Read and download NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Globalisation And The Indian Economy in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science. You can download latest NCERT books PDF chapterwise free from Studiestoday.com. This Social Science textbook for Class 10 is designed by NCERT and is very useful for students. Please also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science to understand the answers of the exercise questions given at the end of this chapter
NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following NCERT Book Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy in Class 10. This NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy NCERT Book Class 10
Click on the view or download PDF button below to access the Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science book. All Social Science Class 10 NCERT books have been divided into various chapters so that you can download and read them easily. Refer to the section below to access more books of Social Science in Class 10.
Most regions of the world are getting increasingly interconnected. While this interconnectedness across countries has many dimensions — cultural, political, social and economic — this chapter looks at globalisation in a more limited sense. It defines globalisation as the integration between countries through foreign trade and foreign investments by multinational corporations (MNCs). As you will notice, the more complex issues of portfolio investment have been left out. If we look at the past thirty years or so, we find that MNCs have been a major force in the globalisation process connecting distant regions of the world. Why are the MNCs spreading their production to other countries and what are the ways in which they are doing so? The first part of the chapter discusses this. Rather than relying on quantitative estimates, the rapid rise and influence of the MNCs has been shown through a variety of examples, mainly drawn from the Indian context. Note that the examples are an aid to explain a more general point. While teaching, the emphasis should be on the ideas and examples are to be used as illustrations.
You can also creatively use comprehension passages like the one given after Section II to test and reinforce new concepts. Integration of production and integration of markets is a key idea behind understanding the process of globalisation and its impact. This has been dealt with at length in this chapter, highlighting the role of MNCs in the process. You have to ensure that the students grasp this idea with sufficient clarity, before moving on to the next topic.
Globalisation has been facilitated by several factors. Three of these have been highlighted: rapid improvements in technology, liberalisation of trade and investment policies and, pressures from international organisations such as the WTO. Improvement in technology is a fascinating area for students and you may, with a few directions, encourage them to do their ow explorations. While discussing liberalisation, youhave to keep in mind that the students areunaware of what India was like in the pre-liberalisation era. A role-play could be conceived to compare and contrast the pre and post-liberalisation era. Similarly, international negotiations under WTO and the uneven balances in power are interesting subjects that can be covered in a discussion mode rather than as lectures.
The final section covers the impact of globalisation. To what extent has globalisation contributed to the development process? This section draws on the topics covered in Chapters 1 and 2 (for example, what is a fair development goal), which you can refer to. Also, examples and activities drawn from the local environment are a must while discussing this section. This might include contexts that have not been covered in the chapter, such as the impact of imports on local farmers, etc. Collective brainstorming sessions can be conducted to analyse such situations.
Sources for Information The call for a fairer globalisation has been given, among others, by the International Labour Organisation — www.ilo.org. Another interesting resource is the WTO website http://www.wto.org. It gives access to the variety of agreements that are being negotiated at the WTO. For company related information, most MNCs have their own websites. If you want to critically look at the MNCs, one recommended website is www.corporatewatch.org.uk.
Globalistation And The Indian Economy
Before You Read:
• Globalisation: Globalisation is a process of international integration arising from the interchange of world views, products ideas and other aspects of a culture.
• Privatization: Privatization is the transfer of a business, industry, or service from public to private ownership and control.
• Liberalization: Liberalization refers to the reduction or elimination of government regulation or restrictions on private business and trade.
• Multinational Corporation (MNC): MNC is an enterprise operating in several countries but managed from one country or group that derives a quarter of its revenue from operations outside of its home country.
- MNC owns or controls production in more than one nation.
- MNC’s set up offices and factories for production in regions where they can get cheap labour and other resources.
• Investment: The money that is spent to buy assests such as land,building, machines and other equipments is called investment.
• Foreign Trade: Foreign trade is basically trade between two different countries of the world. It is also known as international trade.
• World Trade Organization: (WTO) World trade organization is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. The main aim of this organization is to liberalize the law of trade between the nations.
• Foreign Investment: Foreign investment is when a company or individual from one nation invests in assets or ownership stake of company based in another nation.
• Special Economic Zone (SEZ): SEZ is a special economic zone of a country that is subject to unique economic regulations that differs from other areas in the same country. These regulations tend to be conductive to foriegn direct investment.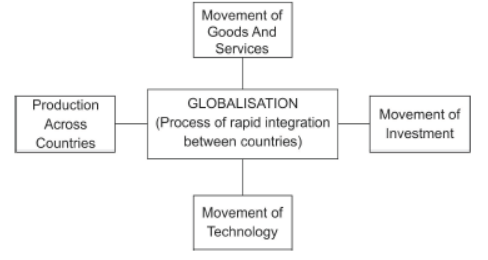
Production across countries
Before Globalisation After Globalisation
• Production was organized • Production organized in other
with in countries countries (more than one)
• What crossed the boundaries • Multinational corporations
were raw materials, food stuffs
and imported finished goods.
• Main channel of connecting • MNC own or control production
countries was trade. in more than one nation.
• Production Across Countries: Trade was the main channel connecting distant countries. Large companies, which are how called mutinational corporations (MNCs) play a major role in trade.
An MNC is a company that owns or controls production in more than one nation. MNC’s set up offices and factories for production in region where they can get cheap labour and other resources so that the company can earn greater profits.
• Interlinking Production Across Countries:
- The money that is spent to buy assets such as land, bulding machines and other equipment is called investment.
- An investment made by MNC’s is called foriegn investment.
- MNC’s are exerting a strong influence on production at these distant locations. As a result, production in these widely dispersed locations is getting interlinked.
• MNC’s Interlink Production Across Countries: MNC’s are spreading their production and interacting with local producers in various countries across the globe.
(i) By setting up partnerships with local companies.
(ii) By using the local companies for supplies.
(iii) By closely competing with the local companies or buying them up.
MNC’s set up production jointly with local companies which benefits local companies in the following ways:
(i) First MNC’s can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.
(ii) Second MNC’s might bring with them the latest technology for production.
• Foreign Trade And Integration Of Markets: Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets. Producers can sell their products not only in markets located with in the country but can also compete in markets located in their countries of the world. Similarly, buyers have the options to choose among various goods beyond domestically produced goods. Thus,foreign trade results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
• Globalisation: Globalisation is the process of rapid integration or interconnection of countries. MNC’s are playing a major role in the globalisation process.
- More and more goods and services, investments and technology are moving between countries.
- There is one more way in which the countries can be connected.
This is through the movement of people between countries.
• Factors That Have Enabled Globalisation Technology: Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process. This has made possible much faster delivery of goods across long distances at lower casts. The developements in information and communication technology have made information instantly accessible.
• Liberalisation of Foriegn Trade and Foreign Investment Policy:
- Trade barriers are some restrictions that have been setup by governments.
- The government can we trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kinds of goods and how much of reach, should come into the country. Tax on imports is an example of trade barrier.
- Removing barriers or restructions set by the government on trade is known as liberalisation.
• World Trade Organisation (WTO): WTO is an organisation whose aim is to liberalise international trade.
- At present 164 countries are currently members of WTO.
• Impact of Globalisation in India: Globalisation has affected the lives of people in India in following manner:
- It has provided greater choice to consumers who now enjoy improved quality of and lower prices on several products.
- It has resulted in higher standards of living.
- Globalisation has also created new opportunities for companies providing services particularly in the IT sector.
MCQs
Question. Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as :
(a) privatisation.
(b) globalisation
(c) liberalisation.
(d) socialisation
Answer. B
Question. Why did the government decide to remove barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment?
(a) Because the government wanted to earn the foreign exchange.
(b) Because the government decided that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the world.
(c) Because the government wanted to maintain good relations with other countries.
(d) None of the above.
Answer. B
Question. How much did Ford Motors invest in India in 1995?
(a) ₹ 1670 crore
(b) ₹ 1770 crore
(c) ₹ 2700 crore
(d) ₹ 2770 crore
Answer. B
Question. “MNCs keep in mind certain factors before setting up production”. Identify the incorrect option from the choices given below
(a) Availability of cheap skilled and unskilled labour
(b) Proximity to markets
(c) Presence of a large number of local competitors
(d) Favourable policy of the government.
Answer. C
Question. Ford Motors entered the Indian automobile business in collaboration with which Indian manufacturer?
(a) Maruti Suzuki
(b) TATA Motors
(c) Mahindra and Mahindra
(d) Toyota
Answer. C
Question. Ranbaxy is a multinational company which is associated with:
(a) automobiles
(c) medicines
(b) nuts and bolts
(d) information technology
Answer. C
Question. Globalisation has posed the major challenges for:
(a) Big producers
(b) Small producers
(c) Rural poor
(d) None of these
Answer. Small producers
Question. Which of the following is an example of a trade barrier?
(a) Foreign investment
(b) Delay or damage of goods
(c) Tax on inputs
(d) None of these.
Answer. Tax on imports
Fill in the blanks.
1. A ___________ is a company that owns and controls production in more than one nation.
1. Chinese toys are more popular in the Indian markets because of the ________ and ______.
2. Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as __________
4. The full form of SEZs is ______
5. Rapid improvement in technology has stimulated the _________ process.
6. The money that is spent to buy assets such as land, building, machines and other equipment is called __________.
7. Investment made by MNCs is called _________.
8. __________ an American company, is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers with production spread over 26 countries of the world.
9. __________ is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries.
10. ________ has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries.
11. Governments can use ________. to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kinds of goods and how much of each, should come into the country.
12. The aim of ________ is to liberalise international trade.
13. ___________ has resulted in greater competition among producers—both local and foreign. As a result, people today, enjoy much higher standards of living.
14. Companies who set up production units in the Special Economic Zones do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of ______ years.
Answer.
1. MNC
2. Cheaper prices and new designs
3. Liberalisation
4. Special Economic Zones
5. Globalisation
6. Investment
7. Foreign investment.
8. Ford motors
9. Globalisation
10. Information and communication Technology (IT)
11. Trade barriers
12. World Trade Organisation (WTO)
13. Globalisation
14. Five
Fill in the Blanks:
1. Removing barriers or restrictions set by goverment is called ..............
2. ............... is the indian manufacturer with which ford motors have entered in the indian automobile business.
3. ................ has been bought by cargill foods and MNC.
4. Ford motor was established in india in the year ................
5. The new economic policy was adopted by india in .................
6. SEZ refers to ........................
7. The full form of WTO is ..........................
8. ..................... means allowing the private sector to set up industries which were earlier reserved for the public sector.
Answer. 1. Liberalisation
2. Mahindra and Mahindra
3. Parakh foods
4. 1995
5. 1992
6. Special economic zone
7. World trade organization
8. Privatization
ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question. Define M.N.C.
Answer. A multinational corporation is a corporate organization that owns or controls production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
Question. What is Privatization?
Answer. Privalization: The transfer of ownership, property or business from the government to the private sector is termed privalization.
Question. What is SEZ?
Answer. A special economic zone is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from teh rest of teh country.
Question. What is Globalization?
Answer. Globalisation is a process of international integration arising from the interchange of world views, products ideas and other aspects of a culture.
Question. Which sector of economy is still lagged behind even after the globalization?
Answer. Agriculture sector.
Question. When did India adopted the new economic policy?
Answer. In 1992.
Question. What is WTO?
Answer. W.T.O (World Trade Organization) It is an organization which is in favour of increasing the world trade through globalization.
Question. Define Investment.
Answer. An investment is an asset or item accured with the goal of generating income or recognition.
Question. What is liberalization?
Answer. Liberalization refers to elimination of government regulation or restrictions on private busniess and trade.
Question. What is foreign investment?
Answer. Foreign investment is when a company or individual from one nation invests in assests or ownership stakes of company based in another nation.
Question. What are Multi-National Corporations (MNCs)?
Answer. A Multi-National Corporation (MNC) is a company that owns or controls production in more than one nation. The goods and services are produced globally. The production process is divided into small parts and spread out across the globe.
Question. Explain ‘what is investment? Give a few examples of investment.
Answer. Investment is buying of an asset in the form of a factory, a machine, land and building, etc. (Physical assets) or shares (monetary assets) for the purpose of making or sharing profits of the enterprises concerned.
Common investments are: buying land, factories, machines for faster production, buying small local companies to expand production, cheap labour, skilled engineers, IT personnel, etc.
Question. Why is ‘tax’ on imports known as a trade barrier?
Answer. Tax on imports is known as a trade barrier because it increases the price of imported commodities. It is called a barrier because some restriction has been set up.
Question. Give one characteristic feature of a ‘Special Economic Zone’?
Answer. Special Economic Zones or SEZs are industrial zones set up by the government having word class facilities such as electricity, water, roads, transport, storage, recreational and educational facilities. Companies who set up production units in SEZs are exempted from taxes for an initial period of five years.
Question. What do you understand by the term ‘Foreign Direct Investment’?
Answer. FDI is the investment of foreign capital in the economic and productive activities of a country by foreign companies or MNCs with the aim of expanding capacity and production to earn profits.
Question. Why had the Indian Government put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment after independence? State any one reason.
Answer. The Indian government after independence had put barriers to foreign trade and investment.
• This was done to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
• To protect the Indian economy from foreign infiltration in industries affecting the economic growth of the country as planned.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Explain any three factors that have enabled globalisation.
Answer. Rapid improvement in Transportation Technology: This had made possible much faster delivery of goods across long distances at lower cost.
Development in Information and Communication technology: It has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries.
Liberalisation: Countries have removed many of the barriers to foreign trade and foreign investments and then promoted globalisation.
Question. What were the reasons putting barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment by the government of India after Independence?
Answer. To protect the producers within the country from foreign competition. Industries were just coming up in the 1950s and 1960s, and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to come up. India allowed imports of only essential items such as machinery, fertilisers, petroleum etc.
Question. Why did the government of India wish to remove barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment starting around 1991?
Answer. The government decided that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the globe.
It felt that competition would improve the performance of producers within the country.
Power fun International Organisations supported this decision.
Question. What is WTO? What is its main aim and also mention one of its limitation?
Answer. World Trade Organisation an International Organisation that dealing with rules of international trade and making trade between countries should be trade. Its main aim is to liberalise international trade. Limitation: Though WTO is supposed to allow free trade for all, in practice, it is seen that the developed countries have unfairly retained trade barriers.
Question. How the globalisation and greater competition among producers - both local and foreign producers has been advantage to consumers?
Answer. a) There is greater choice before these consumers.
b) The quality of the products have improved and the customers get the products at lower prices.
c) People enjoy higher standard of living
Question. Mention any three steps that have taken by the government of India to attract foreign invest meant in recent years?
Answer. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) have been set up to have world class facilities such as electricity, water, roads, transport, storage, recreational and educational facilities.
b) Companies who set up production units in the SEZs do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of five years.
c) Government has allowed flexibility in the labour laws. Instead of hiring workers on a regular basis, companies hire workers ‘flexibly ’
for short periods when there is intense pressure of work. This is done to reduce the cost of labour for the company.
Long Answer Questions
Question. What are the various ways in which MNC’s control production in other countries.
Answer. (a) by buying local companies of an area
(b) by making partnership with the local companies
(c) by placing orders with small produces
Question. Supposing you find two people arguing: One is saying globalisation has hurt our country’s development. The other is telling, globalisation is helping India develop. How would you respond to these arguments?
Answer. Both the arguments are right to some extent. Globalisation has hurt our country’s development as well as helped our country develop. In other words, we can say that globalisation has positive as well as negative impact on our country’s development. Positive impact of the globalisation on India
(i) Availability of variety of products which enabled the consumers to have greater choice and enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products.
(ii) This led to higher standard of living.
(iii) Increase in foreign direct investment and creation of new jobs in certain industries.
(iv) Top Indian companies have been benefited by investing in new technology and production methods along with successful collaborations with foreign companies.
(v) Globalisation has enabled some large Indian company to emerge as multinationals themselves. For example, Tata Motors, Infosys, Ranbaxy etc.
(vii) Enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as multinationals, created new opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those involving IT.
Negative impact of the globalisation on India
(i) Small producers failed to compete and got perished. Rising competition has led to shutting down of many units. Many workers became jobless.
For instance, batteries, capacitors, plastics, toys, dairy products and vegetable oil are the examples of the industries which have been hit hard due to hard competition.
(ii) Globalisation and pressure of competition have substantially changed the lives of workers. Faced with growing competition most employers these days prefer to employ workers ‘flexibly’. This means that workers ’ jobs are no longer
Question. In what ways has competition effected the workers, the Indian exporters of the garment industries and MNCs?
Answer. Workers: Earlier a factory used to employ workers on a permanent basis, now they employ workers only on a temporary basis so that they do not have to pay workers for the whole year. Workers also have to put in very long working hours and work night shifts on a regular basis during the peak season. Wages are low and workers are forced to work overtime to make both ends meet. They are denied their fair share of benefits
Indian Exporters: Large MNCs in the garment industry in Europe and America order their products from Indian exporters. These large MNCs with worldwide network look for the cheapest goods in order to maximise their profits. To get these large orders, Indian garment exporters try hard to cut their own costs. As cost of raw materials cannot be reduced, exporters try to cut labour costs.
MNCs : They are able to find the cheapest goods in order to maximise their profits.
Competition among large the garment exporters has allowed these MNCs to make large profits.
Question. What is fair globalisation? What measures can be taken by the Govt. of India to make globalisation more fair?
Answer. Fair globalisation means creating equal opportunities for all and also ensuring that the benefits of globalisation are shared in a better way.
The government can play a major role in making this possible. Its policies must protect the interests, not only of the rich and the powerful, but all the people in the country.
It can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and the workers get their rights.
It can support small producers to improve their performance till the time they become strong enough to compete.
If necessary, the government can use trade and investment barriers. It can negotiate at the WTO for ‘fairer rules’.
It can also align with other developing countries with similar interests to fight against the domination of developed countries in the WTO.
EXERCISES
1 What do you understand by globalisation? Explain in your own words.
2. What was the reasons for putting barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment by the Indian government? Why did it wish to remove these barriers?
3. How would flexibility in labour laws help companies?
4. What are the various ways in which MNCs set up, or control, production in other countries?
5. Why do developed countries want developing countries to liberalise their trade and investment? What do you think should the developing countries demand in return?
6. “The impact of globalisation has not been uniform.” Explain this statement.
7. How has liberalisation of trade and investment policies helped the globalisation process?
8. How does foreign trade lead to integration of markets across countries? Explain with an example other than those given here.
9. Globalisation will continue in the future. Can you imagine what the world would be like twenty years from now? Give reasons for your answer.
10.Supposing you find two people arguing: One is saying globalisation has hurt our country’s development. The other is telling, globalisation is helping India develop. How would you respond to these organisations?
11. Fill in the blanks.
Indian buyers have a greater choice of goods than they did two decades back. This is closely associated with the process of ______________. Markets in India are selling goods produced in many other countries. This means there is increasing ______________ with other countries. Moreover, the rising number of brands that we see in the markets might be produced by MNCs in India. MNCs are investing in India because _____________ ___________________________________________ . While consumers have more choices in the market, the effect of rising _______________ and ______________has meant greater _________________among the producers.
Please refer to attached file for NCERT Class 10 Economics Globalisation And The Indian Economy
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Resources and Development |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Water Resources |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Agriculture |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Lifelines of National Economy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Power Sharing |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Federalism |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Political Parties |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History The Age of Industrialisation |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History Print Culture and the Modern World |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Development |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Money And Credit |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Globalisation And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Consumer Rights |
NCERT Book Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
The above NCERT Books for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy have been published by NCERT for latest academic session. The textbook by NCERT for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Social Science Class 10 is being used by various schools and almost all education boards in India. Teachers have always recommended students to refer to Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy NCERT etextbooks as the exams for Class 10 Social Science are always asked as per the syllabus defined in these ebooks. These Class 10 Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy book for Social Science also includes collection of question. Along with Social Science Class 10 NCERT Book in Pdf for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy we have provided all NCERT Books in English Medium for Class 10 which will be really helpful for students who have opted for english language as a medium. Class 10 students will need their books in English so we have provided them here for all subjects in Class 10. You can download free NCERT Social Science Class 10 Textbook PDF and all chapters by clicking on the links above
You can download the NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, you can click on the link above and download chapter wise NCERT Books in PDFs for Class 10 for Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Yes, the NCERT Book issued for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy have been made available here for latest academic session
You can easily access the link above and download the Class 10 NCERT Books Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy for each chapter

