MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. Which one of the following pairs of geographical areas show maximum biodiversity in our country ?
(a) Sunderbans and Rann of Kutch
(b) Eastern Ghats and West Bengal
(c) Eastern Himalaya and Western Ghats
(d) Kerala and Punjab.
Answer. C
Question. If the high altitude birds become rare or extinct, the plants which may disappear along with them are
(a) pine
(b) oak
(c) orchids
(d) Rhododendrons
Answer. B
Question. The Montreal protocol refers to
(a) persistent organic pollutants
(b) global warming and climate change
(c) substances that deplete the ozone layer
(d) biosafety of genetically modified organisms
Answer. C
Question. A tree species in Mauritus failed to reproduce because of the extinction of a fruit-eating bird.Which one of the following was that bird?
(a) Dove
(b) Dodo
(c) Condor
(d) Skua
Answer. B
Question. The map given below indicates the former and the present distribution of an animal.
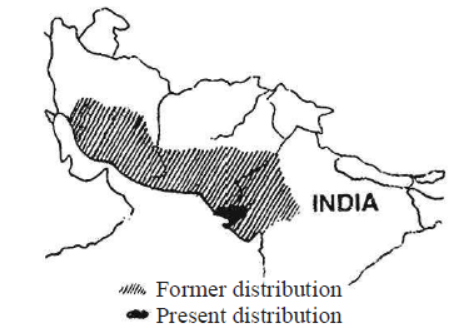
Which animal could it be?
(a) Wild ass
(b) Nilgai
(c) Black buck
(d) Lion
Answer. A
Question. Tectonic is the study of
(a) volcanos
(b) earth’s crust
(c) sand dunes
(d) Sun
Answer. B
Question. If the Bengal tiger becomes extinct
(a) Hyenas and wolves will become scare
(b) The wild area will be safe for man and domestic animals
(c) Its gene pool will be lost for ever
(d) The population of beautiful animals like deers will be stabilized.
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following is considered a hot-spot of biodiversity in India ?
(a) Indo-Gangetic Plain
(b) Eastern Ghats
(c) Aravalli Hills
(d) Western Ghats
Answer. D
Question. The largest Tiger reserve in India is
(a) Nagarhole
(b) Valmiki
(c) Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
(d) Periyar
Answer. C
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : Tropical rain forests are disappearing fast from developing countries such as India.
Reason : No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Diversity observed in the entire geographical area is called gamma diversity.
Reason : Biodiversity decreases from high altitude to low altitude.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : A sanctuary is formed for the conservation of animals only.
Reason : Restricted human activities are allowed in sanctuaries.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion: Communities that comprise of more species tend to be more stable.
Reason: A higher number of species results in less animal variation in total biomass
Answer. A
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Name any two sanctuaries in India.
Answer. Keoladeo Ghana bird sanctuary, Bharatpur (Rajasthan) and Periyar sanctuary (Kerala).
Question. What is Red Data Book?
Answer. The Red Data Book is a compilation of data on species threatened with extinction and is maintained by IUCN.
Question. About 200 species of Cichlid fish became extinct when a particular fish was introduced in Lake Victoria of Africa. Name the invasive fish.
Answer. Nile perch.
Question. What is the expanded form of IUCN?
Answer. International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources.
Question. Why is genetic variation important in the plant Rauwolfia vomitoria?
Answer. Genetic variation affects the variation in potency and concentration of the drug reserpine in the medicinal plant Rauwolfia.
Question. What are Ramsar sites?
Answer. Ramsar sites are conserved wetlands which are of international importance.
Question. Western Ghats have a greater amphibian diversity than the Eastern Ghats. What do you infer from the above two statements?
Answer. It can be inferred that Western Ghats have a greater species diversity.
Short Answer Questions
Question. What is the ecological importance of biodiversity?
Answer. The ecological importance of biodiversity:
(i) Biodiversity is required for maintaining and sustainable use of goods and services from ecosystem.
(ii) Various insects help in pollination.
(iii) Various micro-organisms help in the decomposition of organic matter thereby increasing the soil fertility and cleaning the environment.
(iv) Various drugs and medicines are extracted from plants.
Question. In the biosphere immense biological diversity exists at all levels of biological organisation. Explain any two levels of biodiversity.
Answer. Genetic diversity
• It is the measure of variety in genetic information contained in the organisms over its distributional range.
• It enables a population to adapt to its environment.
• For example, medicinal plant Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in Himalayan ranges shows variation in potency and concentration of the active chemical reserpine that it produces.
• There are more than 50,000 genetically different strains of rice and 1,000 varieties of mango in India.
(ii) Species diversity
• It is a measure of the variety of species and their relative abundance present within a region.
• For example, the Western Ghats have a greater amphibian species diversity than the Eastern Ghats.
Question. What is the significance of the slope of regression in a species–area relationship?
Answer. Slope of regression in a species–area relationship indicates that species richness decreases with the decrease in area. Regression coefficient (Z) is 0.1–0.2 regardless of the taxonomic group or the region. However, when very large areas like the entire continent is analysed, it was found that slope of the line is much steeper with Z values in the range of 0.6 – 1.2.
Question. Which region/biome in the world is considered as the ‘Lungs of the planet’? Give two reasons for its degradation.
Answer. The Amazon rain forests are considered as the lungs of the planet. They are cut and cleared for cultivation of soya beans. Some part has been converted into grass lands for raising beef cattle.
Question. Why are certain regions on the Earth called hot-spots? Name any two hot-spots in India.
Answer. Certain regions have been declared as “hot spots” for maximum protection of these regions which have high levels of species richness and high degree of endemism.
Western Ghats and Sri Lanka and Himalayas are two example of hot-spots.
Question. Why are conventional methods not suitable for the assessment of biodiversity of bacteria?
Answer. Many bacteria are not culturable under normal condition in the laboratory. This becomes a problem in studying their morphological, biochemical and other characterisations which are useful for their assessment. Thus conventional methods are not suitable.
Question. List the features that make a stable biological community.
Answer. Features of a stable biological community are as follows:
(i) Communities should have greater biodiversity for greater stability.
(ii) It should be able to prevent invasion by alien species.
(iii) It should be able to restore itself in a short period of time.
(iv) Variations should be minimal in the community.
Question. Write any three hypotheses put forth by ecologists explaining the existence of greater biodiversity in tropical regions than in temperate regions.
Answer. The three hypotheses to explain species richness in tropics are:
(i) The constant environment in tropics promotes niche specialisation and increased species diversity.
(ii) There is longer exposure to solar radiation in the tropical regions that contributes directly to higher productivity and indirectly to greater species diversity.
(iii) There occurred no glaciation in tropical region and it remained undisturbed. Thus organisms living in tropics continued to flourish and evolved more species diversity.
Question. Where would you expect more species biodiversity— in tropics or in polar regions? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Answer. More biodiversity is found in the tropics. This is because tropical regions remain undisturbed from frequent glaciations as in polar regions. Also, the tropics are less seasonal/more constant.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Explain the effect on the characteristics of a river when urban sewage is discharged into it.
Answer. —Rise in organic matter, leads to increased microbial activity/growth of microbes.
—It results in decrease in dissolved oxygen/rise in Biochemical Oxygen Demand.
—Leads to fish mortality/algal bloom/colour change/foul odour/increase in toxicity. (Any two)
Question (a) What are the two types of desirable approaches to conserve biodiversity? Explain with examples bringing out the difference between the two types.
(b) What is the association between the bumble bee and its favourite orchid Ophrys? How would extinction or change of one would affect the other?
Answer. (a) (i) In situ conservation (On site conservation)
This approach involves protection of species in their natural habitat.
(ii) Ex situ conservation (Off-site conservation)
• This approach involves placing threatened animals and plants in special care units for their protection.
• India has 35 botanical gardens and 275 zoological parks where animals which have become extinct in wild are maintained.
(b) Commensalism because Ophrys employs sexual deceit to get pollination by species of bee as petal of its flower bears resemblance to female of the bee in size, colour and markings and so male bee is attracted to what it perceives as female; pseudo copulates with the flower and thus pollinates it. If the female bee’s colour patterns change even slightly due to any reason during evolution, pollination success will be reduced unless the orchid flower co-evolves to maintain the resemblance of its petal to the female bee.
Question. Why should biodiversity be conserved? List any two ethical arguments in its support.
Answer. The biodiversity should be conserved because of the following reasons: (Any two)
(i) Narrowly utilitarian arguments for deriving direct economic benefit from nature.
(ii) Broadly utilitarian arguments as biodiversity plays a major role in many ecosystem services.
(iii) Ethical reasons: There is a need to realise that every species has an intrinsic value and we need to pass on our biological legacy to future generations.
Question. (a) Taking one example each of habitat loss and fragmentation, explain how are the two responsible for biodiversity loss.
(b) Explain two different ways of biodiversity conservation.
Answer. (a) • There are four major causes of biodiversity loss. These are also known as ‘The Evil Quartet’.
(i) Habitat loss and fragmentation
• Destruction of habitat is the primary cause of extinction of species.
• The tropical rainforests initially covered 14 per cent of the land surface of earth, but now cover only 6 per cent of land area.
• The Amazon rainforest (called the “lungs of the planet”) is being cut and cleared for cultivation of soya beans and for conversion into grasslands for raising beef cattle.
• When large-sized habitats are broken or fragmented due to human settlements, building of roads, digging of canals, etc., the population of animals requiring large territories and some animals with migratory habitats declines.
(b) In situ conservation (On site conservation)
This approach involves protection of species in their natural habitat.
(a) Biodiversity hotspots
• These are regions of high levels of species richness and high degree of endemism.
• Endemic species are species confined only to a limited region.
• There are 34 hotspots in the world.
• In India, the three hotspots are Western Ghats and Sri Lanka, Indo–Burma and Himalaya.
• Biodiversity hotspots cover less than 2% of earth’s land area, but they harbour large number of species. Thus, they could reduce mass extinction by 30%.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity And Conservation Question Bank

