Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Worksheet Set C. Download printable Biology Class 12 Worksheets in pdf format, CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Worksheet has been prepared as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Also download free pdf Biology Class 12 Assignments and practice them daily to get better marks in tests and exams for Class 12. Free chapter wise worksheets with answers have been designed by Class 12 teachers as per latest examination pattern
Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Biology Worksheet for Class 12
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf in Class 12. This test paper with questions and solutions for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for tests and exams and help you to score better marks
Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Worksheet Pdf
Very Short Answer
Q1) Define mutation?
Q2) What is pleiotropic gene?
Q3) What are alleles?
Q4) Which is not an autonomous feature of a gene?
Q5) What are genes?
Short Answer
Q6) Define polygenic inheritance?
Q7) What do you mean by the chromosomal theory of inheritance?
Q8) What do you understand by the law of dominance?
Q9) What do you mean by the law of independent assortment?
Q10) What do you mean by law of segregation?
Long Answer
Q11) Explain about genetic disorders?
Q12) State the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Q13) State the difference between monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross?
Q14) Write short note on sex determination?
Q15) Distinguish between chromosome and genes?
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Write the types of sex determination mechanisms the following crosses show. Give an example of each type.
(i) Female XX with Male XO
(ii) Female ZW with Male ZZ
Answer. (i) Male heterogamety, Grasshopper
(ii) Female heterogamety, Birds
Question. Mention the type of allele that expresses itself only in homozygous state in an organism.
Answer. Recessive allele.
Question. Write the percentage of F2 homozygous and heterozygous populations in a typical monohybrid cross.
Answer. The ratio of a typical monohybrid cross is 1 : 2 : 1 where 50% are homozygous and 50% are heterozygous populations. (25% homozygous dominant, 25% homozygous recessive)
Question. Why do normal red blood cells become elongated sickle shaped structures in a person suffering from sickle cell anaemia?
Answer. Due to point mutation, glutamic acid (Glu) is replaced by valine (Val) at the sixth position of b-globin chain of haemoglobin molecule. Under oxygen stress erythrocytes lose their circular shape and become sickle-shaped.
Question. Name the type of cross that would help to find the genotype of a pea plant bearing violet flowers.
Answer. Test cross.
Question. A cross was carried out between two pea plants showing the contrasting traits of height of the plant. The result of the cross showed 50% of parental characters. Name the type of cross.
Answer. Test cross
Question. A human being suffering from Down’s syndrome shows trisomy of 21st chromosome. Mention the cause of this chromosomal abnormality.
Answer. Due to non-disjunction i.e., 21st pair of chromosomes fail to separate during gametogenesis.
Therefore, the gamete possesses 24 chromosomes instead of 23. When such a gamete fuses with another gamete, the zygote will have three copies of chromosome 21 causing trisomy.
Question. Why, in a test cross, did Mendel cross a tall pea plant with a dwarf pea plant only?
Answer. To determine the genotype of the tall plant, whether it is homozygous dominant or heterozygous,as dwarfness is a recessive trait which is expressed only in homozygous condition and he was sure of genotype of dwarf plant.
Question. Name the stage of cell division where segregation of an independent pair of chromosomes occurs.
Answer. Anaphase-I of Meiosis-I.
Question. Name the respective pattern of inheritance where F1 phenotype
(a) does not resemble either of the two parents and is in between the two.
(b) resembles only one of the two parents.
Answer. (a) Incomplete dominance (b) Dominance
Question. Name a human genetic disorder due to the following:
(i) An additional X-chromosome in a male
(ii) Deletion of one X-chromosome in a female
Answer. (i) Klinefelter’s Syndrom e (ii) Turner’s Syndrome
Short Answer Questions
Question. How would you find genotype of a tall pea plant bearing white flowers? Explain with the help of a cross. Name the type of cross you would use.
Answer. It can be done by a test cross. This is done by crossing the plant with homozygous recessive parent. If the ratio of progeny is 1 : 1, then the genotype of the plant is heterozygous.
Question. When a tall pea plant was selfed, it produced one-fourth of its progeny as dwarf. Explain with the help of a cross.
Answer. Production of one-fourth dwarf progeny on selfing of a tall pea plant indicates that the plant is heterozygous. This can be explained with the cross as follows:
Question. A teacher wants his/her students to find the genotype of pea plants bearing purple coloured flowers in their school garden. Name and explain the cross that will make it possible.
Answer. Test cross will be done.
• It is a method devised by Mendel to determine the genotype of an organism.
• In this cross, the organism with dominant phenotype (but unknown genotype) is crossed with the recessive individual.
• In a monohybrid cross between violet colour flower (W) and white colour flower (w), the F1 hybrid was violet colour flower. The test crosses are:
Question. When does a geneticist need to carry a test cross? How is it carried?
Answer. Geneticists carry out a test cross to find out the genotype of the unknown parent. This is carried out by crossing the progeny with the homozygous recessive parent.
Question. Mendel crossed plants that bred true for yellow seeds with plants that bred true for green seeds.
All seeds in the F1 generation were yellow. Work out the inheritance involved in this cross by using symbols for the trait. Which trait was dominant?
Answer.
Question. A cross was carried out between two pea plants showing the contrasting traits of height of the plant. The result of the cross showed 50% of parental characters.
(i) Work out the cross with the help of a Punnett square.
(ii) Name the type of the cross carried out.
Answer. (i)
(ii) Test cross
Question. What is a test cross? How can it decipher the heterozygosity of a plant?
Answer. A cross to analyse whether genotype of dominant individual is homozygous or heterozygous is called test cross.
On crossing with a recessive parent, if 50% of progeny have dominant trait and 50% have recessive trait then the plant is said to he heterozygous.
In the first cross the tall parent plant is heterozygous for the trait, in second cross tall parent plant is homozygous for the trait, hence the respective observation.
Question. How does a test cross help to determine the genotype of an individual?
Answer. In a test cross the individual of unknown genotype is crossed with the recessive parent. If all progenies are dominant, then the genotype exhibits homozygosity and if the progenies have a dominant to recessive ratio 1 : 1, then the genotype exhibits heterozygosity.
Question. Human blood group is a good example of multiple allelism and co-dominance. Justify.
Answer. Multiple allelism: Generally in an individual or population, only two alleles of a trait govern the character, but in case of ABO blood group, three alleles IA, IB and i are found to govern blood group in human population. This is multiple allelism.
Co-dominance: Allele IA and IB when present in an individual, both being dominant express their own types of sugars or traits. Thus, exhibiting co-dominance.
Question. With the help of one example, explain the phenomena of co-dominance and multiple allelism in human population.
Answer. ABO blood group in human being is an example of multiple allelism and co-dominance. There are three alleles for the gene I, i.e., IA, IB, and i, thus, exhibiting multiple allelism.
When IA and IB are present together the blood group is AB. Both A and B blood groups are expressed. This is called co-dominance.
Question. Give an example of an autosomal recessive trait in humans. Explain its pattern of inheritance with the help of a cross.
Answer. Sickle cell anaemia is an autosomal recessive trait in humans. The disease is controlled by a single pair of alleles HbA and HbS. Only the homozygous individuals HbS HbS show the diseased phenotype. The heterozygous individuals (HbAHbS) are carriers.
Question. Recently a baby girl has been reported to suffer from haemophilia. How is it possible? Explain with the help of a cross.
Answer. It is possible to have a haemophilic girl if a carrier woman married a haemophilic man as shown here: (Image 168)
Question. Haemophilia is a sex-linked inheritance condition in humans where a simple cut causes nonstop bleeding. Study the pedigree chart showing the inheritance of haemophilia in a family. Answer the questions that follow:
Give reasons which explain that haemophilia is
(i) sex-linked, and
(ii) caused by ‘X’-linked gene.
Answer. (i) Haemophilia is sex-linked because it shows transmission from unaffected carrier female to some of the male progeny.
(ii) Haemophilia is caused by ‘X’-linked gene because the heterozygous female for haemophilia may transmit the disease to sons. It appears more in males because of only one X chromosome.
Question. A colour-blind man marries a woman with normal vision whose father was colour-blind.
Work out a cross to show the genotype of the couple and their respective sons.
Answer. The father of normal woman is colour-blind, so the woman will be carrier, i.e., XXC.
Question. Marriage between a normal couple resulted in a son who was haemophilic and a normal daughter. In course of time, when the daughter was married to a normal man, to their surprise, the grandson was also haemophilic.
(a) Represent this cross in the form of a pedigree chart. Give the genotypes of the daughter and her husband.
(b) Write the conclusion you draw from the inheritance pattern of this disease.
Answer. (a)
(b) Sex-linked recessive inheritance pattern.
Question. Two heterozygous parents are crossed. If the two loci are linked what would be the distribution of phenotypic features in F1 generation for a dihybrid cross?
Answer. If the two loci are completely linked, then there would be no segregation and the F1 generation will exhibit parental characteristics only. But if the two loci are incompletely linked, then segregation would occur partly and the F1 generation will exhibit both parental and recombinant characteristics but the recombinants will be in a very small proportion depending on distance between gases.
Long Answer Questions
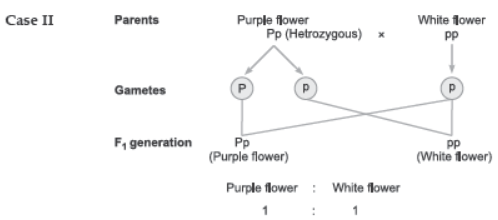
Question. For flower colour in pea, the allele for purple flower (P) is dominant to the allele for white flower (p). A purple flowered plant therefore could be of genotype PP or Pp. What genetic cross would you make to determine the genotype of a purple flowered plant? Explain how your cross gives you the correct genotype of the purple flowered plant?
Answer. The genotype of a purple flowered plant can be determined by conducting a test cross i.e., crossing the purple flowered plant with homozygous recessive individual i.e., pp.
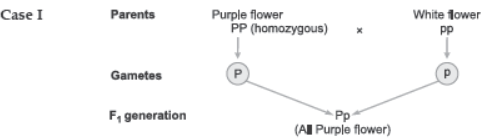
If the F1 generation produces purple and white flowers in 1:1 ratio, the parent would be heterozygous, i.e., Pp.
Question. How are dominance, co-dominance and incomplete dominance patterns of inheritance different from each other?
Answer. Dominance: It is a phenomenon in which when two contrasting alleles are present together, only one expresses itself and is called dominant whereas the other which does not express itself is called recessive e.g., Tt – ‘T’ is dominant over t (dwarfness).
Co-dominance: It is a phenomenon in which when two contrasting alleles are present together, both the alleles express themselves e.g., IA IB genotype gives blood group AB.
Incomplete dominance: It is a phenomenon in which when two contrasting alleles are present together neither of the alleles is dominant over other and the phenotype formed is intermediate of the two alleles. e.g.,
Red flower × White flower → Pink flower colour
RR × rr Rr
Question. Both Down’s syndrome and Turner’s syndrome are examples of chromosomal disorders. Cite the differences between the two.
Answer. Differences between Down’s syndrome and Turner’s syndrome (Table 178)
Question. During his studies on genes in Drosophila that were sex-linked. T.H. Morgan found population phenotypic ratios deviated from expected 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. Explain the conclusion he arrived at.
Answer. (i) He observed that when the two genes in a dihybrid cross are located on the same chromosome,the proportion of parental gene combinations in the progeny was much higher than the nonparental or recombination of genes.
(ii) Morgan and his group found that when genes were grouped on the same chromosome, some genes are tightly linked and show less recombination.
(iii) When the genes are loosely linked they show higher recombination.
Question. A red-eyed heterozygous female fruit fly is crossed with a red-eyed male. Work out all possible genotypes and phenotypes of the progeny. Comment on the pattern of inheritance of eye colour in fruit flies.
(ii) The gene for eye colour is sex-linked and is present on X chromosome.
The character passes into the male from female and the male passes it to the female in the next generation. Male has only one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome with no corresponding allele.
In humans, male heterogamety is observed. They exhibit XY type of sex determination.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Worksheet Set C
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
The above practice worksheet for Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation has been designed as per the current syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students studying in Class 12 can easily download in Pdf format and practice the questions and answers given in the above practice worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest practice worksheets with solutions have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology students to get all the latest study material free of cost. Teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the practice sheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. After solving these you should also refer to Class 12 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Biology have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

