Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Worksheet Set C. Download printable Biology Class 12 Worksheets in pdf format, CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Worksheet has been prepared as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Also download free pdf Biology Class 12 Assignments and practice them daily to get better marks in tests and exams for Class 12. Free chapter wise worksheets with answers have been designed by Class 12 teachers as per latest examination pattern
Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Biology Worksheet for Class 12
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf in Class 12. This test paper with questions and solutions for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for tests and exams and help you to score better marks
Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Worksheet Pdf
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. Azolla is used as a biofertilizer because it
(a) multiplies very fast to produce massive biomass
(b) has association of nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium
(c) has association of nitrogen-fixing Cyanobacteria
(d) has association of mycorrhiza
Answer. C
Question. Pruning of plants promotes branching because the axillary buds get sensitized to
(a) ethylene
(b) gibberellin
(c) cytokinin
(d) indole acetic acid
Answer. C
Question. Somaclonal variation can be obtained by
(a) application of colchicine
(b) irradiation with gamma rays
(c) tissue culture
(d) hybridisation
Answer. C
Question. Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab by one of the breeding technique in which superior male of one breed is mated with superior females of another breed.
Identify the breeding technique from the option given below.
(a) Inbreeding
(b) Out crossing
(c) Out breeding
(d) Cross breeding
Answer. D
Question. The chemical which are produced by host plantsdue to infection as a defence reaction to pathogen, are called
(a) phytotoxin
(b) toxin
(c) phytotron
(d) phytoalexins
Answer. D
Question. Biodiversity loss occurs due to the reasons given below.
(i) Habitat loss and fragmentation
(ii) Co-extinction
(iii) Over-exploitation
(iv) Alien species invasion
Identify the correct reasons.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer. D
Question. In an experiment freshly hatched larvae of an insect (Khapra beetle) were reared on a basal diet (complete diet without cholesterol) with increasing amounts of cholesterol. Results obtained are shown in the given graph.
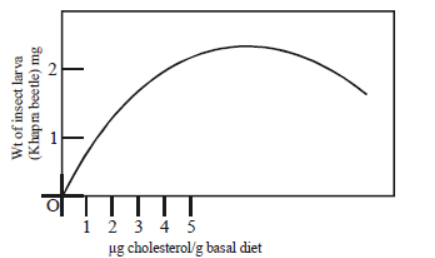
The graph indicates
(a) cholesterol is an essential dietary requirement of khapra beetle.
(b) growth of khapra beetle is directly proportional to cholesterol concentration.
(c) cholesterol concentration of 2 μg/g diet is the optimum level.
(d) growth of khapra beetle is inhibited when cholesterol concentration exceeds 5 μg/g diet.
Answer. A
Question. Essential oils are those which
(a) are essential to the plant itself
(b) are used as lubricants
(c) produce perfumes
(d) are essential for human beings
Answer. C
Question. Coconut water is rich in
(a) auxins
(b) gibberellins
(c) abscisic acid
(d) cytokinin
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is the pair of biofertilizers?
(a) Azolla and BGA
(b) Nostoc and legume
(c) Rhizobium and grasses
(d) Salmonella & E. coli
Answer. A
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following five responses.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
(e) If the Assertion is incorrect but the Reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : In plant tissue culture somatic embryos can be induced from any plant cell.
Reason : Any viable plant cell can differentiate into somatic embryos.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Use of fertilizers greatly enhances crop productivity.
Reason : Irrigation is very important in increasing crop productivity.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Fish meal is a rich source of protein for cattle and poultry.
Reason : Fish meal is produced from non-edible parts of fishes like fins, tail etc.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Cattle breeds can be improved by super ovulation and embryo transplantation.
Reason : Superovulation in high milk-yielding cows is induced by hormonal injection.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion (A) : Vernalization is acceleration of subsequent flowering by low temperature treatment.
Reason (R) : Site of vernalization is apical meristem.
Answer. B
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Name the following:
(a) The semi-dwarf variety of wheat which is high-yielding and disease-resistant.
(b) Any one inter-specific hybrid mammal.
Answer. (a) Kalyan Sona/Sonalika
(b) Mule/Hinny/Liger/Tigon
Question. Select two disease resistant crop varieties from the list of crop varieties given below: Himgiri, Pusa Gaurav, Pusa Komal, Pusa A-4
Answer. Himgiri; Pusa Komal
Question. What can be used as the reference material for comparison of any new improved variety?
Answer. The best available local cultivar.
Question. Identify two correct statements from the following:
(i) Apiculture means apical meristem culture.
(ii) Spinach is iron-enriched.
(iii) Green revolution has resulted in improved pulse-yield.
(iv) Aphids cannot infest rapeseed mustard.
Answer. (ii) and (iv) are correct.
Question. A herd of cattle is showing reduced fertility and productivity. Provide one reason and one suggestion to overcome this problem.
Answer. Inbreeding depression or continuous inbreeding may be the reason of reduced fertility and productivity. To overcome this, the cattle should be mated with unrelated superior cattle of the same breed.
Short Answer Questions
Question. If your family owned a dairy farm, what measures would you undertake to improve the quality and quantity of milk production?
Answer. The following efforts need to be put in:
(i) The cattle in the dairy farm must be housed and fed properly.
(ii) Cleanliness should be maintained in the milking area.
(iii) The health of the dairy cattle should be of utmost importance and a veterinary doctor must visit regularly.
(iv) Regular inspections of the farm, maintaining records, identification and rectification of problems should be done along with maintaining precautionary measures.
(v) Milking should be done in a dirt-free area and all the sanitary conditions should be maintained.
(vi) High-yielding and disease-resistant breeds can be selec tetod maximis ebenefits.
Question. List the two steps that are essential for carrying out artificial hybridisation in crop plants and why.
Answer. (a) Selection of parents: Only those plants should be selected which have desired traits.
(b) Crossing over: Pollen grains from selected male plant is collected and transferred to the female plant after which it is bagged.
Question. Briefly describe various steps involved in plant breeding.
Answer. • Earlier methods of plant breeding involved crossing or hybridising pure lines, followed by artificial insemination to produce plants of desirable traits.
• The major steps in breeding a new genetic variety of a crop are as follows:
(i) Collection of variability
• Genetic variability is the root of any breeding programme.
• Pre-existing genetic variability is collected from wild varieties, species and relatives of the cultivated crop species.
• These are evaluated for their characteristics and preserved for effective exploitation of the natural genes.
• The entire collection of diverse alleles for all genes in a given crop is called germplasm collection.
Question. Name the improved characteristics of wheat that helped India achieve green revolution.
Answer. (i) Semi-dwarf nature
(ii) Quick yielding feature
(iii) High yielding feature
(iv) Disease resistant feature
Question. “Artificial insemination helps overcome several problems of normal mating in cattle”. Do you agree? Support your answer with any three reasons.
Answer. This statement is completely justified.
(i) It helps in selective breeding in animals.
(ii) Semen of a single bull can be used to impregnate several females.
(iii) Quality semen is available in preserved form all the time at all places.
(iv) Frozen semen can be exported or imported. It is the most reliable method.
(v) It does not spread contagious diseases.
Question. What is apiculture? How is it important in our lives?
Answer. Apiculture is the rearing, caring and management of honeybees for obtaining honey and wax.
Importance:
(i) It produces beeswax, used in the industry for making cosmetics, polishes, etc.
(ii) Honey has high nutritive value.
(iii) Bees act as pollinators of many crop species like sunflower, Brassica, etc, and thus increases crop yield.
Question. What is outbreeding? Mention any two ways it can be carried out.
Answer. Outbreeding refers to the breeding of unrelated animals either of the same breed but not having common ancestors or of different breeds or even different species.
It can be carried out by:
(i) Outcrossing
(ii) Cross-breeding
(iii) Interspecific hybridisation
Question. Differentiate between outbreeding and outcrossing.
Answer. Outbreeding is breeding of unrelated animals (having no ancestors for 4–6 generations) belonging to same breed or different breeds or different species.
Outcrossing is breeding within the animals of same breed having no common ancestors for 4–6 generation on either side of the pedigree.
Question. What kind of areas are suitable for practicing apiculture? Write the scientific name of the variety commonly reared for the purpose.
Answer. Bee pastures of wild shrub, fruit orchards and cultivated crop are suitable for practicing apiculture.
The commonly reared variety for this purpose is Apis indica.
Question. Name any two common Indian millet crops. State one characteristic of millets that has been improved as a result of hybrid breeding so as to produce high yielding millet crops.
Answer. Maize, jowar, bajra (Any two) Resistant to water stress has been improved.
Question. Give two examples of biofortified crops. What benefits do they offer to the society?
Answer. Maize, wheat, rice, bathua, spinach, pulses have biofortified varieties. Maize hybrids have twice the amount of amino acids, fortified wheat variety has high protein content, fortified rice has high quantity of iron. Consumption of such biofortified foods will enrich the nutritive value of our common foods and will vastly improve public health. It may even help overcome several nutrient deficiency disorders latent in our country.
Question. Enumerate four objectives for improving the nutritional quality of different crops for the health benefits of the human population by the process of “Biofortification”.
Answer. (i) Improving protein content and quality.
(ii) Improving oil content and quality.
(iii) Improving vitamin content and quality.
(iv) Improving micronutrient or mineral content.
Question. Scientists tried to develop a single plant exhibiting the characteristic of tomato and potato by using cells from tomato and potato plants respectively. Name the procedure and list the steps to achieve this.
Answer. The procedure followed by the scientists is somatic hybridisation.
It involves isolation of protoplast of tomato cell and potato cell having desirable character. These protoplasts fused to get hybrid protoplast which was further grown to form a new plant.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Explain the importance of “selection” during inbreeding in cattle.
Answer. Selection during inbreeding helps in accumulation of superior genes and elimination of less desirable genes. It increases homozygosity, pure lines, true breeding and helps to restore fertility.
It also helps to increase yield or productivity. The cattle produces more milk per lactation, produces superior progeny and produces disease resistant breeds.
Question. Expand MOET. Explain the procedure of this technology in cattle improvement.
Answer. MOET stands for Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology.
Procedure
(i) A cow is administered hormones with FSH-like activity to induce follicular maturation and super-ovulation.
(ii) The cow produces i6n−s 8te aodnoeef eggggs produ ncoerdmally.
(iii) It noisw , ei ther ma wteidth an elite bour lal rtificial inseminatio n cairs roieudt.
(iv) When the fertilised eggs attain 8−32 cells stage, they are non-surgically removed and transferred to a surrogate mother.
(v) The genetic mother can now be again super-ovulated.
Question. (a) Name the Indian scientist whose efforts brought ‘green revolution’ in India.
(b) Mention the steps that are essentially carried out in developing a new genetic variety of crop under plant breeding programme.
Answer. (a) M.S. Swaminathan brought green revolution in India.
(b) The steps are:
(i) Collection of variability.
(ii) Evaluation and selection of parents.
(iii) Cross hybridisation among the selected parents.
(iv) Selection and testing of superior recombinants.
(v) Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars.
Q. 10. Name the technique and the property of plant cells that can help to grow somaclones of certain desired variety of apple. Explain how somaclones of apple can be obtained in the lab so as to get the desired variety on a large scale.
Ans. Tissue Culture or micropropagation can help grow somaclones because of the property of totipotency in plant cells.
Explants of apple plant (any small part) is taken and grown in a test tube under sterile conditions in (special) nutrient media. The nutrient media contains sucrose, inorganic salts, amino acids and vitamins, with growth regulators.
Question. (a) What is micropropagation? Why are the plants produced by micropropagation called somaclones?
(b) Name the technique by which healthy plants can be recovered from the diseased plants.
Answer. (a) Micropropagation is the method of growing a number of plants through tissue culture. Since tissue culture involves only mitotic divisions, the plantlets formed are genetically identical and hence are called somaclones.
(b) Meristem culture.
Question. Explain the process of artificial hybridisation to get improved crop variety in (i) plants bearing bisexual flowers (ii) female parent producing unisexual flowers.
Answer. (i) In plants bearing bisexual flowers, the anthers are removed from the flower before they dehisce. This is called emasculation. The emasculated flowers are covered with a bag of
butter paper to prevent contamination of stigma with unwanted pollen. This process is called bagging. When this stigma attains receptivity, mature pollen grains are dusted on the stigma and the flowers are rebagged to allow the fruits to develop.
(ii) If the female parent produces unisexual flowers, there is no need of emasculation. The flower buds are bagged before the flowers open. When the stigma becomes receptive, pollen is dusted ons tigma and t hfleower isr ebagged.
Question. (a) Write the desirable characters a farmer looks for in his sugarcane crop.
(b) How did plant breeding techniques help north Indian farmers to develop cane with desired characters?
Answer. (a) The desirable characters for a sugarcane crop are high yield, thick stem, high sugar content and ability to grow in their areas.
(b) Saccharum barberi had poor sugar content and yield but Saccharum officinarum had thicker stems and higher sugar content but it could not be grown in northern India. By crossing
Saccharum officinarum, the south Indian variety with Saccharum barberi, the north Indian low yield variety, the farmers developed cane having desired characteristics.
Question. Differentiate between somaclones and somatic hybrids. Give one example of each.
Answer.
| S. No. | Somaclones | Somatic hybrids |
| (i) | These are genetically identical to the original plant from which they are grown. |
These are formed by fusion of somatic protoplasts obtained from different varieties or species of plant. |
| (ii) | These are produced by tissue culture or micropropagation. |
These are produced by somatic hybridisation. |
| (iii) | Example: Tomato, banana, etc. |
Example: Pomato formed by fusion of tomato and potato. |
Question. State the economic value of Saccharum officinarum in comparison to S.barberi.
Answer. Saccharum officinarum has higher sugar content and its stems are thicker, while Saccharum barberi has poor sugar content and yield.
Question. Name any two diseases the ‘Himgiri’ variety of wheat is resistant to.
Answer. Himgiri variety of wheat is resistant to leaf and stripe rust and Hill bunt diseases.
Question. Write the names of two semi-dwarf and high yielding rice varieties developed in India after 1966.
Answer. Jaya and Ratna
Question. State the importance of biofortification.
Answer. Biofortification is the breeding of crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher proteins and healthier fats, to improve the public health by practical means.
Question. Suggest the breeding method most suitable for animals that are below average in milk productivity.
Answer. Outcrossing is the most suitable breeding method for animals that are below average in milk productivity. It is the mating of animals within the same breed but having no common ancestors on either side of their pedigree upto 4-6 generations.
Question. Write an alternate source of protein for animal and human nutrition.
Answer. The alternate source of protein for animal and human nutrition is single cell protein (SCP).
Question. What is economic value of Spirulina?
Answer. Spirulina is a microorganism (blue green algae), which is used as human food rich in protein, minerals, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins.
Question. What is single cell protein? How is it produced?
Discuss its importance. In what ways is it useful to humans?
Answer. The microorganisms such as bacteria, yeasts, filamentous algae, are treated in various ways to be used as food and are called single cell protein (SCP). The term SCP does not indicate its actual meaning because the biomass is not only obtained from unicellular microorganisms but also from multicellular microorganisms. Microbes like Spirulina can be grown on waste water from potato processing plants (containing starch), straw,
molasses, animal manure and even sewage, to produce food rich in proteins, minerals, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins. Commercial production of SCP is mostly based on yeasts and some other fungi. Advantages of SCP are as follows:
(i) It provides a protein rich supplement in human diet.
(ii) It reduces the pressure on agricultural production systems for the supply of the required proteins.
(iii) SCP production is based on industrial effiuents so it helps to minimise environmental pollution.
Question. Identify the two correct statements from the following :
(a) Apiculture means apical meristem culture.
(b) Spinach is iron-enriched.
(c) Green revolution has resulted in improved pulse-yields.
(d) Aphids cannot infest rapeseed mustard.
Answer. Statement (b) and (d) are correct.
Question. Why is the enzyme cellulase used for isolating genetic material from plant cells but not for animal cells?
Answer. Cellulase enzyme digests cellulose present in cell wall of plant cells. As animal cell does not possess cell wall hence cellulase enzyme is not used in case of animal cell.
Question. (a) Why are the plants raised through micropropagation termed as somaclones?
(b) Mention two advantages of this technique.
Answer. (a) Micropropagation is the tissue culture technique used for rapid vegetative multiplication of ornamental plants and fruit trees by using small explants. This method of tissue culture produces several plants. Each of these plants is genetically identical to the original plant from which they were grown. Hence, plants obtained by micropropagation constitute a somaclone.
(b) Advantages of micropropagation are : (i) A large number of plantlets are obtained within a short period and in a small space. (ii) The rare plants and endangered species are multiplied by this method and such plants are saved.
Question. (a) Write the two limitations of traditional breeding technique that led to promotion of micropropagation.
(b) Mention two advantages of micropropagation.
(c) Give two examples where it is commercially adopted.
Answer. (a) Two limitations of traditional breeding techniques that led to promotion of micropropa- gation are :
(i) They have limited production therefore it failed to keep pace with the demand.
(ii) They were unable to provide sufficiently fast and efficient system for crop improvement.
(b) Two advantages of micropropagation are :
(i) It helps in producing thousands of plants from a single plant in very short duration.
(ii) It is useful in the recovery of healthy plant from a virus infected plant.
(c) Commercial production of ornamental plants like lily, orchids, eucalyptus and fruits like tomato, apple, banana etc. is commenced through micropropagation. Sterile plants or plants which cannot maintain their characters by sexual reproduction can be multiplied by this method.
Question. A sugarcane has been affected by virus. How can a virus free cane be developed from it? Explain the procedure.
Answer. A virus-free sugarcane can be obtained from infected sugarcane plant by meristem culture. Although, the plant is infected with a virus, yet the meristem is free of virus. It is because meristem is a localised group of actively dividing cells, hence virus cannot invade them. Meristem culture involves the use of explants like shoot tips and nodal segments. The explant or shoot tip is grown in a test tube under sterile conditions on a medium containing a cytokinin (generally BAP). The plantlets of sugarcane thus obtained are subjected to hardening and ultimately established in the field. Thus, cane plants obtained are free of virus.
Question. Mention the property of plant cells that has helped them to grow into a new plant in invitro conditions. Explain the advantages of micropropagation.
Answer. Totipotency is the property by which whole plant is regenerated from any cell or explant in in vitro condition.
Question. Scientists have succeeded in recovering healthy sugarcane plants from a diseased one.
(a) Name the part of the plant used as explant by the scientists.
(b) Describe the procedure the scientists followed to recover the healthy plants.
(c) Name this technology used for crop improvement.
Answer. (a) Explant used by scientists in this case could be any meristematic cell or tissue viz. shoot tip or nodal segment.
(b) Procedure followed by scientists to recover healthy plants is :
– Preparation of suitable nutrient medium as per objective of culture.
– Selection of explants such as shoot tip.
– Sterilisation of explants with disinfectants.
– Inoculation of the explant into nutrient medium under sterile condition.
– Incubating the culture under appropriate physical conditions i.e., artificial light (16 hours of photoperiod), temperature (–26°C) and relative humidity (50-60%):
– Regeneration of plants from cultured plant tissues.
– Hardening of plantlets
– Transfor of regenerated plantlets to the greenhouse or field conditions.
(c) Plant tissue culture (micropropagation)
Question. A banana herb is virus-infected. Describe the method that will help in obtaining healthy banana plants from this diseased plant.
Answer. case of asexually reproducing crops like banana, virus infections spread rapidly. This is because the vegetative propagules from virus-infected plants contain virus particles. But the shoot apical meristems and some young tissues surrounding them are often free from viruses. Meristem culture, therefore, is often useful in recovering virus-free plants from virus-infected plants or clones.
The explants commonly used in meristem culture are shoot tips and nodal segments. These explants are cultured on a medium containing a cytokinin (generally BAP). The plantlets thus obtained are subjected to hardening and, ultimately, established in the field.
Question. (a) Name the technology that has helped scientists to propagate on a large scale the desired crops in a short duration. List the steps carried out to propagate the crops by the said technique.
(b) How are somatic hybrids obtained?
Answer. (a) The technique that has helped scientists to propagate the desired crops in short duration is called tissue culture or micropropagation.
Plant tissue culture can be defined as the technique of maintaining and growing of plant cells, tissues and organs on a suitable culture medium in vitro under controlled environmental conditions.
The basic technique of plant tissue culture involves the following steps :
(i) Preparation of suitable nutrient medium and storage into suitable containers.
(ii) Selection of explants such as shoot tip and sterilisation by disinfectants.
(iii) Inoculation (transfer) of the explants into the suitable nutrient medium under sterile conditions.
(iv) Growing the culture in the growth chamber or plant tissue culture room, having the appropriate physical conditions i.e., artificial light (16 hours of photoperiod), temperature (–26°C) and relative humidity (50- 60%).
(v) Regeneration of plants from cultured plant tissues and hardening.
(vi) Transfer of plantlets to the greenhouse or field conditions following acclimatisation of regenerated plants.
(b) Isolated naked protoplasts from two different varieties of plants each having a desirable character can be fused to get hybrid protoplasts, which can be further grown to form new plant. These hybrids obtained are called somatic hybrids.
Question. What is somatic hybridisation ? Explain the various steps involved in the process. Mention any two uses of somatic hybridisation.
Answer. Somatic hybridisation is the process of fusing protoplasts of somatic cells derived from different varieties or species of plants, on a suitable nutrient/ culture medium, to produce a somatic hybrid. Pomato is a somatic hybrid between tomato and potato.
Steps involved in somatic hybridisation are :
– Removal of cell wall of the fusing cells by digestion with a combination of pectinase and cellulase; which results in the formation of protoplasts.
– Fusion between protoplasts of selected parents induced by the use of polyethylene glycol (PEG) or a very brief high voltage electric current.
– These are cultured on a suitable medium, regenerate cell walls and begin to divide to produce plantlets which are the somatic hybrids.
Process of somatic hybridisation can be illustrated by the following figure.
Question. What is meant by the term breed ? What are the objectives of animal breeding?
Answer. A group of animals related by descent and similar in most characters like general appearance, features, size, configuration etc, is called a breed.
The main objectives of animal breeding are :
(i) To produce high yielding varieties of animals like high milk producing varieties in cattle, more egg producing varieties in chicken, more wool bearing varieties in sheep etc.
(ii) To produce draught or powerful varieties for doing work like in cattle, buffaloes, etc.
(iii) To produce disease resistant varieties in many of the livestocks.
Question. (a) Name any two fowls other than chicken reared in a poultry farm.
(b) Enlist four important components of poultry farm management.
Answer. (a) Poultry is rearing of domesticated fowl (birds) used for their meat and eggs. Two fowls reared in a poultry farm other than chicken are ducks and turkeys.
(b) Important components of poultry farm management are as follows :
(i) Selection of disease free and suitable breeds
(ii) Proper and safe farm conditions
(iii) Proper feed and water
(iv) Hygeine and healthcare
Question. Enumerate any six essentials of good, effective dairy farm management practices.
Answer. Six essentials of good, effective dairy farm management practices are:
(i) Animals should be kept in a well - ventilated shed with a pucca floor and a proper drain channel. (ii) Cows should be milked gently, quickly, fully and hygienically.
(iii) Shed should be disease free.
(iv) In summer, adequate amount of fresh and clean drinking water should be provided. Sprinkling of water in the shed also reduces the heat stress.
(v) In winter and during rains, the animals should be kept under cover especially at night.
(vi) Regular visit by a veterinary doctor is be mandatory.
Question. High yielding cattle is a good solution for food enhancement. How does the MOET technology help to increase the herd size ?
Answer. Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Techno- logy (MOET) is a programme for herd size improvement. In this method, hormones (with FSH-like activity) are given to the cow for inducing follicular maturation and superovulation i.e., instead of one egg, which they usually give per cycle, they produce 6-8 eggs. The cow is either mated with the best bull or artificially inseminated. The embryos at 8-32 celled stages are recovered and transferred to surrogate mothers. The genetic mother is available for another super ovulation. MOET has been done in cattle, sheep, rabbits, buffaloes, mares etc. High milk giving breeds of females and high quality meat (lean meat with less lipid) giving bulls have been bred successfully to obtain better breed in a short time.
Question. Differentiate between inbreeding and outbreeding in cattle. State one advantage and one disadvantage for each one of them.
Answer. When breeding is done between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations, it is called inbreeding. Outbreeding is the breeding between the unrelated animals which may be between individuals of the same breed (but having no common ancestor for 4-6 generations) i.e., outcrossing or between different breeds (crossbreeding) or different species (interspecific hybridisation).
Advantages : (i) Inbreeding increases homozygosity. It also helps in accumulation of superior genes and elimination of less desirable genes.
(ii) Outbreeding is the best breeding method for animals that are below average in productivity in milk production, growth rate in beef and cattle. Disadvantages : (i) Continued inbreeding reduces fertility and even productivity. This is called inbreeding depression. (ii) Outbreeding leads to elimination of recessive characters whereas desired combinations of characters may appear in low frequency.
Very Short Answer
Question. Define biofortification?
Answer. Biofortification is the idea of breeding crops to increase their nutritional value. This can be done either through conventional selective breeding, or through genetic engineering.
Question. Define breed?
Answer. A breed is a specific group of domestic animals having homogeneous appearance homogeneous behaviour, and other characteristics that distinguish it from others.
Question. What is totipotency?
Answer. The capacity to generate a whole plant from any cell or explant is called totipotency.
Question. What is poultry?
Answer. Poultry is the class of domesticated fowl used for food or for their eggs.
Question. What are the major roles in our efforts to increase the food production?
Answer. Biological principles as applied to animal husbandry and plant breeding have a major role in our efforts to increase food production.
Short Answer
Question. What do you understand by the inbreeding depression?
Answer. Inbreeding depression is the reduced biological fitness in a given population as a result of inbreeding, or breeding of related individuals. Population biological fitness refers to an organism's ability to survive and perpetuate its genetic material. Inbreeding depression is often the result of a population bottleneck.
Question. What do you mean by poultry farm management?
Answer. Poultry farm management usually refers to the husbandry practices or production techniques that help to maximize the efficiency of production. Poultry farm management aims at maximizing returns with minimum investment.
Question. Define animal husbandry?
Answer. Animal husbandry helps us in developing high yielding breeds of various domestic animals through cross breeding. Thus, animal husbandry increases the availability of various food products such as milk, eggs and meat, which are obtained from domestic animals.
Question. What do you understand by the dairy farm management?
Answer. Dairy farm Management enables experts to relentlessly work towards making dairy products reach almost each and every household of India, effortlessly and like
clockwork. Running and managing a dairy needs immaculate presence of mind, depth of knowledge and exceptional multi-tasking skills.
Question. What do you understand by cross-breeding?
Answer. Crossbreeding is the mating of two animals that are different breeds within the same species, for example, a Ragamuffin is a crossbreed formed by mating the same species (cat), but different breeds (Ragdoll and Himalayan). A mule, on the other hand, is a hybrid animal formed by the mating of a donkey and a horse i.e. two different species.
Long Answer
Question. Explain plant breeding and the steps in breeding a new genetic variety of crop?
Answer. Plant breeding is the purposeful manipulation of plant species in order to create desired genotypes and phenotypes for specific purposes. This manipulation involves either controlled pollination, genetic engineering, or both, followed by artificial selection of progeny. Plant breeding programmes are carried out in a systematic way, so the main steps in breeding a new genetic variety of a crop are:
1. Collection of variability: Genetic variability from various wild relatives of the cultivated species is collected to maintain the genetic diversity of a species. The entire collection of the diverse alleles of a gene in a crop is called the germplasm collection.
2. Evaluation and selection of parents: The germplasm is evaluated to identify plants with desirable combination of characters. Selection of parents is picking up seeds of only those plants for multiplication which have the desired traits.
3. Cross hybridisation among the selected parents: Hybridisation is the most common method of creating genetic variation. Hybridisation is crossing of two or more types of plants for bringing their traits together in the progeny. The individuals or lines used in hybridisation are called parents.
4. Selection and testing of superior recombinants: The selection and testing of superior recombinants involve picking up the better ones from the entire crop plants. Selfing the selected plant for several generations to obtain the homozygous inbred pure line. Such selected homozygous inbred pure line plants
are used in the process of the next step called hybridization.
5. Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars: The newly selected lines are evaluated for their yield and other agronomic traits of quality, disease resistance etc. these selected cultivars are then tested with local best cultivar and then are released for commercialisation.
Question. Write short note on bee-keeping and fisheries?
Answer. Bee-keeping: Beekeepers are also called honey farmers, apiarists, or less commonly, apiculturists The term beekeeper refers to a person who keeps honey bees in beehives, boxes, or other receptacles. A beekeeper (or apiarist) keeps bees in order to collect their honey and other products that the hive produce (including beeswax, propolis, flower pollen, bee pollen, and royal jelly), to pollinate crops, or to produce bees for sale to other beekeepers. Beekeeping requires low investments due to which farmers, along with agriculture also do beekeeping to generate additional income. It also helps in crosspollination as pollens are transferred from one flower to another by the bees while collecting nectar. Beekeeping is the science and art of rearing bees. It is important to keep bees for the production of honey, beeswax, propolis, pollen (bee bread), royal jelly and bee venom; for food, medicine and income. Beekeeping is also important for pollination and recreational activities.
Fisheries: A fishery exists for the purpose of providing human food, although other aims are possible such as sport or recreational fishing or obtaining ornamental fish or fish products such as fish oil. Fishery also refers to the occupation of capturing and processing fish for profit. These countries aren't just impacting fish stocks within their own borders and off their own coasts they're also affecting other nations. Some countries depend on fishing for their primary source of food. Fisheries management employs activities that protect fishery resources so sustainable exploitation is possible, drawing on fisheries science and possibly including the precautionary principle. Fishing includes the harvesting of aquatic bio resources and in cases stipulated by law for the adoption, processing, transportation, storage and shipment of catches of aquatic resources, and the production of fish and other products from them.
Question. State the difference between inbreeding and outbreeding?
Answer. 1. Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the breeding of organisms that are closely related genetically whereas outbreeding is the production of offspring from the breeding of organisms that are genetically unrelated.
2. Inbreeding occurs between genetically similar organisms whereas outbreeding occurs between genetically somewhat dissimilar organisms.
3. Inbreeding is used for the development of pure lines by increasing heterozygosis whereas outbreeding is used for the production of hybrid species with desirable characteristics.
4. Closely-related organisms are used in inbreeding whereas unrelated organisms are used in the outbreeding.
5. Mating occurs between individuals of the same species in inbreeding whereas mating occurs between separate species, genera, breeds or varieties.
Question. Write short note on tissue culture?
Answer. Tissue culture is the growth of tissues or cells in an artificial medium separate from the organism. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. In this process the growth medium or culture solution is very important as, it is used for growing plant tissue because it contains various plant nutrients in the form of 'jelly' known as agar and plant hormones which are necessary for the growth of plant. Tissue culture involves the use of small pieces of plant tissue or explants which are cultured in a nutrient medium under sterile conditions. Using the appropriate growing conditions for each explant type, plants can be induced to rapidly produce new shoots, and, with the addition of suitable hormones new roots. Plant tissue culture is a collection of techniques used to maintain or grow plant cells, tissues or organs under sterile conditions on a nutrient culture medium of known composition. It is widely used to produce clones of a plant in a method known as micro propagation. A tissue culture typically takes 10-14 weeks, beginning with clipping very small leaf, stem and root samples to obtain cells and then letting them establish themselves in a nutrient mix, where they eventually multiply. Those cells grow into leaves and stems without roots.
Question. Write short note on single cell protein?
Answer. Single-cell proteins are the dried cells of microorganism, which are used as a protein supplement in human foods or animal feeds. Single-cell protein refers to the crude; a refined or edible protein extracted from pure microbial cultures, dead, or dried cell biomass. They can be used as a protein supplement for both humans and animals. Microorganisms like algae, fungi, yeast, and bacteria have very high protein content in their biomass. The production of single cell protein takes place in a fermentation process. This is done by selected strains of microorganisms which are multiplied on suitable raw materials in technical cultivation process directed to the growth of the culture and the cell mass followed by separation processes. Single-cell protein (SCP) refers to protein derived from cells of microorganisms such as yeast, fungi, algae, and bacteria, which are grown on various carbon sources for synthesis. Single Cell Protein (SCP) offers an unconventional but plausible solution to this problem of protein deficiency being faced by the entire humanity.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Stategies for Enchancement in Food Production Worksheet Set C
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
The above practice worksheet for Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production has been designed as per the current syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students studying in Class 12 can easily download in Pdf format and practice the questions and answers given in the above practice worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest practice worksheets with solutions have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology students to get all the latest study material free of cost. Teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the practice sheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. After solving these you should also refer to Class 12 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production Class 12 Biology have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement In Food Production test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

