c) 1 & 4
- d) 2 & 4
Answer: 2 & 3
Question: If the volume of closed vessel in which the following simple reaction is carried out is reduced to one-third of original volume, the rate of reaction becomes
2NO (g) + O2(g) →2NO2(g)
- a) One-third
- b) Three times
- c) Nine times
- d) Twenty seven times
Answer: Twenty seven times
Question: For the reaction A + B → products, it is found that order of A is 2 and the order of B is 3 in the rate expression. When the concentrations of both A and B are doubled the rate will increase by a factor
- a) 10
- b) 16
- c) 32
- d) 28
Answer: 32
Question: Nitric oxide (NO) reacts with oxygen to produce nitrogen dioxide
then rate law is
- a) Rate = K’ [NO][O2]
- b) Rate = K’ [NO][O2]2
- c) Rate = K’ [NO]2[O2]
- d) Rate = K’ [NO]3[O2]
Answer: Rate = K’ [NO]2[O2]
Question: For a first order reaction, the time taken to reduce the initial concentration to a factor of 1/4 is 10 minute If the reduction in concentration is carried out to a factor of ,1/16 then time required will be
- a) 10 minutes
- b) 20 minutes
- c) 40 minutes
- d) 60 minutes
Answer: 20 minutes
Question: For the reaction,
The relation between K1, K2 and K3 is
- a) 2K1= K2= 4K3
- b) K1= K2= K3
- c) 2K1= 4K2= K3
- d) K1= 2K2= 3K3
Answer: 2K1= K2= 4K3
Question: For the reaction,
the rate of disappearance of NO2 will be
- a) K1[N2O4] – K2[NO2]2
- b) 2K1[N2O4] – 2K2[NO2]2
- c) K2[NO2]2 – K1[N2O4]
- d) 2K2[NO2]2 – 2K1[N2O4]
Answer: 2K2[NO2]2 – 2K1[N2O4]
Question: For a homogeneous gaseous reaction A→ B + C + D, the initial pressure was P0 while pressure after time ‘t’ was P if (P > P0). The expression for the rate constant K is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
MCQs for Chemical Kinetics Chemistry Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Chemistry to develop the Chemistry Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Chemistry will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Chemistry so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the NEET MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Chemical Kinetics for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by NEET for Full Syllabus Chemistry Chemical Kinetics have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Chemical Kinetics MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry Chemical Kinetics

