Read and download NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Manufacturing Industries in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science. You can download latest NCERT books PDF chapterwise free from Studiestoday.com. This Social Science textbook for Class 10 is designed by NCERT and is very useful for students. Please also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science to understand the answers of the exercise questions given at the end of this chapter
NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following NCERT Book Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries in Class 10. This NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries NCERT Book Class 10
Click on the view or download PDF button below to access the Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Social Science book. All Social Science Class 10 NCERT books have been divided into various chapters so that you can download and read them easily. Refer to the section below to access more books of Social Science in Class 10.
Production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw materials to more valuable products is called manufacturing. Do you know that paper is manufactured from wood, sugar from sugarcane, iron and steel from iron ore and aluminium from bauxite? Do you also know that some types of clothes are manufactured from yarn which itself is an industrial product?
People employed in the secondary activities manufacture the primary materials into finished goods. The workers employed in steel factories, car, breweries, textile industries, bakeries etc. fall into this category. Some people are employed in providing services. In this chapter, we are mainly concerned with manufacturing industries which fall in the secondary sector.
The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of manufacturing industries.
IMPORTANCE OF MANUFACTURING
Manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of development in general and economic development in particular mainly because–
• Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
• Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
• Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
• Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous.
India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible.
Agriculture and industry are not exclusive of each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity. They depend on the latter for raw materials and sell their products such as irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, plastic and PVC pipes, machines and tools, etc. to the farmers. Thus, development and competitiveness of manufacturing industry has not only assisted agriculturists in increasing their production but also made the production processes very efficient.
In the present day world of globalisation, our industry needs to be more efficient and competitive. Self-sufficiency alone is not enough. Our manufactured goods must be at par in quality with those in the international market. Only then, will we be able to compete in the international market.
Objective Questions
Question. The first Jute mill was set up in ……………
(a) Kolkata
(b) Bengaluru
(c) Hyderabad
(d) Mumbai
Answer. A
Question. The shore-based Iron and Steel plant of India is at ……………
(a) Salem
(b) Bhadravathi
(c) Vishakhapatnam
(d) Durgapur
Answer. C
Question. Agency that market steel for the public sector plants is ______
(a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c) TATA steel
(d) MNCC
Answer. B
Question. The first successful cotton textile mill was established in______
(a) Kolkata
(b) Chennai
(c) Mumbai
(d) Coimbatore
Answer. C
Question. The only Software Technology Park is located in which one of the following north-eastern states is at ________
(a) Himachal Pradesh
(b) Manipur
(c) Mizoram
(d) Assam
Answer. D
Question. Oil India Ltd is _______ type of Industry on the basis of ownership
(a) Joint sector Industry
(b) Cooperative Sector
(c) Public sector
(d) Private sector
Answer. A
Question. The products produced from the primary activity are manufactured at ____ level
(a) Secondary
(b) Tertiary
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Answer. A
Question. Industries based on Agriculture are called _______
(a) Key Industries
(b) Mineral Based Industry
(c) Agro-Based Industry
(d) Basic Industry
Answer. C
Question. ________ sector industries are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both.
(a) Public
(b) Private
(c) Joint
(d) Cooperative
Answer. D
Question. Match the items of column A with that of Column B
A B
(i) Cotton Textile (a) Bengaluru
(ii) Jute Textile (b) Jamshedpur
(iii) Iron and Steel (c) Noida
(iv) Electronic goods (d) Mumbai
(v) Software Park (e) Hugli
(1) (i) a, (ii) b (iii) c (iv) d (v) e
(2) (i) d (ii) e (iii) b (iv) a (v) c
(3) (i) c, (ii) d (iii) b (iv)a (v) e
(4) (i) d, (ii) e (iii) c (iv) b (v) e
Answer. B
Question. Complete the diagram of an ‘Ideal location of an Industry’-
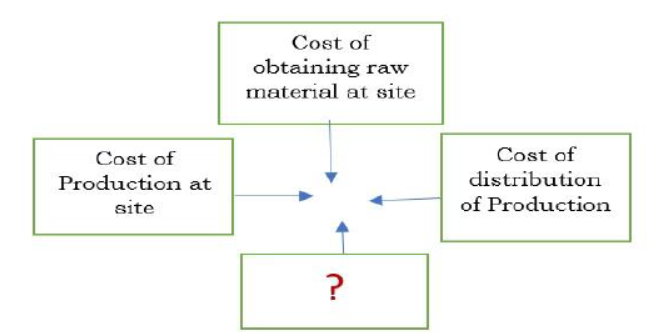
(a) Decision to locate factory at site
(b) Transport Facility
(c) Marketing
(d) Government Policies
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following is a Basic Industry?
(a) Sugar
(b) Cotton
(c) Jute
(d) Iron and Steel
Answer. D
Source based questions-
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Our manufactured goods must be at par in quality with those in the international market. Only then, will we be able to compete in the international market. Over the last two decades, the share of the manufacturing sector has stagnated at 17 per cent of GDP – out of a total of 27 per cent for the industry which includes 10 per cent for mining, quarrying, electricity and gas. This is much lower in comparison to some East Asian economies, where it is 25 to 35 per cent. The trend of growth rate in manufacturing over the last decade has been around 7 per cent per annum. The desired growth rate over the next decade is 12 per cent. Since 2003, manufacturing is once again growing at the rate of 9 to 10 per cent per annum. With appropriate policy interventions by the government and renewed efforts by the industry to improve productivity, economists predict that manufacturing can achieve its target over the next decade. The National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC) has been set up with this objective.
Question. What is the criterion to fulfil for Indian goods to be able to compete in the international market?
(a) Indian goods should be less expensive
(b) Indian goods should be more expensive.
(c) The quality of Indian goods should be enhanced.
(d) The quality of Indian goods should be decreased.
Answer. C
Question. What is the current share of contribution of the manufacturing sector to the Indian GDP?
(a) 17
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 27
Answer. A
Question. How can we improve the productivity of the manufacturing sector?
(a) Reinvigorate the primary sector.
(b) Change the tertiary sector
(c) Policy interventions by the government
(d) Change the activities involved in the secondary sector
Answer. C
Question. What is the difference between Indian and the East Asian economies with respect to the contribution of the Manufacturing Sector?
(a) Contribution is greater in the East Asian Economies.
(b) Contribution is lesser in the East Asian Economies.
(c) Contribution is equal in the East Asian Economies.
(d) There is no contribution in the East Asian Economies.
Answer. A
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange. Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible.
Question. The aim of establishing industries in tribal and backward areas is for-
(a) Bringing about modern goods
(b) Bringing down regional disparities
(c) Eradication of unemployment and poverty
(d) Quality production
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following options does not help in modernising agriculture?
(a) Manufacturing farm equipment
(b) Providing unskilled labour force
(c) Supplying fertilizers and pesticides
(d) Producing tube well pumps and sprinklers
Answer. B
Question. In order to attract foreign manufacturing firms, a country needs to develop:
(a) Agrarian facilities
(b) Cultivable lands
(c) Cultural festivals
(d) Infrastructure facilities
Answer. D
Question. Manufacturing provides job opportunities to reduce dependence on agriculture. Identify which sector the following jobs belong to:
(1) Agriculture (i) Secondary
(2) Manufacturing (ii) Tertiary
(3) Research and Development (iii) Primary
(a) 1(i) 2(ii) 3(iii)
(b) 1(iii) 2(i) 3(ii)
(c) 2(i) 1(ii) 3(iii)
(d) 3(i), 2(ii), 3 (iii)
Answer. B
NTPC is a major power providing corporation in India. It has ISO certification for EMS (Environment Management System) 14001. The corporation has a proactive approach for preserving the natural environment and resources like water, oil and gas and fuels in places where it is setting up power plants. This has been possible through optimum utilisation of equipment adopting latest techniques and upgrading existing equipment. Minimising waste generation by maximising ash utilisation.
Providing green belts for nurturing ecological balance and addressing the question of special purpose vehicles for afforestation. Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system and liquid waste management. Ecological monitoring, reviews and online database management for all its power stations
Question. NTPC is the abbreviation of ______
(a) National Textile Production Company
(b) National Technology Production Company
(c) National Tuberculosis Prevention Corporation
(d) National Thermal Power Corporation
Answer. D
Question. The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with _________ concerns.
(a) social
(b) cultural
(c) environmental
(d) political
Answer. C
Question. Find the odd one out from the following statements regarding the approach of preserving the natural environment-
(a) Providing green belts
(b) Upgrading equipment
(c) Deforestation
(d) Waste management
Answer. C
Question. What are the raw material for thermal power?
(a) Coal and Petroleum
(b) Boiling water
(c) Sun’s heat
(d) None of the above
Answer. A
The electronics industry covers a wide range of products from transistor sets to television, telephones, cellular telecom, telephone exchange, radars, computers and many other equipment required by the telecommunication industry. Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India. The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to the success of IT industry in India. A major impact of this industry has been on employment generation.
Question. Which of the following industries manufacture computers?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Information Technology
(c) Electronic
(d) Steel
Answer. C
Question. Which city is known as electronic capital of India?
(a) Mumbai
(b) Pune
(c) Delhi
(d) Bengaluru
Answer. D
Question. In which of the following sectors do IT industry belong to-
(a) Primary
(b) Tertiary
(c) Secondary
(d) All of the above
Answer. B
Question. Which one of the following industries provide single window service and high data communication facility to software experts-
(a) Automobile industry
(b) Chemical industry
(c) Iron and Steel industry
(d) Information Technology
Answer. D
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question. Agriculture’ and ‘industry’ are complimentary to each other.” Explain
Answer. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive of each other. They Move hand in hand,
(1) The agro-based industries have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
(2) The agro-based industries depend on agriculture for raw materials. Manufacturing industries sell their products such as fertilizers, insecticides, irrigation pumps, PVC pipes, machines and tools, etc. to the farmers.
(3) Thus, development and competitiveness of manufacturing industry has not only assisted agriculturists in increasing their production but also made production process very efficient.
Question. Why is least cost known as decision making factor for an ideal location of an industry?
Answer. It includes all important factors like distance from raw material sources, nearness to market, transport and communication facilities etc which motivates the industrialist in investment.
Question. Write the basic inputs of Iron and Steel industry
Answer. Coking coal, limestone and manganese
Question. What are agglomeration economies?
Answer. Many industries tend to come together to make, use of the advantages offered by the urban institutions such as banking, insurance, transport, labour. This is known as agglomeration economies
Question. Why do our industries need to be more efficient and competitive in the present day of globalization?
Answer. Our industries need to be more efficient and competitive in the present day globalization because:
(1) Our manufactured goods must be at par in quality with those in the international market.
(2) Only then we will be able to compete in the international market.
(3) India will have to develop its industries if it wants to be internationally developed.
Question. Why have the demands of jute products increased internally as well as globally? Explain any two reasons.
Answer.
(1) The demand of jute products increased internally due to the Government policy of mandatory use of jute packaging.
(1) The demand of jute products has also increased globally due to environment friendliness.
(2) The global concern for environment friendly, biodegradable materials has opened the opportunity for jute products.
Question. How are integrated steel plants different from mini steel plants?
Answer. (1) Integrated Steel Plant is larger in size than Mini Steel Plant.
(2) Integrated Steel Plant handle everything in one single Complex From putting together raw material to steel making, rolling and shaping while the Mini steel Plants use steel scrap, sponge iron and sometimes steel ingots supplied by integrated Steel Plants.
(3) Integrated Steel Plants manufacture all types of steel but Mini steel Plants produce mild and alloy steel of give specification
Question. How is the information technology industry gaining importance in India?
Answer. (1) Generates employment - employed over one million and expected to increase in coming years. It is encouraging to know that 30% of the people employed in this sector are women.
(2) This is a major foreign exchange earner industry.
(3) The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to success of IT industry India.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question. “The textile industry is the only industry that is self-reliant and complete in the value-chain? Justify this statement?
Answer.
(1) It contributes significantly to industrial production (14%).
(2) It employs the second largest number of people , that is, 35 million persons directly.
(3) Its share in the foreign exchange earnings is significant at about 24.6%.
(4) It contributes 4% towards GDP.
(5) It is the only industry in the country which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain, i.e., from raw material to its highest value- added products.
Question. Explain five different ways to control environmental degradation caused by industries.
Answer.
(1)Careful planning and setting of industries
(2) Better design and operation of equipment to increase efficiency and reduce noise
(3) Proper selection of fuel and its utilisation
(4) Prevention of smoke by using of oil or gas instead of coal in industries
(5) Minimising use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages
(6) Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements
(7) Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds
(8) Reduction of particulate matter in the air by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators process.
Click on the below link to download NCERT Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Manufacturing Industries
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Resources and Development |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Water Resources |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Agriculture |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Contemporary India Lifelines of National Economy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Power Sharing |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Federalism |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Political Parties |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Political Science Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History The Age of Industrialisation |
| NCERT Book Class 10 History Print Culture and the Modern World |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Development |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Money And Credit |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Globalisation And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Book Class 10 Economics Consumer Rights |
NCERT Book Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
The above NCERT Books for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries have been published by NCERT for latest academic session. The textbook by NCERT for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Social Science Class 10 is being used by various schools and almost all education boards in India. Teachers have always recommended students to refer to Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries NCERT etextbooks as the exams for Class 10 Social Science are always asked as per the syllabus defined in these ebooks. These Class 10 Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries book for Social Science also includes collection of question. Along with Social Science Class 10 NCERT Book in Pdf for Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries we have provided all NCERT Books in English Medium for Class 10 which will be really helpful for students who have opted for english language as a medium. Class 10 students will need their books in English so we have provided them here for all subjects in Class 10. You can download free NCERT Social Science Class 10 Textbook PDF and all chapters by clicking on the links above
You can download the NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, you can click on the link above and download chapter wise NCERT Books in PDFs for Class 10 for Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Yes, the NCERT Book issued for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries have been made available here for latest academic session
You can easily access the link above and download the Class 10 NCERT Books Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries for each chapter

