Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment Set B. Get printable school Assignments for Class 10 Geography. Class 10 students should practise questions and answers given here for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Geography in Class 10 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 10 Geography prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources
Class 10 Geography students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources in Class 10. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Geography will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 10 Geography Assignment
WHAT IS A MINERAL?
- We all use numerous products made from minerals every day. Pencils are made from mineral graphite. Cooking utensils are made using materials that are derived from different minerals.
- To define a 'mineral' geologists have fixed certain criteria - They are
- naturally occurring
- inorganic
- solid
- definite chemical composition
- ordered internal structure
ff "Naturally occurring" means that people did not make it. Steel is not a mineral because it is an alloy produced by people. "Inorganic" means that the substance is not made by an organism. Wood, coal and pearls are made by organisms and thus are not minerals. "Definite chemical composition" means that all occurrences of that mineral have a chemical composition that varies within a specific limited range. For example: the mineral halite (known as "rock salt" when it is mined) has a chemical composition of NaCl. It is made up of an equal number of atoms of sodium and chlorine.
-"Ordered internal structure" means that the atoms in a mineral are arranged in a systematic and repeating pattern. "Solid" means that it is not a liquid or a gas at standard temperature and pressure. Although, over 2000 minerals have been identified, only a few are abundantly found in most of the rocks. A particular mineral that will be formed from a certain combination of elements depends upon the physical and chemical conditions under which the material forms. This, in turn, results in a wide range of colours, hardness, crystal forms, luster and density that a particular mineral possesses. Geologists use these properties to classify the minerals.
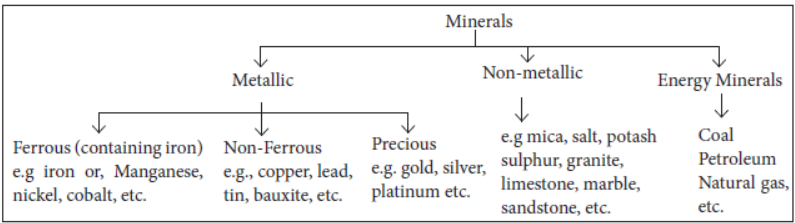
For general and commercial purposes minerals can be classified as under and includes energy minerals.
In simple terms a mineral is a homogenous, naturally occurring substance with definable internal structure.
MODE OF OCCURRENCE OF MINERALS
1. In igneous and metamorphic rocks: The smaller occurrences are called veins and the larger occurrences are called lodes. They are usually formed when minerals in liquid/ molten and gaseous forms are forced upwards through cavities towards the earth’s surface, they then cool down and solidify. Examples: tin, copper, zinc, lead, etc.
2. In sedimentary rocks: In these rocks, minerals occur in beds or layers. They form as a result of deposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal strata. Coal, iron ore, gypsum, potash salt and sodium salt are the minerals found in sedimentary rocks.
3. By decomposition of surface rocks: Decomposition of surface rocks and removal of soluble constituents leaves a residual mass of weathered material which contains ores. Bauxite is formed in this way.
4. As alluvial deposits: These minerals are found in sands of valley floors and the base of hills.These deposits are called placer deposits.They generally contain those minerals which are not corroded by water. Examples; gold, silver, tin, platinum, etc.
5. In ocean water : Most of the minerals in ocean water are too widely diffused to be of economic importance. But common salt, magnesium and bromine are mainly derived from ocean waters.Most of the minerals in India are nationalized and their extraction is possible only after obtaining due permission from the government. But in most of the tribal areas of the north-east India, minerals are owned by individuals or communities. In Meghalaya, there are large deposits of coal, iron ore, limestone and dolomite etc. Coal mining in Jowai and Cherapunjee is done by family members in the form of a long narrow tunnel. This is known as ‘Rat hole’ mining.
- In India we have a rich and varied mineral resources distributed in different parts of the country. Broadly speaking, peninsular rocks contain most of the reserves of coal, metallic minerals, mica and many other non-metallic minerals. Sedimentary rocks on the western and eastern flanks of the peninsula, in Gujarat and Assam have most of the petroleum deposits.
- Rajasthan with the rock systems of the peninsula, has reserves of many non-ferrous minerals. The vast alluvial plains of north India are almost devoid of economic minerals. These variations exist largely because of the differences in the geological structure, processes and time involved in the formation of minerals.
FERROUS AND NON-FERROUS MINERALS
- Ferrous Minerals : Ferrous minerals account for about three fourths of the total value of the production of metallic minerals. They provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical industries. India exports substantial quantities of ferrous minerals after meeting her internal demands.
NON -METALLIC MINERALS
- Mica is a mineral which is made up of a series of plates or leaves. The mica sheets can be so thin that a thousand of them can be layered into a few centimeter-thick mica sheet. Mica has excellent di-electric strength, low power loss factor, insulating properties and resistance to high voltage. Mica is widely used in electric and electronic industries.
- Mica deposits are found in the northern edge of the Chota Nagpur plateau. Koderma-Gaya- Hazaribagh belt of Jharkhand is the leading producer of mica. Ajmer in Rajasthan and Nellore in Andhra Pradesh are the other important producers of mica.
ROCK MINERALS
Limestone
- Limestone is found in association with rocks composed of calcium carbonates or calcium and magnesium carbonates. It is found in sedimentary rocks of most geological formations. Limestone is the basic raw material for the cement industry and essential for smelting iron ore in the blast furnace.
Hazards of Mining
- Mining is a hazardous industry; both for the workers and for the residents. The Miners have to work under tough conditions where no natural light is available. There is always a risk of collapse of mine roof, inundation with water and fire. The areas around mines face the problem of too much dust from the mines. Slurry from mines damages the roads and the farmland. Houses and clothes become dirty more often than in other areas. Miners are at great risk of getting afflicted with pulmonary disorders. Cases of respiratory tract diseases are very high in mining areas.
- The water sources in the region get contaminated due to mining. Dumping of waste and slurry leads to degradation of land, soil, and increase in river pollution.
- Strict safety regulations and implementation of environmental laws are essential to prevent mining from becoming a “killer industry”.
CONSERVATION OF MINERALS
- The total volume of workable mineral deposits is an insignificant fraction i.e. one per cent of the earth’s crust. We are rapidly consuming mineral resources that takes millions of years to form.
- Compared to the present rate of consumption, the replenishment rate of minerals is very slow. Mineral resources are, therefore, finite and non-renewable. Due to this, it is important that we conserve the mineral resources.
- A concerted effort must be made in order to use our mineral resources in a planned and sustainable manner. Improved technologies need to be constantly evolved to allow use of low grade ores at low costs. Recycling of metals, using scrap metals and other substitutes are steps in conserving our mineral resources for the future.
ENERGY RESOURCES
- Conventional Energy Resources: Firewood, cattle dung cake, coal, petroleum, natural gas and electricity (both hydel and thermal). ff Non-conventional Energy Resources: Solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas and atomic energy.
- Firewood and cattle dung cake: As per estimates, more than 70% of energy needs in rural households is met by firewood and cattle dung cake. A decreasing forest area is making it difficult to use firewood. Dung cake can be put to better use in the form of manure and hence its use should also be discouraged. Further they cause severe household pollution.
- Coal : India is highly dependent on coal for meeting its commercial energy requirements.Depending on the degree of compression during its formation and stage of life-cycle, there are varieties of coal.
(a) Lignite : It is a low grade brown coal. It is soft and has high moisture content. Neyveli in Tamil Nadu has the main reserves of lignite coal. This type of coal is used for electricity generation.
(b) Bituminous coal : Coal which was formed because of increased temperature and was buried very deep is called bituminous coal. This is the most popular coal for commercial use. High grade bituminous coal is ideal for use in metallurgy.
(c) Anthracite coal : This is the highest quality hard coal.
- In India, coal occurs in rock series of two main geological ages. The Gondwana coal was formed over 200 million years ago. The tertiary deposits are about 55 million years old. The major sources of Gondwana coal are located in the Damodar valley (West Bengal- Jharkhand). In this belt; Jharia, Raniganj and Bokaro are important coalfields. Coal deposits are also present in the Godavari, Mahanadi, Son and Wardha valleys.
- Tertiary coal is found in the north-eastern states of Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland. Coal is bulky and heavy and needs to be transported to the place where it is used. That is why major coal users are located near the coal-mines.
Petroleum
- After coal, the next major energy resource in India is petroleum. Petroleum is a major source of fuel for various uses. Petroleum industry acts as nodal industry for a variety of industries such as plastic, synthetic textiles, fertilizer, pharmaceuticals and other chemical industries.
- Most of the petroleum in India occurs in anticlines and fault traps in the rock formations of the tertiary age. The oil bearing layer is a porous limestone or sandstone through which oil may flow. The intervening non-porous layers prevent the oil from rising or sinking. Petroleum is also found in fault traps between porous and non-porous rocks. Gas usually occurs above the oil because it is lighter than oil.
- Mumbai High produces about 63% of India’s petroleum, Gujarat produces 18% and Assam 13%. Ankeleshwar is the most important oil field in Gujarat. Assam is the oldest oil producing state of India. Important oil fields of Assam are Digboi, Naharkatiya and Moran-Hugrijan.
Natural Gas
- Natural gas is found along with or without petroleum. It is used as fuel and also as industrial raw material. Large reserves of natural gas have been discovered in the Krishna-Godavari Basin. Gulf of Cambay, Mumbai High and Andaman Nicobar Islands are also important areas with large reserves of natural gas.
- The 1700 km long Hazira-Vijaipur-Jagdishpur pipeline links Mumbai High and Bassein with the fertilizer, power and industrial complexes in western and northern India. Natural gas is mainly used by the fertilizer and power industries. Now-a-days, use of CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) is increasing as vehicle fuel in the country.
Electricity
- Electricity has a very wide range of applications in the modern world. Its percapita consumption is often treated as an index of development. Electricity is generated mainly in two ways: by running water which drives hydro turbines to generate hydro electricity; and by burning other fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas to drive turbines to produce thermal power.
- Once generated both the kinds of electricity are exactly the same. Bhakra Nangal, Damodar Valley Corporation, Kopili Hydel Project, etc. are major hydroelectric producers in the country. At present, there are over 300 thermal power stations in India.
Non-conventional Sources of Energy
- fWe are largely dependent on fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, gas) for generation of electricity. Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in future, which in turn has serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy. Moreover, increasing use of fossil fuels also causes serious environmental problems.
- Hence, there is a pressing need to use renewable energy sources like solar energy, wind, tide, biomass and energy from waste material. These are called nonconventional energy sources.
- fNuclear Energy: Nuclear energy is obtained by altering the structure of atom. When the structure of an atom is altered, too much energy is released in the form of heat. This heat is utilized to generate electric power. Uranium and Thorium are used for generating atomic power. These minerals are available in Jharkhand and the Aravalli ranges of Rajasthan. The Monazite sand of Kerala is also rich in Thorium.
- fSolar Energy: Photovoltaic technology is used to convert solar energy into electricity. The largest solar plant of India is located at Madhapur near Bhuj. Solar energy holds great promises for the future. It can help in minimizing the dependence on firewood and animal dung cakes in rural areas. This will also help in conservation of fossil fuels.
- Wind Power : India has great potential of wind power. The largest wind farm cluster is located in Tamil Nadu from Nagarcoil to Madurai. Apart from these, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep have important wind farms. Nagarcoil and Jaisalmer are well known for effective use of wind energy in the country.
- Biogas : Biogas can be produced from shrubs, farm waste, and animal and human waste. Biogas is more efficient than kerosene, dung cake and charcoal. Biogas plants can be set up at municipal, cooperative and individual levels. The gobar gas plants provide energy and also manure.
- Tidal Energy : Floodgate dams are built across inlets. The water flows into the inlet during high tide and gets trapped when the gate is closed. Once the tide recedes, the gates are opened so that water can flow back to the sea. The flow of water is used to run the turbine to generate electricity. A 900 mw tidal energy power plant is set up by the National Hydropower Corporation in the Gulf of Kutch.
- Geo Thermal Energy : We know that the inside of the Earth is very hot. At some places, this heat is released on the surface through fissures. Groundwater in such areas becomes hot and rises up in the form of steam. This steam is used to drive turbines. Two experimental projects have been set up in India to harness geothermal energy. They are; the Parvati valley near Manikarn in Himachal Pradesh and the Puga Valley in Ladakh.
Conservation of Energy Resources
- Energy is a basic requirement for economic development. Every sector of the national economy – agriculture, industry, transport, commercial and domestic – needs inputs of energy.
- The economic development plans implemented since Independence necessarily required increasing amounts of energy to remain operational. As a result, consumption of energy in all forms has been steadily rising all over the country.
- Thus there is an urgent need to develop a sustainable system of energy development. Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources are the twin planks of sustainable energy. ff India is presently one of the least energy efficient countries in the world. We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources.
- For example, as concerned citizens we can do our bit by using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles; switching off electricity when not in use, using powersaving devices and using non-conventional sources of energy. After all, “energy saved is energy produced”.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources
(b) Petroleum
(d) Paper
Answer : B
(b) Iron ore
(d) Silver ore
Answer : B
(b) minerals
(d) none of these
Answer : A
(b) Talc
(d) All of these
Answer : A
(b) Limestone
(d) Mica
Answer : A
(b) rocks
(d) none of these
Answer : A
(b) Neyeli
(d) Bokaro
Answer : B
(b) Aluminium oxide
(d) Silica
Answer : C
(b) manganese
(d) zinc
Answer : C
(b) Odisha
(d) Jharkhand
Answer : B
(b) Vishakhapatnam
(d) Mangaluru
Answer : B
(a) internal structure
(b) structure
(c) shape
(d) outer structure
Answer : A
Question. Limestone is the basic raw material of
(a) Paper industry
(b) Cement industry
(c) Sugar industry
(d) Textile industry
Answer : B
Question. Which one of the following minerals is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of weathered material?
(a) Coal
(b) Bauxite
(c) The Gold
(d) Zinc
Answer : A
Question. In which region of India tidal energy is produced?
(a) Gulf of Kuchchh
(b) Puga Valley of Ladakh
(c) Gulf of Cambay
(d) Madhapur near Bhuj
Answer : A
Question. Which fuel mineral provides energy to industry as well as for domestic needs?
(a) Coal
(b) Natural gas
(c) Firewood
(d) Petroleum
Answer : A
Question. Which one of the following is largely derived from ocean water?
(a) Bauxite
(b) Magnesium
(c) Gold
(d) Mica
Answer : B
Question. In which one of the following states the largest wind farm cluster is located?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Kerala
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer : D
Question. The highest quality of hard coal is:
(a) Lignite
(b) Bituminous
(c) Peat
(d) Anthracite
Answer : A
Question. Which one of the following is an essential feature of Mica?
(a) It is a metallic mineral made up of a series of plates
(b) It can be clear, black, green, red, yellow or brown.
(c) It is not used in electric and electronic industry.
(d) It cannot be easily split into thin sheets
Answer : B
Question. Which one of the following non- conventional sources of energy is harnessed near Manikarn in Himachal Pradesh?
(a) Geothermal Energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Solar energy
(d) Tidal Energy
Answer : A
Fill In The Blank
Question. Geologist define............. as a naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.
Answer : Minerals
Question. Sedimentary rocks on the western and eastern flanks of the Peninsula, in Gujarat and Assam have most of the - - - - - - - - - - -
Answer : Petroleum Deposits
Question. Rocks are combination of homogeneous substances called - - - - - - -
Answer : Minerals
Question. …………………is obtained from bauxite ore.
Answer : Aluminium
Question. …………………..is thebasic mineral and the backbone of industrial development.
Answer : Iron Ore
Question. India is critically deficient in the Reserve and production of..............
Answer : Colper
Question. …………………… is a fossil fuel which is present below natural gas.
Answer : Petroleum
Question. ……………must be present in metallic minerals.
Answer : Metal
True/False
Assertion And Reason
Very Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources
Question : Which minerals are largely derived from ocean waters?
Answer : Common salt, magnesium and bromine are some minerals largely derived from ocean waters.
Question : How are ferrous minerals important?
Answer : They are important because they provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical industries.
Question : How is Nuclear energy obtained?
Answer : Nuclear energy is obtained by altering the structure of atoms. When such an alteration is made, much energy is released in the form of heat and this is used to generate electric power. Uranium and Thorium, which are available in Jharkhand and the Aravalli ranges of Rajasthan are used for generating atomic or nuclear power. The monazite sands of Kerala is also rich in Thorium.
Question : What are the various uses of coal?
Answer : Coal provides a substantial part of the nation’s energy needs. It is used:
(i) for power generation
(ii) to supply energy to industry as well as for domestic needs. India is highly dependent on coal for meeting its commercial energy requirements.
Question : How is natural gas used?
Answer : Natural gas is used as a source of energy as well as an industrial raw material in the petrochemical industry.
Question : Why is natural gas considered an environment-friendly fuel?
Answer : Natural gas is considered an environment-friendly fuel because of low carbon dioxide emissions.
Question. What is a mineral ?
Answer : Mineral is a “homogenous” naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.
Question. What is Thermal electricity?
Answer : Electricity generated by using coal, Petroleum and natural gas.
Question. What is an ‘ore’ ?
Answer : The term ‘ore’ is used to describe an accumulation of any material mixed with other elements.
Question. Define Rat-Hole Mining?
Answer : Coal mining in Jowal and Cherapunjee is done by family member in the form of a long narrow tunnel known as rat hole mining.
Question. Distinguish between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals?
Answer : Ferrous minerals are the metallic minerals containing iron. For e.g.- Iron ore, Manganese, Nickel, Cobalt etc.
While non-ferrous minerals are also metallic, but they do not contain iron. For e.g.- Manganese, Nickel, Cobalt etc.
Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources
Question. How are minerals formed in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Answer : In igneous and metamorphic rocks, minerals can occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints. The smaller deposits are called veins, and the larger ones are called lodes.
Question. What are the chief characteristics of mica?
Answer : It is a mineral made up of a series of plates or leaves. (ii) It splits easily into thin sheets. (iii) These sheets can be so thin that a thousand plates can be layered into a mica sheet of a few centimetres high. (iv) Due to its excellent di-electric strength, low power loss factor, insulating properties and resistance to high voltage, mica is one of the most indispensable minerals used in electric and electronic industries.
Question. Why is conservation of mineral resources essential? Explain any three reasons.
Answer : Conservation of mineral resources is essential because: (i) Minerals are indispensable part of our life. (ii) It is available in limited quantity. (iii) Takes millions of years to get formed. (iv) They are finite and non-renewable resources. (v) Continued extraction leads in increasing costs.
Question. What are the uses of energy resources?
Answer : (i) Energy is required for all activities. It is needed to cook, to provide light and heat. (ii) It is used to propel vehicles. (iii) It is also used to drive machinery in industries.
Question. What are the various uses of petroleum?
Answer : I) Petroleum is also an important energy source in India after coal. ii) It provides fuel for heat and lighting, lubricants for machinery and raw materials to a number of manufacturing Industries. iii)Mineral oil is used in lotions and moisturiser. Petroleum refineries act as a ‘nodal industry’ for synthetic textile, fertiliser and numerous chemical industries.
Question : What are the Petroleum producing areas in India. Explain.
Answer : Most of the petroleum producing areas in India are associated with anticlines and faults traps in the rock formations of the tertiary age. In the region folding, anticlines or domes, it occurs where oil is trapped in the crest of the uphold. Petroleum is also found in fault traps between porous rocks.
Major petroleum producing areas of India are …
1) ASSAM- Digboi, Naharkatia, Moran-Hugrijan, Namdang region
2) GUJRAT- Ankeleshwar, Lunez, Navgan
3) MUMBAI HIGH
4) Godavari – Mahanadi basin
Question : “Discovery and use of iron brought a radical change in human life” prove it with three examples.
Answer : a) Revolution in agriculture-different type of tools invented like axe, hook, plough etc.
b) Revolution in industry-different tools and machines like spinning.
c) Revolution in transportation- bullock-cart, ships, boats etc.
Question : Describe the various forms in which minerals occur.
Answer : a) In igneous and metamorphic rocks ( cracks, crevice, faults or joints)
b) In beds or layers of sedimentary rocks due to deposition, accumulation and concentration.
c) Decomposition of surface rocks
d) Alluvial deposits in sands of valleys and the base of hills as “ Placer Deposits”
Question : Why is mining activity often called a “Killer Industry”. Give three reasons.
Answer : a) High risk involved
b) Due to poisonous fumes, mines are vulnerable to workers for pulmonary diseases.
c) Risk of collapsing mines roofs, and fires in coal mines.
d) Water sources get contaminated
Question : How is biogas produced? Why it is called ‘Gobar gas plant’ in rural area?
Answer : (i) Biogas is produced from shrubs, farm waste, animal and human wastes. It is mostly used for domestic consumption in rural areas.
(ii) Decomposition of organic matter yields gas, which has higher thermal efficiency in comparison to kerosene, dung cake and charcoal.
(iii) Biogas plants are set up at municipal, cooperative and individual levels. Biogas plants using cattle dung are known as Gobar gas plants in rural India.
(iv) These provide twin benefits to the farmer in the form of energy and improved quality of manure.
(v) Biogas makes the most efficient use of cattle dung.
(vi) It prevents the loss of trees and manure due to burning of fuel wood and cow dung cakes.
Question : Which is the next major source of energy after coal, in India? Describe any two advantages of it.
Answer : Petroleum is a major energy source in India after coal. The two advantages of petroleum are:
(i) It provides fuel for heat and lighting, lubricants for machinery and raw materials for a number of manufacturing industries.
(ii) Petroleum refineries act as a “nodal industry” for synthetic textile, fertiliser and numerous chemical industries.
(iii) About 63 per cent of India’s petroleum production is from Mumbai High, 18 per cent comes from Gujarat and 16 per cent from Assam.
Question : Give three reasons in the favour of use of ‘Atomic energy’.
Answer : a) Coal and natural oil are exhaustible.
b) Nuclear power plants are easy to handle
c) Most developed countries are utilizing this energy successfully
d) It can be useful in fields of medicines and agriculture
e) Hydel energy is not satisfactory due to environmental issues
Question : Why does solar energy in Rajasthan have greater potential as non –conventional source of energy?
Answer : a) Hot and dry region
b) Clear sky almost whole year
c) Cheaper installation
d) Renewable and pollution free energy source.
e) Government motivation
Question : “India is highly dependent on coal for meeting its commercial energy requirement.” Support the statement with three arguments.
Answer : (i) In India, coal is the most abundantly available fossil fuel. It provides a substantial part of the nation’s energy needs.
(ii) It is used for power generation, to supply energy to industry as well as for domestic needs.
(iii) It is used as a raw material in the making of coal tar and coal gas.
Long Questions for Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources
Question : Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India? What are the four major forms of it? Write main features of each form.
Answer : Coal is an important and abundantly available fossil fuel in India. It is formed due to the compression of plant material over millions of years. It is a bulky material and loses weight on use as it is reduced to ash.
The four major forms of coal are:
(i) Peat: Decaying plants in swamps produce peat. It has a low carbon and high moisture contents and low heating capacity.
(ii) Lignite is a low grade brown coal, which is soft with high moisture content. The principal lignite reserves are in Neyveli in Tamil Nadu and are used for generation of electricity.
(iii) Bituminous coal is buried deep and subjected to increased temperatures. It is the most popular coal in commercial use. Metallurgical coal is high grade bituminous coal which has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces.
(iv) Anthracite is the highest quality hard coal.
Question : What is Non - Conventional sources of energy? Discuss two sources of such types of energy.
Answer : Sources of energy which are renewable, eco-friendly and newer one are called non conventional sources of energy i.e. wind energy, geothermal energy, tidal energy etc.
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY:
Geothermal energy refers to the heat and electricity produced by using the heat from the interior of the earth. Where the geothermal gradient is high , high temperature is found at shallow depth . There are several hot springs in India which could be used to generate electricity. Two projects, one is MANIKARAN in Himachal and second in PUGA VALLEY in Ladakh has been set up in India to harness Geothermal energy.
TIDAL ENERGY:
Oceanic tides can be used to generate electricity .During high tides water flows into the inlet and get trapped when it is closed. After the fall of tide the water flows back to the sea via pipe lines that carry it through power generating turbines. In India gulf of Kutch provides ideal conditions for tidal energy.
Question : India now ranks as a “WIND SUPER POWER “in the world. Why?
Answer :
• India gets advantage of trade winds, western lies and monsoon winds.
• Wind energy completely pollution free and non exhaustible that’s why it becomes popular.
• India has an ambitious program to install 250 wind driven turbines with total capacity of 45 mega watts spread over 12 suitable locations.
• India’s potential wind power generation is of 50000 megawatts of which ¼ can be easily harnessed.
• Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu have favorable conditions for wind energy. Wind power plant at LAMBA in Gujarat, is the largest in Asia.
Question : How can we conserve energy resources in India? Explain.
Answer : Following efforts can be made to conserve energy resource in India:
i. Using public transport instead of individual vehicles.
ii. Switching of electricity when not in use.
iii. Using power saving devices.
iv. More and more use of non conventional source of energy as they are renewable and eco-friendly.
v. In automobiles electrical motors should be introduced.
vi. Intensified exploration and research of new sources of energy.
Source based questions
Read the given text and answer the following questions:
Megha has taken a loan of Rs 5 lakhs from the bank to purchase a house. The annual interest rate on the loan is 12 percent and the loan is to be repaid in 10 years in monthly installments. Megha had to submit to the bank,documents showing her employment records and salary before the bank agreed to give her the loan. The bank retained as collateral the papers of the new house, which will be returned to Megha only when she repays the entire loan with interest.
Question : Define collateral?
Answer : Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestocks, deposits with banks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Read the given text and answer the following questions:
In recent years, the central and state governments in India are taking special steps to attract foreign companies to invest in India. Industrial zones, called Special Economic Zones (SEZs), are being set up. SEZs are to have world class facilities: electricity, water, roads, transport, storage, recreational and educational facilities. Companies who set up production units in the SEZs do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of five years.
Government has also allowed flexibility in the labour laws to attract foreign investment.
The companies in the organized sector have to obey certain rules that aim to protect the workers’ rights. In the recent years, the government has allowed companies to ignore many of these. Instead of hiring workers on a regular basis, companies hire workers ‘flexibly’ for short periods when there is intense pressure of work. This is done to reduce the cost of labour for the company.
However, still not satisfied, foreign companies are demanding more flexibility in labour laws.
Question : What is SEZ (Special Economic Zone)?
Answer : Special Economic Zone are industrial zones setup by government to direct foreign companies to invest in India.
Read the given text and answer the following questions:
Ever since humans appeared on the earth, they have used different means of communication. But, the pace of change, has been rapid in modern times. Long distance communication is far easier without physical movement of the communicator or receiver. Personal communication and mass communication including television, radio, press, films, etc. are the major means of 4 communication in the country. The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personal written communications. Cards and envelopes are considered first-class mail and are airlifted between stations covering both land and air. The second-class mail includes book packets, registered newspapers and periodicals. They are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport. To facilitate quick delivery of mails in large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently. They are called Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical Channel.
Question : Differentiate between mass communication and personal communication.
Answer : Mass Communication is the medium which provides entertainment as well as creates awareness among the masses. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books, films etc.
whereas Personal Communication is between person to person. (ii) Any other relevant point (Any one)
Read the above passage and answer the following questions
Question : How can you say that people played an important role in the struggle for a fair globalisation?
Answer : WTO is supposed to allow free trade for all, but in practice the developed countries have retained trade barriers. Against it, massive campaigns and representation were organised by the people's organisations. As a result, WTO's decisions relating to trade and investments were influenced. This way people played an important role in a fair globalisation.
Question : What values you have learnt from the passage?
Answer : From the given passage I have learnt the values of fairness and protest against unfavourable measures.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Hindi Assignment |
CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Geography released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 10 Geography regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 10 Geography practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Geography by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 10 Geography also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Geography have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 10 Geography students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 10 Geography which you can use to further make your self stronger in Geography.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Geography Class 10 Assignments for chapter Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 10 Geography Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 10 Geography with answers relating to Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 10 Geography mock tests for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 10 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 10 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 10 Geography worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 10 Geography MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 10 Geography
How to practice CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 10 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 10 Geography, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 10 Geography Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Geography Class 10 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 10 Geography have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 10
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources Class 10 Geography

