Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Manufacturing Industries Assignment. Get printable school Assignments for Class 10 Geography. Class 10 students should practise questions and answers given here for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Geography in Class 10 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 10 Geography prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Class 10 Geography students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries in Class 10. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Geography will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Geography Assignment
Manufacturing Industries
Points to Remember: Production of more valuable goods in large quantities after processing the raw material is called manufacturing. The extensive form of manufacturing is called Industry.
Cotton Textile Industry
• First successful cotton textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854.
• Mahatma Gandhi laid emphasis on the spinning of yarn and wearing khadi so that weavers could get employment.
• In the early years the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujrat. Availability of raw material, market, transport facilities (port), labour and moist climate contributed towards its localisation.
• While spinning continues to be centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamilnadu, weaving is highly decentralized to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and design of weaving in cotton, silk,zari, embroidery, etc.
Jute Industry
• India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods and stands at second place as an exporter after Bangladesh.
• In India Jute Industry is highly concentrated mainly around the banks of Hugli River-
(a) Proximity of the jute producing area
(b) Inexpensive transportation,
(c) Cheap labour
(d) Abundant water supply
(e) Kolkata as a large urban centre provides banking, insurance and port facilities for export to the jute goods.
• Challenges faced by the industry include the stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitute and from other competitors like Bangladesh, Brazil etc. However the National Jute policy ensured good prices to jute farmers.
Sugar Industry
• India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies the first place in the production of gur and khandsari.
• Sugar mills in India spread over Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra,Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Gujarat.
• In recent years there is a tendency for the mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states especially in Maharashtra.
This is because-
(a) Higher sucrose content in the sugar cane,
(b) Cool climate,
(c) Moreover the cooperatives are more successful.
• Major Challenges-
(a) Seasonal nature,
(b) Old and inefficient methods of production,
(c) Transport delay
Iron and Steel Industry
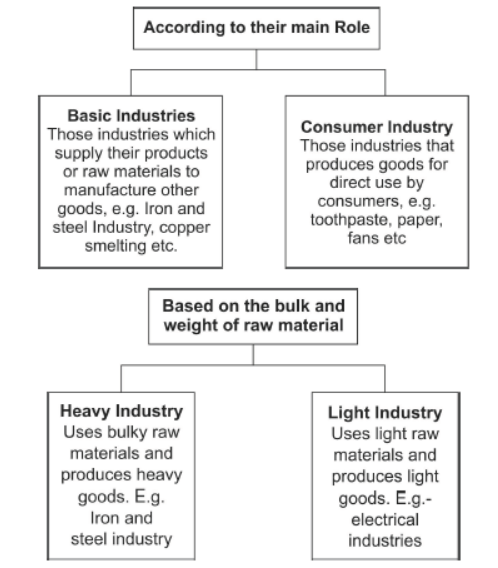
• The iron and steel Industry is the basic industry since all the other industries- heavy, medium, and light depends on it for their machinery.
• Iron ore, coking coal and limestone in the ratio of 4:2:1.
• In the year 2016 with 95.6 million tons of steel production, India ranked third among the world crude steel producers. It is the largest producer of sponge Iron.
• Most of the public sector undertakings market their steel through Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL).
• Chotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of Iron and Steel industries. It is because
(a) Low cost iron ore,
(b) High grade raw materials in proximity,
(c) Cheap labour
(d) Local market
Reasons for its not growing in full potential in India-
(a) High costs and limited availability of coking coal,
(b) Lower productivity of labours,
(c) Irregular supply of energy,
(d) Poor infrastructure
Aluminium Smelting
• Aluminium Smelting is the second most important metallurgical industry in India.
• It is light, resistant to corrosion, a good conductor of heat, mailable and becomes strong when it is mixed with other metals.
• Aluminium smelting plants in India are located in Odisha, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh ,Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
Two key need areas for the establishment of this industry are-
• Uninterrupted power supply,
• Availability of cheap raw material.
Chemical Industry
• Both organic and inorganic types of chemicals are produced in India.
• Organic chemicals include petrochemicals, which are used for manufacturing of synthetic fibers, synthetic rubber, plastics, dye-stuffs, drugs and pharmaceuticals.
• Inorganic chemicals include sulphuric acid, nitric acid, alkaline, soda ash.
• It contributes approximately 3% of the GDP.
• It is the third largest in Asia and occupies the twelfth place in the world.
Fertiliser Industry
• The fertilizer industry is centered around the production of nitrogenous fertilizers (mainly Urea), Phosphatic fertilizers and ammonium phosphate (DAP) and complex fertilizers.
• Potash is entirely imported as the country does not have any reserves of commercially usable potassium compound.
• After the Green Revolution the industry expanded to several other part of the country.
Cement Industry
• This industry requires bulky and heavy raw materials like limestone, silica, aluminium and gypsum.
• Coal and electric power are needed apart from rail transportation.
• It is used for construction activities.
• Its plants are located in Gujarat due to its access to the market in the gulf countries.
Automobile Industry
• Automobiles provide vehicle for quick transportation of goods and passengers.
• After the liberalization the coming in of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market.
• The industry is located around Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Pune,Chennai, etc.
Information Technology and Electronic Industry
• It covers a wide range of products from transistor sets to television, telephone, cellular telecom, pager, telephone exchange, radars. Computers and many more equipment.
• Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India.
• The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to the success of IT industry in India.
Methods to Control Pollution
• Use of three R's (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle)
• Rainwater harvesting
• Treatment of Industrial waste
• Use of renewable sources of energy
• Development of new techniques which is durable and cause less pollution.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing Industries
Question : Which of the following industries has been a major foreign exchange earner in the last few years?
(a) Tourism Industry
(b) Information Technology Industry
(c) Engineering Industry
(d) Electronics Industry
Answer : B
In question assertion (A) and its reason (B) is given below. Read the following statements and choose the right answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is the not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is incorrect
(d) R is correct but A is incorrect.
Question. Assertion (A): Iron and steel industry is called a basic industry.
Reasoning (R): Every other industries-light, medium or heavy industries are dependent on it.
Answer. Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question. Assertion (A): In recent years there is a tendency for the mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states especially in Maharashtra
Reasoning (R): Sucrose content in the sugar cane is higher.
Answer. Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Source Based Questions
1. Read the extract and answer the following questions
Challenges faced by the industry include stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitutes and from other competitors like Bangladesh, Brazil, Philippines, Egypt and Thailand. However, the internal demand has been on the increase due to the Government policy of mandatory use of jute packaging. To stimulate demand, the products need to be diversified. In 2005, National Jute Policy was formulated with the objective of increasing productivity, improving quality, ensuring good prices to the jute farmers and enhancing the yield per hectare. The main markets are U.S., Canada, Russia, United Arab Republic, U.K. and Australia. The growing global concern for environment friendly, biodegradable materials has once again opened the opportunity for jute products.
Question. Which Industry the paragraph is talking about?
(a) Cotton
(b) Sugar
(c) Jute
(d) Silk
Answer. C
Question. What is/are the major challenge/s to the industry mentioned in the paragraph?
(a) International competition
(b) Synthetic substitute
(c) Both
(d) None of these
Answer. C
Question. When was the National Jute Policy formulated?
(a) 2004
(b) 2005
(c) 2006
(d) 2001
Answer. B
Question. What is the cause of increase in demand of the product?
(a) Government policy of mandatory use in packaging
(b) Diversifying the products
(c) Global concern for environment
(d) All of the above
Answer. D
Very Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing Industries
Question : What happened to our traditional industries during the colonial period?
Answer : Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the mill-make cloth from England.
Question : What is the position of India in the production of sugar in world?
Answer : India holds second position in the production of sugar.
Question : Examine what are the causes of industrial pollution of freshwater resources?
Answer : Fresh water sources are polluted by organic and inorganic wastes and effluents discharged by industries into rivers. The main culprits are paper and pulp, chemical, textile petroleum, refineries, tanneries, etc.
Question : Name the industry which is seasonal in nature.
Answer : Sugar industry.
Question : Industrialisation and urbanization go hand in hand‘. Explain.
Answer : (i) Cities provide market and also provide services such as banking, insurances, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice etc. to the industries.(ii) Industrial workers need houses and other facilities. The provision of these facilities can convert a small town into big cities.
Question : What is agglomeration economies?
Answer : Cities provide market and other facilities like banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants, and financial advice etc. to the industry. Many industries tend to come together to make, use of the advantages offered by the urban institutions. This is known as agglomeration economies.
Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing Industries
Question. India is an important iron and steel producing country in the world. Yet we are not able to perform to our full potential.” Suggest and explain any three measures to get full potential.
Answer : India is an important iron and steel producing country in the world, yet we are not able to perform to our full potential largely due to:
a. High costs and limited availability of cooking coal.
b. Lower productivity of labour.
c. Irregular supply of energy and
d. Poor infrastructure.
Question. Mention the various measures taken by the government to boost the production of jute goods.
Answer : Various steps taken by the government to boost the production of Jute are:
a. In 2005, National Jute Policy was formulated with the objective of increasing productivity.
b. Improvement of quality.
c. Ensuring good prices to the jute farmers and enhancing the yield per hectare.
Question. Why was the cotton textile industry concentrated in the cotton growing belt in the early years? Explain.
Answer : Cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt in the early years because:
a. Availability of raw cotton e.g. belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
b. Nearness to market.
c. Transport
d. Port facilities
e. Cheap labour
f. Moist climate.
Question. Mention any two factors that have contributed to a healthy growth of the automobile industry in India. Name two centres where this industry is located.
Answer : a. The introduction of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market.
b. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) brought in new technology and aligned the industry, with global developments. The two centres 1 of automobile industry are Jamshedpur and Gurgaon.
Question. “Agriculture gives boost to the industrial sector.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : Agriculture gives boost to the industrial sector:
a. Agriculture provides raw material to industries.
b. Agriculture provides market for industrial products.
c. Agriculture helps boost new industrial products.
d. The industries such as cotton, jute, silk, woollen textiles, sugar and edible oil, etc., are based on agricultural raw materials.
Question. Analyse any three major challenges faced by the sugar industry in India.
Ans : Major challenges of sugar industry are:
a. Seasonal nature of the industry.
b. Old and inefficient methods of production.
c. Transport delay in reaching sugar factories and the need to maximise the use of bagasse.
Question. What challenges are faced by the jute textile industries in India? Mention the main objectives of National Jute Policy, 2005.
Answer : Problems faced by jute mills:
a. Stiff competition in international market from countries like Bangladesh, Brazil, Philippines, Egypt, etc.
b. Stiff competition from synthetic fibre
c. Products need to be diversified.
In 2005, National Jute Policy was formulated with the objective of increasing productivity, improving quality, ensuring good prices and enhancing the yield per hectare.
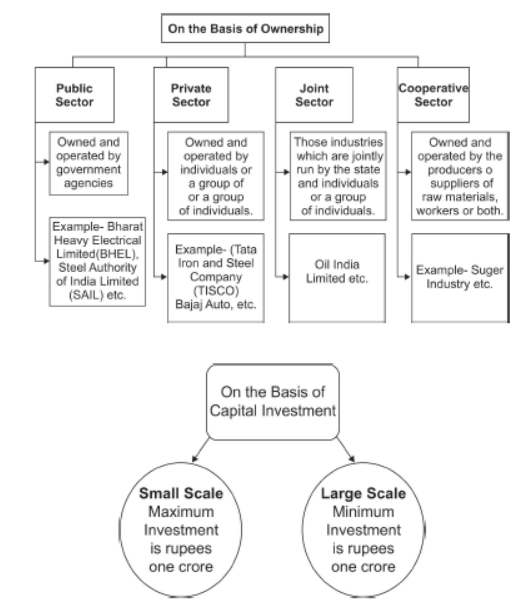
Question. Classify industries on the basis of capital investment.
How are they different from one another ? Explain with examples.
Answer : (i) Classification of the industries on the basis of capital investment:
(a) Small Scale Industry
(b) Large Scale Industry
(ii) Difference: If the investment is more than one crore on any industry, it is considered as a large scale industry. For example, Iron and Steel Industry/ Cement Industry (any other relevant example). While the investment is less than one crore on an industry, it is considered as a small scale industry e.g., Plastic industry, toy industry.
Question. Classify industries on the basis of their main role. How are they different from each other?
Answer : According to their main role:
a. Basic or key industries which supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods e.g., Iron and steel and copper smelting, aluminium smelting.
b. Consumer industries that produce goods for direct use by consumers-sugar, toothpaste, paper, sewing machines, fans etc,
Question. “Environmental degradation has been seen everywhere.” Explain any three values that can help to prevent environment degradation.
Answer : Steps to minimise environmental degradation:
a. Optimum utilisation of equipments, adopting latest techniques.
b. Upgrading existing equipments.
c. Minimising waste generation by maximising ash utilization.
d. Providing green belts for nurturing ecological balance.
e. Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, water recycling system and liquid waste management.
Question. What is the meaning of manufacturing industry?
Why is it considered the backbone of economic development? Give two reasons.
Answer : Production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw materials to more valuable products is called manufacturing.
It is considered as backbone of development because:
a. It not only helps in modernising agriculture but also forms the backbone of our economy.
b. Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country.
Question. Examine the impact of liberalisation on automobile industry of India.
Answer : Impact of liberalisation on automobile industry are:
a. Multi-utility vehicles have been introduced.
b. The coming of new and contemporary models.
c. Healthy growth of the market.
d. FDI in new technology.
e. Aligned the industry with global development.
f. Industry has experienced a quantum jump.
Question. How has the ever increasing number of industries in India made worse position by exerting pressure on existing fresh water resources? Explain.
Answer : a. Industries apart from being heavy users of water also require power to run them.
b. Today large industrial houses are as common place as the industrial units of many MNCs are exerting pressure on freshwater sources.
c. Industrialisation followed by the urbanisation multiplying the problems of water scarcity and exerting pressure on water sources causing their depletion.
Question. Why is there a tendency for the sugar mills to concentrate in Southern states of India in recent years ? Give three reasons.
Answer : Shifting of sugar industries to Southern states is because:
a. Sugarcane that grows there has a higher sucrose content.
b. Favourable climate provides longer crushing period and growing season.
c. Cooperatives are successful in these states.
d. Modem mills have more crushing capacity.
Question. “Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a country’s development”. Examine the statement.
Answer : a. Steel production is the backbone of any country’s economy since it is the basic unit for the development of the nation.
b. Almost every industry depends on iron and steel for its manufacturing and production.
c. In today’s era of globalisation, consumption of goods is increasing. Thus, it can be concluded that growth in production of steel is regarded as the index of country’s development.
Question. Why is cotton textile industry the largest industry in India today? Give any three reasons.
Answer : a. Cotton textile industry contributes 14 percent of the total industrial production.
b. It provides employment to 35 million persons directly, the second largest after agriculture.
c. It earns foreign exchange of about 24.6 percent (4 percent of GDP).
Question. Explain any three factors which were responsible for the concentration of cotton textile industry in Maharashtra and Gujarat in early years.
Answer : a. Availability of raw cotton.
b. Ready markets are available.
c. Well-developed means of transportation.
d. Abundant skilled and unskilled labour at cheap rate.
e. Moist climate which is suitable for the cotton industry.
Question. Suggest any three measures to reduce the industrial pollution of freshwater resources.
Answer : a. Minimising use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages.
b. Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
c. Treatment of hotwater and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
Question. “Many of our spinners export cotton yarn while apparel manufacturers have to import fabric.” Explain this statement with appropriate reasons.
Answer : a. The weaving, knitting and processing units cannot use much of the high quality yarn that is produced in the country. Therefore, many of our spinners export cotton yarn while apparel/garment manufacturers have to import fabric.
b. If weaving sector is improved, then yarn can be used in the country and garments can be exported to earn foreign exchange for the country.
Question. “The iron and steel industry is the basic as well as heavy industry.” Support the statement with three points.
Answer : Iron and steel industry is the basic industry as:
a. All the other industries depend on it for their machinery.
b. Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods.
c. It provides variety of consumer goods.
d. Construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipments, are the gift of iron and steel industry.
Question. Examine what are the causes of industrial pollution of freshwater resources.
Answer : Freshwater sources are polluted by organic and inorganic wastes and effluents discharged by industries into rivers. The main culprits are paper and pulp, chemical, textile, petroleum refineries, tanneries industries etc.
Question. Explain the factors responsible for localisation of jute textile mills mainly on the banks of the river Hugh.
Answer : Factors responsible for their location in the Hugli basin are as follows:
a. Proximity of the jute producing areas,
b. Inexpensive water transport, supported by a good network of railways, roadways and waterways to facilitate movement of raw material to the mills,
c. Abundant water for processing raw jute,
d. Cheap labour from West Bengal and adjoining states of Bihar, Odisha and Uttar Pradesh.
e. Kolkata as a large urban centre provides banking, insurance and port facilities for export of jute goods.
Question. What are the three main reasons for shifting of the sugar mills to Maharashtra in recent years.
Answer : There are three main reasons which are as follows:
a. The cane produced has a higher sucrose content.
b. The cooler climate which ensures a longer crushing season.
c. The cooperatives are more successful in this state.
Question. Describe any five factors responsible for the concentration of iron and steel industry in and around Chota Nagpur Plateau region.
Answer : Factors responsible for concentration df iron and steel industries in Chhota Nagpur Plateau:
a. Low cost of iron-ore
b. High grade raw material in proximity,
c. Cheap labour.
d. Vast growth potential in the home market.
e. Good transport connectivity.
f. Availability of water resources.
Question. Distinguish between an integrated steel plant and a mini steel plants stating three points of distinction.
Answer : a. An integrated steel plant is larger than a mini steel plant.
b. Mini steel plant use steel scrap and sponge iron while Integrated steel plant use basic raw materials i.e. iron ore for making steel.
c. Mini steel plant produces mild and alloy steel while integrated steel plant produces only steel.
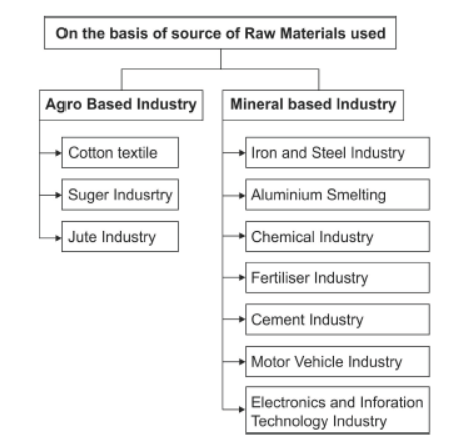
Question. Define the term manufacturing. Classify industries on the basis of source of raw materials used.
Answer : Definition: “Production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw materials to more valuable products is called manufacturing.”
Classification:
a. Agro-based: Cotton, woollen, jute, silk textile, etc.
b. Mineral-based: Iron, steel, cement etc.
Question. Describe any three major problems faced by the weaving and processing sectors in cotton textile industry.
or
Describe any three major problems faced by cotton textile industry in India.
Answer : Problems of cotton textile industry are:
a. Although production has increased, it is still not enough and imports are needed.
b. Erratic power supply and outdated machinery.
c. Low output of labour.
d. Stiff competition from synthetic fabrics.
Question. What is the importance of the Information Technology sector for the Indian economy? Explain.
Answer : The importance of IT sector is as follows:
a. It has provided employment to over one million people.
b. This industry is said to be a major foreign exchange earner.
c. It has helped in the growth of the service sector.
d. It provides employment to innumerable men and women.
Question. Explain any three factors responsible for the location of cotton textile industry in Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
Answer : a. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities,
b. cheap labour and;
c. moist climate have caused the concentration of cotton textile industries in Mumbai and Ahmedabed region.
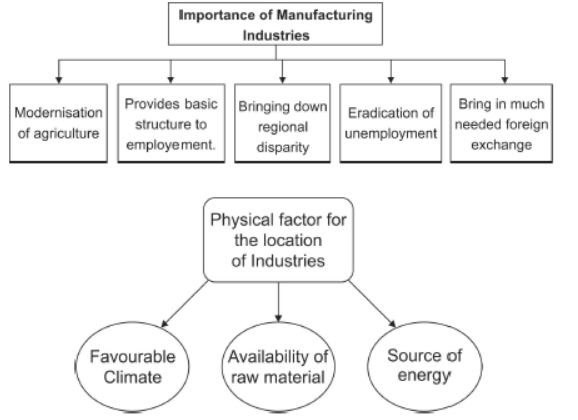
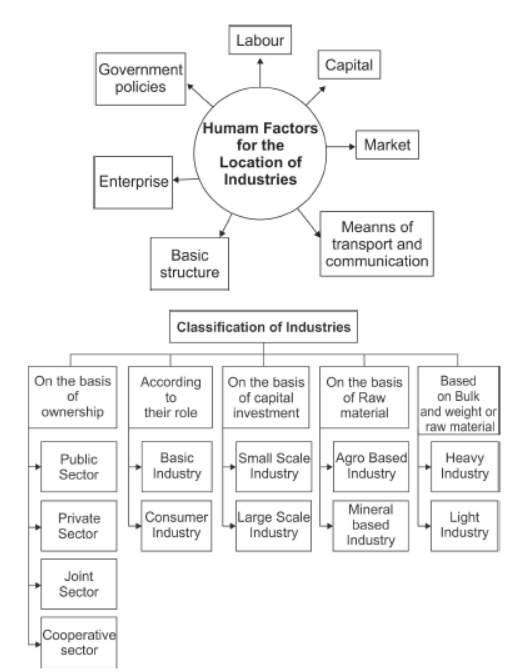
Question : Name three physical factors and three human factors that affect the location of industries.
Answer : Physical factors and three human factors that affect the location of industries are:
(i) Availability of raw materials (ii) Availability of power resources
(iii) Suitable climate (iv) Availability of water Human factors that affect the location of industries are:
(i) Availability of labour (ii) Availability of market (iii) Government policies
Question : Which region in India has the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries?
Answer : The Chhotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries.
Question : What is the large scale and small scale industries? Give examples.
Answer : Those industries that employs large number of workers in each unit and having large production level are known as large scale industries. e.g. cotton textile industry. The industry that employs small number of workers in each unit and having small production level is known as small scale industry. e.g. readymade garment industries.
Question : Explain any three factors that affect the location of industries in a region.
Answer : The location of industries are influenced by several factors:
1. Availability of Raw Material: The industries are largely located at the places where the raw material is available in abundance and at cheaper rates in close proximity.
2. Favourable Climate: The industries are densely found in the regions where the climate is favourable for its growth and functioning. For instance, in Maharashtra, due to the presence of humid climate all the year around the thread does not break frequently. And this type of the climate is favourable for the cotton textiles industries.
3. Market: Market in the nearby areas is also an important requirement for the location of industries for selling of goods manufactured. The regions having market in the adjoining regions to sell-off the finished goods are likely to have more industries.
Long Questions for Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing Industries
Question : Explain with examples, how do industries give boost to the agriculture sector?
Answer : (a) Industries provide agricultural implements machine and other products to the agricultural sector such as PVC pipes, irrigation pumps, fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides etc.
(b) Due to these products provided by the industries to the agricultural sector, the agricultural production increases. These inputs also improve the efficiency of production.
(c) Green revolution in Punjab and Uttar Pradesh was achieved only because the industries provided products like fertilizers and tractors and irrigation pumps to the farmers.
(d) Thus, agricultural development is possible only due to the support from the manufacturing industries
(e) Because of the inputs from the industry the employment opportunities in the agricultural sector also increases.
Question : 'Agriculture' and 'Industry' are complementary to each other." Explain with five examples.
Answer : (i) Agro industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
(ii) Industries depend on agriculture for their raw materials.
(iii) Industries sell their products such as irrigation pumps, fertilisers, etc., the farmers.
(iv) Industries have made production processes of agriculture very efficient.
(v) Income generated by industrial sector makes its workers richer so they can afford more food stuff. Similarly money is the hand of agricultural labour makes him able to afford more manufactured goods.
Question : "The iron and steel industry is the basic as well as heavy industry." Support the statement with three points.
Answer : Iron and steel industry is the basic industry as :
(i) All the other industries depend on it for their machinery.
(ii) Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods.
(iii) It provides variety of consumer goods.
(iv) Construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment, are the gift of iron and steel industry.
Question : Explain any five factors affecting the location of a industry.
Answer : The factors affecting the location of a industry :
(i) Availability of raw material.
(ii) Availability of cheap labour.
(iii) Availability of capital and bank facilities.
(iv) Availability of power and other infrastructure.
(v) Proximity to markets.
(vi) Proximity of adequate and efficient means of transport.
Question : Describe any five factors responsible for the concentration of iron and steel industry in and around Chota Nagpur Plateau region.
Answer : Factors responsible for concentration of iron and steel industries in Chhota Nagpur Plateau :
(i) Low cost and high quality of iron-ore
(ii) High grade raw material in proximity
(iii) Cheap labour
(iv) Vast growth potential in the home market
(v) Good transport connectivity
(vi) Availability of water resources
Question : Chhotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries. Give reasons for it.
Answer : It is because of the relative advantages this region has for the development of this industry. These include:
(i) Chhotanagpur plateau region has large reserves of iron ores. Low cost of iron ore is avast able here
(ii) High grade raw materials in proximity is available in this region
(iii) Cheap labour is available
(iv) Vast growth potential in the home market is possible.
Question : Why does the textile industry occupy a unique position in the Indian economy?
Answer : (i) The textile industry contributes significantly to industrial production. i.e. 14%.
(ii) 35 million persons are directly engaged in this industry. Thus, it is the second largest industry after agriculture in employment generation.
(iii) It contributes 4% towards GDP.
(iv) It is the only industry in India which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain, i.e. from raw material to the highest value added products.
Question : Explain with examples, how do industries give boost to the agriculture sector?
Or
“Agriculture and industry move hand in hand”. Analyse the statement with three examples.
Answer : Agriculture and industry move hand in hand. This can be proved with the help of the following three examples.
(i) The agro-industries have enhanced agriculture by raising its productivity.
(ii) They depend on the latter for raw materials and sell their products like irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, plastic and PVC pipes, agricultural machines and tools etc. to the farmers.
(iii) Development and competitiveness of manufacturing industry has not only assisted agriculturists in increasing their production but also made the production processes efficient.
Question : State the major challenges of jute industry that are leading to its decline in India.
Answer : The major challenges before jute industry leading to its decline are:
1. After the partition, most of jute producing areas have gone to east Pakistan, now Bangladesh, and thus jute industry is facing the problem of shortage of raw material.
2. India is facing high cost production and stiff international competition, especially from Bangladesh, and international market like Brazil and Philippines are also giving serious challenges to India.
3. Continuous decline in the demand of jute due to increase in the demand of its substitutes is another major problem faced by this industry.
4. Old and outdated machinery is another major problem leading to decline in the production of jute products.
Question. In 1857 where the first cotton mill of India was founded
(a) Mysore
(b) Madras
(c) Surat
(d) Bombay
Answer: D
Question. Largest producer of Jute and Jute made goods
(a) Bangladesh
(b) India
(c) Sri Lanka
(d) Brazil
Answer: B
Question. Iron and steel is a
(a) an agro base industry
(b) a chemical industry
(c) basic industry
(d) tertiary industry
Answer: C
Question. Durgapur is situated in
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Orissa
(c) Chhattisgarh
(d) West Bengal
Answer: D
Question. Chemical industries usually are located near
(a) Iron and steel industries
(b) Thermal power plant
(c) Oil refineries
(d) Automobile industry
Answer: C
Question. STP is the Abbreviation of
(a) System tech park
(b) Software Technology Park
(c) State thermal plant
(d) Software Technology Picket
Answer: B
Question. NTPC is the Abbreviation of
(a) National Textile Production Company
(b) National Technology Production Company
(c) National Thermal Power Corporation
(d) National Tuberculosis Prevention Corporation
Answer: C
Question. Atomic power plant causes
(a) Water Pollution
(b) Noise Pollution
(c) Air Pollution
(d) Heat Pollution
Answer: D
Question. Manufacturing industries includes
(a) Crop production
(b) Fish production
(c) Plantation
(d) Sugar Production
Answer: D
Question. Manufacturing industries includes
(a) Converting raw material into ready good
(b) Transporting raw material
(c) Producing raw material
(d) Procuring raw material
Answer: A
LONG TYPE QUESTION ANSWER
Question. Which factors are responsible for the decentralization of cotton textile mills in India?
Answer:
(i) Cotton textile have a very high demand throughout the country.
(ii) Major inputs like banking, electricity, transportation are available in almost every part of the country.
(iii) Textile industry is labour intensive industry and labour is easily available in Indi(a)
(iv) Textile industry requires less technological inputs and can be carried out using simple tools and machines.
Question. Cotton textile industry has close links with agriculture. Explain.
Answer:
(i) The industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton bull pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing.
(ii) Agriculture provides raw material to the industry i.e. raw cotton.
Question. What are the major problems of cotton textile industry?
Answer:
(i) Lack of good quality long staple cotton
(ii) Erratic power supply
(iii) Out dated machinery and technology
(iv) Low output of workers
(v) Stiff international competition
Question. What were the major objectives of National Jute Policy 2005? Why is the internal demand for jute increasing?
Answer:
(i) To increase the productivity
(ii) To improve the quality
(iii) Ensuring good prices to the jute farmers
(iv) Enhancing the yield per hectare
The internal demand for jute has been on the increase because -
(i) Government policy of mandatory use of jute packaging
(ii) The growing global concern for environment friendly biodegradable materials.
Question. India is an important iron and steel producing country in the world yet , we are not able to perform to our full potential. Give any four reasons.
Answer:
(i) High Costs and Limited availability of coking coal.
(ii) Lower productivity of labour
(iii) Shortage of power
(iv) Poor infrastructure.
(v) Low Investment in Research and Development.
Question. Why is iron and steel industry called a basic industry?
Answer: Iron and steel industry is called the basic industry because:
(i) It is the industry which lays the foundation of rapid development of other industries such as heavy Engineering, defence equipment, automobiles, aeroplanes etc.
(ii) It is also helpful in providing employment.
(iii) It also helps in the development of agriculture.
Question. What is importance of the manufacturing industries?
Answer:
1. Employment generation: Manufacturing industry is the main source of employment for large number of skilled as well as unskilled workers.
2. Foreign exchange: Export of manufactured goods bring foreign exchange to India.
3. Reduction of pressure on land: Manufacturing industry produces products of daily needs and helps the common people to fulfill their basic needs. It reduces pressure on agricultural sector for employment.
4. Removal of economic problems: Industrial development is a precondition for the removal of economic problems like poverty, unemployment and economic inequality. It also helps in bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
Question. What is the importance of Jute Industry?
Answer:
1. Employment- The jute industry supports 2 61 Lakh workers directly another 40 lakh small and marginal farmers who are engaged in cultivation of jute and Mesta.
2. Products: Jute industry provides products of daily use like jute bags, ropes, mats etc.
3. Foreign Exchange: Exports of raw jute and manufactured goods bring foreign exchange
4. Promotion of Small Scale Industry: Many products of the jute industry are manufactured by cottage and small scale industry. So it promotes decentralization of industry.
Question. The sugar industry is now shifting from north to south. Mention main reasons.
Answer: North India is regarded as the main centre of the sugar industry and Uttar Pradesh is the leading producer.
Over the time the sugar industry is shifting towards south India. The main reasons behind shifting of the sugar industry towards south India are:
(i) The sugar contents in the cane is higher i.e. 10.5% in Maharashtra and other southern states.
(ii) Climate is suitable for the cultivation of sugarcane.
(iii) South has better export facilities as compared to North.
(iv) Cooperative sugar mills are more successful in management in south India.
(v) The Peninsular climate helps to extend the crushing season by two months in the south India than north India.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography India Land and People Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Water Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Water Resources Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Minerals And Energy Resources Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Life Lines of National Economy Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Forest and Wild Life Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Water Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Agriculture Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Agriculture Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Minerals and Energy Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Manufacturing Industries Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing Industries Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Civics Popular Struggles and Movements Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Civics Popular Struggles and Movements Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles and Movements Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History Nationalism In India Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History Nationalism In India Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism In India Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Hindi Assignment |
CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Geography released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 10 Geography regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 10 Geography practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Geography by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 10 Geography also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Geography have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 10 Geography students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 10 Geography which you can use to further make your self stronger in Geography.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Geography Class 10 Assignments for chapter Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 10 Geography Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 10 Geography with answers relating to Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 10 Geography mock tests for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 10 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 10 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 10 Geography worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 10 Geography MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 10 Geography
How to practice CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 10 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 10 Geography, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Geography Class 10 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Geography have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Geography

