Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity And Conservation Worksheet Set B. Download printable Biology Class 12 Worksheets in pdf format, CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Worksheet has been prepared as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Also download free pdf Biology Class 12 Assignments and practice them daily to get better marks in tests and exams for Class 12. Free chapter wise worksheets with answers have been designed by Class 12 teachers as per latest examination pattern
Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Biology Worksheet for Class 12
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf in Class 12. This test paper with questions and solutions for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for tests and exams and help you to score better marks
Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Worksheet Pdf
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions : In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
(A) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(B) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A) : Biodiversity means diversity at species level.
Reason (R) : Biodiversity is a diversity not only at species level but at all levels of biological organization.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion (A) : Process of extinction is random and fast.
Reason (R) : Any species which can not adapt itself according to the environment, it cannot survive.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion (A) : Western ghats of India are one of the hot-spots of biodiversity.
Reason (R) : Western ghats have greater amphibian diversity than eastern ghats.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion (A) : Sacred groves are highly protected.
Reason (R) : They are of religious importance to the communities.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion (A) : There is more species biodiversity in tropical latitudes than in temperate ones.
Reason (R) : Tropical environments, unlike temperate ones, are less seasonal, relatively more constant and predictable.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion (A) : Loss of habitat is the main cause of loss of biodiversity.
Reason (R) : This causes the increase in edge area and reduction in core area.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion (A) : Percentage of animals is more than the percentage of plants.
Reason (R) : 70% of all the species are animals, while plants contribute nearly 22% of the total.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion (A) : Biosphere reserves are also included under the ex-situ conservation strategies.
Reason (R) : Cropping and grazing are allowed in the transition zone of biosphere reserve.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion (A) : Biologists are not sure about total number of prokaryotic species
Reason (R) : Nearly 45,000 species of plants and twice as many of animals have been recorded from India
Answer : C
Question. Assertion (A) : Many species like Stellar’s sea cow, passenger pigeon, etc., became extinct due to over exploitation.
Reason(R) : Over exploitation is a major cause of biodiversity loss.
Answer : B
Case-based MCQs
Attempt any four sub-parts from each question. Each
I. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Excessive exploitation of species, whether a plant or animal reduces the size of its population, so it becomes vulnerable to extinction. Such as Dodo and passenger pigeon have become extinct due to over exploitation by humans. Thus, the world is facing accelerated rates of species extinctions, largely due to human interference.
Question. Identify a cause of biodiversity loss that is not included in evil quartet?
(A) Co-extinction
(B) Pollution
(C) Alien species invasion
(D) Habitat loss and fragmentation
Answer : B
Question. The species that have become extinct due to over exploitation is/are :
(A) Stellar’s sea cow
(B) Yucca moth
(C) Blatta orientalis
(D) Nile Perch
Answer : A
Question. Factors which make species susceptible to extinction are :
(A) Small population size
(B) Higher status of trophic level
(C) Inability to switch over to alternate food
(D) All of the above
Answer : D
Direction : In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Pollution reduces species biodiversity.
Reason : Spillover of oil in sea causes death of several marine animals.
Answer : C
Question. ___________is the first major cause of species extinction.
(A) Coextinction
(B) Over exploitation
(C) Habitat destruction
(D) Alien species invasion
Answer : C
II. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Pollution, climate changes, over-exploitation by human etc., are responsible for changes in the ecosystem. Change in an ecosystem is responsible for
depletion in biodiversity which directly or indirectly affects human beings and their surrounding. So, it is important to conserve the biodiversity. There are various methods like in-situ conservation, exsitu conservation by which we can conserve our biodiversity.
Question. Main cause of extinction of animals and plants is :
(A) Habitat loss and fragmentation
(B) Competition between species
(C) Over-exploitation
(D) Alien species invasion.
Answer : A
Question. Protected areas are example of
(A) In-situ conservation
(B) Ex-situ conservation
(C) Cryopreservation
(D) Green houses.
Answer : A
Question. How many biodiversity hot-spots are identified globally ?
(A) 20
(B) 3
(C) 36
(D) 50
Answer : C
Question. Species at the high risk of extinction in the future is called :
(A) Vulnerable
(B) Extinct
(C) Endemic
(D) Critically Endangered
Answer : D
Question. Name the National Aquatic Animal of India ?
(A) Sea-horse
(B) Gangetic shark
(C) Blue whale
(D) River dolphin
Answer : D
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What is genetic diversity?
Answer. It is the measure of variation in genetic information contained in the organisms.
Question. What is mass extinction?
Answer. Due to natural calamities like volcanic eruptions, prolonged drought, heavy rains, earthquakes, asteroid collision, etc., a large number of species become extinct at the same time which is called mass extinction.
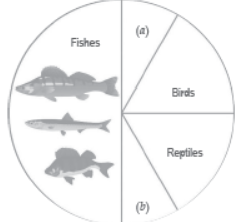
Question. Identify ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the figure given below representing proportionate number of major vertebrate taxa.
Answer. a → Mammals
b → Amphibians
Question. Name the three important components of biodiversity.
Answer. The three important components of biodiversity are: genetic diversity, species diversity and ecological diversity.
Question. India has more than 50,000 strains of rice. Mention the level of biodiversity it represents.
Answer. 50,000 strains of rice represent genetic biodiversity.
Question. Name the unlabelled areas ‘a’ and ‘b’ of the pie chart (given alongside) representing the global biodiversity of invertebrates showing their proportionate number of species of major taxa.
Answer. a → Insects;
b → Molluscs

Short Answer Questions
Question. Assess the effects of loss of biodiversity in a region. Mention any four such effects.
Answer. (i) Decline in plant production and animal species.
(ii) Lowered resistance to environmental perturbations such as drought.
(iii) Increased variability in certain ecosystem processes such as plant productivity/water use/pest and disease cycles.
(iv) Increased rate of species extinction.
Question. Narrowly utilitarian arguments are put forth in support of biodiversity conservation. Explain the other two arguments that are put forth in support of the same cause.
Answer. Broadly utilitarian arguments
OU Biodiversity plays a major role in maintaining and sustaining supply of goods and services from various species as well as ecological systems.
OU The different ecological services provided are:
Ethical reasons
OU There are thousands of plants, animals and microbes on this earth which are not useless. Every one has some intrinsic value even if it is not of any economic value to us.
OU It is, therefore, our moral duty to ensure well-being of all the living creatures for the utilisation of future generations.
Question. State how does ex-situ conservation help in protecting biodiversity.
Answer. Ex situ conservation (Off-site conservation)
QU This approach involves placing threatened animals and plants in special care units for their protection.
QU India has 35 botanical gardens and 275 zoological parks where animals which have become extinct in wild are maintained.
Question. Differentiate between in situ and ex situ approaches of conservation of biodiversity.
Answer.
Question. Seeds of different genetic strains are kept for long periods in seed banks. Explain the conservative strategy involved in this process.
Answer. The strategy is called Ex-situ conservation. In this technique, seeds are preserved in viable and fertile condition for long periods using cryopresrvation techniques.
Question. Discuss one example, based on your day-to-day observations, showing how loss of one species may lead to extinction of another.
Answer. In case a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated within an obligatory way also become extinct. For example,
(i) When a fish species which is a host for a number of parasites becomes extinct, the parasite species which are uniquely dependent on the host fish will also become extinct.
(ii) The insects may be polyphagous (feed on more than one plant species) or monophagous (feed on only one particular plant species) in nature. The monophagous insect species are valuable and may become extinct if the plant species upon which it feeds becomes extinct.
Question. How is biodiversity important for ecosystem functioning?
Answer. Importance of biodiversity for ecosystem functioning:
(i) Stability: Biodiversity is an important aspect for stability of an ecosystem. Ecologists believe that communities with more species tend to be more stable than those with less species.
(ii) Productivity: Ecosystem with higher biodiversity show more productivity than ecosystems with lower biodiversity. David Tilman’s long-term ecosystem experiments using outdoor plots provide confirmation.
(iii) Ecosystem health: Rich biodiversity is not only essential for ecosystem health but imperative for the survival of the human race on earth. Species are interlinked and so, killing or disappearance of one would effect the others also.
(iv) Resilience: Increased biodiversity provides resilience of the ecosystem against natural or man-made disturbances.
Question. Justify with the help of an example where a deliberate attempt by humans has led to the extinction of a particular species.
Answer. When Nile perch, a large predator fish, was introduced in Lake Victoria, it started feeding on the native fish, Cichlid fish. As a result, Cichlid fish became extinct and Nile perch, not finding any food for itself, died too.
Question. The species diversity of plants (22 per cent) is much less than that of animals (72 per cent).
What could be the explanations to how animals achieved greater diversification?
Answer. Animals have achieved greater diversification than plants due to following reasons:
(i) They are mobile and thus can move away from their predators or unfavourable environments.
On the other hand, plants are fixed and have fewer adaptation to obtain optimum amount of raw materials and sunlight therefore, they show lesser diversity.
(ii) Animals have well-developed nervous system to receive stimuli against external factors and thus can respond to them. On the other hand, plants do not exhibit any such mechanism, thus, they show lesser diversity than animals.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Alien species are highly invasive and are a threat to indigenous species. Substantiate this statement with any three examples.
Answer. Exotic species are defined as species that have been introduced from another geographic region to an area outside its natural range. For example,
(i) Parthenium, Lantana and Eichhornia are the exotic species of plants that have invaded the native species of India and caused environmental damage.
(ii) Introduction of African catfish Clarias gariepinus for aquaculture purpose is posing threat to many indigenous catfish.
(iii) Nile perch introduced into lake Victoria in East Africa led to the extinction of cichlid fish.
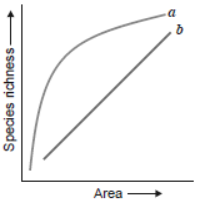
Question. The graph shows species-area relationship:
(a) If b denotes the relationship on log scale-
(i) Describe a and b.
(ii) How is slope represented? Give the normal range of slope.
(iii) What kind of slope will be observed for frugivorous birds and mammals in a tropical forest?
(b) Species diversity of plants (22%) is much less than that of animals (72%). Analyze the reasons for greater diversity of animals as compared to plants.
Answer. (a) (i) a is S = CA2

b is log S = log C + Z log A
(ii) Slope is Z (regression coefficient). Its normal value ranges from (iii) In frugivorous birds and mammals, value of Z=1.15
(b) Reasons for greater diversity of animals are:
(i) Animals are mobile and can avoid predator or unfavourable event.
(ii) Well developed nervous system to receive stimuli against external factors and respond to them.
Question. The given graph alongside shows species–area relationship. Write the equation of the curve ‘a’ and explain.
Answer. The equation of the curve ‘a’ is S = CAZ.
(i) Within a region, species richness increases with increasing explored area but only up to a limit.
(ii) Relationship between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa turns out to be rectangular hyperbola.
Question. (a) Why should we conserve biodiversity? How can we do it?
(b) Explain the importance of biodiversity hotspots and sacred groves.
Answer. (a) • Biodiversity is important for ecosystem health and for survival of human race on earth. There are
three main reasons for conserving the biodiversity which have been classified into the following categories:
(i) Narrowly utilitarian arguments
• Human beings derive direct economic benefits from nature, like food, firewood, fibre, construction material, industrial products (resins, gums, dyes, tannins, etc.) and medicinally important
products.
• More than 25 per cent of the drugs are derived from plants and about 25,000 species of plants are used by native people as traditional medicines.
(b) Conservation of Biodiversity
• Biodiversity can be conserved by protecting its whole ecosystem.
• There are two basic approaches for conservation of biodiversity.
(i) In situ conservation (On site conservation)
This approach involves protection of species in their natural habitat.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity And Conservation Worksheet Set B
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
The above practice worksheet for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation has been designed as per the current syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students studying in Class 12 can easily download in Pdf format and practice the questions and answers given in the above practice worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest practice worksheets with solutions have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology students to get all the latest study material free of cost. Teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the practice sheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. After solving these you should also refer to Class 12 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Biology have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

