NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs. NEET UG students can acces the biggest database of MCQs on Studiestoday.com. This collection of MCQs have been prepared by the best NEET teachers in the country. NEET students should download and practice these questions to get better marks in examinations.
Important Points
It is said that equilibrium is established when number of molecules moving from liquid state to vapour state and number of molecules moving from vapour state to liquid state are same and it is dynamic. Equilibrium is established in both physical and chemical types of reactions. At this point of time the rates of forward and reverse reactions become equal. Equilibrium constant Kc is expressed as the ratio of the multiplication of concentration of products to the multiplication of concentration of reactants; concentration of each can be expressed as power of their stoichiometric coefficient.
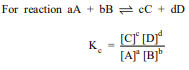
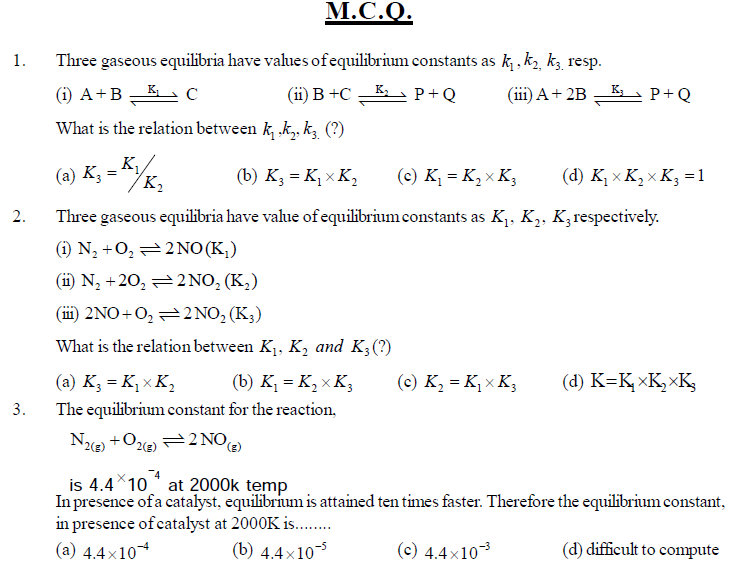
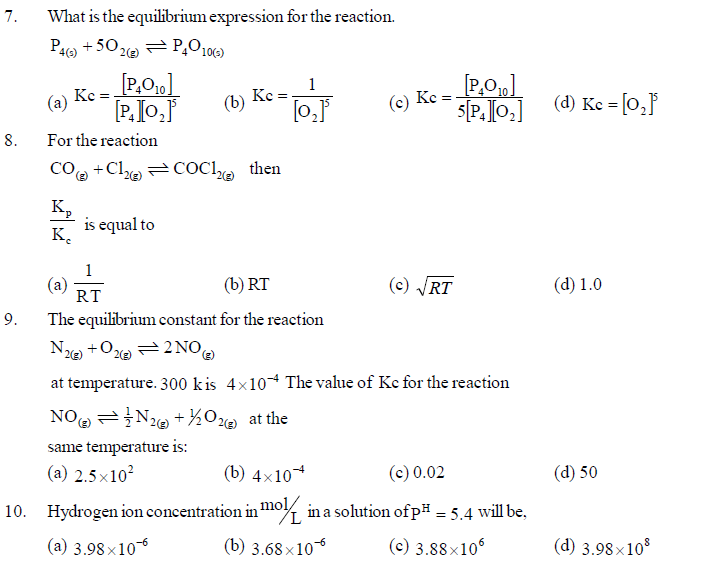
Equilibrium constant has constant value at constant temperature and at this stage macroscopic properties like concentration, pressure, etc become constant. For gaseous reaction Kp is taken instead of Kc and partital pressure of gaseous reactants and products are expressed instead of concentrations. The relation between Kp and Kc is expressed as Kp = Kc(RT)Dng. In which direction reaction will occur (forward or reverse) can be expressed by reaction quotient Qc which is equal to Kc at equilibrium. Le Chatelier's principle, mentions that if the equilibrium gets disturbed by change in factors like concentration, temperature, pressure etc., then equilibrium will move in the direction whereby the effect has been minimised or made negligible and the value of equilibrium constant will not change. This can be used in industries to know how equilibrium can be obtained by study of changes in factors like concentration, pressure, temperature, inert gas etc. In industries, we can change or control factors
accordingly so that reaction shifts from reactants to products (left to right). If catalyst is used, only the rate of required reaction will increase but no change will occur in amounts of reactants or products because the effect on forward and reverse reactions will be the same and so equilibrium constant will not change.
The substances which allow the electric current to pass through their aqueous solutions are called electrolytes. Acid, base and salt are electrolytes because their aqueous solutions conduct electric current. The reason for the conduction of electric current in aqueous solution of electrolyte is the formation of ions due to dissociation or ionisation which conducts electric current. While the weak electrolytes are incompletely dissociated and so the equilibrium is established between its ions and undissociated molecules. This is called ionic equilibrium.
According to Arrhenius ionisation theory, acid is called a substance which gives hydrogen ion (H+) and base is called a substanec which gives hydroxyl ion (OH –) on ionisation. According to Bronsted - Lowry theory, acid is defined as a proton donor and base is defined as proton acceptor. Each acid has its conjugute base and each base has its conjugate acid. Hence, it is known as conjugate acid - base or proton - transfer theory. Proton is tranferred between acid and base.
Bronsted - Lowry is more general than Arrhenius definition. According to Lewis' definition, acid means a substance which accepts a pair of electrons and base is a substance which donates a pair of electrons. This definition can be applied to organic chemistry, complex compounds chemistry in addition to acid-base. Hence, it is considered universally acceptable. Ionisation constant is also an equilibrium constant. The ionisation constants of weak acid (Ka) and weak base (Kb) can be determined. Concentration of acid can be expressed as pH = –log10[H3O+]. Hence, pH scale is determined for acid - base. Similary, concentration of OH– can be expressed as pOH = –log10[OH–], ionisation constant of water as pKw = –log10Kw [H3O+] and [OH –] can be calculted by the use of relation pKw = pH + pOH. If pH < 7 solution will be acidic, pH > 7 olution will be basic and pH = 7 solution will be neutral.
Different salts can be obtained by neutralisation of strong or weak acid and strong or weak base. In such salts, acidic, basic and neutral salts are included. When such salts react with water, hydration (hydrolysis) reaction occurs and solution obtained can be acidic, basic or neutral. This is also an equilibrium reaction and so corresponding equilibrium constant for it can be determined. Hydrolysis constant is expressed as Kh. pH or pOH can be calculated from the values of Ka and Kb and the value of Kh characteristic for the particular salt. Some solutions are such whose pH does not change by addition of small amount of acid or base or in case they are being diluted. Such solutions are called buffer solutions which can be acidic, basic or of neutral type. The control of pH is useful in the control of biological reactions in our body and chemical reactions in analytical chemistry, industries etc.
Sparingly soluble salts (whose solubility is less than 0.01M in water) dissolve in water depending on their solubility and equilibrium is established. Hence, equilibrium constant for this can be obtained which is known as solubility product constant or solubility product of the sparingly soluble salt. The study of effect of common ion, acid, etc. on the solubility of sparingly soluble salt can be carried out by application of Le Chatelier's principle. Generally, the solubility of sparingly soluble salt decreases due to effect of common ion. This is used in qualitative analysis. By mixing two solutions, whether precipitates will be obtained or not, can be predicted by comparing concentration product Ip with the solubility product Ksp. If Ip > Ksp precipitation will occur and if Ip < Ksp the precipitation will not occur and if Ip = Ksp, the precipitation will not occur but solution will remain in saturated state.


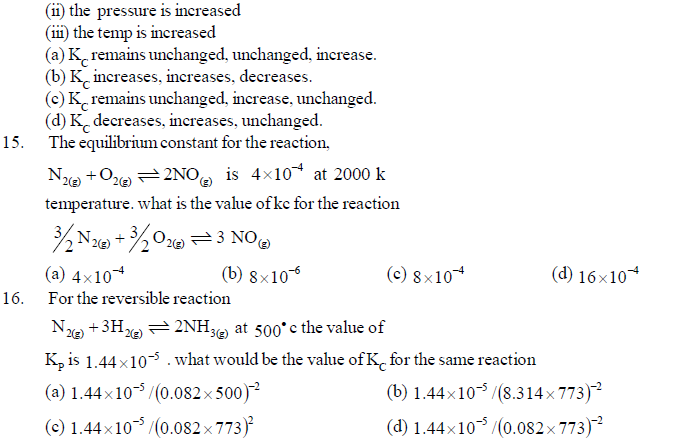


24. Water is a
(a) Protophobic solvent (b) Protophilic solvent
(c) Amphiprotic solvent (d) Aprotic acid
25. Ammonium ion is
(a) Conjugate acid (b) Conjugate base
(c) Neither an acidnor a base (d) both an acid and a base.
77. PH of a solution containing 50 mg of sodium hydroxide in 10 dm3 of the solution is
(a) 9 (b) 3.9031 (c) 10.0969 (d) 10
78. Which one of the following has the lowest PH value ?
(a) 0.1 MHCl (b) 0.1 MKOH (c) 0.01 MHCl (d) 0.01 MKOH
79. Equal volumes of three basic solutions of 11,12 and13 are mixed in a vessel. what will be the H+ ion concentration in the miture ?
(a) 1.11×10-11M (b) 3.7×10-12M (c) 3.7×10-11M (d) 1.11×10-12M
(a) Statement -1 is true.
Statement -2 is true.
Statement-2 is a correct explanation for statement-1
(b) Statement- 1 is true.
Statement-2 is true.
Statement-2 is not a correct explanation of statement-1
(c) Statement-1 is true.
Statement-2 is false.
(d)Statement-1 is false.
Statement-2 is true.
83. For preparing a buffer solution of PH 6 by mixing sodium acetate and acetic acid , the ratio of concentration of salt and acid should be, (Ka=10-5)
(a) 1:10 (b) 10:1
(c) 100:1 (d) 1:100

