Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources Assignment. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Social Science. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Social Science in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Social Science prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources
Class 12 Social Science students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Social Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 12 Social Science Assignment
Minerals and Energy Resources
Points to Remember
• Mineral- Naturally occurring homogeneous substance with a definable internal structure.
• Ores- Naturally occuring substances from which minerals can be extracted profitably.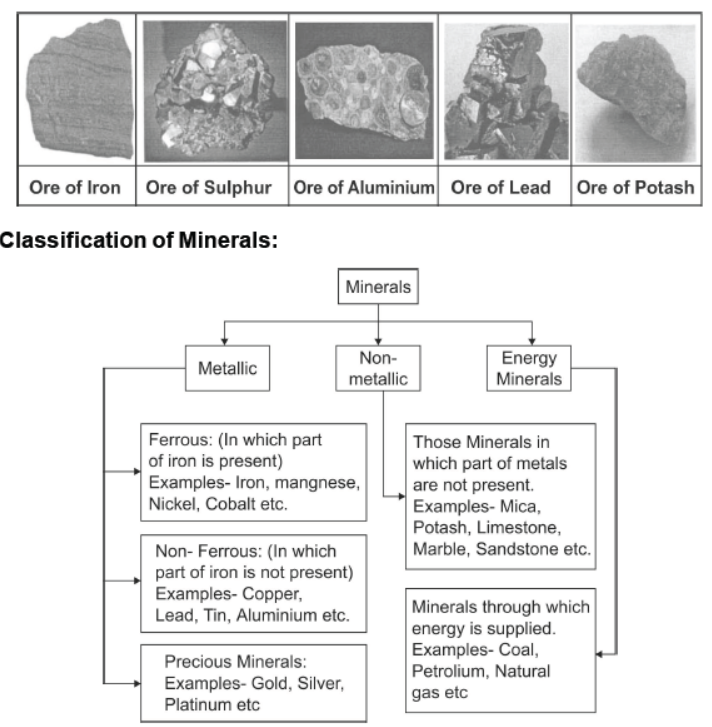
Sources of Minerals:-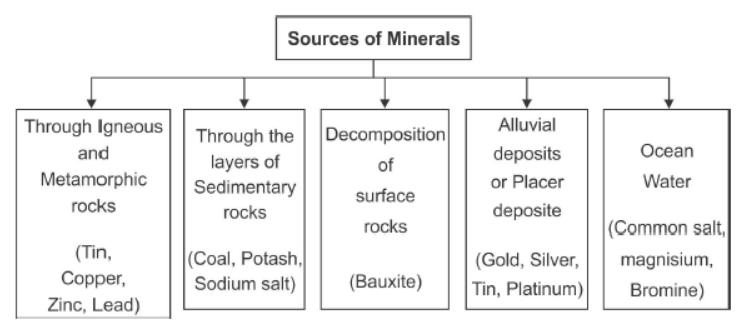
• Mining- The extraction of useful and commerically viable minerals by digging down the earth is called mining.
• Mining is a hazards industry as the resources are dug out from the interior of the earth by making tunnels or pit. During this process risk to the life of the workers are very high due to leakage of poisonous gas or fires or flooding of water into the mine or even collapsing of mine roofs. Along with that workers have also to face health issues.

Need for the conservation of resources/Minerals
• High rate of consumption
• Limited reserves
• Low rate of replenishment
• Ill effects on Environment
Methods to conserve Resources/ Minerals
• Reduce
• Reuse
• Recycle
• Replace
Question. Which one of the following metals can be obtained from Bauxite?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Copper
(c) Iron
(d) Silver
Answer : A
Question. Which one of the following places is known for lignite deposits?
(a) Khetri
(b) Neyeli
(c) Baliadila
(d) Bokaro
Answer : B
Question. Which is the finest iron ore with a very high content of iron?
(a) Magnetite
(b) Haematite
(c) Limonite
(d) None of these
Answer : A
Question. Where is the largest wind farm cluster located in India?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Kerala
(c) Karnataka
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer : D
Question. Iron ore is exported Japan and South Korea via which port?
(a) Chennai
(b) Vishakhapatnam
(c) Haldia
(d) Mangaluru
Answer : B
Question. Which type of sand in Kerala is rich in thorium?
(a) Monazite sands
(b) Gypsum snads
(c) Silica sands
(d) Black sands
Answer : A
Question. The toothbrush and tube containing paste are made up of plastic obtained from
(a) Mica
(b) Petroleum
(c) Fibre
(d) Paper
Answer : B
Question. Which out of the following metallic minerals is obtained from veins and lodes?
(a) Zinc
(b) Limestone
(c) Rutile
(d) Mica
Answer : A
Question. In which kind of rocks are the minerals deposited and accumulated in the stratas?
(a) Igneous rocks
(b) Metamorphic rocks
(c) Sedimentary rocks
(d) None of these
Answer : C
Question. Minerals are generally found in:
(a) ores
(b) rocks
(c) soil
(d) none of these
Answer : A
Question. In India, the Gulf of Khambhat, The Gulf of Kuchch and Gangetic delta provide ideal condition for utilising which energy?
(a) Tidal energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Solar energy
(d) Non-conventional energy
Answer : A
Question. Oceans beds are a treasure house of:
(a) fishes
(b) minerals
(c) tones
(d) none of these
Answer : B
Question. The Badamphar mine in Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar district is situated in which of the following Indian state?
(a) Karnataka
(b) Odisha
(c) Chattisgarh
(d) Jharkhand
Answer : B
Question. Ferrous minerals account for about .......... of the total value of production of metallic minerals.
(a) One-fourth
(b) Two-fourth
(c) Three-fourth
(d) Two-third
Answer : C
Question. Large reserves of natural gas have been discovered in which place in India?
(a) Arabian Sea
(b) Andaman Nicobar Islands
(c) Krishna Godavari Basin
(d) Gulf of Mannar
Answer : C
Question. The white colour in tooth paste comes from which of the following?
(a) Titanium oxide
(b) Fluoride
(c) Silica
(d) Limestone
Answer : A
Question. In which of the following minerals is India sufficient?
(a) Gold
(b) Glass
(c) Limestone
(d) All of these
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is a mineral?
(a) Diamond
(b) Talc
(c) Mica
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. What quantity of India’s petroleum production is obtained from Mumbai High?
(a) 63%
(b) 36%
(c) 69%
(d) 65%
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following mineral is used to reduce cavities in teeth?
(a) Limestone
(b) Aluminium oxide
(c) Fluoride
(d) Silica
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is the basic mineral and the backbone of industrial development?
(a) Zinc ore
(b) Iron ore
(c) Manganese ore
(d) Silver ore
Answer : B
Question. The mineral having wide application in the electrical industry is:
(a) nickel
(b) manganese
(c) iron ore
(d) zinc
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is the highest quality hard coal
(a) Bituminus
(b) Anthrasite
(c) Lignite
(d) None of the above
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following is used as raw material in the cement industry?
(a) Lime stone
(b) Coal
(c) Mica
(d) Aluminium
Answer. A
Question. Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh is famous for coal mine.
Answer. Geothermal energy
Question. Geothermal energy plant is situated in kaiga in Karnataka.
Answer. Atomic energy
FILL IN THE BLANK :
Question. Minerals are usually found in .......... .
Answer : ores
Question. Although, over .......... minerals have been identified, only a few are abundantly found in most of the rocks.
Answer : 2000
Question. In .......... and .......... rocks minerals may occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints.
Answer : igneous, metamorphic
Question. Fluoride which is used to reduce cavities comes from a mineral .......... .
Answer : flourite
Question. Geographers study .......... as part of the earth’s crust for a better understanding of landforms.
Answer : minerals
Question. The sparkle in some toothpaste comes from .......... .
Answer : mica
Question. Rocks are combinations of homogenous substances called .......... .
Answer : minerals
Question. .................... is a source of atomic energy.
Answer. Urenium/Thorium
Question. .................... is the most important industrial ore of iron.
Answer. Hematite
Question. What is ore?
Answer. Naturally occurring substances from which minerals can be extracted profitably.
Question. What is meant by metallic ore?
Answer. Those minerals in which part of metals are found are called metallic minerals.
Question. Write one method of conservation of energy.
Answer. Reduce/reuse/recycle/replace/ any other
Question. Why is Tidal energy called as clean source of energy?
Answer. No harm to environment
Question. Why is coal called as the fossil fuel?
Answer. Because it is formed by the decomposition of fossils that buried deep into the earth millions of year ago.
TRUE/FALSE :
Question. Odisha is the largest bauxite producing state in India.
Answer : True
Question. There are over 380 thermal plants in India.
Answer : False
Question. Anthracite is the highest quality hard coal.
Answer : True
Question. Coal mining in Jowai and Cherapunjee is done by family member in the form of a long narrow tunnel, known as rat hole mining.
Answer : True
Question. The largest solar plant of India is located at Madhpur, near Bhuj.
Answer : True
Question. Thermal energy is obtained by altering the structure of atoms.
Answer : False
Question. Mineral oil is the next major energy resource in India after coal.
Answer : True
Question. Kudremukh mines Madhya Pradesh produces 52% of India’s copper.
Answer : False
ASSERTION AND REASON :
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as :
(a) If Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If Both assertion and reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Conservation of Energy Resources is essential.
Reason : Energy is a basic requirement for economic development.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Geological processes of mineral formation is slow
Reason : Minerals resources are consumed way quickly than they are formed.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives.
Reason : Minerals have a universal use, they are used to manufacture everything we use in our day to day lives.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Iron ore is the basic mineral and the backbone of India.
Reason : India is rich in good quality Iron ore.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Mica is a metallic mineral.
Reason : Mica mineral is the basic raw material for cement industry
Answer : D
Question. Assertion : Natural gas is referred as an environment friendly fuel.
Reason : Natural gas contains low carbon dioxide emissions.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Increased use of fossil fuels creates a healthy environment.
Reason : Fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas are easily obtained from natural resource.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion : Uses of iron brought a radical change in human life.
Reason : Different kinds of tools where invented by using minerals
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Mining activity is often called a “Killer Industry”.
Reason : Mining helps in agriculture.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion : Thermal power stations are located on or near the coalfields.
Reason : Coal is a bulky material, which loses weight on use as it is reduced to ash. Hence, heavy industries and thermal power stations are located on or near the coalfields.
Answer : A
In an assertion (A) and its reason (B) is given below. Read the following statements and choose the right answer from the options given below.
Assertion (A): The activities of fishing come under Primary sector.
Reasoning (R): Fishing depends directly upon natural resources.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is the not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Question. Assertion (A): Mica is a non metallic mineral.
Reasoning (R): No metallic properties are present in Mica.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion (A): Copper is used to make electrical wire.
Reasoning (R): Copper is insulator of electricity.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion (A): Gold and silver is found as 'placer deposite'.
Reasoning (R): These are low reactive metal.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion (A): Solar energy is an example of conventional source of energy.
Reasoning (R): Solar energy is an example of clean energy.
Answer. D
Very Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources
Question : How many thermal power plants are there in India?
Answer : There are over 310 thermal power plants in India.
Question : ‘Different regions of India contain different minerals’. What is the reason behind it?
Answer : It happens because of the difference in the geological structure, processes and time involved.
Question : Name the two countries which import iron ore from India.
Answer : Japan and South Korea.
Question : What are the Khetri mines in Rajasthan famous for?
Answer : The Khetri mines in Rajasthan are famous for copper production.
Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources
Question : Explain any three values attached with the use of minerals in a sustainable manner.
Answer : (i) Our industries and agriculture immensely depend on mineral deposits and the substances manufactured from them. The total volume of workable mineral deposits is an insignificant fraction i.e. one per cent of the earth’s crust. Hence, minerals should be used cautiously.
(ii) The geological processes of mineral formation are so slow that the rates of replenishment are infinitely small in comparison to the present rates of consumption.
(iii) Mineral resources are finite and non-renewable. Rich mineral deposits are our country’s extremely valuable but short-lived possessions.
Question : How do minerals occur in sedimentary rocks?
Answer : (i) In sedimentary rocks a number of minerals occur in beds or layers.
(ii) They have been formed as a result of deposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal strata.
(iii) Coal and some forms of iron ore have been concentrated as a result of long periods under great heat and pressure.
(iv) Another group of sedentary numerals such as gypsum, potash salt and sodium salt are formed as a result of evaporation.
Question : (i) How are deposits of bauxite formed and aluminium obtained?
(ii) What is the utility of aluminium?
(iii) Describe the distribution of aluminium.
Answer : (i) Bauxite deposits are formed due to decomposition of wide variety of rocks rich in aluminium silicates. Ores containing aluminium are obtained from bauxite which is a clay-like substance from which alumina and later aluminium is obtained.
(ii) It is an important metal because it combines the strength of metals such as iron with good conductivity and great malleability.
(iii) Odisha is the largest bauxite producing state. 45% of country’s total production in 2000-2001 was from Orissa. Panchpatmali deposits in Koraput district are the most important bauxite deposits in the state.
Question : How are minerals an indispensable part of our lives? Explain with three examples.
Answer : Minerals from an indispensable part of our lives in the following ways:
(i) From a tiny pin that we use to a towering building or tall ships are all made up of minerals.
(ii) The food that we consume also contains minerals which are essential for the growth of human body.
(iii) Cars, buses, trains and aeroplanes are manufactured with the help of minerals and they run on power resource derived from minerals.
Question : State any two factors affecting the economic viability of mineral reserves.
Answer : (i) The mineral content of the ore must be in sufficient concentration to make its extraction commercially viable.
(ii) The type of formation or structure in which minerals are found determines the relative ease with which mineral ores may be mined. This also determines the cost of extraction.
Question : “Discovery and use of iron brought a radical change in human life” prove it with three examples.
Answer :
a) Revolution in agriculture-different type of tools invented like axe, hook, plough etc.
b) Revolution in industry-different tools and machines like spinning.
c) Revolution in transportation- bullock-cart, ships, boats etc.
Question : Describe the various forms in which minerals occur.
Answer :
a) In igneous and metamorphic rocks ( cracks, crevice, faults or joints)
b) In beds or layers of sedimentary rocks due to deposition, accumulation and concentration.
c) Decomposition of surface rocks
d) Alluvial deposits in sands of valleys and the base of hills as “ Placer Deposits”
Question : Why is mining activity often called a “Killer Industry”. Give three reasons.
Answer : a) High risk involved
b) Due to poisonous fumes, mines are vulnerable to workers for pulmonary diseases.
c) Risk of collapsing mines roofs, and fires in coal mines.
d) Water sources get contaminated
Question : Give three reasons in the favour of use of ‘Atomic energy’.
Answer :
a) Coal and natural oil are exhaustible.
b) Nuclear power plants are easy to handle
c) Most developed countries are utilizing this energy successfully
d) It can be useful in fields of medicines and agriculture
e) Hydel energy is not satisfactory due to environmental issues
Question : Why does solar energy in Rajasthan have greater potential as non –conventional source of energy?
Answer : a) Hot and dry region
b) Clear sky almost whole year
c) Cheaper installation
d) Renewable and pollution free energy source.
e) Government motivation
Long Questions for Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources
Question : What are the different varieties of iron one? How will you differentiate between them? Give any two points.
Answer : Iron-ore is the backbone of India’s industrial development. The different varieties of iron-ore are-Magnetite, hematite, Limonite and Siderite.
• Magnetite is the finest iron-ore with a very high content of iron up to 70%. It has excellent magnetic qualities. it is valuable for electrical industry.
• Hematite is the most important industrial iron-ore in term of quantity used.
It has a slightly lower iron content than 50-60%.
• Limonite has 40-60% iron content.
• Siderite has 40-50% iron content.
Question : What are the Petroleum producing areas in India. Explain.
Answer : Most of the petroleum producing areas in India are associated with anticlines and faults traps in the rock formations of the tertiary age. In the region folding, anticlines or domes, it occurs where oil is trapped in the crest of the uphold. Petroleum is also found in fault traps between porous rocks.
Major petroleum producing areas of India are …
1) ASSAM- Digboi, Naharkatia, Moran-Hugrijan, Namdang region
2) GUJRAT- Ankeleshwar, Lunez, Navgan
3) MUMBAI HIGH
4) Godavari – Mahanadi basin
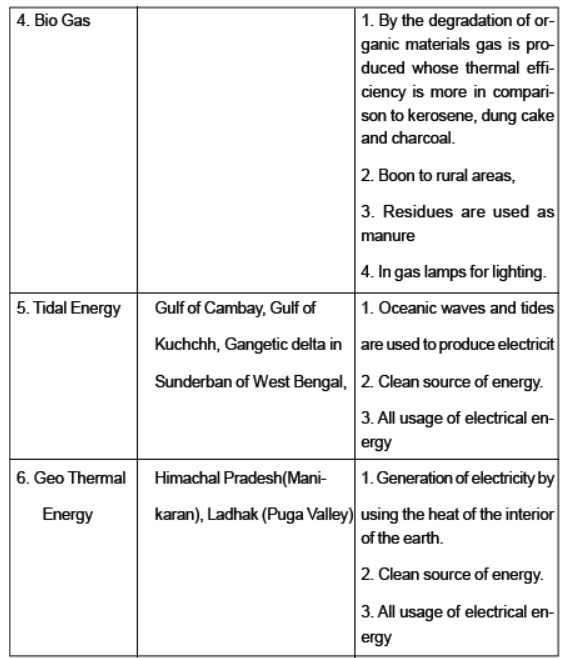
Question : Distinguish between Natural Gas and Bio Gas.
Answer :
• NATURAL GAS
• It is a mixture of combustible gaseous hydrocarbons occurring in the rocks of earth crust.
• This is commercial energy.
• It is used as raw material in the petrochemicals.
• It is transported from one place to another through pipeline.
• Mostly used in urban areas.
• BIO GAS
• It is derived by decomposition of waste of animals and plants with the help of microorganism in presence of water.
• Non commercial energy
• It is produced in tanks
• It is found in rural areas
Question : What is Non - Conventional sources of energy? Discuss two sources of such types of energy.
Answer : Sources of energy which are renewable, eco-friendly and newer one are called non conventional sources of energy i.e. wind energy, geothermal energy, tidal energy etc.
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY:
Geothermal energy refers to the heat and electricity produced by using the heat from the interior of the earth. Where the geothermal gradient is high , high temperature is found at shallow depth . There are several hot springs in India which could be used to generate electricity. Two projects, one is MANIKARAN in Himachal and second in PUGA VALLEY in Ladakh has been set up in India to harness Geothermal energy.
TIDAL ENERGY:
Oceanic tides can be used to generate electricity .During high tides water flows into the inlet and get trapped when it is closed. After the fall of tide the water flows back to the sea via pipe lines that carry it through power generating turbines. In India gulf of Kutch provides ideal conditions for tidal energy.
Question : India now ranks as a “WIND SUPER POWER “in the world. Why?
Answer :
• India gets advantage of trade winds, western lies and monsoon winds.
• Wind energy completely pollution free and non exhaustible that’s why it becomes popular.
• India has an ambitious program to install 250 wind driven turbines with total capacity of 45 mega watts spread over 12 suitable locations.
• India’s potential wind power generation is of 50000 megawatts of which ¼ can be easily harnessed.
• Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu have favorable conditions for wind energy. Wind power plant at LAMBA in Gujarat, is the largest in Asia.
Question : How can we conserve energy resources in India? Explain.
Answer : Following efforts can be made to conserve energy resource in India:
i) Using public transport instead of individual vehicles.
ii) Switching of electricity when not in use.
iii) Using power saving devices.
iv) More and more use of non conventional source of energy as they are renewable and eco-friendly.
v) In automobiles electrical motors should be introduced.
vi) Intensified exploration and research of new sources of energy.
Source based Questions
1. Read the extract and answer the following questions-
We use different things in our daily life made from metal. Can you list a number of items used in your house made of metals. Where do these metals come from? You have studied that the earth's crust is made up of different minerals embedded in the rocks. Various metals are extracted from these minerals after proper refinement. Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives. Almost everything we use, from a tiny pin to a towering building or a big ship, all are made from minerals. The railway lines and the tarmac (paving) of the roads, our implements and machinery too are made from minerals. Cars, buses, trains, aeroplanes are manufactured from minerals and run on power resources derived from the earth. Even the food that we eat contains minerals. In all stages of development, human beings have used minerals for their livelihood, decoration, festivities, religious and ceremonial rites.
Question. Where do we get metals?
Answer. From daily life
Question. Write two uses of minerals from your day to day life.
Answer. Student will give usage from their day to day life
Question. How minerals affected the different stages of development of human being?
Answer. Decoration, festivities and religions ceremonies
Question. Write two energy resources that we get from the earth.
Answer. Coal, Petrolium etc.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography India Land and People Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Water Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Water Resources Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Minerals And Energy Resources Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Life Lines of National Economy Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Forest and Wild Life Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Water Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Agriculture Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Minerals and Energy Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Manufacturing Industries Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing Industries Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Civics Popular Struggles and Movements Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Civics Popular Struggles and Movements Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles and Movements Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History Nationalism In India Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History Nationalism In India Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism In India Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Hindi Assignment |
CBSE Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Social Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Social Science regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Social Science practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Social Science by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Social Science also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Social Science have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Social Science students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Social Science which you can use to further make your self stronger in Social Science.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Social Science Class 12 Assignments for chapter Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Social Science Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Social Science with answers relating to Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Social Science mock tests for Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Social Science worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Social Science MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Social Science
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Social Science, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Social Science Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 12 Social Science have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Contemporary India II Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 12 Social Science

