Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Worksheet Set B. Download printable Biology Class 12 Worksheets in pdf format, CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Worksheet has been prepared as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Also download free pdf Biology Class 12 Assignments and practice them daily to get better marks in tests and exams for Class 12. Free chapter wise worksheets with answers have been designed by Class 12 teachers as per latest examination pattern
Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Biology Worksheet for Class 12
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf in Class 12. This test paper with questions and solutions for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for tests and exams and help you to score better marks
Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Worksheet Pdf
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. Auxanometer is used to measure
(a) length
(b) respiration
(c) transpiration
(d) ascent of sap
Answer. A
Question. Crop rotation is used to increase
(a) soil fertility
(b) pore size and soil particle
(c) organic content of soil
(d) viscosity of soil water
Answer. A
Question. Haploid cultures can be obtained by culturing
(a) pollen grains
(b) embryo
(c) shoot apex
(d) root apex
Answer. A
Question. Somaclonal variation appears in
(a) organisms produced through somatic hybridization.
(b) plants growing in highly polluted conditions.
(c) apomictic plants.
(d) tissue culture raised plants.
Answer. D
Question. A scion is grafted to a stock. The quality of fruits produced will be determined by the genotype of
(a) stock
(b) scion
(c) both stock and scion
(d) neither stock nor scion
Answer. B
Question. Cocoa is the plant from which chocolate is made.Which part is used to extract it?
(a) Flower
(b) Fruit
(c) Seeds
(d) Bark
Answer. C
Question. Bean seeds were planted and put on a sunny windowsill. As the plants grew, their stems bent toward the window. This bending was most likely caused by an
(a) unequal distribution of auxin in the stem.
(b) unequal distribution of a neurotransmitter in the stem.
(c) equal distribution of auxin in the stem.
(d) equal distribution of a neurotransmitter in the stem.
Answer. A
Question. Phytotron is a facility to
(a) grow plants under disease-free conditions.
(b) conserve endangered species of plants.
(c) grow plants under controlled conditions.
(d) induce mutations.
Answer. C
Question. Explant is required to be disinfected before placing in culture. This is done by
(a) autoclaving
(b) ultra-violet rays
(c) clorax or hypochlorite
(d) X-rays
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following is a viral disease of poultry birds?
(a) Anthrax
(b) Ranikhet
(c) Coccidiosis
(d) None of these
Answer. B
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : In plant tissue culture, somatic embryos can be induced from any plant cell.
Reason : Any viable plant cell can differentiate into somatic embryos.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Cattle breeds can be improved by superovulaton and embryo transplantaion.
Reason : Superovulation in high milk-yielding cows is induced by hormonal injection.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : In case of vegetatively propagated crops, pure-line selection is not required.
Reason : Hybrid vigour is mostly used in vegetatively propagated plants.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Yeasts such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae are used in baking industry.
Reason : Carbon dioxide produced during fermentation causes bread dough to rise by thermal expansion.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Somatic embryos can be induced from any cell in plant tissue culture.
Reason : Any living plant cell is capable of differentiating into somatic embryos.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : A major advantage of tissue culture is protoplast fusion.
Reason : A hybrid is formed by the fusion of naked protoplasts of two plants.
Answer. B
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Which part of the plant is best suited for making virus-free plants and why?
Answer. The terminal bud having apical meristem are the best suited parts of plant for making virus-free plant because they are not infected by virus.
Question. State any one significance of interspecific hybridisation in plants.
Answer. It is important for breeding disease-resistant plant varieties.
Question. Name the technology which in addition to tissue culture techniques play a pivotal role in enhancing food production.
Answer. Somatic hybridisation, Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology
Question. Write the names of two semi-dwarf and high yielding rice varieties developed in India after 1966.
Answer. Jaya, Ratna.
Question. Why is mutation breeding necessary for producing disease resistance varieties?
Answer. Because there is limited availability of disease resistance genes in the crop plants and their wild relatives.
Question. Explain what is meant by biofortification.
Answer. Biofortification is a crop breeding programme that is aimed for developing crop with high levels of vitamins, minerals, proteins and fats to improve public health.
Short Answer Questions
Question. State the disadvantage of inbreeding among cattle. How it can be overcome?
Answer. Continuous inbreeding reduces fertility and productivity. This is called inbreeding depression.
This can be overcome by mating with animal of different breeds or individuals of the same breed with unrelated superior animals.
Question. Identify two ways in which Spirulina is helpful to mankind.
Answer. Spirulina is a source of food rich in protein, minerals, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins. It can grow on waste water from potato processing plants, straw, molasses, animal manure and even sewage, so it also reduces water pollution.
Question. Find out what the various components of the medium used for propagation of an explant in vitro are.
Answer. The major components of the medium for in vitro propagation are:
(i) Water (ii) Agar agar (iii) Sucrose
(iv) Inorganic salts (v) Vitamins (vi) Amino acids
(vii) Growth hormones like auxin, cytokinins.
Question. “Growing Spirulina on a large scale is beneficial both environmentally and nutritionally for humans.” Justify.
Answer. Spirulina can be grown easily on materials like waste water from potato processing plants, straw,molasses, animal manure, sewage. This way it reduces environmental pollution and hence is environmentally beneficial. It serves as food rich in protein, carbohydrate, fats, vitamins and minerals. Thus, it is nutritionally beneficial too.
Question. Identify A, B, C and D in the table given below.
| Crop | Variety | Resistance to disease |
| Wheat | A | Leaf and stripe rust |
| B | Pusa Shubhra | Black-rot |
| Cowpea | Pusa Komal | C |
| Brassica | Karan Rai | D |
Answer. A : Himgiri B : Cauliflower
C : Bacterial blight D : White rust
Question. How are somaclones cultured from explants in in vitro conditions? Why are somaclones so called?
Answer. A part of the plant called explant is taken for tissue culture. The explant is grown in aseptic condition in synthetic/cultural media which is rich in inorganic nutrients, vitamins, amino acids and growth regulators like cytokinin and auxin. The method of growing or producing thousands of plants through tissue culture is called micropropagation.
The plants produced from tissue culture are genetically identical to the original plant from which they are grown, so they are called somaclones.
Question. How has mutation breeding helped in improving the production of mung bean crop?
Answer. Mutation breeding has helped in the production of disease resistant varieties of mung bean crops against yellow mosaic virus and powdery mildew.
Question. Suggest two features of plants that will prevent insect and pest infestation.
Answer. (i) Increasing hair growth on aerial parts of plants.
(ii) Rendering th eflowers necta r less.
(iii) Enabling plants to secrete insect killing chemicals (toxins).
Question. Explain in brief the role of animal husbandry in human welfare.
Answer. Animal husbandry is the practice of taking care and breeding domestic animals by applying scientific principles. It includes feeding, breeding and raising animal livestock whose primary purpose is to provide meat and milk. Milk is considered as an important article of regular diet.
The animal protein is obtained from beef, cattle, sheep and meat of goats. Eggs and poultry meat also serve as sources of animal protein. Thus, animal husbandry plays an important role in human welfare by providing us milk, eggs, meat, wool, silk, honey, wax and many other products. Also, rearing of animals provide useful employment to many.
Question. Fill in the blanks.
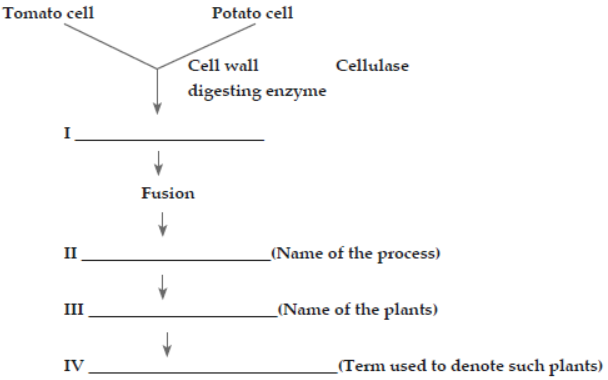
Answer. I— Protoplasts; II— Somatic hybridisation; III— Pomato; IV— Somatic hybrid
Question. Name any five hybrid varieties of crop plants which have been developed in India.
Answer. (i) Cauliflower varieties — Pusa Shubhra and Pusa Snowball K-1
(ii) Brassica varieties — Pusa Swarnim (Karan rai)
(iii) Wheat varieties — Himgiri
(iv) Rice varieties — Jaya and Ratna
(v) Chilli varieties — Pusa Sadabahar.
Question. Suryakant had banana plantation in his field. Quality of the fruit was excellent but the yield suffered due to infection of the plants by a virus. Suggest a fast and efficient method to get healthy and a large number of plants in the next generation without compromising on the existing quality. Justify the selection of your method.
Answer. He can grow thousands of plants through tissue culture of meristem by micro-propagation. He can remove the meristem and grow it in vitro using tissue culture technique. Although the plant is infected with a virus, the meristem (apical and axillary) is free of viruses.
Long Answer Questions
Question. According to Global Hunger Index, 2014, two billion people suffer from hidden hunger.
Apply your knowledge of plant breeding techniques to suggest a programme to improve public health. Specify four objectives of the programme. Also, mention one example of such a
produce.
Answer. Biofortification can improve public health. It involves breeding crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals, or higher protein and healthier fats.
Breeding for improved nutritional quality is improving:
(i) Protein content and quality;
(ii) Oil conten atnd quality;
(iii) Vitamin content; and
(iv) Micronutrient and mineral content.
In the year 2000, maize hybrids that had twice the amount of the amino acids, lysine and tryptophan, compared to existing maize hybrids were developed. Another example is the wheat variety, Atlas 66, having a high protein content which has been used as a donor for improving cultivated wheat.
Question. (a) State the objective of animal breeding.
(b) List the importance and limitations of inbreeding. How can the limitations be overcome?
(c) Give an example of a new breed each of cattle and poultry.
Answer. (a) Objective of animal breeding is to increase the yield of animal and improve the desirable qualities of the produce.
(b) Importance:
(i) Increases homozygosity
(ii) Evolves pure line
(iii) Expose harmful recessive genes
(iv) Help in accumulation of superior genes
(v) Eliminate less desirable genes.
Limitations:
Inbreeding reduces fertility and productivity (inbreeding depression).
The limitations can be overcome by outbreeding or out-crossing or interspecific hybridisation.
Selected animals may be bred with unrelated superior animals of the same breed.
(c) Hisardale is a new breed developed by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Mirano rams (sheep) and Leghorn is the new breed of chicken and Jersey is improved breed of cattle..
Question. IARI has released several varieties of crop plants that are biofortified. Give three examples of such crops and their biofortifications.
Answer. (i) Bittergourd enriched with vitamin C.
(ii) Carrots enriched with vitamin A.
(iii) Spinach enriched with iron and calcium.
Question. (i) Name the tropical sugarcane variety grown in South India. How has it helped in improving the sugar cane quality grown in North India?
(ii) Identify ‘a’, ‘b’ and ‘c’ in the following table:
| No. | Crop | Variety | Insect Pests |
| 1. 2. 3. |
Brassica Flat Bean (c) |
Pusa Gaurav Pusa Sem 2 Pusa Sem 3 Pusa Sawani Pusa A-4 |
(a) (b) Shoot and Fruit borer |
Ans. (i) Saccharum officinarum is grown in South India. It was crossed with North Indian variety (Saccharum barberi) to combine the desirable qualities of high yield, thick stems high sugar and ability to grow in North India.
(ii) (a) Aphids
(b) Jassids/aphids/fruit borer
(c) Okra B( hindi).
Question. (a) Name the technology that has helped the scientists to propagate on large scale the desired crops in short duration. List the steps carried out to propagate the crops by the said technique.
(b) How are somatic hybrids obtained?
Answer. (a) The technology that has helped the scientists to propagate on large scale the desired crops is tissue culture or micropropagation.
The steps to propagate crops are:
(i) Obtaining an explant from a plant.
(ii) Growing the explant in a test tube under sterile conditions.
(iii) A special nutrient or culture medium is provided for growth.
(b) Isolated single cells are isolated from plants. Their cell walls are digested to obtain protoplasts.
Isolated protoplasts from two different plant varieties are fused to get hybrid protoplasts.
(v) Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars. Newly selected lines are evaluated for yield and other agronomic traits of quality or disease resistance in research fields followed by testing the material in farmers fields for three seasons in different agroclimatic zones.
Question. Differentiate between an inbred line and a hybrid variety of crop. Explain the steps involved in the production of the hybrid variety.
Answer.
| Inbred line | Hybrid variety |
| The continuous inbreeding in a cross-pollinated crop develops a homozygous line called inbred line. |
A hybrid variety is produced by crossing two different species where progeny obtained is used for raising the next seasonal crop. |
Steps involved in hybrid variety production:
Question. Mention the economic value of Apis indica.
Answer. Apis indica is common species of honey bee used in apiculture.
Question. Write the importance of MOET.
Answer. Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET) is the programme used to increase the herd size in a short time.
Question. List any two economically important products for humans obtained from Apis indica.
Answer. Honey and beewax are two economically important products obtained from Apis indica.
Question. Differentiate between outbreeding and outcrossing.
Answer. Out breeding is breeding of unrelated animals which may be between individuals of same breed or between different breeds or different species. Outcrossing is the practice of mating of animals within the same breed but having no common ancestors. This is the best breeding method for animals that are below average in milk production, growth rate in beef cattle, etc. A single outcross often helps to overcome inbreeding depression.
Question. State the disadvantage of inbreeding among cattle. How it can be overcome?
Answer. Continuous inbreeding among cattle leads to reduced fertility and productivity, a phenomenon called inbreeding depression. It can be overcome by mating selected unrelated superior animals of same breed. This helps to restore fertility and yield.
Question. Explain giving reasons, the need to keep the bee-hives in the fields during flowering season.
Answer. Bees are the pollinators of many of our crop species such as sunflower, Brassica, apple and pear.
Keeping beehives in crop fields during flowering period increases pollination efficiency and improves the crop yield. Also bees collect nectar from flowers of these crop plants to make honey hence, honey yield also increases.
Question. How is a pureline in an animal raised ? Explain.
Answer. A pure line in an animal is raised through inbreeding. In this method, superior males and females of the same breed are selected and mated. The progeny obtained from such matings are evaluated and superior males and females among them are identified for further mating. Inbreeding increases homozygosity. It exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection.
Question. MOET programme has helped in increasing the herd size of the desired variety of cattle. List the steps involved in conducting the programme.
Answer. Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer or MOET is a method to improve the herd size of desired variety of cattle. The steps involved in MOET are as follows:-
(i) Hormones (with FSH-like activity) are given to cow for inducing follicular maturation and super ovulation i.e., production of 6-8 ova in one cycle.
(ii) Cow is either mated with best bull or artificially inseminated.
(iii) The embryos with 8-32 cell stages are recovered and transferred to surrogate mother and genetic mother becomes available for new cycle of super ovulation.
Question. Which one of the following is used in apiculture ?
Hilsa, Apis indica, Sonalika
Answer. Apis indica is the most common species of bees used in apiculture. Hilsa is a marine fish. Sonalika is the high yielding and disease resistant variety of the wheat.
Question. List any four important components of Poultry Farm Management ?
Answer. The four important components of poultry farm management are:-
(i) Selection of disease free and suitable breeds: Selection of breeds is the most important aspect. The breed should be disease free and suitable to the environmental conditions.
(ii) Brood house: Brood house should not be crowded and should be rain proof and protected from predators.
(iii) Sanitation and hygiene: The area should be cleaned and disinfected.
(iv) Feed management: Feeding constitutes the major management concern in egg and meat production.
Question. (a) List three advantages of inbreeding in cattle.
(b) Name an improved breed of cattle.
Answer. (a) Three advantages of inbreeding in cattle are:
(i) Inbreeding increases homozygosity. Hence, it is necessary if we want to evolve pureline.
(ii) Inbreeding exposes those recessive genes that are eliminated by selection.
(iii) It helps in accumulation of superior genes and elimination of less desirable genes.
(b) Jersey is an improved breed of cattle.
Question. Mention and describe any three methods to overcome inbreeding depression in animal husbandry.
Answer. Continuous inbreeding usually reduces fertility and productivity. This is called inbreeding depression. Inbreeding depression can be overcome by outcrossing, crossbreeding and interspecific hybridisation. Outcrossing is the practice of mating of animals within the same breed, but having no common ancestors on either side for 4-6 generations.
A single outcross often helps to overcome inbreeding depression. In cross-breeding superior males of one breed are mated with superior females of another breed. Cross-breeding allows the desirable qualities of two different breeds to be combined. In interspecific hybridisation, male and female animals of two different related species are mated.
Question. (a) Mention the kind of areas that are suitable for bee-keeping practices.
(b) Mention any two uses of bee wax.
Answer. (a) Bee-keeping can be practiced in an area where there are sufficient bee pastures of some wild shrubs, fruit orchards and cultivated crops.
(bc) Beewax is used in cosmetics, creams, ointments, paints and polishes.
Question. What is ‘Blue revolution’? Name two freshwater and two marine edible fish.
Answer. Blue revolution is the movement implemented along the same lines as green revolution related to the production of fish and fish products on a large scale. Freshwater edible fishes are rohu and catla. Marine water edible fishes are hilsa and Bombay duck.
Question. List any three outbreeding practices carried out to breed domestic animals. Explain the importance of each one listed.
Answer. The three outbreeding practices carried out to breed domestic animals are: outcrossing, cross- breeding and interspecific hybridisation. Outcrossing is the mating of animals within the same breed but not having common ancestors on either side of their pedigree up to 4-6 generations. Outcrossing is the best breeding method for animals that are below average in milk production, growth rate in beef and cattle etc. Sometimes only one outcross helps to overcome inbreeding depression.
In cross-breeding superior males of one breed are mated with superior females of another breed. crossbreeding allows the desirable qualities of two different breeds to be combined. The progeny hybrid animals may themselves be used for commercial production. Alternatively, they may be subjected to some form of inbreeding and selection to develop new stable breeds that may be superior to the existing breeds e.g., Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams. In interspecific hybridisation, male and female animals of two different species are mated. The progeny obtained from such a mating are usually different from both the parental species. But in some cases, the progeny may combine desirable characters of both the parents. Mule is produced from a cross between female horse (mare) and male donkey.
Question. How has mutation breeding helped in improving the production of mung bean crop?
Answer. In mutation breeding, mutations are induced artificially through the use of chemicals or radiations and plants having desired character are selected as a source in breeding. In mung bean, resistance to yellow mosaic virus and powdery mildew are introduced by mutation breeding.
Question. Name any two common Indian millet crops. State one characteristic of millets that has been improved as a result of hybrid breeding so as to produce high yielding millet crops.
Answer. Jowar and bajra are two Indian millet crops. High yielding hybrid varieties of millet crops are resistant to pest attack and water stress.
Question. Enumerate four objectives for improving the nutritional quality of different crops for the health benefits of the human population by the process of “Biofortification”.
Answer. Biofortification is the breeding of crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher proteins and healthier fats, to improve the public health by practical means. Plant breeding is undertaken for improved nutritional quality of the plants with the objectives of improving :
– Protein content and quality
– Oil content and quality
– Vitamin content
– Micronutrient and mineral content.
Question. Name the following:
(a) The semi – dwarf variety of wheat which is high yielding and disease resistant.
(b) Any one interspecific hybrid mammal.
Answer. (a) Sonalika and Kalyan Sona are semi-dwarf varieties of wheat, which are high yielding and disease resistant.
(b) Mule is an interspecific hybrid mammal, which is produced from a cross between female horse (mare) and male donkey.
Question. Identify A, B, C and D in the following table.
| Crop | Variety | Resistance to Disease |
| A | Himgiri | Hill bunt |
| Brassica | Pusa Swarnim | B |
| Cauliflower | C | Black rot |
| D | Pusa Komal | Bacterial blight |
Answer. In the given table : A – Wheat
B – White rust
Question. Explain the advantage of cross breeding of the two species of sugarcane in India.
Answer. Saccharum barberi was originally grown in North India, but had poor sugar content and yield. However, Saccharum officinarum had higher sugar content and thicker stems but did not grow well in North India. These two species were crossed to have sugarcane varieties combining the desirable qualities of high sugar, high yield, thick stems and ability to grow in the sugarcane belt of North India.
Question. Name and explain the mechanism by which seeds from hybrid plants are developed, that are able to retain the desired hybrid character in the progeny.
Answer. Plant breeding is the purposeful manipulation of plant species in order to create desired plant types that are better suited for cultivation, give better yields and are disease-resistant. The main steps in plant breeding are:-
(i) Collection of variability
(ii) Evaluation and selection of parents
(iii) Cross hybridisation among the selected parents (iv) Selection and testing of superior recombinants (v) Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars.
Question. Enumerate, in sequential order, the 4 steps that a plant breeder should know to obtain a diseaseresistant crop.
Answer. The various sequential steps are : screening germplasm for resistance sources, hybridisation of selected parents, selection and evaluation of hybrids and testing and release of new varieties.
Question. List two steps that help in introducing the desired mutation into the crop.
Answer. The steps in mutation breeding are :
(i) Inducing mutation through various mutagens/methods.
(ii) Screening the plant materials for disease resistance.
(iii) Multiplication for these selected plants for direct use or for use in breeding.
(iv) Hybridisation of the selected plant materials.
(v) Selection for disease resistance, testing and release as a variety.
Question. What is ‘biofortification’ ? Write its importance. Mention the contribution of Indian Agricultural Research Institute towards it with the help of two examples.
Answer. Breeding of crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher proteins and healthier fats is called biofortification. This is the most practical aspect to improve the health of the people.
Plant breeding is undertaken for improved nutritional quality of the plants with the objectives of improving :
– Protein content and quality
– Oil content and quality
– Vitamin content
– Micronutrient and mineral content.
Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi, has also developed many vegetable crops that are rich in minerals and vitamins. For example, vitamin A enriched carrots, pumpkin, spinach; vitamin C enriched bitter gourd, bathua, tomato; iron enriched spinach and bathua and protein enriched beans.
Question. Mention the role of ‘genetic mother’ in MOET.
Answer. In MOET, genetic mother is the biological mother of the offspring. Hormones with FSH like activity are given to genetic mothers for inducing follicular maturation and superovulation. As a result, 6-8 eggs are produced instead of 1 egg per cycle. She is then mated with a superior bull or artificially inseminated. Embryos at 8-32 cell stage are recovered and transferred to surrogate mother and the genetic mother is again available for super ovulation.
Question. Write a professional approach at genetic level that can help the farmer to improve the milk yield of low milk producing cows on his farm.
Answer. Outcrossing is the best breeding method and professional approach that can help farmer improve the milk yield in animals that are below average in milk production.
Question. Write the name of the following :
(a) The most common species of bee suitable for apiculture.
(b) An improved breed of chicken.
Answer. (a) Apis indica
(b) Leghorn is an improved breed of chicken.
Question. How can crop varieties be made disease resistant to overcome food crisis in India? Explain. Name one disease resistant variety in India of:
(a) Wheat to leaf and stripe rust
(b) Brassica to white rust
Answer. Breeding for disease resistant crop varieties is carried out by conventional breeding techniques or by mutation breeding. The conventional method of breeding for disease resistance is hybridisation and selection. The various sequential steps are: screening germplasm for resistance sources, hybridisation of selected parents, selection and evaluation of hybrids and testing and release of new varieties. Conventional breeding is often constrained by the availability of limited number of disease resistance genes that are present and identified in various crop varieties. Inducing mutations in plants sometimes leads to desirable genes being identified. Plants having these desirable characters can either be multiplied directly or can be used in breeding.
(a) Variety of wheat resistant to leaf and stripe rust– Himgiri
(b) Variety of Brassica resistant to white rust – Pusa Swarnim
Question. With advancements in genetics, molecular biology and tissue culture, new traits have been incroporated into crop plants.
Explain the main steps in breeding a new genetic variety of a crop.
Answer. Plant breeding is the purposeful manipulation of plant by crossing different varieties in order to create desired plant types that are better suited for cultivation, give better yields and are disease resistant. Plant breeding involves the following steps :
(i) Collection of variability – Collection and preservation of all the different wild varieties, species and relatives of the cultivated species. The entire collection (of plant/seeds) having all the diverse alleles for all genes in a given crop is called germplasm collection.
(ii) Evaluation and selection of parents – The germplasm is evaluated so as to identify plants with desirable combination of characters.
(iii) Cross hybridisation among the selected parents- Hybridisation is crossing of two or more types of plants for bringing their traits together in the progeny. The procedure of hybridisation involves selection of parents with desired characters, selfing, emasculation, bagging, tagging and artificial pollination.
(iv) Selection and testing of superior recombinants – This is the selection of the plants, from the progeny of hybrids, which have the desired combined character. The selected plants are then self pollinated for several generations to get a uniformity i.e. homozygosity. Selection is of two types: (a) Selection in self- pollinated crops – The degree of cross pollination is less than 5%. There is repeated self pollination of selected plants till superior homozygous genotypes are obtained. The best one is used as new variety. The self-pollinated progeny of homozygous plant constitutes a pure line.
(b) Selection in cross-pollinated crops – The cross- pollinated crops are heterozygous for most of their genes and their population contains plants of several different genotypes. Superior genotype plants are selected and are allowed to crossbreed (these plants are not allowed to self breed) so that heterozygosity is also maintained.
(v) Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars– The newly selected lines are evaluated for their yield and other agronomic traits of quality, disease resistance etc. These selected cultivars are then tested with local best cultivar and are then released for commercialisation.
Question. (a) What is plant breeding? List the two steps the classical plant breeding involves.
(b) How has the mutation breeding helped in improving crop varieties? Give one example where this technique has helped.
(c) How has the breeding programme helped in improving the public nutritional health?
State two examples in support of your answer.
Answer. (a) Plant breeding is an applied branch of botany which deals with the improvement of cultivated varieties (cultivars) of plants. It deals with the improvement in the heredity of crops and production of new crop varieties which are far better than original types in all respects. The main steps in production a new genetic variety of a crop are: evaluation and selection of parents and cross hybridisation among them. Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars are the other steps involved.
(b) It is possible to induce mutations artificially through use of chemicals or radiations (like gamma radiations), and selecting and using the plants that have the desirable character as a source in breeding. This process is called mutation breeding.
Resistance to yellow mosaic virus and powdery mildew in mung bean were introduced by mutations.
(c) Breeding of crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher protein and healthier fats is called biofortification. This is the most practical aspect to improve the health of the people. Plant breeding is undertaken for improved nutritional quality of the plants with the objectives of improving :
– protein content and quality
– oil content and quality
– vitamin content
– micronutrient and mineral content.
Maize hybrids that had twice the amount of the amino acids–lysine and tryptophan, compared to existing maize hybrids were developed in 2000. Wheat variety with high protein content Atlas 66 has been used as a donor for improving cultivated wheat.
Question. How can healthy potato plants be obtained from a desired potato variety which is virus infected? Explain.
Answer. Healthy potato plants can be obtained from the desired potato variety which is virus infected by meristem culture. Cultivation of axillary or apical shoot meristems is called meristem culture. The apical and axillary meristems of the infected plant is virus free because rate of division of meristematic cells is higher than the rate at which virus multiplies hence virus cannot invade newly formed meristematic cell. Meristem is removed and grown in vitro to obtain healthy virus-free potato plants.
Question. Name the technology used in micropropagation of plants. Write the genetic significance of the plants raised through this technique. Give two examples where this technology is commercially exploited.
Answer. The method of producing thousand of plants through tissue culture is called micropropagation. Each of these plants will be genetically identical to the original plant from which they are grown, i.e., they are somaclones. Many important food plants like tomato, banana, apple, etc., have been produced on commercial scale using this method.
Question.What is haploidy? How are haploid plants raised? How are they helpful in plant breeding?
Answer. Individuals or cells that contain one set of chromosomes as in gametes, are called haploids and this condition is called haploidy.
Haploid plants are of great significance as they are used in plant breeding for the production of homozygous plants. Formation of haploids is called haploid production. Haploid individuals arise from the gametes and are sterile hence of no direct value. The chromosome number of these haploids is doubled by using colchicine to obtain homozygous plants.
Question. Differentiate between somaclones and somatic hybrids. Give one example of each.
Answer. Differences between somaclones and somatic hybrids are as follows :
| Somaclones | Somatic hybrids |
| Somaclones are plants that develop from any part of a plant by tissue culture or micropropagation. |
Somatic hybrids are produced by fusion of somatic cells of two different varieties or species. |
| Somaclones are genetically identical to the parent plant from which they are grown. |
Somatic hybrids are genetically di erent from parent plant. |
| New genes cannot be introduced during somaclone formation. |
New genes can be introduced such as male sterility, herbicide resistance,etc., by genetic manipulation during formation of somatic hybrid plants. |
| It helps to evolve pure line. |
Pure lines are not developed. |
| E.g. commercial production of ornamental plants like lily, orchid, eucalyptus and fruits trees like tomato, apple, banana. |
E.g. pomato (somatic hybrid between potato and tomato). Somatic hybrids are also obtained between rice and carrot. |
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Worksheet Set B
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
The above practice worksheet for Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production has been designed as per the current syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students studying in Class 12 can easily download in Pdf format and practice the questions and answers given in the above practice worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest practice worksheets with solutions have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology students to get all the latest study material free of cost. Teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the practice sheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. After solving these you should also refer to Class 12 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Class 12 Biology have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

