Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit Assignment Set B. Get printable school Assignments for Class 10 Social Science. Class 10 students should practise questions and answers given here for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Social Science in Class 10 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 10 Social Science prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit in Class 10. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Social Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Class 10 Social Science Assignment
Objective Questions
Question : Money is based on
(a) double coincidence of wants
(b) single coincidence of wants
(c) Both a and b
(d) none of these
Answer : A
Question : Money is a measured of
(a) currency
(b) value
(c) transfer
(d) all of these
Answer : A
Question : The problem of similar wants made exchange difficult, so a new medium of exchange was developed known as
(a) capital
(b) cost
(c) rent
(d) money
Answer : D
Question : Modern forms of money include which of the following?
(a) Currency notes and coins
(b) Cowrie shells and stones
(c) Gold and silver coins
(d) Grains and cattle
Answer : A
Question : What is the most important function of money?
(a) Used in banking transactions
(b) Payment of loans
(c) Medium of exchange
(d) Stock market exchange
Answer : C
Question : When does credit play a positive role?
(a) When the loan repayment is not done on time but profits are made.
(b) When neither loan repayment is done on time nor are profits made.
(c) When the loan repayment is done on time and profits are made.
(d) None of the above.
Answer : C
Question : What do people belonging to poor households lack?
(a) Proper document
(b) Collateral
(c) Certificate of earning
(d) All of the above.
Answer : D
Question : Why is money called the medium of exchange?
(a) Goods are being bought and sold with the use of money.
(b) Use of money has made things easier to exchange.
(c) Money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process.
(d) Without exchange of money nobody can fulfil his all needs and requirements.
Answer : C
Question : In a SHG most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by
(a) Bank
(b) Members
(c) Non-government organisation
Answer : B
Question : In India which type of currency is widely accepted as a medium of exchange?
(a) Rupee
(b) Dollar
(c) Shilling
(d) Taka.
Answer : A
Question : Who supervises the functioning of formal source of loans?
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(b) State Bank of India
(c) Central Bank of India
(d) Informal money lenders.
Answer : A
Question : Raghav has surplus money so he opens a bank account and deposits in it. Whenever he needs money. he can go to his bank and withdraw from there. This kind of deposit with the banks are known as
(a) demand deposit
(b) term deposit
(c) fixed deposit
(d) surplus deposit
Answer : A
Question : In agricultural stage grains were used as
(a) money
(b) commodity
(c) ingredient
(d) none of these
Answer : A
Question : Banks give out loans and charge ______ on the loan amount from the borrower.
(a) rent
(b) wages
(c) interest
(d) money
Answer : C
Question : Percentage of formal sector in total credit in India in poor household is
(a) 15
(b) 20
(c) 70
(d) 80
Answer : A
Question : Chit fund come under
(a) organised credit
(b) unorganised credit
(c) discounted coupon
(d) none of these
Answer : B
Question : Which among the following is not a feature of informal source of credit?
(a) It is supervised by the Reserve Bank of India.
(b) Rate of interest is not fixed.
(c) Terms of credit are very flexible.
(d) Traders, employers, friends, relatives, etc provide informal credit source.
Answer : A
Question : A trader provides farm inputs on credit on the condition that farmers will sell their crop produce to him at ______ prices so that he could sell them at _____ prices in the market.
(a) high, medium
(b) low, high
(c) medium, high
(d) high, low
Answer : B
Question : Ram and Shyam are small farmers. Ram has taken credit 1.5% per month on < 20000 from a trader while Shyam has taken credit at 8% per annum from bank on the same amount. Who is better off?
(a) Ram is better because he has to do no paperwork.
(b) Shyam is better because his interest payment is less.
(c) Ram is better because he has not paid any collateral.
(d) Both Ram and Shyam are equal so no one is better off.
Answer : B
Fill In The Blank
DIRECTION : Complete the following statements with appropriate word(s).
Question : ______ is used as a substitute for cash.
Answer : Credit card
Question : Banks in India these days, hold about ______ % of their deposits as cash.
Answer : 15%
Question : ......... costs of borrowing increase the debt-burden.
Answer :High
Question : Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on ......... .
Answer : deposits
Question : Since money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called ______ .
Answer : Medium of exchange
True/False
DIRECTION : Read each of the following statements and write if it is true or false.
Question : The main source of income for banks is interest on deposits.
Answer : False
Question : A ‘debt trap’ means overspending till no money is left.
Answer : False
Question : Gramin Bank is the success story that met the credit needs of the poor at reasonable rates in Bangladesh
Answer : True
Rewrite the Statement
Question : It is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their borrowing capacity particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
Answer : It is necessary that bank and cooperatives increase their lending capacity particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
Question : Every loan agreement specifies an interest rate which the borrower must pay to the lender along with the repayment of rest of the interest.
Answer : Every loan agreement specifies an interest rate which the borrower must pay to the lender along with the repayment of the principal.
Question : Banks charge a lower interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
Answer : Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans that what they offer on deposits.
Question : Majority of the credit needs of the urban households are met from informal sources.
Answer : Majority of the credit needs of the rural households are met from informal sources.
Question : The difference between the interest charged on borrowers and paid to depositors is the main source of expense for banks.
Answer : The difference between the interest charged on borrowers and paid to depositors is the main source of income for banks.
Assertion And Reason
One Word Answer Type Questions
Question : What are the functions of a bank ?
Answer : To accept deposit and providing loans.
Question : Who supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans ?
Answer : The Reserve Bank of India.
Question : What is SHG ?
Answer : Self Help Group.
Question : What is the major source of credit for rich household in urban areas ?
Answer : Formal source of credit.
Question : What is the main difficulty of Barter System ?
Answer : The double coincidence of wants.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question : What are the three benefits of money ?
Answer : 1. It provides a generally acceptable medium of exchange.
2. It has people's trust because money has government's approval.
3. It removes the difficulties of the barter system.
Question : What is the main purpose of credit in rural areas ?
Answer : In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production. Crop production involves expenses on seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, water, electricity, repair of equipment, etc.
Question : Why are demand deposits considered as money?
Answer : Demand deposits are considered as money because the depositors may use the cheque facility to expedite transactions. The cheque is a credit instrument which acts as medium of exchange in the transactions.
Question : What is a cheque?
Answer : A cheque is a credit instrument through which the depositor instructs the bank to pay a specific amount from the depositor's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Question : What are the purposes a farmers’ cooperative provides loans for?
Answer : Farmers' cooperative provides loans to its members for the purchase of agricultural equipment, cultivation and agricultural trade, fishery loans, construction of houses and to meet a variety of other expenses.
Question : Which are the formal and informal sources of credit?
Answer : The formal sources of credit include banks and cooperatives, while the informal sources include moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends, etc.
Question : Give any one example of the methods to make payment without using cash.
Answer : Using debit card to book movie tickets, or using Paytm to purchase bread and milk from grocery shop is one exampleof cashless transaction.
Question : How do the members of a cooperative generate their resources ?
Answer : Members of a cooperative pool their resources for cooperation in certain areas. Later on these cooperatives may obtain loan from the banks to fund its members.
Question : What are the two merits of barter system?
Answer : 1. Problem of fake currency does not arise as people exchange goods or services and money is not used as a medium of exchange.
2. Simple system wherein goods are utilised without much wastage as they are produced as per the needs of the society.
Question : Highlight the inherent problem in double coincidence of wants.
Answer : The inherent problem in double coincidence of wants is that both parties must agree to sell and buy each other's commodities.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question : What are “Terms of Credit” ? Are they same for every borrower ?
Answer : Agreement regarding interest rate, collateral and documentation requirement and the mode of repayment etc. together constitute the "Terms of Credit". The terms of credit vary substantially from borrower to borrower depending upon various factors like duration of credit, amount of credit, purpose of credit, past relationship between borrower and lender and isk involved in credit etc.
Question : What are the pre-requisites for the credit system in India to be successful for poor ?
Answer : In order to make the credit system successful in India, it is necessary that banks and cooperative societies expand their lending facilities particularly for poor people in the rural areas, so that their dependence on informal sources of credit reduces. These informal sources charge a very high interest rates from these people which left them with very little income and savings. Hence, credit must be available to this section on soft terms. Another problem which poor people face is that very few of them get the loan. Thus, it is also very necessary that everyone receives these loans so that they don't have to depend on the informal sources.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question : In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower.
Explain?
Answer : Whether a credit would be useful or not, will depend on a number of factors like – risks involved, whether there is some support against a loss, terms of credit etc. It is a fact that in situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower. For example, credit taken by farmers for cultivation might create problems for the farmer at some times. Crop production involves high costs on inputs such as HYV seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation etc. Farmers generally take loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest. But the failure of the crop makes loan repayment impossible. Then in order to repay the loan sometimes, they become bound to sell part of their land. So, their situations become worse than before. The incidences of farmers’ suicides especially in Maharashtra are the burning examples of this situation. Thus, whether a credit would be useful or not, depends on the various risks involved in the situation.
Question : How is money used in everyday life? Explain with examples.
Answer : In everyday life, money is used in following ways:
• It is used as a medium of exchange and facilitates the buying and selling of goods like car, house, food, clothes etc.
• It is used as deposits with the banks or to keep it at home like fixed deposits, bonds etc.
• It is used for borrowing and lending like loan.
Question : How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants? Explain with example of your own.
Answer : In a barter system where goods are directly exchanged without the use of money, double coincidence of wants is an essential feature. By serving as a medium of exchanges, money removes the need for double coincidence of wants and the difficulties associated with the barter system. For example, it is no longer necessary for the farmer to look for a book publisher who will buy his cereals at the same time sell him books. All he has to do is find a buyer for his cereals. If he has exchanged his cereals for money, he can purchase any goods or service which he needs. This is because money acts as a medium of exchange.
Question : How can money be easily exchange for goods or services? Give an example to explain.
Answer : Transactions are made in money because a person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or a service. It solves the problem of double coincidence of wants by acting as a medium of exchange.
For example, a shoe manufacturer wants to sell shoes in the market and wants to buy rice. Under barter system, both parties selling shoes and rice have to agree to buy and sell each other’s commodities and this creates a problem which is referred to as double coincidence of wants. This problem is overcome by the introduction of money. Now, the shoe manufacturer will sell the shoes for money and with that money he can buy rice.
Question : Why is there a great need to expand formal sector of credit in India? Explain any three reasons.
Answer : There is a great need to expand formal sector of credit in India because:
• There is no organisation to supervise the credit activities of lenders in informal sector.
• The rate of interest charged by the informal sector is very high as compared to formal sector.
• People who might wish to start a business by borrowing may not do so because of high cost
of borrowing in informal sector.
• The higher interest rate of borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower in informal sector.
Question : “Most of the poor households still depend on the informal sector for loans, both in rural and urban areas of India.” Support the statement with three examples.
OR
“Poor households still depend on informal sources of credit.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer : Poor households still depend on informal sources of credit because:
• Bank loans require proper documentation and collateral which is rarely available with poor households.
• Informal sources of credit such as moneylenders know the borrowers personally and are often willing to give a loan without a collateral.
• Sometimes, if the borrowers are unable to return the loan, they can get additional loans from moneylenders.
Question : How do SHGs help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral? Explain with an example.
Answer : SHGs help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral in the following ways:
• It is the group that is responsible for the repayment of loan.
• Any case of non-payment of loan by any member is followed up seriously by other members.
• The formal sector is willing to lend to the members of SHGs because of their good track record of managing the credit.
Question : “Money has made transactions easy.” Justify.
Answer : Money has made transactions easy because:
• It can be easily exchanged with any commodity or service.
• It solves the problem of double coincidence of wants.
• It is the perfect store of value.
• It makes economic activities quite independent from each other.
Question : When does credit push the borrower into a debt-trap? Explain with the help of an example.
Answer : In situation with high risks, credit might create problems and pushes the borrower into a debt-trap. He is much worse off than before. For example, crop production involves high costs on inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, water etc. Farmers generally take loans at the beginning of the
season and repay the loan after harvest. But the failure of the crop makes loan repayment impossible. They have to sell part of the land to repay the loan or a fresh loan may be required to repay the previous loan, and the borrower may find himself caught in a vicious circle and recovery from such a situation is very painful.
Question : How is money used as a medium of exchange? Explain with examples
Answer : Money is used as a medium of exchange because it serves as a common medium through which people can carry out buying and selling. Use of money makes economic activities independent of each other. At the same time, it removes the inconvenience caused by the barter system.
For example, a person wants to sell sugar and buy wheat. He has to look for a person who wants sugar and has wheat to sell. In contrast, if in an economy, where money is used, the person who wants to sell sugar only has to look for a buyer for his sugar. The money which he will get can be used to purchase the wheat or any other commodity in the market. Since, money is used in the exchange process it is called a medium of exchange.
Question : How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Answer : We know that banks accept the deposits from the people who have surplus money and also pay an interest on the deposits.
But banks keep only a small portion (15 per cent in India) of their deposits as cash with themselves. This is kept as provision to pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money from their accounts in the bank on any day. They use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans to those who need money. In this way banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money.
Question : What are the modern forms of money? Why is rupee widely accepted as a medium of exchange? Explain two reasons.
Answer : Modern forms of money include paper notes and coins.
Rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange because:
• It is authorised by the government of India.
• The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment and settling the transactions.
Thus, no one can refuse a payment made in rupees.
Question : “The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged because:
• There is no organisation to supervise the credit activities of the lenders in informal sector.
• The informal sector lends at a very high rate of interest and use unfair means to get the money back.
• Higher cost of borrowing means a large part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan. Hence, the borrowers have less income left for themselves.
• Sometimes, due to higher rate of interest, the amount to be repaid becomes higher than the income of the borrower due to that there is always a risk for borrowers to fall in debt-trap.
Question : How does money solves the problem of double coincidence of wants? Explain with an example.
Answer : In barter system, where goods are directly exchanged without the use of money, double coincidence of wants (i.e. a person desires to sell exactly what the other person wishes to buy) is an essential feature. But it, indeed, is a very cumbersome process.
By serving as a medium of exchange, money removes the situation of double coincidence of wants and the difficulties associated with the barter system. For example, it is no longer necessary for a shoe manufacturer to* look for a farmer who will buy his shoes and at the same time sell him wheat. AH he has to do is to find a buyer for his shoes, who will exchange his money for shoes. Now, he can purchase wheat or any other good in the market with the help of the money earned. Thus, the problem of double coincidence of wants gets solved with the use of money.
Question : “Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development.” Assess the statement.
Answer : Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for a country’s development because:
• More lending would lead to higher incomes and encourage people to invest in agriculture, engage in business and set up small industries.
• Cheap credit will enable more investment. This leads to acceleration of economic activity.
• Cheap credit would also allow weaker sections of society to access formal sector of lending and get rid of from informal moneylenders.
• Affordable credit would also end the cycle of debt trap.
• Cheap and easy terms of credit would inspire better investment in technology and thus increase competition.
Question : Why do lenders ask for a collateral while lending? Give any three reasons.
Answer : The lenders ask for a collateral before lending because:
• It is an asset that the borrower owns and uses this as a guarantee to the lender – until the loan is repaid.
• Collateral with the lender acts as a proof that the borrower will return the money.
• By keeping a collateral with the lender, the borrower is bound to be regular in paying the interest because the borrower does not want to lose the collateral.
Question : “Deposits with the banks are beneficial to the depositors as well as to the nation.” Examine the statement
Answer : Deposits with the banks are beneficial to the depositors as well as to the nation in various ways.
Some of them are:
• They provide safe and secure deposits to a person’s money.
• They provide excellent saving and investment options and also help in the growth of the nation.
• They provide interests on the deposited money to the depositors.
• Money can be easily withdrawn from the banks as and when required by the depositors.
• They provide easy loans on nominal rates that make it possible for the common man to build their own assets.
Question : What is a collateral? Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending? Explain
Answer : A collateral is an asset such as land, building, livestock, vehicle or deposits with the banks that the borrower owns and uses this as a guarantee to the lender until the loan is repaid.
The lenders ask for a collateral before lending because:
• It is an asset that the borrower owns and uses this as a guarantee to the lender – until the loan is repaid.
• Collateral with the lender acts as a proof that the borrower will return the money.
• By keeping a collateral with the lender, the borrower is bound to be regular in paying the interest because the borrower does not want to lose the collateral.
Question : How is money transferred from one bank account to another bank account? Explain with an example.
Answer : For payment through cheque, the payer who has an account in the bank, draws out a cheque for a specific amount. The cheque is a statement asking the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
For example, Aman has to pay a specific amount of money to Shruti, say ? 60,000. Aman will write a cheque in the name of Shurti. It means Aman instructs his bank to pay the money to Shurti. Shurti will deposit the cheque in her bank. After two or three days, the money will be transferred from Aman’s account to Shurti’s account.
Question : What are demand deposits? How is money safe in the banks? Explain.
Answer : Deposits in the bank account which are payable on demand are called demand deposits.
Banks accept deposits from number of people. Some part of that money is given out as loan and the other part is kept with the banks for making payments. So, the money is safe with the banks.
The depositors can withdraw their money whenever they want.
Question : Explain with examples, how people are involved with the banks.
Answer : People are involved with the banks in the following ways:
• Depositors
• Borrowers
• The people with excess money deposit it in the banks for safety. In turn they earn interest on the amount deposited.
At the same time, there are people who need money for various activities. They approach the banks for credit. The bank charges interest from the borrowers.
Question : ‘Credit has its own unique role for development.’ Justify the statement with arguments.
Answer : Credit has a unique role in the economic development of the country. It is needed by all the three sectors of the economy.
• In urban sector, big businessmen and small manufacturers need loans either to expand their enterprises, bring new technology or diversifying their businesses.
• In rural sector, the main demand for credit is for crop production. Crop production involves cost of seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, water, electricity, repair of equipments. Cheap credit would thus lead to increase in production.
• Even tertiary sector needs loans to buy the latest equipments and technology. Thus, we can say that credit has a unique role in the development of a country.
Question : What are the main functions of a bank ?
Answer : (i) Accepting deposits and providing loans are the main functions of a bank.
(ii) Banks act as financial mediator or intermediaries between the savers and borrowers.
(iii) Transferring money from one place to another.
(iv) Conducting foreign exchange transactions.
(v) Keeping valuables in safe custody.
(vi) Issuing letters of credit and guarantee.
Question : In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower. Explain.
Answer : A person takes credit or loan with the explicit or implicit understanding of returning that credit amount along with interest to the lender. Sometimes it happens that the purpose for which loan has been taken by the borrower involves high risk due to which return of the loan amount become uncertain. If the returns from the investment made out of loan amount happen to be negative then some or whole of the loan amount may be lost. If the borrower does not have any asset to compensate the lost amount then he may have to take a fresh loan to expedite the loan or credit previously taken. This may lead to debt trap. Debt trap is a situation in which a person has to take new loans to pay the previously taken loans and this is a very serious problem for a person. Sometimes a person who gets into this trap and does not find ways to get out of that, may commit suicide. This has happened with various farmers and businessmen in India.
Question : What is SHG ? What are the two benefits of SHG ?
Answer : Self Help Group is the association of poor people who pool their monetary resources for mutual monetary help in the form of soft term credit facilities to its members. Following
are the two benefits of SHG :
(i) SHG helps its members to acquire credit at reasonable terms.
(ii) It saves the members from the exploitation of informal sources of credit like moneylenders.
Question : ‘Credit has its own unique role for development’. Justify the statement with arguments.
Answer : Role of credit in development :
(i) It creates better facilities for agriculture and industrial activities.
(ii) It helps people from all ways of life in setting up business, increase their earnings and support their family.
(iii) To some people, loan helps a lot in constructing their homes and get rid of monthly rents.
(iv) To others, loan or credit helps a lot in raising their social status by purchasing luxury commodities.
Question : ‘‘Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development.’’ Assess the statement.
Answer : Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country's development because :
(i) Many people who want to start an enterprise by taking loans may not do so because of high cost of borrowing.
(ii) Banks and cooperative societies need to lend more money on lower interest rate.
(iii) This would lead to higher income and many people would borrow at cheap rate of interest.
(iv) People in villages could grow crops, or set up small scale industries.
Question : Explain any three loan activities of banks in India.
Answer : Activities of banks in India which are involved in providing loan facilities:
(i) Banks keep a small proportion of the deposits with them as cash.
(ii) These deposits are used to offer loans to the borrowers.
The banks thus act as intermediaries between those who have surplus funds (depositors) and those who are in need of the funds (borrowers).
(iii) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Question. Why is it necessary for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas?
Answer : (i) Banks and cooperative societies can help people in obtaining cheap and affordable loans.
(ii) This will empower people in a variety of ways. They could grow corps, do business, set up small- scale industries etc. They could set up new industries or trade in goods.
(iii) Loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers. Thus, it is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
Cheap and affordable credit is also important for the country’s development
Question. Which are the modern forms of money?
Answer : The modern forms of money comprises: currency — paper notes and coins.
Unlike the things that were used as money earlier, modern currency is not made of precious metals such as gold, silver, and copper.
And unlike grain and cattle, they are neither of everyday use.
The modern currency is without any use of its own.
Question. What is debt-trap?
Answer : Debt-trap - When a borrower particularly in rural area fails to repay the loan due to the
failure of the crop, he is unable to repay the loan and is left worse off. This situation is commonly called debt-trap. Credit in this case pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.
Question. Why are transactions made in money?
Answer : A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity
or service that he or she might want.
Thus everyone prefers to receive payments in money and
then exchange the money for things that they want.
Question. Which authority does supervise the functioning of formal sources of loans and how?
Answer : 1. Reserve Bank of India.
2. The RBI monitors that the banks actually maintain the cash balance. It also sees that the banks give loans to all rich as well as poor.
Question. Why should credit at reasonable rates from the banks and cooperatives be available for all ?
Answer : Credit at reasonable interest rates should be available for all so that they
may increase their income and help in the over all development of the country.
1. High interest rate do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
2. It is necessary that the banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in rural areas, so that the dependence of the people on informal sources of credit reduces.
3. In addition to this more credit should be given to the poor to get maximum benefit from the cheaper loans.
4. This will help in increasing their income as well as standard of living.
5. Any other relevant point
(Any two points)
Question : What is the main source of a bank’s income?
OR
What is real source of income for banks?
Answer : Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits. The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is the main source of their income.
Question : How does RBI supervise the working of formal sector in India?
Answer : The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans. For instance, we have seen that the banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive. The RBI monitors the banks whether they are actually maintaining cash balance or not. Similarly, the RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profitmaking businesses and traders, but also to small cultivators, small scale industries, small borrowers etc. Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Question : What are the pros and cons of getting loans from informal sources?
Answer : The pros of getting loan from informal sources such as moneylenders is that they know the borrowers personally and hence are often willing to give a loan even without a
collateral. These loans are normally free from various formalities, and, if necessary, the borrower can approach the moneylenders again for loan even without repaying their earlier loans. The cons of getting loan from informal sources are that the moneylenders charge very high rates of interest and they do not keep proper records of the transactions.
Question : Why are most of the poor households deprived from the formal sector of loans?*
Answer : Poor households, even today, prefer to get credit from informal sector rather than the formal sector due to the following reasons:
(i) Relatives and moneylenders are easily accessible. Still in India, several rural areas do not have a bank nearby.
(ii) Norms or rules for lending money are much strict in formal sector as compared to the informal sector.
(iii) Most poor households are still uneducated. The processes and formalities involved to get a loan sanctioned from
formal sector often deter the poor from approaching a bank.
Question : Why is it necessary to increase a large number of banks mainly in rural areas? Explain.
Answer : It is important to open more banks in the rural areas as formal credit sector is missing. The practise of borrowing from informal sector that exists in rural areas, for example local moneylenders, has a number of disadvantages. The informal sector charges a high rate of interest. Informal sector make loans very expensive as there are no external organisations controlling the credit activities of lenders. Informal sector involves high degree of risk as there are no proper set of rules for repayment and there is a lot of exploitation of the poor borrowers. Lenders may exploit the borrowers, they may engage in threats and intimidation to ensure repayment of loans. There is no written agreement between the lender and the borrower. There is no legal recourse in case of informal sources of credit.
Question : What are the factors that influence the usefulness of a loan?
Answer : Whether a loan would be useful or not depends upon two factors, i.e.,
(i) the risks involved in the situation. It means a situation in which return on the loan is uncertain and
(ii) the economic support if there is loss on the amount of debt taken.
Question : ‘‘Deposits with the banks are beneficial to the depositors as well as to the nation.’’ Examine the statement.
Answer : Deposits with banks are beneficial to the depositor as well as to the nation because:
(i) Depositors are able to save their money and earn interest.
(ii) ;Deposits are lent out to borrowers.
(iii) The loans are used for investment.
(iv) Investment increase GDP.
(v) Higher GDP leads to more jobs.
(vi) Banks use a major portion of the money to provide loans to people who are in need of funds.
Question : What happens when there is no one to supervise informal sector lending?
Answer : It gives a kind of liberty to moneylenders to charge whatever interest rate they wish to charge, no matter how high it is. Similarly, there is no one to stop them from using unfair means to get their money back.
Question : Why the poor people depend on informal sources of credit?
Answer : Poor people depend on informal source of credit because banking facilities are not available everywhere in rural India. Even if they are available, it is much more difficult to get a loan from a bank than taking a loan from informal sources because of many formalities involved in it. Non-availability of collateral and guarantor also prevents the poor from getting bank loans.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question : Why is barter system not suitable for a modern economy? What are the merits of money?
Answer : Barter system is the system of transaction between two persons which is executed through the mutual exchange of goods. For example, person A has got rice and wants a blanket, while person B has blanket and wants rice. Both of them have the things which the other one wants. So, the transaction here can take place easily. Such kind of system is suitable for an economy where people have very limited wants, there are few goods and people live in vicinity of each other. Such kind of economy, is normally a backward economy. But in modern economy, people's wants are numerous and innumerable goods and services are produced. Rather, the share of services is much higher in comparison of goods. In such an economy, barter system cannot function. The problem of double coincidence of wants will become so complex that it will convert the modern economy into a backward economy. Money has
solved this problem of double coincidence of wants. The various merits of money are the following:
(i) It has made the buying and selling of goods easier.
(ii) It has removed the problem of double coincidence of wants inherent in the barter system.
(iii) It has helped in the expansion of economy.
(iv) It has general acceptability because of legal sanction provided by the government.
(v) It has helped in the production of multiple of goods.
(vi) It has removed the problem of limited choices forconsumer.
(vii) It has removed the compulsion from the people to accept whatever is available in exchange for goods.
(viii) It has helped in the determination of price of goods and the calculation of national income.
Question : How do the deposits with banks become their source of income?
Answer : The deposits with banks become source of their income because money deposited by depositors is used by banks for giving loans to persons in need of credit. Banks charge
a higher rate of interest on the money they lend. However, the interest provided by banks to their depositors is comparatively low. It is the difference in these two interest
rates that forms the income of the banks.
Question : Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender? Discuss.
Answer : In order to decide whether to take loan from a bank or moneylender, Manav has to consider the following factors:
(i) Availability of banks in the area : Only when banks areavailable in the area, Manav can take loan from them. Otherwise he will have to resort to a moneylender.
(ii) Availability of necessary documents and collateral : If Manav has got the necessary documents and collateral, only then he can take loan from a bank. Otherwise he will have to go to a moneylender. Moneylenders may sometimes lend without collateral and documents if they know the borrower personally.
(iii) Rate of Interest : If Manav does not want to pay higher rate of interest then he will have to take loan from the bank because the moneylenders charge a very high rate of interest.
(iv) Other terms and conditions : Other terms and conditions like tenure of loan, mode of repayment etc. are some other factors which he may have to consider before taking loan
because banks may not be very flexible in terms andconditions, while moneylenders may be.
Question : Differentiate between Informal Sector of Credit and Formal Sector of Credit.
Answer : 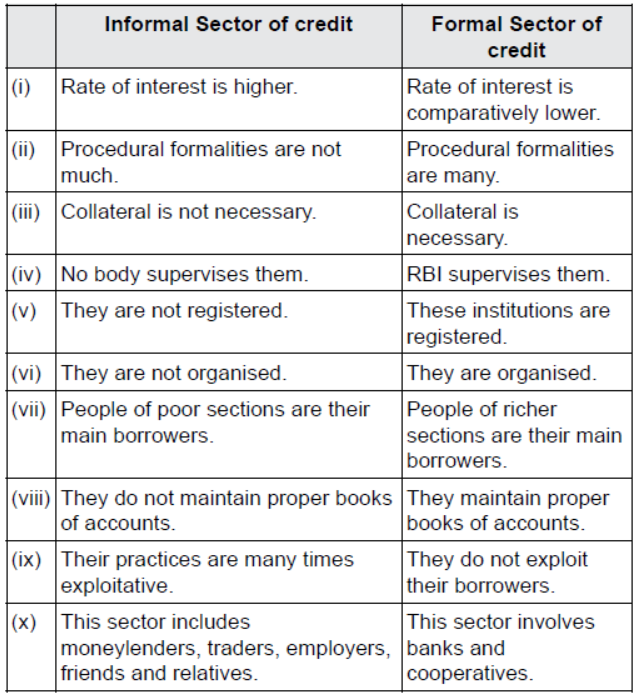
Question : What are Self Help Groups? How do they work? Explain.
Answer : Self Help Groups are organisations of the rural poor, people of same socio-economic background who pool their savings and provide loans to their members. Work of self-help groups:
(i) Generally, self help groups consist of 15 - 20 members.
(ii) Members belong to one neighbourhood.
(iii) They meet regularly.
(iv) Their savings varies form ₹ 25 - ₹ 100 or more per day or per month, as the case may be.
(v) Only members can take loans from the group itself.
(vi) The group charges interest which is less than what the moneylenders charge.
(vii) All the important decisions regarding savings and loans are taken by the members of the group.
(viii) The group is collectively responsible for the repayment of the loan.
(ix) The regular meeting of the group provides a platform to discuss and act upon a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence etc.
Question : Identify how many types of banks are there in India.
Answer : Indian Banking System comprises following types of banks :
(i) The State Bank of India.
(ii) Other Nationalised Banks.
(iii) Regional Rural Banks.
(iv) Private Sector Commercial Banks.
(v) Foreign Banks.
(vi) Cooperative Banks.
(i) The State Bank of India : The State Bank of India emerged from the conversion of the Imperial Bank of India on July 1955. Earlier it was a Private Bank but its 92 percent shares were acquired by Reserve Bank of India. So, it became the first ever government owned commercial bank in the country. In 1959, through an Act, some more State Bank Group banks were created. Now all these group banks have again been merged with the State Bank and now this bank has emerged as the biggest bank of this country.
(ii) Other Nationalised Banks : Other Nationalised Banks comprise of 20 private sector commercial banks which were nationalised in 1969 (14) and 1980 (06). These banks were nationalised with the objective of channelising the power of banking to the bigger goal of development of the country. Government exploited the potential of commercial banking system by extending its reach to every nook and corner of the country. Bank of Baroda, Bank of India, Central Bank etc., are some of the nationalised banks.
(iii) Regional Rural Banks : Regional Rural Banks were created with the special purpose of extending the financial services and credit facilities to the rural areas to solve the problem of rural indebtedness. A Regional Rural Bank is sponsored by a public sector commercial bank which also subscribes to its share capital. A regional rural bank meets the credit requirements of small and marginal farmers, landless labourers, artisans and small entrepreneurs etc. Grameen Bank of Aryavrat, Jamuna Grameen Bank etc. are the names of few Regional Rural Banks.
(iv) Private Sector Commercial Banks : With the financial reforms in banking sector and providing benchmarks in banking, government issued licenses to private banks to start their operations. These banks are in private ownership though they have to follow all the norms laid down by the Reserve Bank of India. HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Yes Bank, ING Vysya Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank are some of the private sector banks in India.
(v) Foreign Banks : Foreign Banks are those banks which have been incorporated in foreign countries while they operate in India through branches and subsidiaries. Apart from financing of foreign trade, these banks contribute a lot in the development of the country by providing much needed credit to the business of the country. HSBC Bank, Bank of America, Industrial Bank of Korea etc. are some of the foreign banks in India.
(vi) Cooperative Banks : A cooperative bank is an institution which is formed by the people of the same profession or other community which have common and shared interests, problems and aspirations. These banks cater to the services like loans, banking, deposits etc. like commercial banks but widely differ in their values and governance structures. The Himachal Pradesh State Co-operative Bank Ltd., The Meghalaya Co-operative Apex Bank Ltd., The Uttar Pradesh Co-operative Bank Ltd., The West Bengal State Co-operative Bank Ltd., The Uttaranchal Rajya Sahakari Bank Ltd. etc. are some of the cooperative banks in India.
Question : Look at a 10-rupee-note. What is written on top? Can you explain this statement?
Answer : The top of the 10-rupee-note contains the promise of the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India in these words "I PROMISE TO PAY THE BEARER THE SUM OF TEN RUPEES. 'This
statement means that the RBI governor promises to pay the value of ten-rupee-note in the form of other denominations of Indian currency equivalent to rupees ten. This promise of
the Governor of RBI represents the legal status of the Government of India to this currency.
Question : Should there be a supervisor, such as the Reserve Bank of India, that looks into the loan activities of informal lenders? Why would its task be quite difficult?
Answer : Yes, there should be a supervisor such as the Reserve Bank of India, that looks into the loan activities of informal lenders because of the following malpractices followed by
informal lenders :
(i) The informal lenders charge arbitrary interest on the loans which may be abnormally high.
(ii) The informal lenders mostly don't keep a proper record of their transactions. So, the borrowers are at their mercy for the calculation of their loan amount and interest.
(iii) The lenders exploit the borrowers by making them perform begar or work without any payment.
(iv) Many times, they use illegal ways to recover money from their borrowers.
Though it is very much required to get such informal moneylenders under the purview of some authority, there are some practical difficulties which hinders such kind of supervision. They are following :
(i) Such moneylenders are innumerable and the transaction may be very small.
(ii) Their counting is not possible as anybody who can lend money may become a moneylender.
(iii) The transaction between the borrower and the lender takes place informally. So, the transaction does not reflect anywhere.
(iv) The amount lend extended borrowed may be anywhere between hundred rupees to lakhs of rupees. Because of such small transactions and a large number of moneylenders, it is not possible for an authority like RBI tosupervise their working.
Question. What is the difference between formal sector loans and informal sector loans? Give two examples of each.
Or
Mention three points of difference between the formal sector and informal sector loans.
Answer : Formal Sector Loans:
(1)Comparatively rate of interest charged is lower than that of the informal sector loans.
(2) RBI supervises their function of giving loans.
(3) Collateral is required to obtain credit.
(4) Rich urban households depend largely on formal sources of credit.
(5) Examples: Banks and Co-operatives.
Informal Sector Loans:
(1) Higher interest rates on loan are charged.
(2) No organization is there to supervise its lending activities.
(3) They are ready to give loans without collateral.
(4) Poor households largely depend on informal sources.
(5) Examples : Traders, employers, money-lenders, relatives, friends, etc.
Question. What are formal sources of credit? Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
Or
Why do we need to expand formal source or credit in India? Explain any four reasons.
Or
Describe two reasons why banks and cooperative societies must increase their lending in rural areas. Give three suggestions for how it can be achieved. Give two reasons.
Answer : (1) The formal source of credit includes a loan from banks and co-operatives.
(2) We need to expand formal sources of credit in India for the following reasons :
(i) Formal sources of credit are less risky and they charge a low rate of interest.
(ii) The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans. It monitors the banks in actually maintaining a cash balance.
(iii) RBI ensures that loans are given not only to the profit-making businessmen and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, small borrowers, etc.
(iv) Compared to the formal lenders, most of the informal lenders charge higher interest rates. Thus, the cost to the borrower becomes much higher that leads to less income. Also, the borrowers may become victim to debt-trap. So, formal sector loans help reduce dependence on informal sources of credit.
(v) Due to the high interest rates of the informal source of credit, people who might wish to start an enterprise by borrowing, may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing.
(vi) Cheap and affordable credit by the formal sector is crucial for the country’s development.
Question : Analyse the role of credit for development.
OR
‘Credit has its own unique role for development’, justify the statement with argument.
Answer : The credit facility is a boon for a country's development. It represents the expanded purchasing power in the hands of the borrowers to meet their various requirements. It is the
sacrifice of the savers which helps the borrowers to expand their production and income of the country. It helps in generating those productive resources which could not have been generated in the absence of purchasing power. We can see the practical examples of various business houses like Reliance and Tata who with the help of credit established big business houses and generated large employment. Similar examples may be seen all around us where the people have taken loans to start various businesses and for building homes and gaining educationetc. All these have contributed a lot in the development of the country and raising the standard of living of the borrowers. But credit helps a borrower only when the terms of credit are reasonable. Unfortunately, these terms of credit are not very much favourable in the informal sources of credit which lead to the exploitation of borrower which may be harmful for development. Hence, it is for this reason that the formal sources of lending like banks and cooperatives must expand, so that the positive contribution of credit may lead
to overall development.
Question : Raman is a leading businessman of the city. He wants to expand his business. Why do you think he will get loan from banks?
Answer : Following are the various reasons which indicate that there is a great possibility of Raman getting loans from formal sources like banks:
(i) As Raman is a leading businessman of the city, he may be rich. The richer section of the society is comparatively better educated and it can understand very well the formal
procedures of getting credit from the formal sources of credit.
(ii) The richer section of the society has proper documents, guarantees or collateral which they can offer to the bank or any other institution. Poor section generally lacks in all such
things.
(iii) The richer section of the society has better repayment capacity. So, their chances of backtracking on the repayment are lesser. In the case of poor section, such chances of failure of repayments may be higher.
(iv) The richer section of the society has regular interaction with the formal sector institutions in terms of deposits and withdrawals. Such kind of interaction increases the trust of
the formal sector in richer section of the society. So, the above mentioned are some of the reasons which indicate that Raman may get loan from a bank easily.
Question : How are deposits with the bank beneficial for individual as well as for the nation ? Explain with examples.
Answer : (i) Banks accept deposits and also pay an interest on the deposits. In this way, people's money is safe with the banks and it earns an interest as well.
(ii) People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require.
(iii) Banks keep only a small portion of their deposits as cash.
Then they use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans.
(iv) There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people. This creates employment and
income for the people of a nation and contributes to national development.
Question : Why should credit at reasonable rates from the banks and cooperatives be available for all ?
Answer:
1. Credit at reasonable interest rates should be available for all so that they may increase their income and help in the overall development of the country.
2. High interest rate does little to increase the income of the borrowers.
3. It is necessary that the banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in rural areas, so that the dependence of the people on informal sources of credit reduces.
4. In addition to this more credit should be given to the poor to get maximum benefit from the cheaper loans.
5. This will help in increasing their income as well as standard of living.
Question : Describe the pattern of formal and informal sources of credit in urban areas. Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit ?
Answer:
(1) The people in the urban areas are divided into four categories :
• Poor households
• Households with few assets
• Well-off households
• Rich households.
85 per cent of the poor households take loans from informal sources whereas only 10 per cent of the rich households take loans from informal sources. 90 per cent of the rich households take loans from the formal sources.
(2) In urban areas, poor households suffer at the hands of informal sources. The same is the position in rural areas. Most of the informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans.
As a result of it, larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan. In some cases, the amount to be repaid becomes greater than the income of the borrower. This leads to debt-trap. These reasons make it necessary to expand the formal sources of credit i.e., banks and cooperatives which will make available cheap and affordable credit to the people.
Question : What are Self-Help Groups ? Describe in brief their functioning including their aim and importance.
Answer:
(1) Atypical Self-Help Group has 15-20 members, usually belonging to one neighborhood who meet and save regularly.
(2) The functioning of SHGs is as given below :
1. Aim : The aim of Self-Help Group is to organize rural poor, women in particular and collect their savings and to take loans from the group to meet their needs. The group takes loan from the bank to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
2. Working of the SHG : Decisions on loans and savings are taken by the group members. All matters relating to the purpose, amount, interest rate, repayment schedule are decided by the group members. The group is responsible for the repayment of the loan. Non-repayment of loan by any member is followed up seriously by other members of the group.
3. Importance :
(a) SHGs have helped borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral because the banks are willing to lend to the poor women organized in SHGs, even though they have no collateral as such.
(b) The borrowers can get timely loans at a reasonable interest rate.
(c) It has helped women in the rural areas to become financially self-reliant.
(d) The meetings of the groups provide a platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition and domestic violence.
Thus, SHGs are playing a significant role in the improvement of the condition of the poor, particularly women.
Question : “Deposits in the hanks are beneficial to the depositors as well as to nation.” Examine the statement.
Answer:
(1) Deposits are beneficial to the depositors as mentioned below :
• Banks accept the deposit and pay as interest rate on the deposits.
• Money is safe with the bank.
• People (depositors) may withdraw the money as and when they require.
• Depositors may make payments through cheques instead of cash.
(2) Deposits are beneficial for the banks too as mentioned below :
• Banks keep only a small proportion of deposits. Now days, banks keep about 15 per cent as cash in order to pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money from the bank on any given day.
• Bank use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans. There is huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people. Businessmen and other entrepreneurs take loans from the banks and open factories. They help in the advancement of the economy. Thus the deposits are beneficial to the nation.
Question : Explain three terms of credit
Answer:
(1) The terms of credit are as mentioned below :
1. Interest rate.
2. Collateral and documentation requirement.
3. Mode of repayment.
(2) The terms of credit vary substantially from one credit arrangement to another.
(3) Interest rate in the formal sector e., banks and cooperative is about 9-10 per cent but in informal sector, the moneylender and grain merchants etc. charge much higher interest. Thus the cost to the borrower of informal loans is much higher.
(4) Moneylenders take collateral such as land. As the interest rate is higher and if the borrower is unable to repay for any reason, they try to exploit the borrower by taking control of the collateral e.,land etc.
(5) Banks insist on documentation requirement and collateral before granting loans. That is why it becomes difficult for the poor to get loans from the banks.
Source / Case Based Questions
Question : Answer the following questions on the basis of data :
Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country's development. The various types of loans or credits can be grouped as formal sector loans and informal sector loans. Among the former are loans from banks and cooperatives. The informal lenders include moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends. Banks and cooperatives give loans on a lesser interest rate than the informal sector. But bank loans require proper documents and collateral. Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons why bank loans are not available to small farmers and people who wish to start small industries. Compared to the formal lenders, most of the informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans. Thus, the cost to the
borrower of informal loans is much higher. Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan. For these reasons, banks and
cooperative societies need to lend more to the poorer section of people. This would lead to higher incomes and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs. They could grow crops, do business, set up small-scale industries etc. They could set up new industries or trade in goods.
(i) Identify the types of loans or credits can be grouped into:
(a) Formal sector
(b) Informal sector
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Only option (a)
Answer : (c) Both (a) and (b)
(ii) What is the main reason that bank loans are not available to small farmers?
(a) Lack of proper documents
(b) Absence of collateral
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer : (b) Absence of collateral
(iii) Which of the following is not a part of informal source of lenders?
(a) RBI
(b) Commercial banks
(c) Moneylenders living in rural areas
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer : (d) Both (a) and (b)
(iv) Which one of the following statements is true regarding loans provided by formal and informal sector?
(a) Formal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans than informal lenders.
(b) Informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans than formal lenders.
(c) Cost to the borrower of informal loans is much lower than formal loans.
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer :(b) Informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans than formal lenders.
Question : Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follows:
Source A - Medium of exchange
In an economy where money is in use, money by providing the crucial intermediate step eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants. It is no longer necessary for the shoe
manufacturer to look for a farmer who will buy his shoes and at the same time sell him wheat. All he has to do is find a buyer for his shoes. Once he has exchanged his shoes for oney, he can purchase wheat or any other commodity in the market. Since money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called a medium of exchange.
Source B - Issuing of currency
As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency. Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India. No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
Source C - Credit arrangement
Interest rate, collateral and documentation requirement, and the mode of repayment together comprise what is called the terms of credit. The terms of credit vary substantially from one credit arrangement to another. They may vary depending on the nature of the lender and the borrower. The next section will provide examples of the varying terms of credit in different credit arrangements.
(i) Why money acts as an intermediary in the exchange process?
Ans. Money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process because it is considered as a medium of exchange.
(ii) Do any individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency in India?
Ans. As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency. Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
(iii) What are terms of credit?
Answer : The interest rate, collateral and documentation requirement, and the mode of repayment together comprise terms of credit.
Question : What does higher cost of borrowing means?
Answer : This means a large part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan. Hence, borrowers have less income left for themselves.
Question : Which segment of the society receives formal credit?
Answer : It is the richer segment of society which receives formal credit.
Question : What are the difficulties from which the barter system of exchange suffers?
Answer : (i) Lack of double coincidence of wants.
(ii) Valuations of all the goods cannot be done easily.
(iii) Certain products cannot be divided.
Question : What do people do with extra money?
Answer : They deposit it with the banks by opening a bank account in their name.
Question : Give some common examples of collateral used for borrowing.
Answer : Property such as land titles, deposits with banks, livestock are some common examples of collateral used for borrowing.
Question : While taking a loan, borrowers look for easy terms of credit. What do is this mean?
Answer : This means low interest rate, easy conditions for repayment and less collateral and documentations requirements.
Question : Why do we consider demand deposits as money?
Answer : Demand deposit constitute money in modern economy as they are accepted widely as a means of payment along with currency.
Question : Mention three limitations of the barter system.
Answer : The three limitations of the barter system are:
(i) Lack of double coincidence of wants. It means, both the parties have to agree to sell and buy each others’ commodities.
(ii) Valuations of all the goods cannot be done easily.
(iii) There are certain products which cannot be divided.
Question : Why are the deposits in the banks called ‘demand deposits’? What are the benefits of deposits with the banks?
Answer : People deposit extra cash with the bank by opening a bank account in their name. Banks accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount of interest. People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Question : What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words.
Answer : Self-Help Groups (SHGs) consist of certain members who pool their savings and constitute a fund which is further used in making finance and advances to other members. The SHGs help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral. They can get timely loans at a reasonable interest rate. They help women to become self-reliant.
Question : Why is cheap and affordable credit important for the country’s development? Explain three reasons.
Answer : Cheap and affordable credit is important for the country’s development because of the following reasons:
(i) This would lead to higher incomes and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(ii) They could grow crops, do business, set up small scale industries etc.
(iii) They could set up new industries or trade in good. All these lead to the country’s development.
Question : Why is the rupee widely accepted as a medium of exchange?
Answer : (i) India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the central government.
(ii) As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency.
(iii) Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transaction in India.
(iv) No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
Question : Differentiate between formal and informal sources of credit. Explain problems faced by borrowers of loan from informal sources.
Answer :
The moneylenders charge very high rates of interest keep no records of transactions and harass the poor borrowers.
Question : What are the reasons why the banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers?
Answer : The banks are sometimes not willing to lend to certain borrowers because of the following reasons:
(i) Some persons are not able to produce certificate of their earning.
(ii) There are some people who have a history of non-repayment of loans.
(iii) There are other people who are not able to produce documents of their employment.
(iv) Some persons have nothing to give to bank as collateral.
(v) There are a few others who fail to produce two persons who can stand as surety in case he is unable to repay the loan.
Question : Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
Answer : (i) Compared to the formal lenders most of the informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans. It means that the cost to the borrower of the informal loans is much higher.
(ii) Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of earning of the borrowers is used to repay the loan and they have less income left for themselves.
(iii) The high rate of interest of borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower and this could lead to increasing debt and debt-trap.
(iv) People who might wish to start an enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing.
(v) For these reasons banks and cooperatives need to lend more. This would lead to higher incomes and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(vi) They could grow crops, do business, set up small-scale industries etc. They could set up new industries or trade in goods.
(vii) Cheap and affordable credit is important for the country’s development. Hence, it is necessary to expand formal sources of credit in our country.
Question : The following table shows people in a variety of occupations in urban areas. What are the purposes for which the following people might need loans? Fill in the column.
Next, classify the people into two groups based on whom you think might get a bank loan and those who might not. What is the criterion that you have used for classification?
Answer :
The criterion I have used for the classification mentioned above is firstly, whether the borrower has the potential to repay the loan or not. Those with job security will certainly get a loan from a bank because they have the capability to give repayment installments. The second basis of classification is whether the borrower has a collateral or not, on which to guarantee his/her loan. These two are the basic prerequisites for getting a loan from a bank.
CASE BASED STUDY QUESTIONS
PASSAGE 1
The other form in which people hold money is as deposits with banks. At a point of time, people need only some currency for their day-to-day needs. For instance, workers who receive their salaries at the end of each month have extra cash at the beginning of the month. What do people do with this extra cash. They deposit it with the banks by opening a bank account in their name. Banks accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits and in this way people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount as interest. People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Question : What do workers do with extra cash?
Answer: The workers deposit the extra cash in the banks by opening a bank account in their name. Banks accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits.
Question : When can people withdraw money?
Answer: People have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require.
Question : Name the other form in which people hold money?
Answer: Deposits with Bank
PASSAGE 2
Demand deposits are another interesting facility. It is this facility which lends it the essential characteristics of money that of a medium of exchange. You would have heard of payments being made by cheques instead of cash. For payment through cheque, the payer who has an account with the bank, makes out a cheque for a specific amount. A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Question : What is a cheque?
Answer: A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Question : Who issues a cheque?
Answer: The account holder who has an account with the bank.
Question : What benefit would you find with cheque transaction?
Answer: 1. It allows to have cashless transaction.
3. It can be used in distant places.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography India Land and People Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Water Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Water Resources Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Minerals And Energy Resources Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Life Lines of National Economy Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Forest and Wild Life Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Water Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Agriculture Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Minerals and Energy Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Manufacturing Industries Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing Industries Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Civics Popular Struggles and Movements Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Civics Popular Struggles and Movements Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles and Movements Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History Nationalism In India Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History Nationalism In India Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism In India Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Hindi Assignment |
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Social Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 10 Social Science regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 10 Social Science practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Social Science by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 10 Social Science also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Social Science have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 10 Social Science students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 10 Social Science which you can use to further make your self stronger in Social Science.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Social Science Class 10 Assignments for chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 10 Social Science Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science with answers relating to Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 10 Social Science mock tests for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 10 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 10 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 10 Social Science worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 10 Social Science MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 10 Social Science
How to practice CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 10 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Social Science Class 10 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Class 10 Social Science have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Class 10
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit Class 10 Social Science

