Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet Set D. Download printable Biology Class 12 Worksheets in pdf format, CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Worksheet has been prepared as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Also download free pdf Biology Class 12 Assignments and practice them daily to get better marks in tests and exams for Class 12. Free chapter wise worksheets with answers have been designed by Class 12 teachers as per latest examination pattern
Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Biology Worksheet for Class 12
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf in Class 12. This test paper with questions and solutions for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for tests and exams and help you to score better marks
Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Worksheet Pdf
Question. Write the scientific name of the pathogen that causes amoebic dysentery. Enumerate four symptoms of the disease. How is the disease transmitted?
Answer. Amoebiasis is caused by monogenic protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. It is characterised by abdominal pain, mild diarrhoea alternating with constipation, passing out of mucus and blood in faeces. The infection occurs by the cysts of Entamoeba present in the stool of infected person, through the agency of houseflies.
Question. Describe the asexual and sexual phases of life cycle of Plasmodium that cause malaria in humans.
Answer. Life cycle of Plasmodium requires two hosts for completion, such a two host life cycle is called digenetic.
I. Life cycle of Plasmodium in Man - Asexual phase
(i) Infective stage of Plasmodium is sporozoite. When the mosquito bites another human, sporozoites are injected with bite.
(ii) Parasites (sporozoites) reach the liver through blood.
(iii) The parasite reproduces asexually in liver cells, bursting the cells and releasing into the blood.
(iv) Parasites enter the red blood cells (RBCs) and reproduce asexually there bursting the red blood cells and causing cycles of fever and other symptoms. Released parasites infect new red blood cells.
(v) Sexual stages develop in RBCs.
II. Life cycle of Plasmodium in female anopheles mosquito - Sexual phase
(i) Female mosquito takes up gametocytes with blood meal.
(ii) Fertilisation and development take place in the mosquito’s stomach.
(iii) The zygote elongates and becomes motile called ookinete.
(iv) The ookinete moves and bores through the wall of the stomach of female Anopheles mosquito. The ookinete changes to oocyst on the surface of the stomach.
(v) Inside the oocyst, sporozoites are formed which are released in the body cavity of the mosquito.
(vi) Mature infective stages (sporozoites) move to different organs of the body cavity but many of them penetrate salivary glands of mosquito.
(vii) When the female Anopheles mosquito bites a healthy person, the sporozoites are injected in his/ her blood alongwith saliva.
Question. How do cytokine barriers help in evading viral infections?
Answer. Interferons are cytokine barriers. These are low molecular weight proteins secreted by virus infected cells, which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
Question. In what way is monocyte a cellular barrier with reference to immunity?
Answer. Monocytes are motile and phagocytic leucocytes. They engulf bacteria and cellular debris and constitute cellular barriers of innate immunity.
Question. Why is colostrum a boon to the newborn baby?
Answer. Colostrum (mother’s first milk) is rich in IgA antibodies. It provides passive immunity to new born and protects it from various diseases.
Question. Name any two types of cells that act as ‘cellular barriers to provide innate immunity in humans.
Answer. Certain types of leukocytes (WBCs) like polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL- neutrophils) and natural killer cells in the blood are cellular barriers, which provide innate immunity in humans.
Question. Why is secondary immune response more intense than the primary immune response in humans?
Answer. Secondary immune response is quicker and more intense than the primary immune response because the memory B cells are present to quickly deal with the invading microbes by forming antibodies. Body “remembers” that it previously encountered this type of infection.
Question. What is an autoimmune disease? Give an example.
Answer. Autoimmune disease is a condition in which body’s immune system attacks self-cells. E.g., rheumatoid arthritis.
Question. When does a human body elicit an anamnestic response?
Answer. Human body elicits an anamnestic response (secondary response) to the subsequent encounter with the same pathogen to which the body had previously encountered (primary response).
Question. State two different roles of spleen in the human body.
Answer. Spleen is the secondary lymphoid organ. It is the site where proliferation and differentiation of B and T lymphocytes takes place and in fetus, spleen produces all types of blood cells.
Question. How do interferons protect us?
Answer. Virus infected cells produce an antiviral protein called interferon which on reaching the nearby infected cells, make them resistant to viral infection.
Question. What is it that prevents a child to suffer from a disease he/she is vaccinated against? Give one reason.
Answer. Vaccine is suspension or extract of weakened (attenuated/ dead) pathogens of disease which when injected into healthy person provides it active acquired immunity to the disease.
Vaccination stimulates the antibody production and formation of memory cells without causing the disease. This protects the child by neutralising the pathogenic agents during infection.
Question. Some allergens trigger sneezing and wheezing in human beings. What causes this type of response by the body?
Answer. Sneezing and wheezing in human beings to some allergens is caused due to exaggerated response of the immune system.
Question. A boy of ten years had chicken-pox. He is not expected to have the same disease for the rest of his life. Mention how it is possible.
Answer. A body when encounters a pathogen (in this case chicken pox) for first time produces antibodies, that results in memory of the first encounter to protect the body in future from the same disease.
Question. What role do macrophages play in providing immunity to humans?
Answer. Macrophages are phagocytic cells that remove bacteria or other foreign bodies from blood or tissues and display their antigen to alert the lymphocytes and stimulate them.
Question. It was diagnosed by a specialist that the immune system of the body of a patient has been suppressed. Name the disease the patient has been suffering from and its causative agent.
Answer. In immunodeficiency diseases, the immune system of the body gets weakened, leading to repeated microbial infections. The patient is suffering from AIDS (Acquired Immune deficiency Syndrome) caused by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
Question. Name an allergen and write the response of the human body when exposed to it.
Answer. Pollen grain is an allergen. Exposure to pollen causes hay fever. It is the form of allergy due to pollen of grasses, trees and other plants. It is characterised by inflammation of the membrane lining the nose and sometimes of the conjunctiva. The symptoms are sneezing, running nose and watering eyes due to histamine release.
Question. Differentiate between active and passive immunity.
Answer. The given table shows differences between active and passive immunity:
| Active immunity | Passive immunity |
| It is developed when the person’s own cells produce antibodies in response to infection or vaccine. |
It is developed when antibodies produced in other organisms are injected into a person to counter act antigen such as snake venom. |
| It provides relief only after long period. |
It provides immediate relief. |
| It has no side effects. | It may cause reaction. |
| It is long lasting. | It is not long lasting. |
Question. A student on a school trip started sneezing and wheezing soon after reaching the hill station for no explained reasons. But, on return to the plains, the symptoms disappeared. What is such a response called? How does the body produce it?
Answer. Hill station and plains do have different weather conditions and environment. Sneezing and wheezing on hill station is due to exposure to different allergens, this response is called allergy. It is a hypersensitive response of a person to foreign substance coming in contact with or entering the body. Allergy involves IgE antibodies and release of chemicals like histamine and serotonin from mast cells.
Question. A young boy when brought a pet dog home started to complain of watery eyes and running nose. The symptoms disappeared when the boy was kept away from the pet.
(a) Name the type of antibody and the chemicals responsible for such a response in the boy.
(b) Mention the name of any one drug that could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Answer. (a) Such a response in the boy is called allergy which occurs due to production of IgE antibodies and chemicals like histamine and serotonin from the mast cells.
(b) Anti-histamine could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Question. A student on a school picnic to a park on a windy day started sneezing and having dificulty in breathing on reaching the park. The teacher enquired whether the student was allergic to something.
(a) What is an allergy?
(b) Write the two unique characteristics of the system involved in the response observed in the student.
Answer. (a) Allergy is a hypersensitive response to foreign substances, coming in contact with or entering the body. It is characterised by sneezing, watery eyes, difficulty in breathing etc.
(b) Two unique characteristics of system involved in allergic response are :
(i) The body will produce Ig E antibodies
(ii) The body will release chemicals like histamine and serotonin from the mast cells.
Question. How does a vaccine for a particular disease immunise the human body against that disease?
Answer. Vaccine is a preparation of dead/weakened germs of a disease which on inoculation into healthy person provides temporary/permanent active/ passive immunity by inducing antibody formation. The antibodies produced in the body against these antigens would neutralise the pathogenic agents during actual infection. The vaccines also generate memory B and T cells that recognise the pathogen quickly on subsequent exposure and attack the invaders with a large production of antibodies.
Question. Write the events that take place when a vaccine for any disease is introduced into the human body.
OR
Why is a person with cuts and bruises following an accident administered tetanus antitoxin?
Give reasons.
Answer. In vaccination, a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogens or weakened pathogen is introduced into the body. These antigens generate the primary immune response, and the memory B and T cells. When the vaccinated person is attacked by the same pathogen again, the existing memory T or B cells recognise the antigen quickly and attack the invaders with massive production of lymphocytes and antibodies.
OR
A person with cuts and bruises following an accident has chances of getting infected from tetanus. So, in this case quick immune response is required which is provided by giving the patient tetanus antitoxin which is a preparation containing preformed antibodies to the toxin.
Question. (a) Highlight the role of thymus as a lymphoid organ.
(b) Name the cells that are released from the above mentioned gland. Mention how they help in immunity.
Answer. (a) Thymus is a primary lymphoid organ where the maturation of T-lymphocytes takes place. Thymus atrophies with age.
(b) T-lymphocytes are released from thymus. T cells provide cell-mediated immunity and defend against pathogens including protists and fungi that enter the cells.
Question. Name and explain the two types of immune responses in humans.
Answer. Immune response is the specific reactivity induced in a host by an antigenic stimulus. It is of two types - primary and secondary immune response.
(i) The reaction of the body’s immune system to the first attack of microbes (antigens) is called primary immune response. It takes much longer time to develop because of the requirement of suitable receptor development. This response is feeble and declines rapidly. This produces both receptors and memory cells.
(ii) The reaction of the body’s immune system to any subsequent infection of the same microbe is termed secondary immune response. It is quicker and more intense than primary immune response because memory B cells present quick response against invading microbes.
Question. Name the two types of immune systems in a human body. Why are cell mediated and humoral immunities so called?
Answer. Two types of immune systems in human body are : Antibody Mediated Immune System (AMIS) and Cell Mediated Immune System (CMIS). Antibody-mediated (or humoral) immunity is associated with the appearance of antibodies, secreted by B-lymphocytes, in the extracellular fluids such as plasma, lymph and external secretions. Cell-mediated immunity is mediated by T-lymphocytes that defend against pathogens including protists and fungi that enter the cells.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Name the two intermediate hosts which the human liver fluke depends on to complete its life cycle so as to facilitate parasitization of its primary host.
Answer. Snail and Fish
Question. When does a human body elicit an anamnestic response?
Answer. At the time of secondary response.
Question. How does haemozoin affect the human body when released in blood during malarial infection?
Answer. Haemozoin is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days during malarial infection.
Question. State the functions of mast cells in allergy response.
Answer. Mast cells release chemicals like histamine and serotonin in allergic response.
Question. What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency in the immune system of the infected person?
Answer. The virus enters macrophages after getting into the body of individual where RNA forms viral DNA by reverse transcription. The viral DNA gets incorporated in the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viral copies. The newly produced virus particles attack helper T-cells and thus the number of T-cells decrease. Since the helper T-cells are essential for functioning of immune system, the person suffers from various diseases due to deficient immune system.
Question. State two different roles of spleen in the human body.
Answer. Spleen is the secondary lymphoid organ that stores lymphocytes, it filters microbes and acts as a reservoir to store erythrocytes (Any two).
Question. Name any two physiological barriers that provide innate immunity?
Answer. Acid in stomach/saliva in mouth/tears in eyes. (Any two)
Question. How is a cancerous cell different from a normal cell?
Answer. (i) There is no adherence in cancerous cell whereas normal cells remain adhered to one another.
(ii) Tumour is formed in cancerous cells due to repeated uncontrolled cell division whereas it is absent in normal cells.
(iii) Cancerous cells have no definite lifespan but normal cells have definite lifespan and old cells are replaced by new cells.
Short Answer Questions
Question. List the symptoms of ascariasis. How does a healthy person acquire this infection?
Answer. Symptoms of ascariasis: Internal bleeding, muscular pain, anaemia, blockage of intestinal passage.
A healthy person can acquire this infection by intake of water, vegetables/fruits/foods
contaminated with eggs of the parasite.
Question. Why an immunosuppressive agent is taken after an organ transplant?
Answer. Our immune system is capable to differentiate between ‘self’ and ‘non-self’ cells/tissues. The graft (grafting) is a non-self tissue which may be rejected by our immune system. So, to prevent the rejection, immunosuppressants are taken after the transplant.
Question. Name the causative organism of the disease amoebiasis. List three symptoms of the disease.
Answer. Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebiasis.
Symptoms are constipation, abdominal pain/cramps, stool with excess mucous/blood clots.
Question. Identify a, b, c and d in the following table:
| S.No. | Name of the human disease | Name of the causal bacteria/virus | Specific organ or its part affected |
| (i) | Typhoid | Salmonella typhi | a |
| (ii) | Common cold | b | c |
| (iii) | Pneumonia | Streptococcus pneumoniae | d |
Answer. (a) small intestine (b) Rhino virus
(c) nose and respiratory passage (d) alveoli of lungs
Question. Identify A, D, E and F in the diagram of an antibody molecule given below:

Answer. A—Antigen binding site D—Light chain
E—Heavy chain F—Disulfide bridge.
Question. Name the host and the site where the following occur in the life-cycle of a malarial parasite:
(a) Formation of gametocytes]
(b) Fusion of gametocytes
Answer.
| Host | Site of occurrence | |
| (a) Formation of gametocytes | Human | Red blood cells |
| (b) Fusion of gametocytes | Anopheles mosquito | Intestine |
Question. A student on a school trip started sneezing and wheezing soon after reaching the hill station for no explained reasons. But, on return to the plains, the symptoms disappeared. What is such a response called? How does the body produce it?
Answer. Such a response is called allergic reaction or allergy. On exposure to allergens like dust, pollens,etc., chemicals like histamine and serotonin are released from the mast cells, resulting in an allergic response.
Question. Differentiate the following and give examples of each:
(a) Innate and acquired immunity
(b) Active and passive immunity
Answer. (a)
| S.No. | Innate immunity | Acquired immunity |
| (i) | It is present from birth and is inherited from parents. | It is not present from the birth. |
| (ii) | It is non-specific. | It is pathogen specific. |
| (iii) | The various physical, physiological, cellular, cytokine barriers are the basis of innate immunity. | The memory cells formed by B and T-cells are the basis of acquired immunity. |
| (iv) | The innate immunity remains throughout life. | The acquired immunity can be short-lived or life long. |
(b) Active and passive immunity: Refer to Table 8.1.
| S.No. | Active immunity | Passive immunity |
| (i) | It is developed due to contact with pathogen (dead or living) or its antigen, that leads to production of antibodies in the host body. | It is developed when readymade antibodies are injected into the body to protect body against foreign agents. |
| (ii) | It has no or only few side effects. | It may cause a reaction. |
| (iii) | It is slow but long lasting. | It is fast but lasts only for few days. |
| (iv) | It takes time to develop its response. | It is used when the immune response has to be faster. |
| (v) | For example, vaccination for polio, etc. | For example, administration of tetanus antitoxins, antibodies in colostrum, etc. |
| (vi) | Injecting microbes deliberately during immunisation or infections organisms entering body induce active immunity. | Foetus receives some antibodies from their mother through placenta during pregnancy,which induce passive immunity. |
Question. Name and explain the two types of immune responses in humans.
Answer. The two types of immunity are active immunity and passive immunity.
Active immunity: Immunity developed in the host body due to production of antibodies in response to antigens.
Passive immunity: When ready-made antibodies are directly given to protect the body against foreign agents.
OR
The two types of immunity are humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity.
Humoral immunity: Immune responses given by antibodies found in the blood.
Cell-mediated immunity: Activation of T-lymphocytes mediate this immunity.
OR
The two types of immunity are primary immunity and secondary immunity.
Primary immunity: When our body encounters a pathogen for the first time, it produces primary response.
Secondary immunity: Subsequent encounter with the same pathogen generates highly intensified secondary response or secondary immunity.
Question. If a regular dose of drugs or alcohol is not provided to an addicted person, he shows some withdrawal symptoms. List any four such withdrawal symptoms.
Answer. The withdrawal symptoms are:
(a) Anxiety (b) Shakiness
(c) Nausea (d) Sweating
Question. List the two types of immunity a human baby is born with. Explain the differences between the two types.
Answer. The two types of immunity a human baby is born with are innate and passive/acquired immunity.
Innate immunity is a non-specific type of defence that provides barrier to the entry of antigens. Passive immunity is a pathogen-specific type of defence in which readymade antibodies are directly given to protect body against foreign agents. The foetus receives antibodies through the placenta.
Question. Identify A, B, C and D in the replication of HIV (retrovirus).
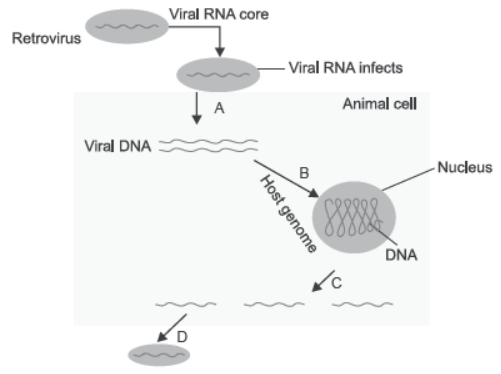
Answer. (A) Reverse transcription.
(B) Viral DNA incorporates into host genome.
(C) New viral RNA produced by infected cell.
(D) New viruses can infect other cells.
Question. A child is born with ADA - deficiency
(a) Suggest and explain a procedure for possible life-long (permanent) cure.
(b) Name any other possible treatment for this disease.
Answer. (a) Gene therapy, lymphocytes from the blood of a patient are grown in a culture outside the body, functional ADA, cDNA is introduced into these lymphocytes, these cells are returned to the patient's body at early embryonic stage.
(b) Bone marrow transplantation, enzyme replacement therapy
Question. (a) Write the scientific names of the causative agent and vector of malaria, and write its symptoms.
(b) Name any two diseases spread by Aedes sp.
Answer. (a) Plasmodium vivax / P. falciparum / P.malariae, vector-Female Anopheles mosquito
Symptoms - chill , high fever
(b) Dengue, Chikungunya.
Question. Two children, A and B aged 4 and 5 years respectively visited a hospital with a similar genetic disorder. The girl A was provided with enzyme replacement therapy and was advised to revisit periodically for further treatment. The girl B was, however, given a therapy that did not require revisit for further treatment.
(a) Name the ailments the two girls were suffering from?
(b) Why did the treatment provided to girl A required repeated visits?
(c) How was the girl B cured permanently?
Answer. (a) Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency
(b) In Enzyme Replacement Therapy functional ADA is introduced to the patient (by injection), this therapy is not completely curative as enzyme can act only for a limited time period.
(c) [As there is no permanent cure at the age of five hence 1 mark of this answer allocated to part (b)]
Question. (i) What is an ‘‘allergic reaction’’ ?
(ii) Name any two drugs used to quickly reduce the symptoms of allergy.
(iii)Why do more and more children in metro cities of India suffer from allergies and asthma?
Answer. (i) The exaggerated response of the immune system to certain antigens present in the environment is called allergic reaction. 1
(ii) Anti-histamine, adrenaline, steroids.
(iii) Due to deteriorating air quality, sensitivity to the environment, allergens, lowering of immunity due to modern day lifestyle (which could be due to the protected environment provided largely in life).
Question. Name a human disease, its casual organism, symptoms (any three) and vector, spread by intake of water and food contaminated by human faecal matter.
Ans. Amoebiasis (Amoebic dysentery), Entamoeba histolytica, constipation / abdominal pain / cramps / tools with excess mucus / blood clots (Any three symptoms), Housefly.
Ascariasis, Ascaris, internal bleeding / muscular pain / fever / anaemia / blockage of intestinal passage (Any three symptoms), Housefly.
OR
Typhoid, Salmonella typhi, high fever / weakness / stomach pain / constipation / headache / loss of appetite, Housefly. (Any three symptoms)
Question. A farmer while working on his farm was bitten by a poisonous snake. The workers in the farm immediately rushed him to the nearby health centre. The doctor right away gave him an injection to save his life. What did the doctor inject and why ? Explain.
Answer. (i) Antitoxin / Antivenoms / Preformed antibodies.
(ii) Whenever quick immune response is required, we need to directly inject preformed antibodies / Antitoxins.
(iii) To neutralize snake venom quickly, passive immunity is provided.
Question. (i) Why is there a fear amongst the guardians that their adolescent wards may get trapped in drug/alcohol abuse ?
(ii) Explain ‘addiction‘ and ‘dependence‘ in respect of drug / alcohol abuse in youth.
Answer. (i) Adolescents are easily affected by (Vulnerable to) peer pressure, adventure, curiosity, excitement, experimentation and media.
(ii) Addiction : Psychological attachment to certain effects such as Euphoria or temporary feeling of well - being.
Dependence : Tendency of the body to show withdrawal syndrome or symptoms if regular doses of drug or alcohol are abruptly
Question. Medically it is advised to all young mothers that breastfeeding is the best food for their newborn babies. Do you agree? Give reasons in support of your answer.
OR
Why is breastfeeding recommended during the initial period of an infant’s growth ? Give reasons.
Answer. Yes, Breast freeding is considered to be the best food for infants because it provides nutrition (calcium, fats, lactose) / provides (passive) immunity / provides antibodies / Ig A which heps the new born grow healthy and strong. This also protects the infants against allergies, sickness, infections etc.
Question. Explain the following with reference to drug/alcohol abuse : (i) Addiction,
(ii) dependence and (iii) withdrawal symptoms.
Answer. (i) Addiction : Frequent use of drugs or alcohol leads to increase in the level of tolerance of receptors present in our body, thus making these receptors respond to only higher doses of drugs and alcohol.
OR
Psychological attachment to certain effects such as euphoria and temporary feeling of well being associated with drugs and alcohol.
(ii) Dependence : Due to inherent addictive nature and its psychological attachment to drugs or alcohol and are unable to live without them.
Question. On a visit to a Hill station, one of your friends suddenly became unwell and felt uneasy.
(i) List two symptoms you would look for to term it to be due to allergy.
(ii) Explain the response of the body to an allergy.
(iii) Name two drugs that can be recommended for immediate relief.
Answer. (i) Sneezing, watery eyes, running nose, difficulty in breathing. (Any two)
(ii) Body releases antibodies, lgE type and chemicals like histamine and serotonin from mast cells which produce symptoms of allergy.
(iii) Antihistamine, adrenalin, steroids.
Question. State the three characteristics of Acquired Immunity. List the different ways by which it can be attained by humans.
Answer. Characteristics of Acquired Immunity : Pathogen specific / characterized by memory /
Acquired after birth / are of two types : Active and passive/humoral and cell mediated/includes primary response and secondary response.
Way by which it can be attained by humans :
Active Immunity by encountering a pathogen /virulent microbe/suffering from contagious disease. Passive Immunity through immunization / readymade antibodies.
Question. During a school trip to ‘Rohtang Pass’, one of your classmates suddenly developed ‘altitude sickness’. But, she recovered after some time.
(a) Mention one symptom to diagnose the sickness.
(b) What caused the sickness?
(c) How could she recover by herself after some time?
Answer. (a) Nausea / fatigue / heart palpitation.
(b) Low atmospheric pressure at high altitude, body deprived of O2.
(c) Increase in RBC, decreases binding capacity of haemoglobin, increased breathing rate, get acclimatised.
Question. (i) It is generally observed that the children who had suffered from chickenpox in their childhood may not contract the same disease in their adulthood. Explain giving reasons on the basis of such immunity in an individual. Name this kind of immunity.
(ii) What are interferons ? Mention their role.
Answer. (i) The first infection of chickenpox produce a primary response and antibodies are generated against the chickenpox virus, subsequent encounter with the same virus elicits a highly intensified secondary response, due to the memory cells formed during the first encounter, (active immunity). (ii) Proteins secreted by virus infected cells, which protects non-infected cells from viral infection / when a – interferon is given to cancer patient (it activates immune system), destroys tumour.
Question. Prior to a sports events, blood and urine samples of sportspersons are collected for drug tests.
(i) Why is there a need to conduct such tests ?
(ii) Name the drugs the authorities usually look for.
(iii) Write the generic names of two plants from which these drugs are obtained.
Answer. (i) To detect drug abuse / use of banned drugs / use of cannabinoids / anabolic steroids / narcotic analgesic diuretics / hormones / drugs used to accelerate performance / increase muscle strength / bulk / promote aggressiveness / to ensure fair game.
(ii) Cannabinoids / cocaine / coca alkaloid / coke / crack / hashish / charas / ganja / hemp plant extract.
(iii) Cannabis / Atropa / Erythroxylum / Datura.
Question. (i) Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
(ii) Why is colostrum a boon to the newborn baby ?
Answer. (i) Benign tumour remains confined to original location / does not spread to another part of the body / not cancerous.
Malignant tumour is mass of proliferating (neoplastic) cells that invade and damage surrounding tissue / cancerous tumour / tumour showing property of metastasis.
(ii) Colostrum contains antibodies / that provides resistance (immunity) to newborn babies.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) If a patient is advised anti-retroviral drug, name the possible infection he/ she is likely to be suffering from. Name the causative organism.
(b) How do vaccines prevent subsequent microbial infection by the same pathogen?
(c) How does a cancerous cell differ from a normal cell?
(d) Many microbial pathogens enter the gut of humans along with food. Name the physiological barrier that protects the body from such pathogens.
Answer. (a) AIDS is caused by the HIV (Human Immuno- Deficiency Virus).
(b) Vaccines prevent microbial infections by initiating production of antibodies against these antigens to neutralise the pathogenic agents during later actual infection. The vaccines also generatememory – B and T-cells that recognize the pathogen quickly on subsequent exposure.
(c) Normal cells show a property called “contact inhibition” by virtue of which contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth. Cancer cells appear to have lost this property.
These cells grow very rapidly, invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues. Cells sloughed from such tumours reach distant sites through blood, and wherever they get lodged in the body, they start a new tumour there. This property is called metastasis.
Question. (i) Name the drug used
(a) As an effective sedative & pain killer.
(b) For helping patients to cope with mental illness like depression but often misused.
(ii) How does the moderate and high doses of cocaine affect human body
Answer. (i) (a) Morphine, which is obtained from the latex of the poppy plant is used as an effective sedative and pain killer.
(b) LSD (Lysergic acid dimethyl amide) or Barbiturates are used to help the patients to cope with mental illness like depression.
LSD is a hallucinogenic substance, it is synthetically derived from the fungus, Claviceps purpurea.
(ii) Cocaine is a powerful addictive stimulant drug. The source of cocaine is coca leaves (Erythroxylum coca). It can alter brain structure and function if used repeatedly.
Effect of moderate doses of cocaine :
1. Feeling of euphoria and increased energy.
2. Increased in heart beat, respiration rate and blood pressure.
3. Dilated pupils.
4. Feeling of wellness and increased confidence.
Effect of high doses of cocaine :
1. Panic attacks
2. Irritability
3. Anxiety
4. Paranoia.
Long term use of high doses of cocaine can result in weight loss and malnutrition. It may cause Parkinson’s disease.
Question. Define adolescence. Why are adolescents advised not to smoke ? How smoking affects the functioning of the body. Explain in reference to the rise in blood pressure and emphysema.
Answer. Adolescence refers to the period and process of rapid growth and physical and mental development from childhood to adulthood. Adolescents are advised not to smoke because of it’s addictive nature, it is hard to get rid of the use of tobacco. Smoking produces negative effect on the body. Smoking of tobacco is associated with cancer of lungs, urinary bladder, bronchitis, coronary heart diseases, etc. Smoking increases the content of carbon monoxide in the blood which interferes, with the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
The nicotine (of tobacco) stimulates adrenal glands to secrete adrenaline and nor-adrenaline; these hormones increase the blood pressure and heart rate.
1. In the immune system, interferons are a part of
(a) physiological barriers
(b) cellular barriers
(c) physical barriers
(d) cytokine barriers.
2. The letter T in T-lymphocytes refers to
(a) tonsil
(b) thalamus
(c) thymus
(d) thyroid
3. Use of anti-histamines and steroids gives a quick relief from
(a) allergy
(b) nausea
(c) cough
(d) fever
4. The immunoglobulin abundant in colostrum, is
(a) Ig D
(b) Ig A
(c) Ig G
(d) Ig M
5. Diacetyl morphine is commonly known as
(a) cocaine
(b) hashish
(c) ganja
(d) heroin
6. Opium is extracted from
(a) Atropa belladona
(b) Papaver somniferum
(c) Erythroxylum coca
(d) Cannabis sativa
7. The disease chikungunya is transmitted by
(a) houseflies
(b) Aedes mosquitoes
(c) cockroach
(d) female Anopheles
8. Anti venom against snake poison contains
(a) antigens
(b) antigen-antibody complexes
(c) antibodies
(d) enzymes
9. Which of the following glands is large sized at birth but reducies in size with aging?
(a) Pineal
(b) Pituitary
(c) Thymus
(d) Thyroid
10. The substance produced by a cell on viral infection that can protect other cells from further infection is
(a) serotonin
(b) colostrum
(c) interferon
(d) histamine
11. Many diseases can be diagnosed by observing the symptoms in the patient. Which group of symptoms are indicative of pneumonia?
(a) Difficulty in respiration, fever, chills, cough, headache
(b) Constipation, abdominal pain, cramps, blood clots
(c) Nasal congestion and discharge, cough, sorethroat, headache
(d) High fever, weakness, stomach pain, loss of appetite and constipation
12. Transplantation of tissues/organs to save certain patients often fails due to rejection of such tissues/organs by the patient. Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections?
(a) auto-immune response
(b) humoral immune response
(c) physiological immune response
(d) cell-mediated immune response
13. ______ mosquitoes are the vectors of dengue and chikungunya.
14. ______ barriers protect the non-infected cells from further viral infections.
15. Cell-mediated immunity is provided by ______ .
16. Among non-infectious diseases, ______ is the major cause of death.
17. ______ test is performed to confirm typhoid.
18. Plasmodium enters the human body as ______ .
19. ______ is the toxin released by the rupture of RBCs into the blood in a malariainfected person.
20. _____ is the filarial worm.
21. ______ are the physical, chemical and biological agents that cause cancer.
22. Heroin is obtained by _______ of morphine.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet Set D
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
The above practice worksheet for Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases has been designed as per the current syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students studying in Class 12 can easily download in Pdf format and practice the questions and answers given in the above practice worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest practice worksheets with solutions have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology students to get all the latest study material free of cost. Teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the practice sheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. After solving these you should also refer to Class 12 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Class 12 Biology have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

