MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. 10 % law of energy transfer was given by
(a) Lindemann
(b) Tansley
(c) Stanley
(d) Darwin
Answer. A
Question. Flora and fauna in lake or ponds is
(a) lentic biota
(b) lotic biota
(c) abiotic biota
(d) field layer
Answer. A
Question. The enzyme responsible for the reduction of molecular nitrogen to the level of ammonia in the leguminous root nodule is
(a) nitrogenase
(b) nitrate reductase
(c) nitrite reductase
(d) ammoneases
Answer. D
Question. The role of bacteria in carbon cycle is
(a) photosynthesis
(b) chemosynthesis
(c) decomposition of organic compounds
(d) evolution of O2
Answer. C
Question. The function of leghaemoglobin during biological nitrogen fixation in root nodules of legumes is to
(a) convert atmospheric N2 to NH3
(b) convert ammonia to nitrite
(c) transport oxygen for activity of nitrogenase
(d) protect nitrogenase from oxygen
Answer. D
Question. An ecosystem, such as an aquarium, is selfsustaining if it involves the interaction between organisms, a flow of energy, and the presence of
(a) equal numbers of plants and animals
(b) more animals than plants
(c) materials cycles
(d) pioneer organisms
Answer. B
Question. The graph below shows the changes in two populations of herbivores in a grassy field. A possible reason for these changes is that
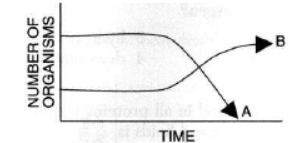
(a) all of the plant populations in this habitat decreased.
(b) population B competed more successfully for food than population A did.
(c) population A produced more offspring than population B did.
(d) population A consumed the members of population B.
Answer. C
Question. The xerophytic plants conserve water by storing it in
(a) intercellular spaces
(b) normal parenchymatous cells
(c) intercellular spaces and parenchymatous cells
(d) parenchymatous cells specialized for this purpose
Answer. D
Question. Most of the desert plants bloom during night time because
(a) their blooming is controlled by low temperature.
(b) they are sensitive to the phases of moon.
(c) the desert insects eat away flowers during day time.
(d) the desert insects are active during night time.
Answer. B
Question. How much portion of the Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) is captured by the plants?
(a) 5 – 10%
(b) 7 – 10%
(c) 8 – 10%
(d) 2 – 10%
Answer. D
Question. Arrange the following ecosystems in increasing order of mean NPP (Tonnes / ha / year)
A. Tropical deciduous forest
B. Temperate coniferous forest
C. Tropical rain forest
D. Temperate deciduous forest
(a) B < A < D < C
(b) D < B < A < C
(c) A < C < D < B
(d) B < D < A < C
Answer. D
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : A network of food chains existing together in an ecosystem is known as food web.
Reason : An animal like kite cannot be a part of a food web.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Pyramid of energy may be upright or inverted.
Reason: Only 20% of energy goes to next trophic level.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Biotic community has higher position than population in ecological hierarchy.
Reason : Population of similar individuals remains isolated in the community.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Net primary productivity is gross primary productivity minus respiration.
Reason : Secondary productivity is produced by heterotrophs.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Net primary productivity is gross primary productivity minus respiration.
Reason : Secondary productivity is produced by heterotrophs.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : In a food chain, members of successive higher levels are fewer in number.
Reason : Number of organisms at any trophic level depends upon the availability of organisms which serve as food at the lower level.
Answer. D
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What is the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), in the incident solar radiation?
(a) 100%
(b) 50%
(c) 1–5%
(d) 2–10%
Answer. (b) 50%
Question. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers
(d) Decomposers
Answer. (a) Producers (decomposers can be maximum but they are excluded from the food chain).
Question. The second trophic level in a lake is
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Benthos
(d) Fishes
Answer. (b) Zooplankton
Question. Secondary producers are
(a) Herbivores
(b) Producers
(c) Carnivores
(d) None of the above
Answer. (b) Herbivores
Question. Name the basic requirement of any ecosystem to function and sustain properly.
Answer. A constant input of solar energy is the ultimate source of all energy and requirement of any ecosystem to function and sustain properly.
Question. Define primary production.
Answer. It is defined as the amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a certain time period by plants during photosynthesis.
Question. What is net primary productivity?
Answer. The amount of energy or biomass remaining in a producer after meeting the cost of its respiration and is passed on to next trophic level is called the net primary productivity.
Question. Differentiate between standing state and standing crop in an ecosystem.
Answer. In an ecosystem, standing crop is the mass of living material in each trophic level at a particular time. Whereas standing state refers to the amount of nutrients in the soil at any given time.
Question. Why is the rate of assimilation of energy at the herbivore level called secondary productivity?
Answer. It is because the biomass available to the consumer for consumption is a resultant of the primary productivity from plants.
Short Answer Questions
Question. How are productivity, gross productivity, net primary productivity and secondary productivity interrelated?
Answer. Productivity is the rate of biomass production. GPP is rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis.
GPP – R = NPP = 1
Where NPP is biomass available to consumers for secondary productivity. Secondary productivity is rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Question. “It is possible that a species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.” Explain with the help of one example.
Answer. For example, sparrow is an omnivore. When it eats seeds, fruits or any other plant products, it occupies the primary trophic level. Whereas, when it eats worms and any other insect, it occupies the secondary trophic level. Thus, it occupies more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem.
Question. Justify the importance of decomposers in an ecosystem.
Answer. Decomposers which are heterotrophic organisms, mainly fungi and bacteria, break down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water and nutrients. They meet their energy and nutrient requirements by degrading dead organic matter or detritus. These are also known as saprotrophs. Decomposers secrete digestive enzymes that breakdown dead and waste materials into simple, inorganic materials, which are subsequently absorbed by them.
Question. Construct a pyramid of biomass starting with phytoplanktons. Label three trophic levels. Is the pyramid upright or inverted? Why?
Answer.
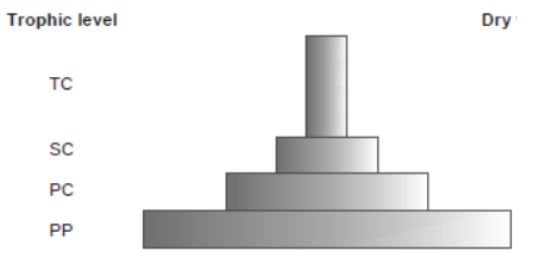
The pyramid is inverted because the biomass of fishes is much more than that of the phytoplanktons.
Question. Why is earthworm considered a farmer’s friend? Explain humification and mineralisation occurring in a decomposition cycle.
Answer. Earthworms help in breakdown of complex organic matter as well as loosening of the soil. This helps in the proper growth of the crops. Therefore, they are considered farmer’s friend.
Humification: The process of accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance, called humus, that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate is called humification. Humus being colloidal is reservoir of nutrients.
Mineralisation: The process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes to release inorganic nutrients is called mineralisation.
Question. What is an incomplete ecosystem? Explain with the help of a suitable example.
Answer. An ecosystem is a functional unit with biotic and abiotic factors interacting with one another resulting in a physical structure. Absence of any component will make an ecosystem incomplete as it will hinder the functioning of the ecosystem. Examples of such an ecosystem can be a fish tank or deep aphotic zone of the oceans where producers are absent.
Question. Primary productivity varies from ecosystem to ecosystem. Explain.
Answer. Primary productivity varies from ecosystem to ecosystem because it depends on the plant species inhabiting the area and their photosynthetic activity. It also depends on various environmental factors, which vary in different ecosystems.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Describe the inter-relationship between productivity, gross primary productivity and net productivity.
Answer. Productivity is the rate of biomass production per unit area over a period of time.
Gross primary productivity is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis in an ecosystem.
Net productivity is the gross primary productivity minus respiration losses.
Question. Name the pioneer species on a bare rock. How do they help in establishing the next type of vegetation? Mention the type of climax community that will ultimately get established.
OR
Explain how does a primary succession start on a bare rock and reach a climax community.
Answer. Primary succession on rocks
• Lichens are the pioneer species on a bare area.
• The lichen secretes some acids to dissolve rock and help in weathering and soil formation.
• Later, some small bryophytes invade and hold the small amount of soil.
Question. (a) Draw the pyramids of biomass in a sea and in a forest. Explain giving reasons why the two pyramids are different.
(b) “Pyramid of energy is always upright.” Explain.
Answer. (a)
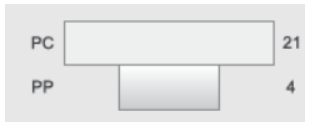
The pyramid of biomass in sea is inverted because the biomass of fish far exceeds that of phytoplankton. Whereas the pyramid of biomass in a forest ecosystem is upright, because the biomass decreases as the trophic level increases.
(b) Pyramid of energy is never inverted because when energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step and only 10% is passed on to next trophic level. Each bar in the energy pyramid indicates the amount of energy present at each trophic level at a given time.
Question. Name the type of food chains responsible for the flow of larger fraction of energy in an aquatic and a terrestrial ecosystem, respectively. Mention one difference between the two food chains.
Answer. In aquatic system, grazing food chain and in terrestrial ecosystem, detritus food chain is responsible for flow of larger fraction of energy.
For difference,
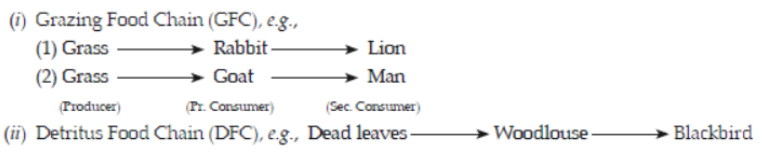
Question. Explain xerarch succession highlighting the xeral communities.
Answer. The series of development stages of biotic succession in an arid area are is termed as xeroseres while biological succession on an arid area is called xerarch.
Primary succession on rocks
• Lichens are the pioneer species on a bare area.
• The lichen secretes some acids to dissolve rock and help in weathering and soil formation.
• Later, some small bryophytes invade and hold the small amount of soil.
Question. Where and how does the primary succession occur? Explain.
Answer. Primary succession occurs on newly cooled lava or bare rocks or newly created pond or reservoir. (Any two)
Primary succession in water
• The pioneer species are phytoplanktons.
• The phytoplanktons are replaced by free-floating angiosperms.
Primary succession on rocks
• Lichens are the pioneer species on a bare area.
• The lichen secretes some acids to dissolve rock and help in weathering and soil formation.
Question. Draw and complete the following model of carbon cycle filling a, b, c, d, e and f.
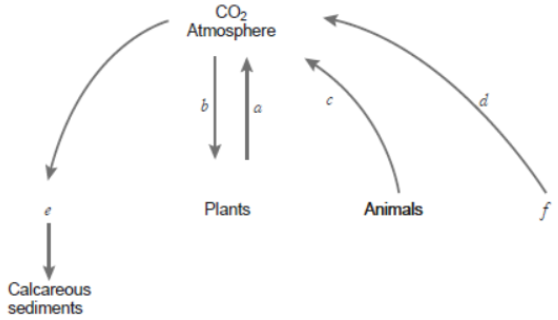
Answer. (a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Respiration
(d) Combustion of fossil fuels
(e) Aquatic food chain
(f) Coal, oil.
Question. (a) State any two differences between phosphorus and carbon cycles in nature.
(b) Write the importance of phosphorus in living organisms.
Answer. (a) Table 14.14: Differences between phosphorus and carbon cycles
(b) Phosphorus is a major constituent of biological membranes, nucleic acids and cellular energy transfer system.
Question. Describe the effects of human activities in influencing natural ecosystem cycles with special reference to carbon cycle.
Answer. Human activities have significantly influenced the carbon cycle. Rapid deforestation and massive burning of fossil fuels for energy and transport have significantly increased the rate of release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas which allows the solar radiations to enter but prevent the escape of heat radiations of longer wavelength. The absorbed radiations again come to earth’s surface and heat it up. Thereby increasing the average temperature of surface of the earth, i.e., global warming.

