Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Geography Lifelines Of National Economy Worksheet Set A. Students and teachers of Class 10 Social Science can get free printable Worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 10 students should practice questions and answers given here for Social Science in Class 10 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 10 Social Science Worksheets prepared by teachers as per the latest Social Science books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
Class 10 Social Science students should download to the following Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Class 10 worksheet in PDF. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Social Science Worksheet for Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
The pace of development of a country greatly depends upon the production of goods and service. The production becomes efficient when the raw materials reach the factories timely as needed. The finished products should also be efficiently moved out through the distribution channels so as to reach the consumers.
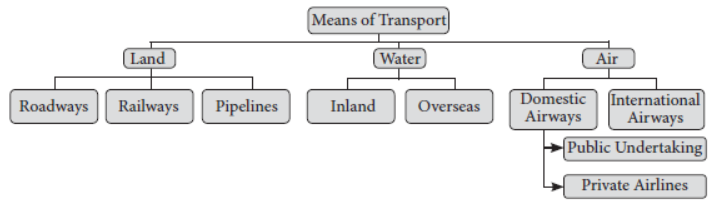
Therefore, efficient means of transport are prerequisites for fast development. Movement of these goods and services can be over land, water and air. Thus, the various means of, transport can also be classified into land, water and air transport. Today, our world has become small in terms of time it takes to cover distances. This has been possible because of efficient transport and modern communication systems.
Now India is well-linked internally and externally with rest of the world very efficiently.
Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and the Internet, etc. have been contributing to the Indian socio-economic progress in many ways.
TRANSPORT – ROADWAYS, RAILWAYS, PIPELINES, WATERWAYS, AIRWAYS
Transport plays an important role in the economy. The different modes of transport are as follows :
Roadways
India has the second largest road network in the world, aggregating to about 5.6 million km (March 2016). In India, roadways have preceded railways. They still have an edge over railways in view of the ease with which they can be built and maintained. The growing importance of road transport vis-àvis rail transport is rooted in the following reasons:
(a) Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
(b) Roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
(c) Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
(d) Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
(e) It also provides door-to-door service; thus, the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
(f) Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport, such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
Classification of Roads in India
Golden Quadrilateral : The Golden Quadrilateral is a highway network connecting many of the major towns, such as Chennai, Kolkata, Delhi and Mumbai. Other cities connected by this network are Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Bhubaneswar, Jaipur, Kanpur, Pune, Surat, Vijayawada, Ajmer and Vizag. It is the longest highway project is India and 5th longest in the world at 5846 km. In January 2012, the project was declared complete.
The major objective of these Super Highways is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India. These highway projects are being implemented by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI). ff National Highways : National Highways link extreme parts of the country. The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) is the authority responsible for the development, maintenance and management of National Highways entrusted to it. After the formation of NHAI in 1988 the national highways are looked after by it. A number of major National Highways run in North-South and East-West directions. The famous Sher Shah Suri Marg between Delhi and Amritsar is called National Highway 1.
- State Highways: Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as State Highways. These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (PWD in State and Union Territories.
- District Roads: These roads connect the district headquarters with other places of the district. These roads are maintained by the Zila Parishad.
- Other Roads: Rural roads, which link rural areas and villages with towns, are classified under this category. These roads received special impetus under the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana. Under this scheme special provisions are made so that every village in the country is linked to a major town in the country by an all season motorable road.
- Border Roads: Apart from these, Border Roads Organization a Government of India undertaking constructs and maintains roads in the bordering areas of the country. This organization was established in 1960 for the development of the roads of strategic importance in the northern and northeastern border areas. These roads have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain and have helped in the economic development of these area.
Road Density
We have defined road density as the length of road per 100 sq. km of area. Distribution of road is not uniform in the country. Density of all roads varies from only 12.14 km in Jammu & Kashmir to 517 km in Kerala with the national average of 142.68 km ( 2011).
Road transportation in India faces a number of problems. Keeping in view the volume of traffic and passengers, the road network is inadequate. About half of the roads are unmetalled and this limits their usage during the rainy season. The National Highways are inadequate too. Moreover, the roadways are highly congested in cities and most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
Railways
Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India. Indian Railways is the 4th largest rail-network in the world. It has a network of 7349 stations and route length of 67368 km, 49% of which are electrified. As of March 2017, it had 277,987 freight wagons, 70,937 passenger coaches and 11,452 locomotives. Indian Railways have locomotive and coach-production facilities at several locations in India. It is the world's eighthlargest employer, it hats 1.308 million employees as of March 2017.
Railways also make it possible for us to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances. Apart from an important means of transport, the Indian Railways have been a great integrating force for more than 150 years. Railways in India bind the economic life of the country as well as accelerate the development of the industry and agriculture
Gauge (in m) Route (km) % of total)
Broad Gauge 1.676m 61680 92 %
Meter Gauge 1 m 3479 05%
Narrow Gauge 0.762
& 0.610 m 2208 03%
Pipelines
- Pipeline transport is the transportation of goods or materials through a pipe. In the past, pipes were used to transport water to cities and industries. Now, these are also used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big thermal power plants. Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into slurry.
- The far inland locations of refineries like Barauni, Mathura, Panipat and gas based fertilizer plants have been functioning only because of pipelines. Initial cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs are minimal. It rules out trans-shipment losses or delays.
- There are three very important networks of pipeline transportation in the country.
1. Naharkatia-Nunmati-Barauni Pipeline (1167 km): From oil field in upper Assam to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh), via Guwahati, Barauni and Allahabad. It has branches from Barauni to Haldia, via Rajbandh, Rajbandh to Maurigram and Guwahati to Siliguri.
2. Salaya-Koyali-Mathura Pipeline (1256 km) : From Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar in Punjab, via Viramgam, Mathura, Delhi and Sonipat. It has branches to connect Koyali (near Vadodara, Gujarat) Chakshu and other places.
3. Hajira-Bijapur-Jagdishpur (HBJ) Gas Pipeline (1750 km) : Gas pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects Jagdishpur in Uttar Pradesh, via Vijaipur in Madhya Pradesh. It has branches to Kota in Rajasthan, Shahajahanpur, Babrala and other places in Uttar Pradesh.
Other important pipelines are
4. Mumbai High-Mumbai-Ankleshwar- Kayoli Pipeline: (210 km)
5. Jamnagar-Loni LPG Pipeline: (1269 km)
6. Kandla-Bhatinda Pipeline: (1331 km) Waterways
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods. It is a fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport. India has inland navigation waterways of 14,500 km in length. Out of these only 3,700 km are navigable by mechanised boats.
The following waterways have been declared as the National Waterways by the Government:
(a) The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km)-N.W. No.1
(b) The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km)-N.W. No.2
(c) The West-Coast Canal in Kerala (Kottapurma- Komman, Udyogamandal and Champakkara canals-205 km) – N.W. No.3
(d) Specified stretches of Godavari and Krishna rivers along with Kakinada Puducherry stretch of canals (1078 km) – N.W. No.4
(e) Specified stretches of river Brahmani along with Matai river, delta channels of Mahanadi and Brahmani rivers and East Coast Canal (588 km) – N.W. No.5
A good amount of transportation also takes place in Mandavi, Zuari and Cumberjua, Sunderbans, Barak, backwaters of Kerala and tidal stretches of some other rivers.
Major Sea Ports
The coastline of India (7,516.6 km), is dotted with 12 major and 181 medium and minor ports. The major ports handle 95 per cent of India’s foreign trade.
- Kandla in Kuch was the first port developed soon after Independence to ease the volume of trade on the Mumbai port. It is a tidal port, catering to export and import of grains and industrial products of the north-west India.
- Mumbai is the biggest port with a spacious natural and well-sheltered harbor.
- The Jawaharlal Nehru port was planned with a view to decongest the Mumbai port and serve as a hub port for this region.
- Marmagao port (Goa) is the premier iron ore exporting port of the country. This port accounts for about fifty per cent of India’s iron ore export.
- New Mangalore port, located in Karnataka caters to the export of iron ore concentrates from Kudremukh mines. Kochi is the extreme south-western port, located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbor.
- On the east coast, is the port of Tuticorin, in Tamil Nadu. This port has a natural harbor and rich hinterland. It handles a large variety of cargo to even our neighboring countries like Sri Lanka, Maldives, etc. and the coastal regions of India.
- Chennai is one of the oldest artificial ports of the country. It is ranked next to Mumbai in terms of the volume of trade and cargo.
- Vishakhapatnam is the deepest landlocked and well-protected port. This port was, originally, conceived as an outlet for iron ore exports.
- Paradip port located in Orissa, specializes in the export of iron ore.
- Kolkata is an inland riverine port. This port serves a very large and rich hinterland of Ganga-Brahmaputra basin. Being a tidal port, it requires constant dredging of Hoogly.Haldia port was developed as a subsidiary port, in order to relieve growing pressure on the Kolkata port.
Airways
- The air transport was nationalized in 1953.On the operational side, Air India, (subsidiary of Indian Airlines), and different private scheduled airlines provide domestic air
- services. Air India, Jet Airways, SpiceJet, etc., provides international air services.
- Pawan Hans Ltd. provides helicopter services to Oil and Natural Gas Commission in its offshore operations, to inaccessible areas and difficult terrains like the north-eastern states and the interior parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttaranchal.
- Air travel can cover very difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense forests and also long oceanic stretches with great ease. The air travel, today, is the fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport. That is why it is a preferred mode of travel in the north east.
COMMUNICATION
We use different means of communication in our day-to-day life. Be it personal communication mediums such as telephones, letters, etc. or means of mass communication, such as radio, television or the newspaper; we use all of them.
- The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personal written communications.
- Cards and envelopes are considered first–class mail and are airlifted between stations.
- The second–class mail includes book packets, registered newspapers and periodicals. They are carried by surface mail, by land and water transport.
- To facilitate quick delivery of mails in large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently. They are called Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical Channel.
Telephone
India has one of the largest telephone networks in Asia. In order to strengthen the flow of information from the grassroot to the higher level, the government has made special provision to extend twenty-four hours STD facility to every village in the country. There is a uniform rate of STD facilities all over India. It has been made possible by integrating the development in space technology with communication technology.
Mobile Telephones
India is one of the fastest growing mobile networks in the world. Mobile phones have changed the way Indians conducted business. Now even low-income group people like vegetable vendors, plumbers and carpenters get better business because they are connected through mobile phones. The call rates of mobile telephony have become very affordable.
Mass Communication
- Mass communication provides entertainment and creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books and films. All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country. Doordarshan, the national television channel of India, is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world. It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
- Newspapers: India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually. They are of different types depending upon their periodicity. Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects. Largest number of newspapers published in the country are in Hindi, followed by English and Urdu.
- Films: India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short films; video feature films and video short films. The Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC), is the authority to certify both Indian and foreign films.
INTERNATIONAL TRADE
- Trade between two countries is called international trade. It may take place through sea, air or land routes. Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. It is, therefore, considered the economic barometer for a country.
- Export: When the goods are sent to other country for sale it is called as export.
- Import: When the goods come from another country to be sold in India it is called import.
- Balance of Payment : This is the difference of revenue between export and import of a country. When export is higher than import then this is a situation of favorable balance of payment. On the other hand, when the import is higher than export then this is a situation of unfavorable balance of payment.
Top Indian Exports (2017 -Billion Dollars)
Product Billion $ Percent of total
Petroleum Products 62 22%
Gems and Jewelry 42 15%
Automobiles 14.5 5%
Machinery 13.6 5%
Biochemicals 12 4%
Pharmaceuticals 11.7 4%
Major Imports by India (2017 -Billion Dollars)
Product Billion $ Percent of total
Petroleum Products 123 27.7%
Gems and Jewelry 74 16.7%
Electrical Machinery 47 10.6%
Computers etc. 36 8.1%
Organic chemicals 18 4%
Special Plastics 13 2.9%
TOURISM AS A TRADE
- Tourism is very important for the Indian economy. According to the World Travel & Tourism Council tourism generated US$230 billion or 9.4% of the nation's GDP in 2017 and supported 41.622 million jobs, 8% of its total employment.
- Over 10 million foreign tourists arrived in India in 2017. Domestic tourist visits to all states and Union Territories numbered 1,036.35 million (in 2012).
- Tourism also promotes national integration,provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits. It also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage.
- It also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage. Foreign tourists visit India for heritage tourism, eco-tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, medical tourism and business tourism.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Lifelines of National Economy
Question : Which one of the following organisations constructs Border roads in India?
(a) PWD
(b) CPWD
(c) BRO
(d) NHAI
Answer : C
Question. Which one is not an important destination of Foreign tourists in India?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Goa
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
Answer : A
Question : Which one of the following terms is used to describe trade between two or more countries?
(a) Internal trade
(b) International trade
(c) External trade
(d) Local trade
Answer : B
Question : Delhi and Mumbai are connected by ......... .
(a) National Highway-15
(b) National Highway-1
(c) National Highway-7
(d) National Highway-8
Answer : D
Question : Which of the following promotes national integration and provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits?
(a) Tourism
(b) Sports
(c) Services
(d) National Heritage
Answer : A
Question : In which of the following states, gas pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects Jagdishpur?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Bihar
(d) Himachal Pradesh
Answer : B
Question : The density of road is measured at a distance of per __________ .
(a) 50 sq. km.
(b) 100 sq. km.
(c) 200 sq. km.
(d) 250 sq. km.
Answer : B
Question : The focus of Digital India Programme is on being transformative to realise ______.
(a) IT (Indian Talent) + IT (Information Technology) = IT (Indian Tomorrow)
(b) IT (Indian Tomorrow) + IT (Information Technology) = IT (Indian Talent)
(c) IT (Indian Talent) - IT (Information Technology) = IT (Indian Tomorrow)
(d) Indian Talent - India Tomorrow = Information Technology
Answer : A
Question : Which country among the following has the largest telecom network in Asia?
(a) China
(b) Nepal
(c) India
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer : C
Question : Which state has the lowest density of roads ?
(a) Goa
(b) Sikkim
(c) Jammu and Kashmir
(d) Kerala
Answer : C
Question : Which of the following was the first port developed soon after Independence to reduce the volume of trade on Mumbai port?
(a) Kandla
(b) Karachi
(c) Kochi
(d) Vizag
Answer : A
Question : Which of the following ports was planned with a view to decongest the Mumbai port and serve as a port to this region?
(a) Kandla port
(b) Marmagao port
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru port
(d) None of the above
Answer : C
Question : The first train steamed off from Mumbai to Thane in 1853, covering a distance of :
(a) 32 km
(b) 51 km
(c) 49 km
(d) 34 km
Answer : D
Question : Solids can also be transported through pipelines when converted into :
(a) Liquids
(b) Slurry
(c) Gas
(d) Powder
Answer : B
Question : How many networks of pipeline transportation are there in the country ?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer : B
Question : How long is the coastline of India ?
(a) 7516.6 km
(b) 7416.6 km
(c) 6416.6 km
(d) 7517.6 km
Answer : A
Question : Which among the following is the other name of Kandla Port?
(a) Deepdayal port
(b) Deendayal port
(c) Tidal port
(d) Landlocked port
Answer : B
Question : Identify the means of transport with the help of following features :
(i) It is the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
(ii) It also makes conducting multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances possible.
(iii) It binds the economic life of the country as well as accelerate the development of the industry and agriculture.
Answer : Railways
Question : Study the picture and answer the question that follows:
Which of the following best signifies the above image?
(a) Railway
(b) Waterways
(c) Airways
(d) Roadways
Answer : A
Question : _______is the biggest port with a spacious natural and well-sheltered harbour.
(a) Mumbai
(b) Kolkata
(c) Chennai
(d) Goa
Answer : A
Question : Which of the following ports is in Karnataka :
(a) Marmagao
(b) New Mangalore
(c) Bangalore
(d) Kandla
Answer : B
Question : Which of the following options is correct about air travel?
I. Fastest
II. Most Comfortable
II. Prestigious mode of transport
IV. Cheapest means of transport
Options :
(a) I,III, IV
(b) I, II, III
(c) II, III, IV
(d) I, III, IV
Answer : B
Question : Which among the following is the main source of water transport?
(a) Oceans
(b) Seas
(c) Inland waterways
(d) Rivers
Answer : B
Question : The National Highway links ______ parts of the country.
(a) extreme
(b) major
(c) state capital
(d) district
Answer : A
Question : Which one of the following is the eastern terminal of East-West Corridor?
(a) Shillong
(b) Silvassa
(c) Silchar
(d) Singrauli
Answer : C
Question : Which roads are all weather roads ?
(a) Metalled
(b) Un-metalled
(c) Border Roads
(d) All of these
Answer : A
Question. The biggest port is
(a) Mumbai port
(b) Marmagao port
(c) New Mangalore port
(d) Kandla port
Answer : A
Question. Which one of the following ports is the deepest land-locked and well protected port along the east coast?
(a) Chennai
(b) Paradip
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Vishakhapatnam
Answer : D
Question : The National Highway that covers most of Rajasthan is ......... .
(a) National Highway-15
(b) National Highway-8
(c) National Highway-1
(d) National Highway-2
Answer : D
Assertion and Reasoning Based Questions
Mark the option which is most suitable:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertion : Mass communication promotes national integration and provides entertainment.
Reason : It strengthens democracy in the country by providing news to the masses. They feel attached to the country and a feeling of nationalism arises in them.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Tourism promotes national integration.
Reason : Millions of people are directly engaged in tourism industry.
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Waterways is the cheapest means of transport.
Reason : It is a fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Trade is considered as the economic barometer of the country.
Reason : Trade helps largely in developing countries like India. Advancement of trade is an index to its economic prosperity.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Cost of laying pipelines is less but subsequent running costs are maximum.
Reason : Pipelines facilitate easy transportation of goods.
Answer : (d) A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertion : Communication is unessential requirement of human life.
Reason : Communication between people creates awareness.
Answer : (d) A is false but R is true.
Very Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Lifelines of National Economy
Answer : Silcher (Assam) and Porbander (Gujarat) are the two extreme cities which are connected by East-West Corridors.
Question : Which port is located in Orissa?
Answer : Paradip port is located in Orissa.
Question : Which is a major commodity imported by India?
Answer : Petroleum and petroleum products.
Question : Name the mode of transportation that reduces trains-shipment losses and delays in the supply of petroleum and gases?
Answer : Pipelines
Question : Name the places which are important destinations of foreign tourists in India.
Answer : Rajasthan, Goa, Jammu and Kashmir and temple towns of south India.
Question : What is the length of inland waterways in India? How much waterway is navigable by mechanical boats?
Answer : India has inland navigation water ways of 14,500 km in length. Out of these only 3,700 km are navigable by mechanised boats.
Question : Which cities are connected by NH1?
Answer : Delhi and Amritsar are connected by NH1.
Question : Which is the iron ore exporting port of the country?
Answer : Marmagao port is the premier iron ore exporting port of the country. This port accounts for about fifty percent of India's iron ore export.
Question : Name the river which is related to ‘National Waterways’ No. 1.
Answer : Ganga.
Question : What are State Highways and who maintains them?
Answer : Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as State Highways. These are maintained by the State Public Works Department.
Question : What are District Roads and who maintains them?
Answer : District roads connect the district headquarters with other places of the district. These roads are maintained by the Zila Parishad.
Question : What is meant by ‘Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojna’?
Answer : ''Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojna'' provides special provisions to every village in the country and links it to a major town in the country by an all season commutable road.
Question : What is the principal mode of transportation?
Answer : Railways are the principal mode of transportation.
Question : Which is the cheapest mode of transportation?
Answer : Waterways are the cheapest mode of transportation.
Question : Where and why was the first sea port developed in India?
Answer : Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port developed soon after the Independence to ease the volume of trade on the Mumbai port.
Question : What is the importance of Kandla port?
Answer : Kandla port is a tidal port. It caters to the convenient handling of exports and imports of highly productive granary and industrial belt stretching across the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, etc.
Question : What was the objective of the Border Road Organisation?
Answer : It was established in 1960 for the development of the roads of strategic importance in the northern and north-eastern border areas.
Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Lifelines of National Economy
Question : Describe any five major problems faced by road transport in India.
Answer : Major problems of roadways are:
(i) Distribution of road is not uniform in the country.
(ii) Keeping in view the volume of traffic and passengers, the road network is inadequate.
(iii) About half of the roads are unmetalled and this restricts their usage during the rainy season.
(iv) The National Highways are inadequate too.
(v) Moreover, the roadways are highly congested in cities
(vi) Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
(vii) Poor maintenance is also a big problem.
Question : State three points regarding the importance of pipelines in transportation.
Answer : Pipeline transport network is a new arrival on the transportation map of India. Earlier it was used to transport water but these days it is used for the following:
(i) Transport of crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertiliser factories and big thermal power plants is done with the help of pipelines.
(ii) Even solids can be transported through pipelines when converted into slurry.
(iii) The far inland locations of refineries and gas-based fertiliser plants could be thought of only because of pipelines.
(iv) Initial cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs are minimal.
(v) It rules out trans-shipment (during transportation) losses or delays.
Question : What do you mean by the density of the roads? Name the state with
(i) Highest density of roads
(ii) Lowest density of roads
Answer : The length of road per 100 Sq. km of area is known as density of roads.
(i) The state with highest density of roads – Kerala
(ii) The state with lowest density of roads – Jammu & Kashmir.
Question : How many major ports does India have? Name any four points. What is the percentage of foreign trade handled by the major ports?
Answer : India has 12 major ports.
Name of four ports.
(i) Kandla in Kuchchh (ii) Mumbai port
(iii) Marmagao port (Goa) (iv) Kochchi port
95% of India’s foreign trade of is handled by the twelve major ports.
Question : Why is the importance of road transport in comparison to rail transport growing in India?
Or
Why is road transport more useful than rail transport in India? Explain four reasons.
Answer : The growing importance of road transport in comparison to rail transport is because of the following reasons:
(i) Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railways lines.
(ii) Roads can pass through comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
(iii) Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
(iv) It provides door to door services thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
(v) It is used as feeder to other modes of transport. To reach any destination be it railway station, sea port or airport, one needs to travel through roads.
Question : Write a report on newspapers.
Answer : Newspapers are the major source of mass communication which spread awareness among the people about various national and international activities, incidents, programmes, sports, education etc. India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually. They are of different types depending upon their periodicity. Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects. The largest number of newspapers published in the country is in Hindi, followed by English and Urdu.
Question : What is international trade?
Answer : The exchange of goods and services between two or more countries is known as International Trade. It is also considered as an economic barometer because of the advancement of international trade a country leads to economic prosperity. Income earned from international trade constitutes a major part in the net national income.
Question : What are advantages of water transport ?
Answer : Advantages of water transport are :
(i) Water transport is the cheapest means of transport.
(ii) It is a suitable means to carry heavy and bulky goods.
(iii) Water transport is fuel efficient and environment friendly mode.
Question : What is ‘balance of trade’?
Answer : The difference between export and import is known as balance of trade. If the value of export is more than the imports, it is called favourable balance of trade. Similarly, if the exports are less than the imports it is called unfavourable balance of trade. A favourable balance of trade is considered good for the economic development of a country.
Answer : Railways are the principal mode of transportation :
(i) The Indian railways is the largest public sector venture in the country.
(ii) They cover long distances.
(iii) They transport massive number of passengers as nicely as goods and objects at a time.
(iv) Superfast passenger trains and items trains furnish relaxed journey.
(v) Goods trains transport heavy and bulky raw material to the manufacturing centers and completed goods to the market.
Long Questions for Class 10 Social Science Lifelines of National Economy
Answer : Efficient means of transport and communication has coverted the world into a larger village which can be understood through following points.
(i) Through transport and communication, we are well-linked with the rest of the world.
(ii) India is united despite its vast size, diversity and linguistic, and sociocultural plurality.
(iii) Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc., lead to India's socio-economic progress in many ways.
(iv) The trades from local to international levels have added to the strength of our economy.
(v) It has enriched our life and moulded the socio-economic life of the nation.
Question. Roadways have an edge over the Railways.’’ Justify the statement.
Answer:
Roadways have an edge over railways.
i. Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railw ay liens.
ii. Road can traverse comparatively more dissected an d undulating topography.
iii. Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse m ountains such as the Himalayas.
iv. Road transport economical in transpiration of few person and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
v. It also provides door-to-door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
vi. Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and ports.
Question. Describe the role of mass communication in India.
Answer:
(i) Mass communication provides entertainment.
(ii) Creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines,books and films.
(iii) All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages.
(iv) Doordarshan broadcasts programmes of entertainment, educational, sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
(v) India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually
(vi) Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects to create awareness among people in different parts of the country.
(vii) India produces short films; video feature films and video short films.
(viii) Mass media creates awareness among people on various socio-economic and political issues.
Question. Describe the benefits of Roadways.
Answer:
(i) Roads need less capital than the railways.
(ii) Road transport provides door-to-door service.
(iii) The road transport provides flexible service to men and materials.
(iv) Road transport is useful in small distances.
(v) Road transport is helpful in production of perishable goods as it facilitates the distribution ofperishable goods from point of production topoint of consumption.
(vi) Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
Question. Describe the physical and economic factors that influence the distribution pattern of the Indian railways network.
Answer:
i. Northern Plain: Development due to level land, high population density and rich agricultural recourses.
ii. Peninsular region and theHimalayan region; It is a hilly terrain. The railway tracks are laid through low hills, gap or tunnels.
iii. Deserts of Rajasthan: It is verydifficult to lay railway lines due to sandy plain of western Rajasthan.
iv. Development not suitable in the Swamps of Gujarat, forestedtracts of Madhya Pradesh,Chhattisgarh, Orissa and Jharkhand.
v. The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gapsor passes.
vi. Although the Konkan railway along west coast has been developed but it has also faced a numberof problems such assinking of track in some stretches and landslides.
vii. Railways, being the principle of mode of transportation for freight and passengersin India make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage etc.
Question. ‘‘Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its prosperity.’’ Support the statement with suitableexamples.
Answer:
Advancement of international trade means, a country is getting involved in trade with more and more foreign countries. Thismeans that the value of exports exceeds the value of imports. It is called favorable balance of trade. For example- the developedcountries. The following points justify that advancement to international trade is an index of prosperity:
1. Opening up of an economy to international trade facilitates import and export. Following comparative advantage enables theeconomy to produce more output than what was possible with its own resources.
2. The coming up of MNCs add to the employment opportunities in the country.
3. The country also benefits from the technological and production efficiency brought by theMNCs.
4. Foreign trade enables a country to earn foreign exchange.
5. Foreign investment helps to accelerate the process of growth and development in the country.
Thus, we can say that international trade paces up the process of growth and development in the country, thereby; it can be seenas an index of prosperity of the country.
Question. Highlight the significance of pipelines as the means of transportation, with the help of suitable examples.
Answer:
Significance of Pipelines:
i. Use for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from field to refineries.
ii. Solids can also be transported when converted into slurry.
iii. Inland locations of the refineries.
iv. Initial cost of laying is high but subsequent running cost is minimal.
v. It rules out trans-shipment losses or delays.
vi. Example- From oil field in upper Assam to Kanpur, Gas Pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects
Jagdishpur in UP.
Question. Highlight any five major problems faced by road transport in India.
Answer:
Problems faced by the Road Transport
i. Inadequate road network.
ii. About half of the roads are unmetalled.
iii. The National Highways are inadequate.
iv. Roadways are highly congested mainly in cities.
v. Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
Question. Why is air travel preferred in North-Eastern States of India? Explain with examples.
Answer: Air travel in the N-E states:
i. North Eastern states as a whole is dissected relief.
ii. It covers dense forests.
iii. Floods are frequent in these states.
iv. States have international frontiers along with.
v. Other means of transport - road and railway network are inadequate and not maintainedproperly.
vi. Air Travel saves time in spite of costly fare.
Source/Case Based Questions
Question : Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow :
For a long time, trade and transport were restricted to a limited space. With the development in science and technology, the area of influence of trade and transport expanded far and wide. Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
Today, India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity and linguistic and socio-cultural plurality. Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc. have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways. The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy. It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life.
(i) The world is shrinking because of advancement in _________ and _________ .
(a) science, technology
(b) art, culture
(c) dance, music
(d) all of the above
Answer : (a) science, technology
(ii) Different types of transportation help in socio-economic development of a nation. Identify which domain of the earth the following features of transportation belong to :
Choose the correct option :
(a) a-2, b-3, c-1
(b) a-3, b-1, c-2
(c) a-2, b-1, c-3
(d) a-1, b-3, c-2
Answer : (a) a-2, b-3, c-1
(iii) Which one of the following is not a challenge for India to connect the world?
(a) Complex land features
(b) Cultural and linguistic diversity
(c) Access to sea
(d) Vast area
Answer : (c) Access to sea
(iv) In order to expand its global trade, India needs to :
(a) Invest more in infrastructure.
(b) Develop advance transport and communication network.
(c) Liberalise trade policies.
(d) Restrict import of foreign products.
Answer : (d) Restrict import of foreign products.
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Resources And Development Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Resources And Development Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Resources And Development Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Forest And Wildlife Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Forest And Wildlife Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Forest And Wildlife Resources Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Agriculture Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Power Sharing Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Power Sharing Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Power Sharing Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics Federalism Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Federalism Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Federalism Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Democracy And Diversity Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Democracy Diversity Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Popular Struggles And Movements Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles And Movements Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Political Parties Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Political Parties Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Outcomes Of Democracy Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Challenges To Democracy Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Challenges to Democracy Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 History Nationalism In India Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 History Nationalist Movement In India One Mark Questions |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism in India Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism in India Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Making of a Global World Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Age of Industrialisation Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Development Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Development Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Sectors Of Indian Economy Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Sectors Of Indian Economy Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sectors Of Indian Economy Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Money And Credit Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Money And Credit Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Globalisation and the Indian Economy Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Globalization Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Consumer Awareness Worksheet |
Worksheet for CBSE Social Science Class 10 Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Social Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 10 Social Science on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Social Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to develop the Social Science Class 10 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Social Science in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter.
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy for latest session from StudiesToday.com
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 10 CBSE Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy you can download everything free
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Class 10 Social Science test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy worksheets cover all topics as per the latest syllabus for current academic year.
Regular practice with Class 10 Social Science worksheets can help you understand all concepts better, you can identify weak areas, and improve your speed and accuracy.

