Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproductive Health Worksheet Set A. Download printable Biology Class 12 Worksheets in pdf format, CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health Worksheet has been prepared as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Also download free pdf Biology Class 12 Assignments and practice them daily to get better marks in tests and exams for Class 12. Free chapter wise worksheets with answers have been designed by Class 12 teachers as per latest examination pattern
Chapter 3 Reproductive Health Biology Worksheet for Class 12
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf in Class 12. This test paper with questions and solutions for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for tests and exams and help you to score better marks
Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health Worksheet Pdf
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. GIFT is
(a) transfer of a sperm in fallopian tube of a female with the help of injections.
(b) transfer of a zygote fertilized in vitro in the fallopian tube of female incapable to conceive.
(c) transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into another females fallopian tube who can’t produce an ovum but can provide a good environment for further development.
(d) embryo is developed in vitro and then transferred into female’s tract.
Answer. C
Question. What is the function of copper-T ?
(a) Checks mutation
(b) Stops fertilization
(c) Stops zygote formation
(d) Stops oblituation of blastocoel
Answer. B
Question. Progestasert and LNG-20 are
(a) Implants
(b) Copper releasing IUDs
(c) Non-medicated IUDs
(d) Hormone releasing IUDs
Answer. D
Question. What is the figure given below showing in particular ?
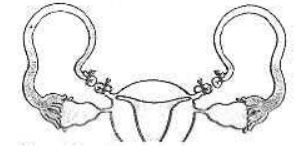
(a) Ovarian cancer
(b) Uterine cancer
(c) Tubectomy
(d) Vasectomy
Answer. C
Question. Match Column -I with Column - II.
Column I Column II
Method Mode of Action
A. The pill I. Prevents sperms reaching cervix
B. Condom II. Prevents implantation
C. Vasectomy III. Prevents ovulation
D. Copper T IV. Semen contains no sperms
(a) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(b) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(c) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – I; D – IV
Answer. A
Question. Select the correct match of the techniques given in column I with its feature given in column II.
Column I Column II
A. ICSI I Artificially introduction of semen into the vagina or uterus.
B. IUI II Transfer of ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube where fertilization occur
C. IUT III Formation of embryo by directly injecting sperm into the
D. GIFT IV Tovraunmsfer of the zygote or early embryo (with upto 8 blastomeres) into a fallopian tube.
E. ZIFT V Transfer of embryo with more than 8 blastomeres into the uterus
(a) A – V; B – IV; C – I; D – III; E – IV
(b) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV; E – V
(c) A – III; B – V; C – II; D – IV; E – I
(d) A – III; B – I; C – V; D – II; E – IV
Answer. D
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : Cu-T and Cu-7 do not suppresses sperm-motility.
Reason : Hormones released by them affect sperm motility.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : HIV infection can be avoided by use of condoms.
Reason : Condoms secrete anti-viral interferons.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Copper-T is an effective contraceptive device in human females.
Reason : Copper-T prevents passage of sperms from vagina upwards into fallopian tubes.
Answer. C
Question. Government of India has raised the marriageable age of female to 18 years and of males to 21 years. Suggest any two more measures adopted by Government for the purpose.
Answer. (i) Incentives given to couples with small families.
(ii) Media publicity through posters of happy couples with two children (Hum Do Humare Do).
(iii) Motivation to promote smaller families by using contraceptive methods.
(iv) Raising marriageable age of females to 18 years & males to 21 years. (Any two)
Question. Why is tubectomy considered a contraceptive method?
Answer. Tubectomy involves cutting a piece of the fallopian tube and tying its ends. This way, the sperms are not able to reach the egg so fertilisation cannot take place. Thus, it acts as a contraceptive method.
Question. A woman’s husband is infertile. So the lady has decided to have baby by taking sperms from sperm bank. Which technique will you suggest for her pregnancy?
Answer. Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection
Short Answer Questions
Question. At the time of Independence, the population of India was 350 million, which exploded to over 1 billion by May 2000. List any two reasons for this rise in population and any two steps taken by the government to check this population explosion.
Answer. Two reasons for increase in population are:
(i) A rapid decline in death rate, maternal mortality rate and infant mortality rate.
(ii) Increase in number of people in reproducible age.
Two steps for checking population explosion:
(i) Statutory raising of marriageable age of the females to 18 years and males to 21 years.
(ii) Incentives given to couples with small families.
Question. The alarming population growth is leading to scarcity of basic requirements. Suggest with reasons, any two population control measures other than contraception to address the situation.
Answer. Following are the population control measures other than contraception:
(a) Advertisements in the media to generate awareness about advantages of small families.
(b) Statutory raising of marriageable age of the female to 18 years and that of males to 21 years,to delay the number of births.
(c) Incentives given to couples with small families, to motivate others to comply. (Any two)
Question. Comment on the RCH programme of the government to improve the reproductive health of the people.
Answer. The basic aims of the RCH programmes are creating public awareness regarding reproductionrelated aspects population growth and providing facilities to build up a healthy society with added emphasis on the health of mother and child.
Question. State True/False with explanation.
(a) Abortions could happen spontaneously too. (True/False)
(b) Infertility is defined as the inability to produce a viable offspring and is always due to abnormalities/defects in the female partner. (True/False)
(c) Complete lactation could help as a natural method of contraception. (True/False)
(d) Creating awareness about sex related aspects is an effective method to improve reproductive health of the people. (True/False)
Answer. (a) True: Due to internal factors like incompatibility, abortion could happen spontaneously.
(b) False: Infertility may also be caused due to male partner when sperm count is low or their mobility is less.
(c) True: Lactational amenorrhea is a method of contraception as ovulation does not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition.
(d) True: Creating awareness about sex-related aspects removes the myths and misconceptions about these problems.
Question. A couple is eager to know the sex of their unborn child. What diagnostic technique will you suggest? What social abuse is associated with the application of this technique?
Answer. Amniocentesis is the suggested diagnostic technique which when applied helps in sex determination of the foetus and may lead to social abuse like female foeticides.
Question. Name an oral pill used as a contraceptive by human females. Explain how does it prevent pregnancy.
Answer. ‘Saheli’ is an oral pill used as a contraceptive by females. Oral pills inhibit ovulation and implantation, as well as, alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent or retard entry of sperms.
Thus, fertilisation and further pregnancy is prevented.
Question. Why is ‘Saheli’ considered to be an improved form of oral contraceptive for human female?
Answer. “Saheli” contains a non-steroidal preparation and is a once-a-week pill, with high contraceptive value and very less side-effects. Therefore, it is considered an improved form of contraceptive pills.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproductive Health Worksheet Set A
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Chapter 3 Reproductive Health CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
The above practice worksheet for Chapter 3 Reproductive Health has been designed as per the current syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students studying in Class 12 can easily download in Pdf format and practice the questions and answers given in the above practice worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest practice worksheets with solutions have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology students to get all the latest study material free of cost. Teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the practice sheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. After solving these you should also refer to Class 12 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 3 Reproductive Health Class 12 Biology have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

