NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Social Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Social Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 1 Resources and development is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 1 Resources and development Class 10 Social Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 1 Resources and development in Class 10. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 1 Resources and development NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
Resource and Development
Key Points to Remember
• Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as 'Resources'.
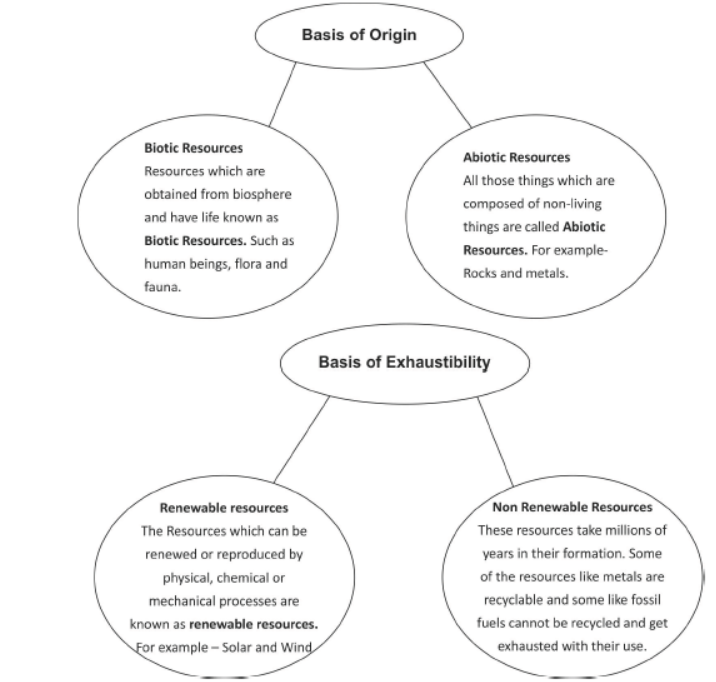
Types of Resources
• Sustainable economic development means "development should take place without damaging the environment, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations".
• Widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources is known as resourcing planning.
• In june, 1992 more than 100 heads of states met in Rio de janeiro in brazil. The rio convention endorsed the global forest principles and adopted agenda 21. It is an agenda to combat environmental damage,poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interest, mutual needs and shared responsibilities.
• According to Mahatma Gandhi ji There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed.
Classification of soil on the basis of color, thickness texture, age, chemical and physical properties.
Keys term of the chapter
(i) Piedmont zone: A piedmont is an area at the base of mountain or mountain range. For ex. piedmont zone of western ghat means the area lying at the foot of western ghats.
(ii) Deccan trap region: The black soil area of peninsular plateau is known as deccan trap. It is formed by lava soils, which is very fertile and useful for the cultivation of cotton.
(iii) Duars, chos and terai: Duars are the flood plains and foot hills of eastern himalayas in north eastern india around bhutan.
Chos : The southern slopes of shiwalik range in punjab and himachal pradesh, devoid of forest cover, highly dissected by seasonal streams called chos.
Terai is a belt of marshy land at the foothills of himalayas in northern india.
(iv) Sustainable econimic development: It means development should take place without damaging the environment and develpoment in the present should not compromise with needs of future generation.
(v) Resource planning: Techniques or skills for proper utilisation of resources is termed as resource planning.
(vi) Conservation of resources: Adequate management of resources,e.g. water, land, plants, soil etc. by man to meet the needs and aspirations of the future generation.
(vii) Afforestation: The process of transforming an area into a forest.
(viii) Alluvial plain: A level tract of land made of alluvium or fine rock material brought down by a river.
(ix) Arable land: Land currently ploughed and cultivated with crops. It is also called cultivable land.
(x) Bangar: The old alluvial desposits which is not fertile.
(xi) Khadar: The new alluvium deposits during floods. It is the most fertile soil.
(xii) Soil erosion: Removal of the upper layer of soil from one place to another by any natural agent or human activities is called soil erosiom.
(xiii) Net sown area: The land that is actually put to cultivation.
(xiv) Gross sown area: It includes net sown area and area cultivated more than once.
(xv) Desertification: It is the process by which an area becomes a desert.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development MCQs
Question. Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(b) Biotic
(c) Flow
(d) Non-renewable
Answer: (d) Non-renewable
Question. Under which of the following type of resource can tidal energy be put?
(a) Replenishable
(b) Human-made
(c) Abiotic
(d) Non-recyclable
Answer: (a) Replenishable
Question. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation
(b) Deforestation
(c) Over irrigation
(d) Overgrazing
Answer: (c) Over irrigation
Question. In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practiced?
(a) Punjab
(b) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
(c) Haryana
(d) Uttarakhand
Answer: (d) Uttarakhand
Question. In which of the following states is black soil found?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Gujarat
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Jharkhand
Answer: (b) Gujarat
Question. One the basis of exhaustibility resources can be classified into following categories:
(a) Biotoc and abiotic
(b) Renewable and non renwable
(c) Individual, community
(d) Potential,developed
Answer : B
Question. Which state amont the north eastern states has been fully surveyed for its land use?
(a) Arunachal pradesh
(b) Manipur
(c) Tripura
(d) Assam
Answer : D
Question. Everthing available in our environment to satisfy our needs is termed as:
(a) Technology
(b) Resource
(c) Natural vegetation
(d) None of these
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is not classified on the basis of status of development?
(a) Potential resource
(b) Developed stock resource
(c) Reserve resource
(d) Renewable resource
Answer : D
Question. The running water cuts through the clayey soils and make:
(a) Bad land
(b) Gullies
(c) Deltas
(d) None of these
Answer : B
Question. Everything available in our environment to satisfy our needs is termed as
(a) technology
(b) resource
(c) natural vegetation
(d) none of these
Answer : B
Question. The resources of ownership are
(a) plantation
(b) pasture land
(c) ponds
(d) all of the above
Answer : D
Question. Resource planning is essential for ___________ existence of all forms of life.
(a) ecological balance
(b) sustainable
(c) exploitation
(d) none of these
Answer : B
Question. On the basis of its origin, resources can be classified into
(a) renewable and non-renewable
(b) continuous and biological
(c) biotic and abiotic
(d) recyclable and non-recyclable
Answer : C
Question. Where was the first international Earth Summit held?
(a) Rio de Janeiro
(b) Geneva
(c) Switzerland
(d) Philippines
Answer : A
Question. Geothermal energy in Puga valley and Parvati Valley are
(a) stock resources
(b) developed resources
(c) reserve resources
(d) potential resources
Answer : B
Question. Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(b) Biotic
(c) Flow
(d) Non-renewable
Answer : D
Question. Land left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year is called ___________.
(a) culturable wasteland
(b) current fallow land
(c) wasteland
(d) none of the above
Answer : B
Question. Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been detrained for utilisation are known
(a) potential resources
(b) stock
(c) developed Resources
(d) reserves
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is not a measure for soil conservation?
(a) strip cropping
(b) terrace cultivation
(c) shelter belts
(d) overdrawing of groundwater
Answer : D
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development Fill in the blanks
Question. Resource are .............. accessible economically feasible and ............acceptable.
Answer : Technologically, culturally
Question. ............. soil is also known as regur and ideal for growing ..............
Answer : Black, cotton
Question. According to their age alluvial soils can be classified as .......... and.................
Answer : Khadar (new), Bangar (old)
Question. ............... aimed at achieving global sustainable development.
Answer : Agenda 21
Question. ................ is the main cause of land degradation in punjab.
Answer : Over irrigation
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development Asseration and Reason Based Questions
Directions: In the following questions (16-20) a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of
(c) If A is true and R is false.
(d) If A is false R is true.
Question. Assertion: Alluvial soil is ideal for growth of paddy, wheat, cereal and pulse crops.
Reason: Alluvial soil is well known for its capacity to hold moisture.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion: The availability of resources is not the only necessary condition for the development of any region.
Reason: Not only availability of resource but also corresponding change in technology is necessary for the development of any region.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion: Resources are free gifts of nature.
Reason: Resources like soil, air, water are available in nature.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion: Terrace cultivation does not restrict soil erosion.
Reason: Running water cuts through the clayey soil and makes deep channels as gullies.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion: Land is a natural resource of utmost importance.
Reason: Land can be used for various purposes.
Answer : A
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development Very Short Answer Questions
Question. When and where was the first International Earth Summit held?
Answer : Rio de Janeiro in Brazil in June 1992, where 100 heads of states met.
Question. What was Agenda 21 of Earth Summit of Rio de Janeiro?
Answer : The agenda was to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease through global cooperation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities.
Question. What is the importance of land as a natural resource?
Answer : Land supports natural vegetation, wild life, human life, economic activities, transport and communication systems.
Question. What is Net Sown Area?
Answer : It is the actual area under cultivation.
Question. Give one characteristic of forest soils.
Answer : In the snow covered areas of Himalayas, these soils experience denudation and are acidic with low humus content.
Question. What is soil erosion?
Answer : The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion.
Question. What is the role of human beings in the development of a resource?
Answer : Human beings transform material available in our environment into resources and use them.
Question. Which resources are community owned resources?
Answer : These are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Example— Public parks, picnic spots, cinema halls, playgrounds, etc.
Question. What are National Resources.
Answer : Technically, all the resources available in a nation are categorised as National Resources.
Example—Minerals, wild life, forests, water resources, land of a nation, roads, railways.
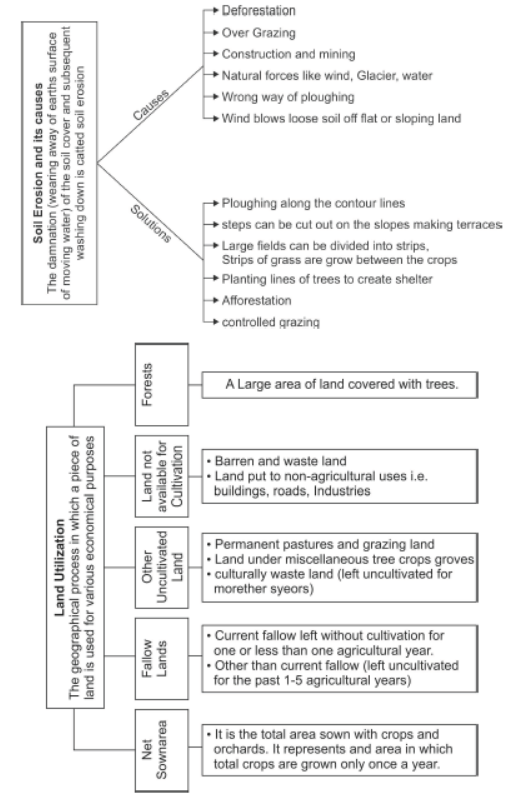
Question. How is soil eroded?
Answer : Soil is eroded due to human activities like deforestation, overgrazing and construction and mining, etc. Natural forces like wind, glacier and water also lead to soil erosion.
Question. How does soil erosion take place due to defective methods of farming?
Answer : Ploughing in a wrong way, i.e., up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion.
Question. What is contour ploughing?
Answer : Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is called contour ploughing.
Question. What is gross cropped area?
Answer : It is the actual area under cultivation along with the fallow land, which is left uncultivated for fertility.
Question. What is waste land?
Answer : Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas and land put to other non agricultural uses including settlements, roads, railways, industries, etc.
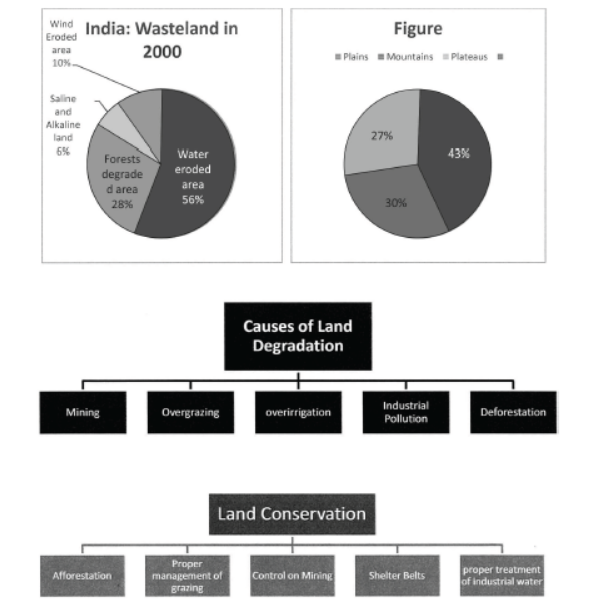
Question. How does land degradation occur?
Answer : Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it, results in land degradation.
Question. In which states is land degraded due to mining?
Answer : In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha, deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation.
Question. In which states is over irrigation responsible for land degradation?
Answer : In the states of Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water-logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
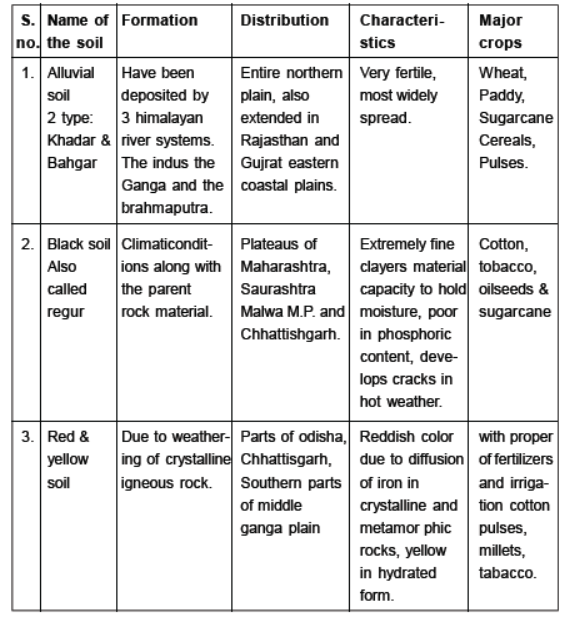
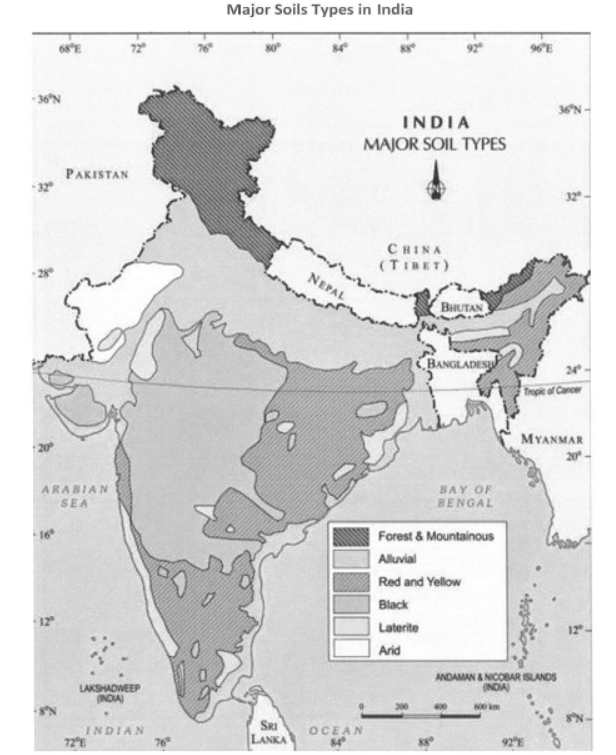
Question. Name three states having black soil and the crop, which is mainly grown in it.
Answer: Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat are states having black soil. Black soil is ideal for growing cotton.
Question. What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Answer: Alluvial Soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast. Three features of alluvial soil:
1.It is very fertile.
2.Ideal for growing sugarcane, wheat and rice
3.The regions of alluvial soils like northern plains are intensively cultivated and densely populated.
Question. What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Answer: In hilly areas, soil erosion can be controlled by the following:
1.Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water.
2.Use of terrace farming techniques in agriculture and
3.Using strips of grasses to check soil erosion by wind and water
Question. What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Answer: Biotic Resources: The resources, which are obtained from the biosphere and have life, are called biotic resources. For example, flora, fauna, fisheries, livestock, etc. Abiotic Resources: The resources, which are composed of non-living things, are called abiotic resources. Such as, water, metals, solar energy, wind, minerals such as gold, iron, copper, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development Short Answer Questions
Question. What is the importance of soil as a resource?
Answer : (i) Soil is the most important renewable natural resource.
(ii) It is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms on the Earth.
(iii) Soil helps in providing food to this Earth.
Question. Describe any three main features of the black soil.
Answer : (i) Black soils are made up of extremely fine; clayey material.
(ii) They are well-known for their capacity to hold moisture.
(iii) They are rich in soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime.
(iv) They develop deep cracks during hot weather, which helps in the proper aeration of the soil.
Question. How are resources associated with colonialism?
Answer : (i) The history of colonisation reveals that rich resources in colonies were the main attractions for the foreign invaders.
(ii) It was primarily the higher level of technological development of the imperial powers, that helped them exploit the resources of the colonies.
Question. Which factors determine the use of land?
Answer : (i) Physical factors—topography, climate, soil types.
(ii) Human factors—Population density, technological capability and culture and tradition, etc.
Question. How is mineral processing responsible for land degradation?
Answer : (i) The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere.
(ii) It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land.
Question. Why are shelter belts grown?
Answer : (i) Planting lines of trees to create shelter also work in a similar way.
(ii) Rows of such trees are called shelter belts.
(iii) These shelter belts have contributed significantly to the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in western India.
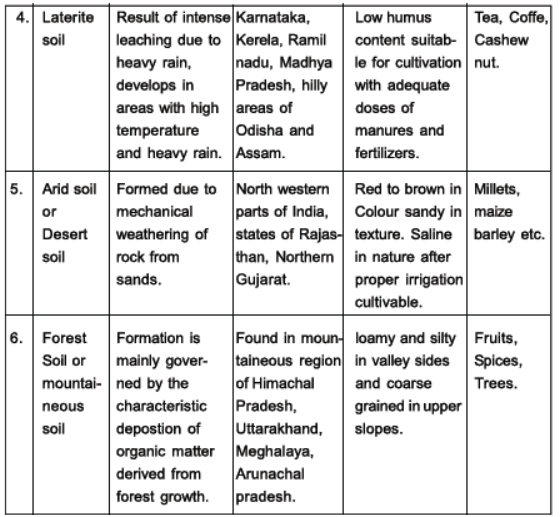
Question. Name the states in which laterite soils are found and give any two characteristics of this soil.
Answer : Laterite soils are found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh and in the hilly areas of Odisha and Assam.
Chief characteristics:
(i) Humus content of the soil is low because most of the microorganisms, particularly the decomposers like bacteria, get destroyed due to high temperature.
(ii) Laterite soils are suitable for cultivation with adequate doses of manures and fertilisers.
Question. Why was the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, 1992 held?
Answer : (i) In June 1992, more than 100 heads of states met in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil for the first International Earth Summit.
(ii) It was held for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
(iii) This convention adopted Agenda 21, for achieving sustainable development in the 21st century.
Question. Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
Answer: The landuse of India is determined both by physical and human factors. Total geographical area of India is 3.28 million sq km, but landuse data is available of for 93% of the total area. Some areas of Jammu and Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China have also not been surveyed. Land resources in India are primarily divided into forest, barren and unculturable wasteland, area under non-agricultural uses, permanent pasture, and grazing land, area under tree crops and groves, culturable wasteland, follow land, current follow, and new sown area. Wasteland includes rocky, arid, and desert areas, and land used for other non-agricultural purposes such as housing, roads, and industry. According to the recent data, about 46.24% of the total land area is net sown area, 22.78% is covered by forests, and 3.38% is used for grazing. The rest is wasteland, with traces of miscellaneous cultivation.
The land under forest has not increased much since 1960–61 because in the post-independence era demand for more land to expand agriculture, Industrialisation, urbanisation, developmental works, and infrastructural facilities, led to clearance of forests areas. Thus, land under forest has increased by only about 4% since 1960-61.
Question. How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Answer: Technical and economic development have led to more consumption of resources on account of various factors such as:
→ Technological development provides sophisticated equipments. As a result, production increases ultimately leading to consumption of more resources.
→ Technological development also leads to economic development. When the economic condition of a country rises, the needs of people also rise. It again results into more consumption of resources.
→ Economic development provides favourable environment for the development of latest technologies. It helps to make or convert various materials found around us into resources. Finally, it results into the consumption of new available resources too.
Project/Activity
Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answe
(i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
(ii) A type of non-renewable resource.
(iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity.
(iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
(v) Plantation of trees on a large scale to check soil erosion.
(vi) The Great Plains of India are made up of these soils.
Answer:
(i) Resources
(ii) Minerals
(iii) Black
(iv) Laterite
(v) Afforestation
(vi) Alluvial
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development Long Answer Questions
Question. Classify resources based on origin.
Answer : Resources can be categorized on the basis of origin: Abiotic resources comprise non-living things (e.g., land, water, air and minerals). Biotic resources are obtained from the biosphere. These have life such as humans, flora and fauna.
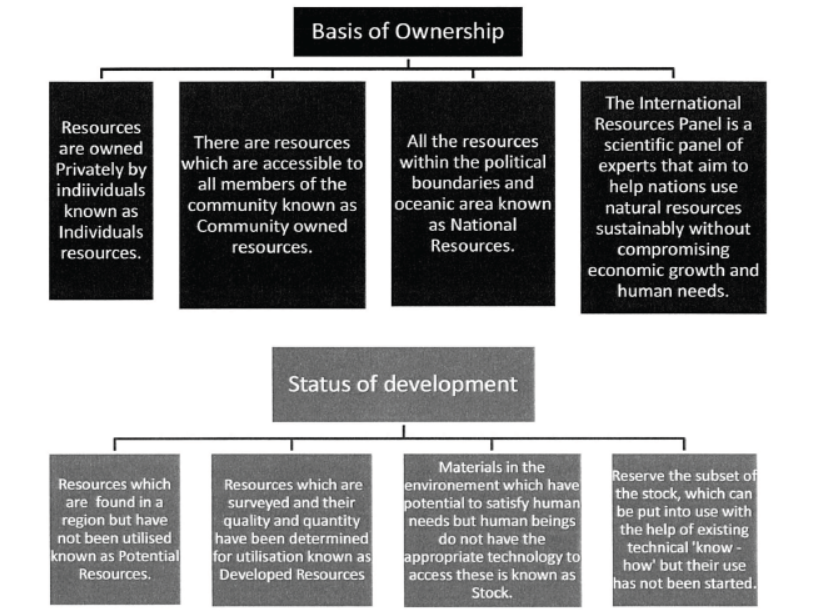
Question. Provide a suitable classification for resources on the basis of ownership. Mention main features of any three types of such resources.
Answer : Classification based on ownership:
Individual: Resources owned by individuals are called Individual Resources. For example – land owned by farmers, house, etc.
Community : Resources owned by community or society are called Community Owned Resources. For example – Graveyard, grazing land, ponds, burial grounds, park, etc.
National Resources : Resources owned by individual nations are called National Resources. The nation has legal powers, to acquire even private property for public good. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife land in the political boundaries and in oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles from the coast (called territorial waters) and the resources in them belongs to the country. For example – Government land, Roads, canals, railway, etc.
International Resources : Resources regulated by International bodies are called International Resources. For example – Ocean and sea beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone is called open sea or ocean. No individual country can utilize these resources without the permission of International bodies.
Question. Which is the main cause of land degradation in Gujarat, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh? How can it be checked? Explain.
Answer : (i) Main Cause : Large scale overgrazing has caused severe land degradation.
Measures to check include:
(a) Afforestation and proper management of grazing.
(b) Planting of shelter belts of plants.
(c) Stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes.
Question. Enumerate any three features of "regur" soil.
Answer : (i) Regur soil is also known as black soil.
(ii) It is ideal for growing cotton, so it is also known as "Black cotton soil".
(iii) It is made up of extremely fine clayey material.
(iv) It is rich in soil nutrients, calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime.
(v) It develops cracks in hot weather.
(vi) It can hold moisture and is sticky when wet.
Question. Describe any five distinct characteristics of 'Arid soils'.
Answer : (i) Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
(ii) Sandy in texture and saline in nature.
(iii) Evaporation from this soil is faster, soil lacks humus and moisture.
(iv) Soil occupied by Kankar.
(v) Kankar restricts the infiltration of water.
Question. Classify the resources on the basis of exhaustibility. State two characteristics of each.
Answer : Renewable Resources : Resources that can be replenished after a short period of time are called Renewable Resources. For example – agricultural crops, wind energy, water, forest, wildlife, etc.
Non-renewable Resources : Resources which takes million years of time to replenish are called non-renewable resources. For example – fossil fuels. We must remember that some resources like metals are recyclable.
Question. Which soil types is made up of lava flows?
Answer : Black soil
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Current fallow land
(ii) Other than current fallow
(iii) Culturable waste land
Answer : (i) Current fallow land : Left uncultivated for one or less than one agricultural year.
(ii) Other than current fallow : Left uncultivated for past 1 to 5 agricultural years.
(iii) Culturable waste lands : Left uncultivated for more than 5 agricultural years.
Question. How are red and yellow soils formed? Why do they look red?
Answer : (i) Red soils develop on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan Plateau.
(ii) These soils develop a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks.
(iii) It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form.
Question. Give any four characteristics of arid soils of India.
Answer : Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
(i) They are sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas, the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
(ii) Due to dry climate, high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture.
(iii) The lower layers of the soil are occupied by Kanker because of the increasing calcium content downwards.
(iv) After proper irrigation, these soils become cultivable as has been in the case of western Rajasthan.
Question. Why do we need to conserve resources?
Answer : (i) The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of any region.
(ii) Resources are vital for any developmental activity.
(iii) But irrational consumption and over utilisation of resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems.
(iv) To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important.
(v) If the present trend of resource depletion by a few individuals and countries continue, the future of our planet is in danger.
Therefore, we need to conserve resources for sustainable existence of all forms of life.
Question. What efforts were made for resource planning in the First Five Year Plan?
Answer : (i) The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of any region. But technological knowledge is an important prerequisite for it.
(ii) There are many regions in our country that are rich in resources but are economically backward; whereas there are some regions which have a poor resource base but are economically developed.
(iii) Resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development.
(iv) In India, development or resource development does not only mean the availability of resources but also the technology, quality of human resources and the historical experiences of the people.
Question. What are the causes of land degradation? What are the ways to solve this problem?
Answer : Causes of land degradation:
(i) Mining sites are abandoned after the excavation work is done, leaving deep scars of overburdening. In states like Odisha, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation.
(ii) Overgrazing in states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra is one of the main reasons behind land degradation.
(iii) Overirrigation and waterlogging lead to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the states of Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh, thereby leading to land degradation.
(iv) Mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceremic industry generate huge quantities of dust in the atmosphere. It stops the infiltration of water in the soil.
(v) Industrial effluents as wastes have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country.
Ways to check land degradation:
(i) Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to check land degradation.
(ii) Planting of shelter belts help in checking the sand causing land degradation near the deserts.
(iii) Overgrazing can be checked and avoided.
(iv) Stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes can also check land degradation.
(v) Proper management of waste land can be taken up.
(vi) Control on mining activities, so that mining does not affect the land and by refilling the scars.
(vii) Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial areas.
Question. What are the non-material things?
Answer: Non-material things are the non-physical needs of the people. This includes equal treatment, freedom, security, respect etc. People prefer to earn more to fulfil their material as well as non-material needs.
Question. What condition may allow women to take up a variety of jobs or run business?
Answer: One important condition that would allow women to take up work or do business is Women Empowerment. It means the social conditions prevalent, which guarantee equality and ability for a woman to enjoy all their rights, get access to resources, income and time, in order to take up employment of their liking or carry out a business for profit. Woman empowerment is aimed the holistic well-being of a woman.
Question. According to the World Bank, What are low-income countries?
Answer: In World Development Report brought out by the World Bank, the countries with per capita income of USD 12736 per annum and above in 2013, are called rich countries and those with per capita income of USD 1570 or less are called low-income countries. India comes in the category of low middle-income countries because its per capita income in 2013 was just US$1570 per income.
Question. What does BMI stand for?
Answer: BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It is the ratio of the height and weight of a person. It is a major indicator of the health of a person. If the BMI is less than 18.5, then the person in undernourished and if it is more than 25, then a person is considered overweight.
BMI= Weight (in kg)/ (Height)2 (in mm)
Question. Start one cause of high infant mortality rate.
Answer: Infant Mortality rate indicates the number of children who die before the age of one year, as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year. One reason for high mortality rate would be public distribution system which provides health and nutritional status to the state.
Question. Which neighbouring country of India has better performance in terms of human development than India?
Answer: Sri Lanka is the neighbouring country of India has better performance in terms of human development than India. Sri Lanka is the island of the nation of south India in the Indian Ocean but yet it is better developed than India.
Question. Why are countries of the Middle East not called ‘developed’ in spite of high per capita income?
Answer: Per capita income is calculated by dividing the total income of a country to the total population of that particular country. It shows the standard of living of the citizens of that particular country. A country with higher per capita income is more developed than others with less per capita income. But countries of the Middle East not called ‘developed’ in spite of high per capita income. The reasons are listed below:
1. Middle Eastern countries have become rich only with the resources available and they have high per capita income due to the oil production. So, they have only one major source of income.
2. Although these countries have very high per capita income, there is an unequal distribution of wealth. The gap between the rich and the poor is very high in these countries.
3. These countries are not considered developed because they lack other basic facilities such as health care and education. Without these basic facilities people of a country cannot contribute much to the national income and thus no development takes place.
Question. Think of any three development goals of a boy from a rich urban family.
Answer: The three development goals of a boy from a rich urban family would be as follows:
1. He may think to get a quality education and pursue his studies abroad.
2. He may require the availability of vocational education and training.3. He may require a new laptop for research work.
Question. What is Human Development Index? Which organization HDI? Explain the three major indicators of HDI.
Answer: Human Development Index is the development of an individual in such a way that he can able to earn and fulfil his materialistic desire. UNDP or the United Nations Development Programme is the organization that measures HDI. Human Development Report 2006 published by UNDP, “Development is based on per capita income, educational levels of the people and their health status.” Therefore the three major indicators of HDI are the per capita income, education and status.
Question. What is meant by sustainable economic development? Give its main features.
Answer: The regular process without harming the productivity of future generation and satisfy the need of the present generation is known as sustainable economic development. This concept stresses the role of the environment as capital that, if exhausted, cannot be replaced. It requires preservation of human capital, physical capital and natural capital. The main features of sustainable economic development are: Reduction in pollution, quality of life of future generation should not reduce, efficient use of natural resources. United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) defined sustainable development as ‘Development that meets the need of the present generation without compromising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs.’
Question. ‘Although the level of income is an important indicator of development, it is an inadequate measure of the level of development.’ Justify the statement.
Answer: Although the level of income is an important indicator of development, it is an inadequate measure of the level of development. Money can buy things that can be one factor on which our life depends like food. But the quality of non-material things like freedom, security and respect cannot be bought with money. We cannot buy pollution free environment, unadulterated medicines and peace with money. Schools, colleges, parks, hospitals etc are the facilities which cannot be run individually. There has to be a collective effort of team work between the government and society in providing these to the general public. Therefore, money in your pocket cannot buy all the goods and services that you may need to live well. Income by itself is not a completely adequate indicator of material goods and services that citizens are able to use.
Question. What are public facilities? Give an example. What values do the public facilities strengthen?
Answer: The facilities which are provided by the Government are considered as a public facility like schools, hospitals, community halls, transport, electricity etc. As we know that Punjab has more income than the average person in Kerala but Kerala has a low infant mortality rate because of a better public system like Public Distribution System which provides health and nutritional status to the state. We need a public facility because we are not able to purchase all things by money. Public facilities are described as institutional places which are basic individual requirements, such as wellness, education, protection, entertainment, and worship. Public facilities establish the value that certain amenities are granted to all residents of the nation irrespective of rich or poor.
Question. We have a fixed amount of renewable resources that cannot be replenished. What does the statement mean? Identify the values that we need to generate to overcome the problem of resources being exhausted.
Answer: Non-renewable resources are the resources which cannot be renewed and only used once. Therefore, resources are scarce and human wants are unlimited. Also, one resource is capable of satisfying more than one needs and it can be put to alternative uses. We have a fixed amount of renewable resources that cannot be replenished. The problem of resources being exhausted can be overcome by the following methods:
1. The treatment of the water returns it into its original state both for domestic, industrial use and for safe disposal. Water treatment is essential since it ensures that there is sufficient water for human use. Management of water is also achieved by a change in lifestyle. Using only the amount of water you require and not leaving taps running will go a long way in conserving water.
2. Recycling and reusing are better alternatives to disposing of some items. For better management and efficient utilization of resources, reduction in the amount of usage is important. Better efficiency constitutes a change of lifestyle which will in turn mean less waste.
3. Nearly all vehicles use fossil fuels to move from one place to another. Discouraging individuals from using individual cars go a long way in reducing the amount of fuel consumed on the global scene. Buses and trains are alternatives to personal vehicles because they have a lower person-to-fuel ratio.
4. Implementation of laws and regulations to curb the waste of resources is important in the management of resources.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Water Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Power Sharing |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Federalism |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Popular Struggles and Movements |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Challenges to Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Print Culture and Modern World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money And Credit |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalization And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Social Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 1 Resources and development of Social Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 1 Resources and development Class 10 chapter of Social Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 1 Resources and development NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Social Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Social Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Social Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Social Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 1 Resources and development Class 10 Social Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 1 Resources and development Social Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 1 Resources and development have been answered by our teachers

