Access the latest CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Question Bank. We have provided free printable Class 12 Biology worksheets in PDF format, specifically designed for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction. These practice sets are prepared by expert teachers following the 2025-26 syllabus and exam patterns issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS.
Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Biology Practice Worksheet for Class 12
Students should use these Class 12 Biology chapter-wise worksheets for daily practice to improve their conceptual understanding. This detailed test papers include important questions and solutions for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction, to help you prepare for school tests and final examination. Regular practice of these Class 12 Biology questions will help improve your problem-solving speed and exam accuracy for the 2026 session.
Download Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Worksheet PDF
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. Acrosome of sperm is formed by
(a) nucleus
(b) golgi bodies
(c) lysosome
(d) E. R.
Answer. B
Question. Immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane called as
(a) chorion
(b) corona radiata
(c) zona pellucida
(d) none of these
Answer. D
Question. The extra-embryonic membranes of mammalian embryo are derived from
(a) trophoblast
(b) follicle cells
(c) inner cell mass
(d) formative cells
Answer. A
Question. Cumulus covers
(a) ovary
(b) ovum
(c) embryo
(d) sperm
Answer. B
Question. Women who consumed the drug thalidomide for relief from vomiting during early months of pregnancy gave birth to children with
(a) no spleen
(b) hare-lip
(c) extra fingers and toes
(d) under developed limbs
Answer. D
Question. A cross section at the midpoint of the middle piece of a human sperm will show
(a) centriole, mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules.
(b) centriole and mitochondria.
(c) mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules.
(d) 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules only.
Answer. C
Question. Prostate gland secretion helps in formation of
(a) larva
(b) semen
(b) cocoon
(c) none of these
Answer. B
Question. Cessation of menstrual cycle in women is called
(a) menopause
(b) lactation
(c) ovulation
(d) parturition
Answer. A
Question. The figure given below shows the sectional view of ovary. Select the option which gives correct identification of marked structure (A to D) and its feature.
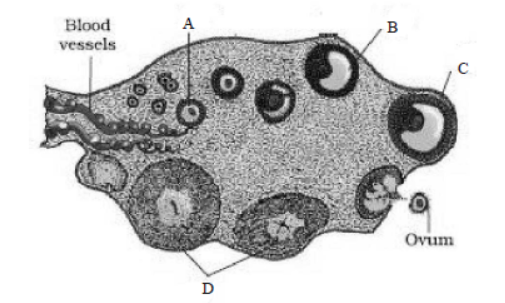
(a) A: Primary follicle, it is also called gamete mother cell.
(b) B: Corpus luteum, it cannot be formed and added after birth.
(c) C: Grafian follicle, mature follicle which ruptures to release secondary oocyte.
(d) D: Tertiary follicle, a large number of this follicle degenerates during the phase from birth to puberty.
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following is true regarding sperm?
(a) Fertilizin: For penetrating egg membrane
(b) Hyalurodinase: For penetrating egg membrane
(c) Acrosin: Dissolves corona radiata
(d) Capacitation: Takes place in penis
Answer. B
Question. Both corpus luteum and macula lutea are
(a) found in human ovaries
(b) a source of hormones
(c) characterized by a yellow colour
(d) contributory in maintaining pregnancy
Answer. C
Question. The given figure shows the human foetus within the uterus with few structures marked as A, B, C and D.
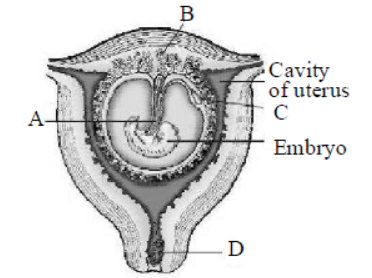
Which of the following options shows the correct labeling?
(a) A→Umbilical cord with its veins, B→Chorionic villi, C→Antrum, D→Plug of mucus in cervix
(b) A→Umbilical cord with its vessels, B→Fimbriae, C→ Oocyte, D→Plug of mucus in vagina
(c) A→Umbilical cord with its vessels, B→Placental villi, C→Yolk sac, D→Plug of mucus in cervix
(d) A→Umbilical cord with its veins, B→Placental villi, C→Trophoblast, D→Plug of mucus in vagina
Answer. C
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : Corpus luteum degenerates in the absence of fertilization.
Reason : Progesterone level decreases.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Clitoris is not remnant of penis in females.
Reason : It also has high blood supply and erectile tissue.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Mammalian ova produces hyaluronidase.
Reason : The eggs of mammal are microlecithal and telolecithal.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Head of sperm consists of acrosome and mitochondria.
Reason : Acrosome contains spiral row of mitochondria.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Females have less stature than males after puberty.
Reason : This happens because of the presence of hCG in the blood of females.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Testicular lobules are the compartments present in testis.
Reason : These lobules are involved in the process of fertilization.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Interstitial cell is present in the region outside the seminiferous tubule called interstitial spaces.
Reason : Interstitial cells provide nutrition to the sertoli cells.
Answer. C
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What name is given to the cells of inner cell mass, that have the potential to give rise to all tissues and organs in a human being?
Answer. Stem cells
Question. Given below are the stages in human reproduction. Write them in correct sequential order.
Insemination, Gametogenesis, Fertilisation, Parturition, Gestation, Implantation
Answer. Gametogenesis, Insemination, Fertilisation, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition.
Question. Name the important mammary gland secretions that help in resistance of the new born baby.
Answer. Colostrum.
Question. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Answer. GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone), LH (Luteinising hormone), FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone), androgen-binding protein (ABP), inhibin and androgens.
Question. How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
Answer. Only one egg is released by a human (female) ovary in a month.
Only one egg is released if the mother gave birth to identical twins.
Yes. Two or more eggs are released in case fraternal twins are born.
Question. Write the location and function of the Sertoli cells in humans.
Answer. Sertoli cells are present in seminiferous tubules. They provide nutrition to the germ cells or sperms.
Question. Name the hormones produced only during pregnancy in a human female. Mention their source organ.
Answer. During pregnancy, placenta produces hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin and human placental lactogen and ovary produces relaxin.
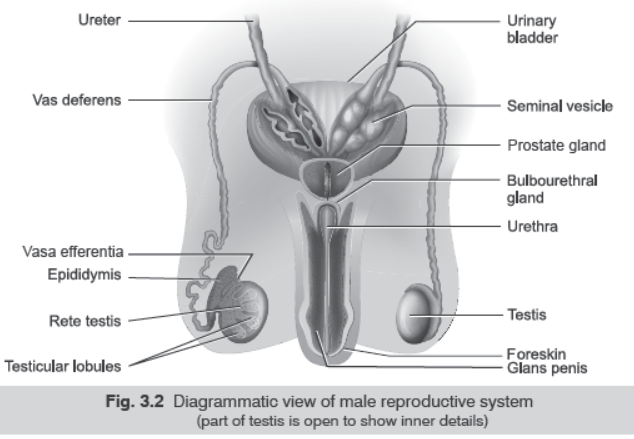
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Answer.
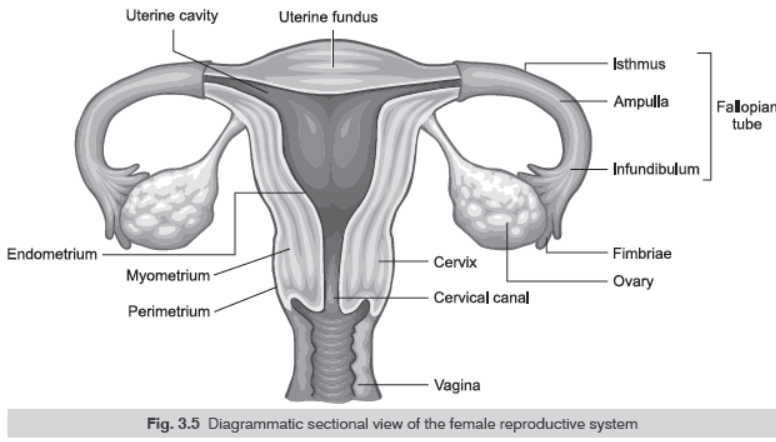
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of the human female reproductive system.
Answer.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Write the location and functions of myometrium and endometrium.
Answer. Endometrium is the inner layer of uterus. It assists in cyclic changes during menstruation and implantation of embryo.
Myometrium is the middle layer of uterus. It consist of smooth muscles and thus assists in contractions of the uterus during parturition.
Question. Where are fimbriae present in a human female reproductive system? Give their function.
Answer. The fimbriae are the finger-like projections present on the edges of infundibulum (fallopian tubes). They help in collection of ovum after ovulation.
Question. What is the number of chromosomes in the following cells of a human female?
(i) Primary oocyte (ii) Ootid
(iii) Secondary oocyte (iv) Follicle cells
Answer. (i) 46 (ii) 23
(iii) 23 (iv) 46
Question. Differentiate between menarche and menopause.
Answer. Menarche is the beginning of menstrual cycle at puberty. It starts at the age of 13−15 years.
Menopause is the cessation of menstrual cycle. It happens around 50 years of age.
Question. Corpus luteum in pregnancy has a long life. However, if fertilisation does not take place it remains active only for 10−12 days. Why?
Answer. This is because of a neural signal given by the maternal endometrium to its hypothalamus in presence of a zygote to sustain the gonadotropin (LH) secretion, so as to maintain the corpus luteum as long as the embryo remains there. In the absence of a zygote, therefore, the corpus luteum degenerates.
Question. Why does corpus luteum secrete large amount of progesterone during luteal/secretory phase of the menstrual cycle?
Answer. The hormone progesterone is essential for the maintenance of endometrium of the uterus. It maintains the endometrial lining of uterus so that the foetus may get implanted in the uterus. So, corpus luteum secretes large amounts of progesterone during the luteal phase of menstrual cycle.
Question. Mention the fate of corpus luteum and its effect on the uterus in absence of fertilisation of the ovum in a human female.
Answer. In the absence of fertilisation, corpus luteum degenerates and this causes disintegration of the endometrium of ovary, leading to menstruation.
Question. Women experience two major events in their life time, one at menarche and the second at menopause. Mention the characteristics of both the events.
Answer. Menarche represents the beginning of menstrual cycle which is an indication of attainment of sexual maturity. Menopause, on the other hand, refers to the cessation of menstruation which in turn means stoppage of gamete production, i.e., it marks the end of reproductive or fertile life of the female.
Question. Write the function of each of the following:
(a) Seminal vesicle
(b) Acrosome of human sperm.
Answer. (a) It is responsible for storage and transport of sperms. It provides secretions for motility and nourishment of sperms.
(b) It helps the sperm to enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum through the zona pellucida and provides enzymes for fertilisation.
Question. Name the cells that nourish the germ cells in the testes. Where are these cells located in the testes?
Answer. The cells that nourish the germ cells in the testes are called Sertoli cells. Sertoli cells are located in the germinal epithelium of the seminiferous tubules.
Question. Write the function of the seminal vesicle.
Answer. Seminal vesicle produces an alkaline secretion that helps to neutralise the acidic environment of the male urethra as well as that of female reproductive tract.
Question. Give reasons for the following :
The human testes are located outside the abdominal cavity.
Answer. The human testes are located outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. The scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes (2- 2.5°C) lower than the normal internal body temperature, necessary for spermatogenesis
Question. Why does failure of testes to descend into the scrotum produce sterility?
Answer. Sterility results because spermatogenesis requires a temperature 2–2.5°C lower than the internal body temperature, which is maintained by scrotum.
Question. What is the function of Leydig’s cells?
Answer. Leydig’s cells synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called androgens.
Question. Explain the role of Sertoli cells in the develop- ment of sperms.
Answer. Sertoli cells are present in between the germinal epithelial cells of the seminiferous tubules. They provide nourishment to the developing spermatozoa and also secrete androgen binding protein that concentrates testosterone in the seminiferous tubules.
Question. Where are the Leydig’s cells present? What is their role in reproduction?
Answer. Leydig’s cells or interstitial cells are small group of cells present between the seminiferous tubules in the connective tissue.
Question. Who discovered Sertoli cells? Mention their role in spermatogenesis.
Answer. Sertoli cells were discovered by Enrico sertoli, an Italian physiologist. He published a description of this cell in 1865. Sertoli cells provide nutrition to germ cells that undergo spermatogenesis to form spermatozoa.
Question. Differentiate between the location and function of Sertoli cells and Leydig’s cells.
Answer.
| Leydig’s cells (Interstitial cells) |
Sertoli cells (Sustentacular cells) |
| They are present in between the seminiferous tubules. |
They are present in between the germinal epithelial cells of the seminiferous tubules. |
| They are found in small groups and are rounded in shape. |
They are found singly and are elongated. |
Question. Write the function of (oviducal) fimbriae.
Answer. Fimbriae help in the collection of ovum, after ovulation.
Question. Explain the functions of myometrium and endometrium in human females.
Answer. Myometrium is middle thick layer of smooth muscles fibres that brings about contraction of the uterus during the delivery of the baby. The endometrium is the inner glandular layer that undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle.
Question. Mention the names and the characteristics of different uterine wall layers in humans. Which one of them undergoes cyclic changes during menstrual cycles?
Answer. The wall of the uterus is composed of three layers of tissues. The perimetrium is an outer thin covering of peritoneum. The myometrium is a middle thick layer of smooth muscle fibres which shows strong contraction during delivery of the baby. The endometrium is inner glandular layer that lines the uterine cavity. The endometrium undergoes cyclical changes during menstrual cycle.
Question. Where are fimbriae present in human female reproductive system? Give their function.
Answer. The edges of the infundibulum possess finger- like projections called fimbriae, which help in collection of the ovum after ovulation.
Question. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Answer. Functions of testis:
(i) It produces sperms (male gametes).
(ii) It secretes male sex hormones i.e., androgens
(e.g., testosterone). Functions of ovary :
(i) It produces ova (female gametes).
(ii) It secretes female sex hormones e.g., estrogen and progesterone.
Question. Name and explain the role of the inner and middle walls of the humans uterus.
Answer. The inner glandular wall of the uterus is known as endometrium.
Role - During the menstrual cycle, the endometrium wall grows into a thick, vascular (blood vessel-rich) glandular layer. This condition of the endometrium favours the implantation of the foetus. If fertilisation does not occur, the endometrium is shed during the hemorrhagic phase of the menstrual cycle.
The middle wall of the uterus is known as myometrium.
Role - It consists of smooth muscles. It exhibits contraction during delivery of the baby.
Question. When do the oogenesis and the spermatogenesis initiate in human females and males respectively?
Answer. Oogenesis begins during embryonic development stage while spermatogenesis begins during puberty.
Question. Mention the difference between spermato- genesis and spermiation.
Answer. The process of formation of sperms is called spermatogenesis while release of sperms from the seminiferous tubules is called spermiation.
Question. Write the function of acrosome of human sperm.
Answer. Acrosome contains enzymes called spermlysins that are used to contact and penetrate the ovum at the time of fertilisation
Question. Where is acrosome present in humans? Write its function.
Answer. Acrosome is present in the head of the human sperm.
Question. List the changes the primary oocyte undergoes in the tertiary follicular stage in the human ovary.
Answer. The primary oocyte grows in size and completes its fist meiotic division within the tertiary follicle.
Question. Define spermiogenesis. Where does it occur?
Answer. The process of transformation of spermatids into sperms is called spermiogenesis. It occurs in seminiferous tubules.
Question. Sperms have a tail whereas eggs do not. Why so?
Answer. Sperms are tailed whereas eggs do not as sperms have to move (tail helps in locomotion) through the cervix, uterus and Fallopian tube to reach to the egg already present there.
Question. Explain the events in a normal woman during her menstrual cycle on the following days:
(a) Ovarian event from 13-15 days
(b) Ovarian hormones level from 16 to 23 days
(c) Uterine events from 24 to 29 days
Answer. (a) During 13-15 days, FSH stimulates the ovarian follicle to secrete estrogens that further stimulate the proliferation of the endometrium of the uterine wall. On 14th day, LH surge causes ovulation.
(b) From 16 to 23 days, the corpus luteum secretes progesterone which is required for the maintenance of endometrium. In the absence of fertilisation, corpus luteum degenerates causing disintegration of endometrium leading to menstruation that takes 3-5 days.
(c) During 24 to 29 days (luteal phase of 15 to
28 days), the luteinising hormone (LH) is secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. LH causes ovulation. The remaining cell of the ovarian follicles are stimulated by the LH to develop corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone. Progesterone stimulates the uterine glands to produce increased amount of watery mucus. During the secretory phase, there is also similar increase in the secretion of watery mucus by the vaginal glands and by the glands of the Fallopian tubes. Progesterone is also essential for maintenance of the endometrium which is necessary for implantation of the fertilised ovum and other events of pregnancy. In the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates. This causes disintegration of the endometrium leading to menstruation marking a new cycle.
Question. Explain the events in a normal woman during her menstrual cycle on the following days :
(a) Pituitary hormone levels from 8 to 12 days.
(b) Uterine events from 13 to 15 days. (c) Ovarian events from 16 to 23 days.
Answer.
(a) From 8-12 days (follicular phase), the level of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) increase gradually and stimulate follicular development as well as secretion of estrogens by growing follicles.
(b) From 13 to 15 days, the endometrium becomes thicker by rapid cell multiplication and there is increase in uterine glands and blood vessels.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Question Bank
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Class 12 Biology
Chapter 2 Human Reproduction CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
Students can use the Chapter 2 Human Reproduction practice sheet provided above to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This solved questions and answers follow the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12 Biology. You can easily download the PDF format and solve these questions every day to improve your marks. Our expert teachers have made these from the most important topics that are always asked in your exams to help you get more marks in exams.
NCERT Based Questions and Solutions for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to create this practice material for students. After solving the questions our teachers have also suggested to study the NCERT solutions which will help you to understand the best way to solve problems in Biology. You can get all this study material for free on studiestoday.com.
Extra Practice for Biology
To get the best results in Class 12, students should try the Biology MCQ Test for this chapter. We have also provided printable assignments for Class 12 Biology on our website. Regular practice will help you feel more confident and get higher marks in CBSE examinations.
You can download the teacher-verified PDF for CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Question Bank from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets for Class 12 Biology are designed as per the latest CBSE academic session.
Yes, our CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Question Bank includes a variety of questions like Case-based studies, Assertion-Reasoning, and MCQs as per the 50% competency-based weightage in the latest curriculum for Class 12.
Yes, we have provided detailed solutions for CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Question Bank to help Class 12 and follow the official CBSE marking scheme.
Daily practice with these Biology worksheets helps in identifying understanding gaps. It also improves question solving speed and ensures that Class 12 students get more marks in CBSE exams.
All our Class 12 Biology practice test papers and worksheets are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format. You can access CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Question Bank without any registration.

