Important Points
Chemical analysis : Analytical chemistry deals with qualitative and quantitative analysis of substances.
Qualitative analysis : A salt consists of two parts known as radicals. The positively charged part of a salt (cation) which has been derived from a base is termed as basic radical and the negatively charged part of salt (anion) which has been derived from an acid is termed as acidic radical. In qualitative inorganic analysis, the given compound is analysed for the basic and acid radicals (i.e., the cations and the anions), that it contains. For example zinc blende is analysed for the Zn2+ and S2- ions that it contains.
Systematic Procedure for Qualitative Analysis of Inorganic Salts
It involves the following steps : (1) Preliminary tests (2) Wet tests for acid radicals and (3) Wet tests for basic radicals.
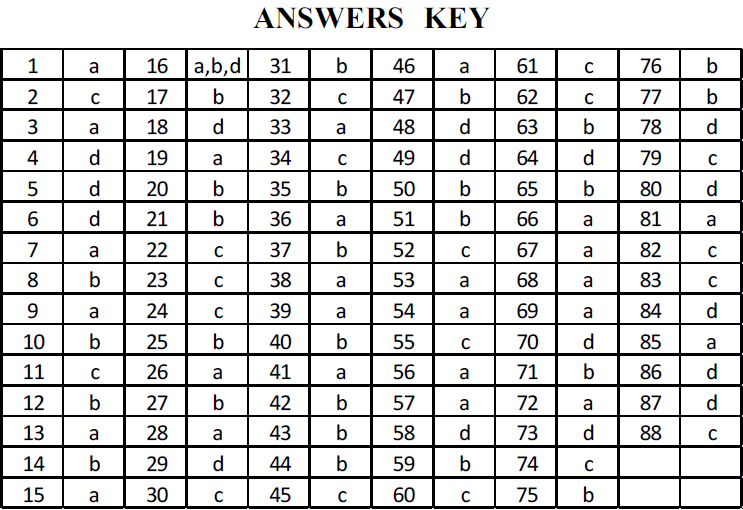
(1) Peliminary Test
(ii) Flame test :
Characteristic flame colour : Certain metals and their salts impart specific colours to Bunsen burner flame.
(a) Pb imparts pale greenish colour to the flame.
(b) Cu and Cu salts impart blue or green colour to the flame.
(c) Ba and its salts impart apple green colour to the flame.
(d) Ca imparts brick red colour to the flame.
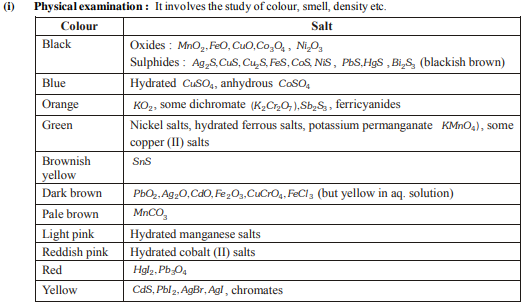
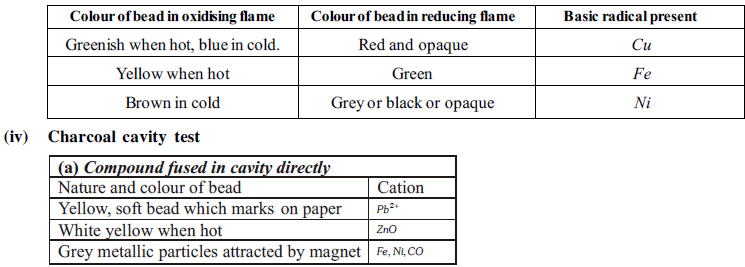
(iii) Borax bead test :
The transparent glassy bead (NaBO2 + B2O3 ) when heated with inorganic salt and the colour produced gives some idea of cation present in it.
(2) Wet tests for acid radicals :
Salt or mixture is treated with dil. H2SO4 and also with conc. separately and by observing the types of gases evolved. Confirmatory tests of anions are performed.
M.C.Q.
1. In borax bead test, which of the following compound is formed
(a) Meta borate (b) Tetra borate (c) Double oxide (d) Ortho borate
2. The metal that does not give the borax-bead test is
(a) Chromium (b) Nickel (c) Lead (d) Manganese
3. Which of the following is coloured compound?
(a) CuF2 (b) CuI (c) NaCl (d) MgCl2
4. The alkaline earth metal that imparts apple green colour to the bunsen flame when introduced in it in the form of its chloride is
(a) Barium (b) Strontium (c) Calcium (d) Magnesium
5. Which gives violet coloured bead in borax bead test
(a) Fe2+ (b) Ni2+ (c) Co2+ (d) Mn2+
6. When concentrated H2SO4 is added to dry KNO3, brown fumes evolve. These fumes are
(a) SO2 (b) SO3 (c) NO (d) NO2
7. Which one of the following salt give green coloured flame when the salt is tested by Pt wire
(a) Barium salt (b) Calcium salt (c) Borate (d) Lead salt
8. Sodium sulphite on heating with dilute HCl liberates a gas which
(a) Turns lead acetate paper black
(b) Turns acidified potassium dichromate paper green
(c) Burns with a blue flame
(d) Smells like vinegar
9. Starch-iodide paper is used for the test of
(a) Iodine (b) Iodide ion (c) Oxidising agent (d) Reducing agent
10. Which of the following salt gives white precipitate with solution and dil. solution and gives green flame test
(a) CuCl2 (b) BaCl2 (c) pbCl2 (d) Cu(NO3)2
11. Two gases when mixed give white dense fumes, the gases are
(a) NH3 and SO2 (b) SO2 and steam (c) NH3 and HCl (d) NH3 and N2O
12. Blue borax bead is obtained with
(a) Zn (b) Cobalt (c) Chromium (d) Fe
13. Which of the following imparts green colour to the burner flame
(a) B(OMe)3 (b) Na(OMe) (c) Al(OPr)3 (d) Sn(OH)2
14. A colourless gas with the smell of rotten fish is
(a) H2S (b) PH3 (c) SO2 (d) None of these
15. MnO2 and H2SO4 added to NaCl, the greenish yellow gas liberated is
(a) Cl2 (b) NH3 (c) N2 (d) H2
16. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct when a mixture of NaCl and K2Cr2O7 is gently warmed with conc H2SO4.
(a) A deep red vapour is evolved
(b) The vapour when passed into NaOH solution gives a yellow solution of Na2Cr2O7
(c) Chlorine gas is evolved
(d) Chromyl chloride is formed
17. Which of the following combines with Fe (II) ions to form a brown complex
(a) N2O (b) NO (c) N2O3 (d) N2O5
18. Which of the following will not produce a precipitate with AgNO3 solution
(a) F– (b) Br– (c) CO32– (d) PO43–
19. Which of the following gives black precipitate when H2S gas is passed through its solution
(a) Acidic AgNO3 (b) Mg(NO3)2 (c) Ammonical BaCl2 (d) Copper nitrate
20. A salt gives violet vapours when treated with conc. H2SO4. It contains
(a) Cl– (b) I– (c) Br– (d) NO3–
21. When water is added to a salt solution containing chloroform, chloroform layer turns violet. Salt contains
(a) Cl– (b) I– (c) NO3– (d) S2–
22. Phosphate radical with ammonium molybdate gives precipitate of which colour
(a) Violet (b) Pink (c) Canary yellow (d) Green
23. Which compound is soluble in NH4OH
(a) PbCl2 (b) PbSO4 (c) AgCl (d) CaCO3
24. Nitrates of all the metals are
(a) Coloured (b) Unstable (c) Soluble in water (d) Insoluble in water
25. Nitrate is confirmed by ring test. The brown colour of the ring is due to the formation of
(a) Ferrous nitrite (b) FeSO4NO (c) FeSO2NO2 (d) Ferrous nitrate
26. Aqueous solution of a salt when treated with AgNO3 solution gives a white precipitate, which dissolves in NH4OH. Radical present in the salt is
(a) Cl– (b) Br– (c) I– (d) NO3–
27. When CO2 is passed into lime water it turns milky. When excess of CO2 is passed, milkyness disappears because
(a) Reaction is reversed (b) Water soluble Ca(HCO3) is formed
(c) Vaporisable calcium derivative is formed (d) None of these
28. A mixture when heated with conc. H2SO4 with MnO2 brown fumes are formed due to
(a) Br– (b) NO3– (c) Cl– (d) I–
29. In the test of sulphate radical, the white precipitate of sulphate is soluble in
(a) Conc. HCl (b) Conc. H2SO4 (c) Conc. HNO3 (d) None of these
30. Which reagent is used to remove SO42– and Cl–
(a) BaSO4 (b) NaOH (c) Pb(NO3)2 (d) KOH
31. ____ is formed when potassium iodide is heated with conc. H2SO4
(a) HI (b) I2 (c) HIO3 (d) KIO3
32. Chromyl chloride test is performed for the confirmation of the presence of the following in a mixture
(a) Sulphate (b) Chromium (c) Chloride (d) Chromium and chloride
33. A solution of a salt in dilute sulphuric acid imparts deep blue colour with starch iodine solution it confirms the presence of which of the following
(a) NO2– (b) I– (c) NO3– (d) CH3 COO–
34. Ammonia reacts with excess of chlorine to form
(a) N2 and HCl (b) NH4Cl and NCl3 (c) NCl3 and HCl (d) N2 and NH4Cl
35. Which of the following anions would decolourise acidified KMnO4 solution
(a) SO42– (b) S2– (c)NO3– (d) CH3 COO–
36. The gas which is absorbed by ferrous sulphate solution giving blackish brown colour is
(a) NO (b) CO (c) N2 (d) NH2
37. Which one of the following anions is not easily removed from aqueous solutions by precipitation
(a) Cl– (b) NO3– (c) CO32– (d) SO42–
38. Na2CO3 cannot be used to identify
(a) CO32– (b) SO32– (c) S2– (d) SO42–
39. The number of hydroxide ions, produced by one molecule of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) on hydrolysis is
(a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 3 (d) 4
40. By passing KMnO4 gas in acidified H2S solution, we get
(a) K2S (b) S (c) K2SO3 (d) MnO2
41. Which of the following doesn’t give a ppt. with silver nitrate solution.
(a) Ethyl bromide (b) Sodium bromide (c)Calcium chloride (d) Sodium chloride
42. Which sulphide is soluble in (NH4)2 CO3
(a) SnS (b) AS2S3 (c) Sb2S3 (d) CdS
43. When acetic acid and K4[Fe(CN)6] is added to a copper salt, a chocolate precipitate is obtained of the compound
(a) Copper cyanide (b) Copper ferrocyanide
(c) Basic copper sulphate (d) Basic copper cyanide
44. A precipitate of the following would be obtained when HCl is added to a solution of stannous sulphide (SnS) in yellow ammonium sulphide
(a) SnS (b) SnS2 (c) Sn2S3 (d) (NH4)2 SnS3
45. The compound insoluble in acetic acid is
(a) Calcium oxide (b) Calcium carbonate (c) Calcium oxalate (d) Calcium hydroxide
46. Which of the following give white precipitate when HCl is added to its aqueous solution
(a) Hg+ (b) Mg++ (c) Zn++ (d) Cd++
47. Reagent used in the qualitative analysis of IVth group is
(a) HCl (b) H2S (alkaline) (c) (NH4)2S (d) None of these
48. Which of the following pairs would be expected to form precipitate when solution are mixed
(a) K+, SO42– (b) Na+, S–2 (c) Ag+, NO3– (d) Al3+, OH–
49. Addition of solution of oxalate to an aqueous solution of mixture of Ba2+, Sr2+ Ca2+ and will precipitate (a) Ca2+ (b) Ca2+, Sr+2 (c) Ba2+, Sr+2 (d) All the three
50. Distinguishing reagent between silver and lead salts is
(a) H2S gas (b) Hot dilute HCl solution
(c) NH4Cl(S) + NH4OH(aq) (solid) + solution (d) NH4Cl(S) (solid) + (NH4)2 CO3(aq) solution
51. The ion that cannot be precipitated by both HCl and H2S is
(a) Pb2+ (b) Cu2+ (c) Ag+ (d) Sn2+
52. Pb(CH3COO)2 gives__clour with H2S
(a) Orange (b) Red (c) Black (d) White
53. Fe2+ ion can be distinguished by Fe3+ ion by
(a) NH4SCN (b) AgNO3 (c) BaCl2 (d) None of these
54. Which of the following change the colour of the aqueous solution of FeCl3
(a) K4[Fe(CN)6] (b) H2S (c) NH4CNS (d) KCNS
55. Which of the following mixture is chromic acid
(a) K2Cr2O7 and HCl (b) K2SO4 conc. H2SO4
(c) K2Cr2O7 and conc. H2SO4 (d) H2SO4 and HCl
56. If Na+ ion and S2– ion is larger than Cl– ion, which of the following will be least soluble in water
(a) MgS (b) NaCl (c) Na2S (d) MgCl2
57. Lead sulphate is soluble
(a) In conc. nitric acid (b) In conc. hydrochloric acid
(c) In a solution of ammonium acetate (d) In water
58. When H2S gas is passed through the HCl containing aqueous solutions of CuCl2, HgCl2, BiCl3 and CoCl2, which does not precipitate out
(a) CuS (b) HgS (c) Bi2S3- (d) CoS
59. Group reagent for analytic group IV is
(a) NH4Cl + NH4OH (b) NH4Cl + NH4OH + H2S
(c) NH4OH + (NH4)2CO3 (d) HCl + H2S
60. When H2S is passed through Hg2S we get
(a) HgS (b) HgS + Hg2S (c) Hg2S + Hg (d) Hg2S
61. [X] + H2SO4 →[Y] a colourless gas with irritating smell
[Y] + K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 → green solution
[X] and [Y] is
(a) SO32–, SO2 (b) Cl–, HCl (c) S–2, H2S (d) CO32–, CO2
62. Concentrated sodium hydroxide can separate a mixture of
(a) Zn2+ and Pb2+ (b) Al3+ and Zn3+ (c) Cr3+ and Fe3+ (d) Al3+ and Cr3+
63. What product is formed by mixing the solution of K4[Fe(CN)6] with the solution of FeCl3
(a) Ferro-ferricyanide (b) Ferric-ferrocyanide (c) Ferri-ferricyanide (d) None of these
64. When H2S is passed through a mixture containing Cu+2, Ni+2, Zn+2 in acidic solution then ion will precipitate
(a) Cu+2, Ni+2 (b) Ni+2 (c) Cu+2, Zn+2 (d) Cu+2
65. Ferric ion forms a prussian blue coloured ppt. due to
(a) K4[Fe(CN)6] (b) Fe4[Fe(CN)6] (c) KMnO4 (d) Fe(OH)3
66. A 0.3 M HCl solution contains the following ions Hg2+, Cd2+, Sr2+, Fe2+ Cu2+. The addition of H2S to above solution will precipitate
(a) Cd, Cu and Hg (b) Cd, Fe and Sr (c) Hg, Cu and Fe (d) Cu, Sr and Fe
67. Which of the following gives a ppt. with Pb(NO3)2 but not with Ba(NO3)2
(a) NaCl (b) Sodium acetate
(c) Sodium nitrate (d) Sodium hydrogen phosphate
68. In the group III radicals, in place of NH4Cl which of the following can be used
(a) NH4NO3 (b) (NH4)2 SO4 (c) (NH4)2 (d) NaCl
69. Which compound does not dissolve in hot dilute HNO3
(a) HgS (b) PbS (c) CuS (d) CdS
70. Which of the following sulphate is insoluble in water
(a) CuSO4 (b) CdSO4 (c) PbSO4 (d) BaSO4
71. Mark the compound which turns black with NH4OH
(a) Lead chloride (b) Mercurous chloride (c) Mercuric chloride (d) Silver chloride
72. Colour of cobalt chloride solution is
(a) Pink (b) Black (c) Colourless (d) Green
73. Nessler’s reagent is used to detect
(a) CrO42– (b) PO43– (c) MnO4– (d) NH4+
74. Fe(OH)3 can be separated from Al(OH)3 by addition of
(a) Dil. HCl (b) NaCl solution
(c) NaOH solution (d) NH4Cl and NH4OH
75. The reagents NH4Cl and aqueous NH3 will precipitate
(a) Ca2+ (b) Al3+ (c) Mg2+ (d) Zn2+
76. Addition of SnCl2 to HgCl2 gives ppt
(a) White turning to red (b) White turning to gray
(c) Black turning to white (d) None of these
77. Heamoglobin is a complex of
(a) Fe3+ (b) Fe2+ (c) Fe4+ (d) Cu2+
78. In Nessler’s reagent for the detection of ammonia the active species is
(a) Hg2Cl2 (b) Hg2+ (c) Hg2I2 (d) HgI42–
79. Which one of the following sulphides is only completely precipitated when the acidic solution is made dilute
(a) HgS (b) PbS (c) CdS (d) CuS
80. A reagent used to test the presence of ion is
(a) H2S (b) NH4CNS (c) K4[Fe(CN)6] (d) K3[Fe(CN)6]
81. The following four solutions are kept in separate beakers and copper metal is put in each of them. Which solution will become blue after some time
(a) AgNO3 solution (b) Zn(NO3)2 solution (c) Ba(NO3)2 solution (d) NaNO3 solution
82. In qualitative analysis, in order to detect second group basic radical, H2S gas is passed in the presence of dilute HCl to
(a) Increase in dissociation of H2S (b) Decrease the dissociation of salt solution
(c) Decrease the dissociation of H2S (d) Increase the dissociation of salt solution
83. Sodium nitroprusside when added to an alkaline solution of sulphide ions produce a
(a) Red colouration (b) Blue colouration (c) Purple colouration (d) Brown colouration
84. If 20 ml of 0.25 N strong acid and 30 ml of 0.2 N of strong base are mixed, then the resulting solution is
(a) 0.25 N basic (b) 0.2 N acidic (c) 0.25 N acidic (d) 0.2 N basic
85. 10 ml of 10 M H2SO4 is mixed to 100 ml 1M NaOH solution. The resultant solution will be
(a) Acidic (b) Neutral (c) Weakly alkaline (d) Strongly alkaline
86. The equivalent weight of KMnO4 in alkaline medium will be
(a) 31.60 (b) 52.66 (c) 79.00 (d) 158.00
87. Phenolphthalein is most suitable indicator for the titration of
(a) CH3COOH and NH4OH (b) CH3COOH and NaOH
(c) HCl and NH4OH (d) H2CO3 and NH4OH
88. 20 ml of a N solution of KMnO4 just reacts with 20 ml of a solution of oxalic acid. The weight of oxalic acid crystals in 1N of the solution is
(a) 31.5 g (b) 126 g (c) 63 g (d) 6.3 g