NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Social Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Social Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 6 Political Parties is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 6 Political Parties Class 10 Social Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 6 Political Parties in Class 10. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 6 Political Parties NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
Political Parties
Key terms and their meaning
1. Political Parties : A group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government.
2. Ruling Party : Political party that runs the government.
3. Defection : Changing party allegiance from the party on which a person got elected to a different party.
4. Affidavit : A signed document submitted to an officer where a person makes a sworn statement regarding his/her personal information.
5. Partisan : A person who is strongly committed to a party, group or faction. Partisanship is marked by a tendency to take a side and inabilit to take a balanced view on an issue.
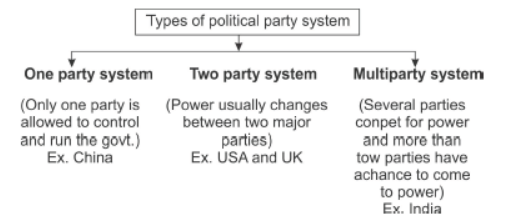
6. One Party System : In some countries only one party is allowed to control and run the government. These are called one party system.
For ex. China.
7. Alliance or Front : When several parties in a multi party system join hands for the purpose of contesting elections and winning power it is called an alliance or front.
8. State Funding of Election : The government should give parties money to support thier election expenses.
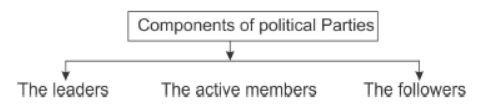
9. Components of Political Parties : The political leaders, the active members and the followers.
10. Opposition Party : The largest non government party or coalition of parties.
Functions of Political Parties
- To contest elections
- Make policies and programmes
- Make laws
- Run Government
- Play role of opposition
- Launch movements for the resolution
- Introduce welfare schemes
- Shape public opinion
How many parties should we have
- It is not something a country can choose.
- It evolves over a long time.
- Depends on the nature of society its social and religious divisons.
- Depends on its history of politics and system of election.
- It cannot be changed very quickly.
Types of Political Party Systems
Necessity of Political Partics
- Modern democracies cannot exist without political parties
- Without parties every candidate in the elections will be independent so no one will be able to make any promises to people about any major policy change.
- Government may be formed but its utility will remain ever uncertain.
- Elected representatives will be accountable to their constituency for what they do in the locality.
- No one will be responsible for how the country will be run.
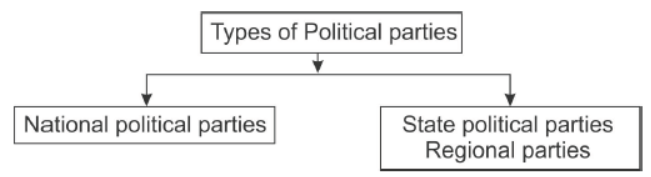
Difference between Natioal parties and State Political Parties
National Political Parties State Political Parties
- Present in several or all - Parties which are present in few
federal units of the federation federal units only.
- A party that secures at least - A party that secures at least 6% of
6% of the total votes in Lok the total votes in an election to the
Sabha elections or Assembly Legislative assembly of a state
elections in 4 states.
- Win at least 4 seats in Lok - Wins at least 2 seats in the legis-
Sabha. lative assembly of a state.
National Parties : There were seven recognised national parties in the country in 2018.
As per latest information after 2019 elections there are 8 national parties in India.


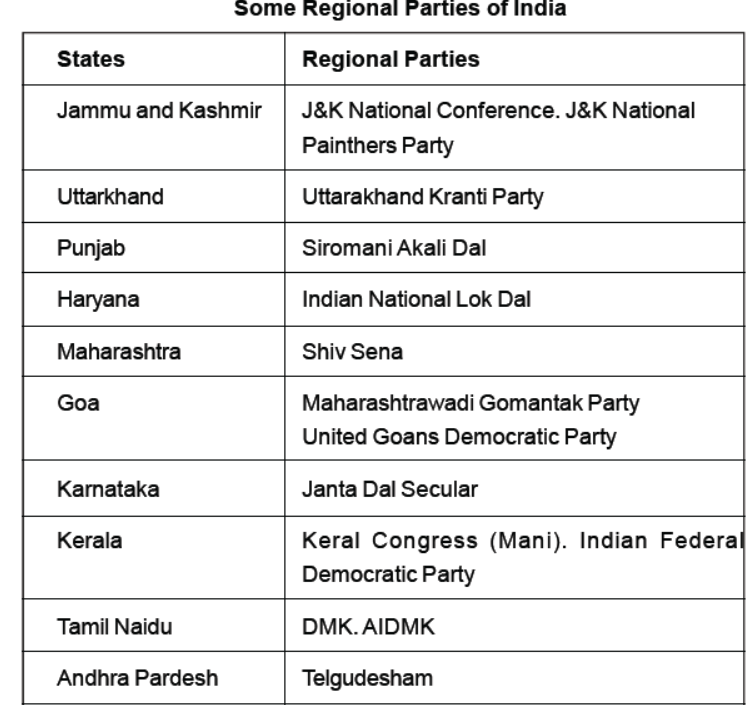
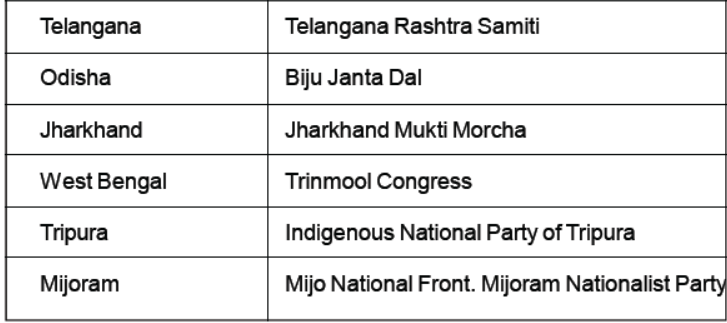
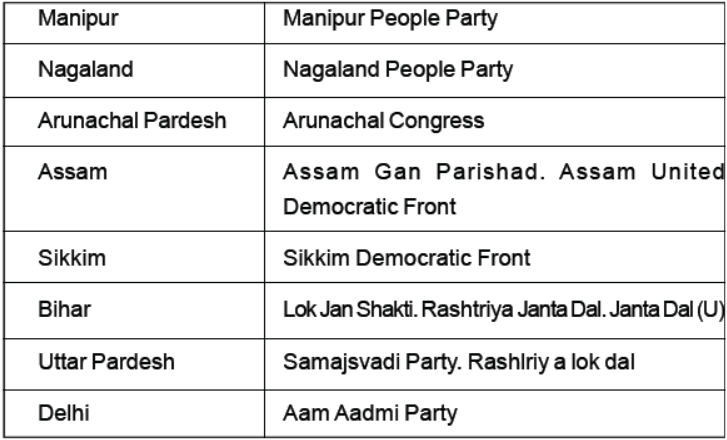
Some interesting Facts
- First General Election held in India in 1951-52 after Independence.
- Pt. Jawahar Lai Nehru became the First Prime Minister of India.
- W.C. Banerjee was the first chairperson of Indian National Congress.
- Shayama Prasad Mukherjee was the first chairperson of Bhartiya Janta Party.
- Sh. Kashiram was the the first chairperson of Bahujan Samaj Party.
- In 1985 Anti-Defection act comes into the power.
MCQ TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Which of these is not a good option for a democratic state ?
(a) One-party system
(b) Two party system
(c) Multi party system
(d) None of these
Answer. A
Question. In Which one of the following states does 'Shiv Sena' exist as a regional party.
(a) Gujarat
(b) Karnataka
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Madhya Pradesh
Answer. C
Question. Who among the following recognises 'Political Parties' in India ?
(a) Election Commission
(b) President of India
(c) Speaker of Lok Sabha
(d) Supreme Court
Answer. A
Question. The political party which believes in Marxism Leninism is .......
(a) Nationalist congress party
(b) Communist party of India
(c) DMK
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Answer. B
Question. Which is not the component of a political party ?
(a) The leaders
(b) The followers
(c) The active members
(d) The ministers
Answer. D
Question. What does the picture show?
A. Role of one party in America
B. Corporate America controls all major Institution of thecountry
C. The party’s symbol is elephant
D Multi-party system
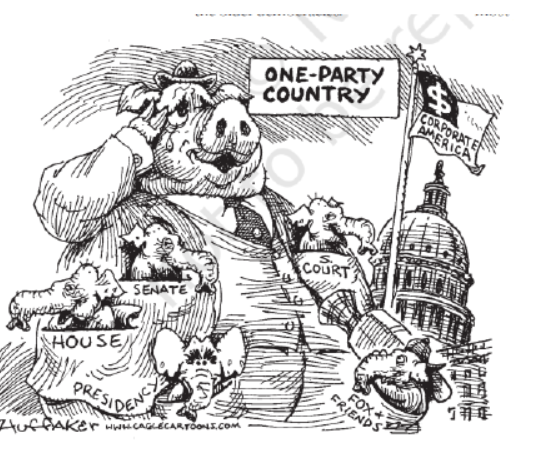

Answer. B
Question. In countries like India, _________ choose candidates for contesting elections.
A. Top party leaders
B. Members of party
C. Supporters of party
D. Government officers
Answer. A
Question. Berlusconi was the Prime Minister of ________. His company owns TV channels, the most important publishing company, a football club (AC Milan).
A. Italy
B. France
C. Poland
D. Germany
Answer. A
Question. Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the Code below in the lists
List 1 List 2
1 Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP): a. 1964
2 Indian National Congress (INC): b. 1980
3 Nationalist Congress Party (NCP) c. 1885
4 Communist Party of India - Marxist (CPI-M) d. 1999
A. 1.b, 2.c, 3. d ,4. a
B. 1.c, 2.b, 3. d ,4. a
C. 1.c, 2.a, 3. b ,4. d
D. 1.b, 2.c, 3. a ,4. D
Answer. A
ASSERTION AND REASON
Two statements are given in the question below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option.
Options
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Question. Assertion: It is mandatory for every candidate who contests election to file an AFFIDAVIT .
Reason: The Supreme Court passed an order to reduce the influence of money and criminals.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion: Political parties are easily one of the most visible institutions in a democracy.
Reason: For most ordinary citizens, democracy is equal to political parties.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion:- China doesn’t follow One party system
Reason:- In China only the communist party is allowed to rule
Answer. D
Question. Assertion A : Only those parties that are recognised as national parties can contest in elections for Parliament
Reason R : Every party in the country has to register with the Election Commission.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion: India has evolved a multiparty system .
Reason: It is because the social and geographical diversity in such a large country is not easily absorbed by two or even three parties
Answer. A
Fill in the blanks:
Question. ____ is the mother party of Bhartiya Janta party.
Answer. Bhartiya Jan Sangha
Question. Bahujan Samaj Party was formed under the leadership of ___ .
Answer. Kanshi Ram
Question. ___ and ___ are examples of two-party system.
Answer. USA and UK
Question. We cannot consider one party system as a good option because this is not a ___ option.
Answer. Democratic
Question. 'State parties' are commonly referred to as ___ .
Answer. Regional parties
Write if the given statement is True/False
Question. In some cases, parties support criminals who can win elections ___ .
Answer. True
Question. National parties have representation in less than four states ___ .
Answer. False
Question. Trinamool congress was formed by Kanshi Ram ___ .
Answer. False
Question. Parties like Samaj Wadi Party and Rashtriya Janta Dal have national level political organisation with units in several states ___ .
Answer. True
Question. In some countries, candidates for electios are selected by members and supporters of a party ___ .
Answer. True
CASE BASED QUESTIONS
1 Now, it is mandatory for every candidate who contests elections to file an AFFIDAVIT giving details of his property and criminal cases pending against him. The new system has made a lot of information available to the public. But there is no system of check if the information given by the candidates is true. As yet we do not know if it has led to decline in the influence of the rich and the criminals.
The Election Commission passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organisational elections and file their income tax returns. The parties have started doing so but sometimes it is mere formality. It is not clear if this step has led to greater internal democracy in political parties. Besides these, many suggestions are often made to reform political parties: A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of political parties. It should be made compulsory for political parties to maintain a register of its members, to follow its own constitution, to have an independent authority, to act as a judge in case of party disputes, to hold open elections to the highest posts. It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a minimum number of tickets, about one-third, to women candidates. Similarly, there should be a quota for women in the decision making bodies of the party.
Question. It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a minimum number of tickets, about one-third, to ------ candidates.
A Dalits
B Women
C Youths
D All the above
Answer. B
Question. Who appoints the Chief Election Commissioner of India?
A Prime Minister
B Governor
C President
D None of these
Answer. C
Question. There were --------- recognised national parties in the country in 2019.
A 7
B 6
C 10
D 5
Answer. A
Question. A signed document submitted to an officer, where a person makes a sworn statement regarding her personal information is known as-------
A Defection
B Affidavit
C Partisan
D Pledge
Answer. B
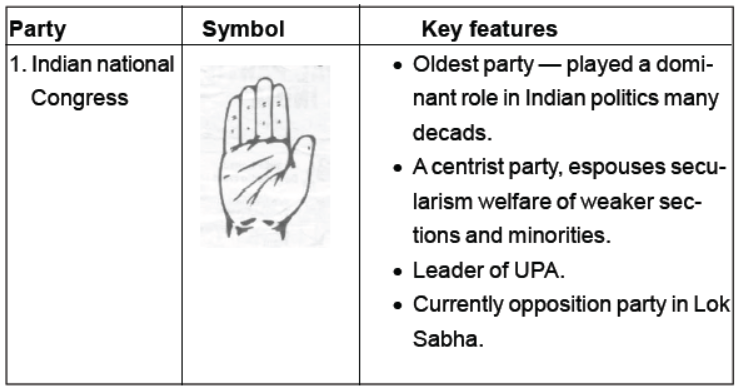
2 Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP): Founded in 1980 by reviving the erstwhile Bharatiya Jana Sangh, formed by Syama Prasad Mukherjee in 1951. Wants to build a strong and modern India by drawing inspiration from India’s ancient culture and values; and Deendayal Upadhyaya’s ideas of integral humanism and Antyodaya. Cultural nationalism (or ‘Hindutva’) is an important element in its conception of Indian nationhood and politics Indian National Congress (INC): Popularly known as the Congress Party. One of the oldest parties of the world. Founded in 1885 and has experienced many splits. Played a dominant role in Indian politics at the national and state level for several decades after India’s Independence . centrist party (neither rightist nor leftist) in its ideological orientation, the party espouses secularism and welfare of weaker sections and minorities . Nationalist Congress Party (NCP): Formed in 1999 following a split in the Congress party . Espouses democracy, Gandhian secularism, equity, social justice and federalism. Wants that high offices in government be confined to natural born citizens of the country. A major party in Maharashtra and has a significant presence in Meghalaya, Manipur and Assam. A coalition partner in the state of Maharashtra in alliance with the Congress . Since 2004, a member of the United Progressive Alliance
Question. Which party supports Gandhian secularism?
A. INC
B.NCP
C.CPI
D.BSP
Answer. B
Question.-------- Political party wants to build a strong and modern India by drawing inspiration from India’s ancient culture and values
A NCP
B.BJP
C.INC
D.AITC
Answer. B
Question. ----- political party espouses secularism and welfare of weaker sections and minorities
A NCP
B.BJP
C.INC
D.AITC
Answer. C
Question. ------believes in Marxism-Leninism, secularism and democracy. Opposed to the forces of secessionism and communalism.
A NCP
B.BJP
C.INC
D.CPI
Answer. D
2 MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. Why political parties are a necessary condition for a democracy?
Answer. Political parties bring various representatives together to form a responsible Government
Question. What you mean by partisan?
Answer. Partisan: A person who is strongly committed to a party, group or faction. Partisanship is marked by a tendency to take a side and inability to take a balanced view on an issue
Question. What are the two ways of carrying out political reforms in a democratic country?
Answer. 1. By empowering people. 2. By spreading political awareness
Question. Give the reason why a multiparty system has evolved in India.
Answer. It is because the social and geographical diversity in such a large country is not easily absorbed by two or even three parties. No system is ideal for all countries and all situations.
Question. What do you understand by a ‘recognised party’?
Answer. A party that gets some privilege such as a unique symbol and other special facilities is called a ‘recognised’ party by the Election Commission.
Question. What is defection? Why do MLAs and MPs commit defection?
Answer. Defection: Changing party allegiance from the party on which a person got elected (to a legislative body) to a different party MLAs and MPs do this in order to become ministers or for cash rewards.
3 MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. Describe the various party system existing in various countries.
Answer. 1.In some countries, only one party is allowed to control and run the government. These are called ONE-PARTY systems.eg China
2.In some countries, power usually changes between two main parties. Such a party system is called TWO-PARTY system. The United States of America and the United Kingdom are examples of two-party system
3.MULTIPARTY SYSTEM(several parties) eg India
Question. Distinguish between Regional party (State) and National party
Answer. STATE PARTY.
A party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a State and wins at least two seats is recognised as a State party.
NATIONAL PARTY .
A party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four States and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha is recognised as a national party.
Question. In what way is an alliance different from a coalition government?
Answer. ALLIANCE
When several parties in a multi-party system join hands for the purpose of contesting elections and winning power, it is called an alliance or a front.
COALITION.
When no single party gets a clear majority in the election and the government is formed by various parties coming together, it is called a coalition.
Question. Political parties play major role in democracy. Explain any three points to justify this statement.
Answer. Parties contest elections
2 Parties put forward different policies and programmes and the voters choose from them.
3 Parties play a decisive role in making laws for a country.
4 Parties form and run governments
5 Those parties that lose in the elections play the role of opposition
6 Parties shape public opinion
5 MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. Lack of internal democracy within parties is a major challenge to political parties allover the world. How far do you agree with it?
Answer. The power is concentrated in one or few leaders at the top
parties do not keep membership registers
parties do not hold organizational meetings
they do not conduct internal elections regularly
ordinary members do not get sufficient information on what happens inside the party.
Question. Elucidate some of the recent efforts taken in our country to reform political parties and its leaders.
Answer. Constitution was amended to stop defection.
Supreme Court passed an order to submit an affidavit giving details of candidates property details and criminal cases pending against him.
The Election Commission made it mandatory for political parties to hold organisational elections and file their income tax returns.
One third seats are reserved for women in local self- government
Question. Name the national party which was formed under the leader ship of Kanshi Ram . Mention any four features of that party.
Answer. 1.Kanshi Ram formed Bahujan Samaj (BSP) party in 1984 for the welfare of bahujan samaj which included dalits, adivasis, OBCs and religious minorities,
2.It was inspired from the ideas and teachings of Sahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Dr. B.R. Ambedkar and others.
3.It has main base in UP, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Delhi and Punjab.
4. Stands for the cause of securing the interests and welfare of the dalits and oppressed people
5.It has formed government in UP several times with the help of other parties,
Question. What is a political party? Suggest and explain any four measures to reform political parties.
Answer. A political party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government. The following reforms could be suggested in order to strengthen parties so that they perform their functions well.
• Regulation of party’s internal affairs: A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of political parties. It should be made compulsory for political parties to maintain a register of their members, to follow their own constitution, to have an independent authority, etc.
• State funding: There should be state funding of elections. The government should give money to parties to support their election expenses to avoid corruption.
• Pressure of public opinion: Political parties can be reformed if people put pressure on them. This can be done through petitions, propaganda and agitations. Pressure groups and media play an important role in it.
• Ensure women participation: It should be made mandatory for all political parties to allot one-third of the tickets to women to ensure their decisive voice in decision making. If the above-mentioned suggestions are taken into consideration, it can be ensured that these could lead to some improvement in the working of the political parties.
Question. ‘Modern democracies cannot exist without political parties.’ Examine the statement.
Answer. In a democratic set-up, political parties are required because without political parties:
• Every candidate in the elections will be independent. No promises could be made and the utility of the government formed will remain uncertain.
• No one will be responsible for running the country.
• Elected representatives will only be accountable to their constituency
• There will be no agency to gather and present different views on various issues to the government.
• No one will be responsible for bringing various representatives together so as to form a responsible government. No mechanism to support the government, make policies and justify or oppose them
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics for chapter 6 Political Parties
Question. State the various functions political parties perform in a democracy.
Answer. The various functions political parties perform in a democracy are:
• Candidates are put forward by political parties to contest in elections. These candidates may be chosen by the top leaders, or by members of the party.
• Parties put forward their policies and programmes for voters to chose from them.
• Political parties play a major role in making laws for the country. No law can become a bill unless majority parties support it.
• Political parties form and run governments.
• Parties that lose election play the role of opposition.to the party in power.
• Parties shape public opinion.
• Political parties form an important link between the government and the people. It is easy for the public to approach their local leader than a government official.The local leader has to listen to the public demand, otherwise he will lose the next election.
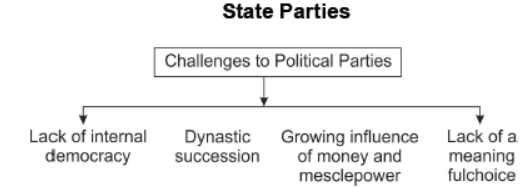
Question. What are the various challenges faced by political parties?
Answer. The various challenges faced by political parties are -
• Lack of internal democracy: This challenge is faced by political parties all over the world. There is a tendency that power is concentrated with some big leaders within the party. Parties do not hold organizational meetings and do not hold internal elections regularly. Ordinary members of a party are not aware of what is going on in the party.
• Dynastic succession: In many parties, top positions are always controlled by members of one family. This is unfair to other members of a party and it is bad for democracy.
• Role of money and muscle power: Parties are mainly interested in winning elections. They tend to use short-cuts to win elections. Parties pick candidates that can raise huge amounts of money. As a result, rich people and companies who fund parties also shape the policies of the party. In many cases, political parties give tickets to criminals who can win the election.
• No meaningful choice: Another challenge is the lack of any meaningful choice to the voters. In recent years, there has been a decline in the ideological differences among parties in most parts of the world. For example, the difference between the Labour Party and the Conservative Party in Britain is very little. They agree on more fundamental aspects but differ only in details on how policies are to be framed and implemented. In India too, the differences among all the major parties on the economic policies have reduced. Those who want really different policies have no option available to them.
Question. Suggest some reforms to strengthen parties so that they perform their functions well?
Answer. Some reforms that are suggested to strengthen parties are -
• A law should be brought into force to regulate internal affairs of political parties. It should be made compulsory for a political party to:
- Maintain a register of its members
- Follow its own constitution
- Have an independent authority to act as judge in case of party disputes
- Hold independent elections for highest posts
• It should be made mandatory for all political parties to give one-third tickets to women candidates. There should also be a quota for women in the decision making body of a party.
• There should be state funding of elections. Funds should be given by the government to the parties for their election expenses.
Question. What is a political party?
Answer. A political party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government. They agree on some policies and programmes for the society with a view to promote the collective good.
Question. What are the characteristics of a political party?
Answer. Important characteristics of political parties are -
• They agree on some policies and programmes for the society with a view to promote the collective good.
• Since there can be different vie\NS on what is good for all, parties try to persuade people why their policies are better than others.
• They seek to implement these policies by winning popular support through elections.
• Parties reflect fundamental political divisions in a society.
• Parties are a part of society and thus involve partisanship. Thus, a party is known by which part it stands for, which policies its supports and whose interests it upholds.
Question. A group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government is called a _
Answer. A group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government is called a political party.
Question. Match List I (organisations and struggles) with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
|
|
List I |
List II |
|
1. |
Congress Party |
A. National Democratic Alliance |
|
2. |
Bharatiya Janata Party |
B. State Party |
|
3. |
Communist Party of India (Marxist) |
C. United Progressive Alliance |
|
4. |
Telugu Desam Party |
D. Left Front |
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
(a) |
c |
A |
B |
D |
|
(b) |
c |
D |
A |
B |
|
(c) |
c |
A |
D |
B |
|
(d) |
D |
c |
A |
B |
Answer. (c)
Question. Who among the following is the founder of the Bahujan Samaj Party?
A.Kanshi Ram
B. Sahu Maharaj
C. B.R. Ambedkar
D. Jotiba Phule
Answer. A. Kanshi Ram
Question. What is the guiding philosophy of the Bharatiya Janata Party?
A. Bahujan Samaj
B. Revolutionary democracy
C. Integral humanism
D. Modernity
Answer. C. Integral humanism
Question. Consider the following statements on parties.
A. Political parties do not enjoy much trust among the people.
B. Parties are often rocked by scandals involving top party leaders. C. Parties are not necessary to run governments.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A,B and C
(b) A and B
(c) B and C
(d) A and C
Answer. (b) A and B
Question. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below:
Muhammad Yunus is a famous economist of Bangladesh. He received several international honours for his efforts to promote economic and social development for the benefit of the poor. He and the Grameen Bank he started jointly, received the Nobel Peace Prize for 2006. In February 2007, he decided to launch a political party and contest in the parliamentary elections. His objective was to foster proper leadership, good governance and build a new Bangladesh. He felt that only a political party different from the traditional ones would bring about new political culture. His party would be democratic from the grassroots level.
The launching of the new party, called Nagarik Shakti (Citizens' Power), has caused a stir among the Bangladeshis. While many welcomed his decision, some did not like it. "Now I think Bangladesh will have a chance to choose between good and bad and eventually have a good government," said Shahedullslam, a government official. "That government, we hope, would not only keep itself away from corruption but also make fighting corruption and black money a top priority."
But leaders of traditional political parties who dominated the country's politics for decades were apprehensive. "There was no debate (over him) winning the Nobel, but politics is different- very challenging and often controversial," said a senior leader of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party. Some others were highly critical. They asked why he was rushing into politics. "Is he being planted in politics by mentors from outside the country," asked one political observer.
Do you think Yunus made a right decision to float a new political party?
Do you agree with the statements and fears expressed by various people? How do you want this new party organised to make it different from other parties? If you were the one to begin this political party, how would you defend it?
Answer. • Yunus did the right thing by forming a new party. He launched a party that was different from traditional parties. His party also promised to be democratic from the grass-root levels. Being democratic from the grass-root level meant the party would not allow power concentration with few top leaders. It would also give a fair chance to young and budding leaders to prosper. Since the party was different from traditional ones, it would give the voters a meaningful choice.
• I agree with the statement made by Shahedul Islam in support of the party. The party would provide the people with a meaningful choice which was not there with traditional parties. It would allow the people to choose a government free from corruption. On the other hand, I do not agree with the fears and apprehensions of the people opposing the new political party. These fears and apprehensions are baseless.
• To make this party different from others, the party should truly be democratic at grass-root level. The leaders and candidates should be selected by open election. The party should maintain a membership register and regularly hold organizational meetings. Moreover, the party must give one-third of the tickets to women candidates and also reserve seats for women in decision making bodies.
• I would defend the party with the following arguments -
- Traditional parties do not offer a meaningful choice to the voters
- They have failed to check corruption and flow of black money
- The party is democratic at grass-root levels which prevents power concentration with a few big leaders
- The party gives a fair chance to young and budding leaders and does not allow power concentration in one family
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties Objective Questions
Question. Consider the following statements about recognised political party.
I. A party that is present in only one of the federal units.
II. A party that is based on regional and communal diversities.
III. A party that is present in several or all units of the federation.
Which of the following statement is correct ?
Codes
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Both I and II
(d) Only III
Answer: D
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the political parties and its strong presence within states.
(a) All India Trinamool Congress — Madhya pradesh
(b) Bahujan Samaj Party — Uttar Pradesh
(c) Nationalist Congress Party — Bihar
(d) Communist Party of India (Marxist) — Punjab
Answer: B
Question. Political Parties are the most visible institutions in a democracy. Which among the following options is incorrect about political parties? Identify.
(a) Political Parties play an important role in law making process.
(b) Political Parties form and run governments.
(c) Political Parties do not shape public opinion.
(d) Political Parties reflect fundamental divisions in a society.
Answer: C
Question. What does the term ‘Partisan’ means? Choose the correct option.
(a) The affair of the state or the science of the governance.
(b) A person who is strongly committed to the party.
(c) The ruling party which runs the government.
(d) A group of people who come together to promote common beliefs.
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following party system does not provide a fair chance for competing parties to gain power?
(a) One-party system
(b) Two-party system
(c) Multi-party system
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: A
Question. What is the guiding philosophy of the Bhartiya Janata Party?
(a) Bahujan Samaj
(b) Revolutionary Democracy
(c) Integral Humanism
(d) Modernity
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following facilities does the Election Commission offer to a recognised political party?
(a) Election funds
(b) Election symbol
(c) Party name
(d) Manifesto
Answer: B
Question. Identify the Political Party with the help of the following information.
• It was formed in 1999 following a split in the Congress party.
• It wants that high offices in the government be confined to natural born citizens of a country.
• It is a major party in Maharashtra and has a significant presence in Meghalaya, Manipur and Assam.
Select the appropriate option from the following:
(a) Communist Party of India - Marxist (CPIM)
(b) All India Trinamool Congress (AITC)
(c) Nationalist Congress Party (NCP)
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Answer: C
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the political parties and their year of formation.
List I List II
(a) Bharatiya Janata Party – 1885
(b) Indian National Congress – 1980
(c) All India Trinamool Congress – 1998
(d) Nationalist Congress Party – 1997
Answer: C
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the political parties and their ideology:
(a) Communist Party of India - Social Justice
(b) Nationalist Congress Party - Gandhian Secularism
(c) Indian National Congress - Modernity
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party - Revolutionary Democracy
Answer: B
Question. Match the following:
| List I | List II |
| A. Congress Party | 1. National Democratic Alliance |
| B. Bhartiya Janata Party | 2. State Party |
| C. Communist Party of India (Marxist) |
3. United Progressive Alliance |
| D. Telugu Desam Party | 4. Left Front |
Codes
A B C D
(a) 3 1 2 4
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 4 3 1 2
Answer: C
Question. In which form of government, rulers are always elected by people?
(a) In democracy
(b) In federalism
(c) In monarchical system
(d) None of the above
Answer: A
Question. Who among the following is the founder of the Bahujan Samaj Party?
(a) Kanshi Ram
(b) Sahu Maharaj
(c) B R Ambedkar
(d) Jyotibha Phule
Answer: A
Question. Identify the political party with the help of the following information.
• It was formed in 1925.
• It believes in Marxism - Leninism, secularism and democracy.
• It opposed the forces of sucessionism and communalism.
Select the appropriate option from the following.
(a) Bhartiya Janata Party (BJP)
(b) Communist Party of India (CPI)
(c) Nationalist Congress Party (NCP)
(d) All India Trinamool Congress (AITC)
Answer: B
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties Assertion-Reason MCQs
Direction Each of these questions contains two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason(R). Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, any one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Question. Assertion (A) The Constitution was amended to prevent elected MLA's and MP's from changing parties.
Reason (R) It should be made mandatory for political parties to give one-third tickets to women candidates.
Answer: B
Question. Assertion (A) Only those parties that are recognised as national parties can contest elections for the Union level.
Reason (R) Recognition to a political party as a national party is accorded by the Election Commission.
Answer: D
Question. Assertion (A) Political Parties play a major role in making laws for the country.
Reason (R) No law can become a bill unless majority parties support it.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) Political Parties do not enjoy much trust among the people in South Asia.
Reason (R) Political Parties are one of the least trusted institutions all over the world.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) Nationalist Congress Party was formed in 1999.
Reason (R) It is a major party in Maharashtra and demands for Gandhian Secularism.
Answer: B
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties Case Based MCQs
Read the given case/source and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option.
We can understand the necessity of political parties by imagining a situation without parties. Every candidate in the elections will be independent. So no one will be able to make any promises to the people about any major policy changes. The government may be formed, but its utility will remain ever uncertain. Elected representatives will be accountable to their locality. But no one will be responsible for how the country will be run.
We can also think about it by looking at the non-party based elections to the Panchayat in many states. Although, the parties do not contest formally, it is generally noticed that the village gets split into more than one faction, each of which puts up a panel of its candidates. Thus it exactly what the party does. That is the reason we find political parties in almost all countries of the world whether these countries are big or small, old or new, developed or developing.
The rise of political parties is directly linked to the emergence of representative democracies. As we have seen, large societies need representatives democracy. As societies became large and complex, they also need some agency to gather different views on various issues and to present these to the government.
Question. Consider the following statements about political parties and choose the correct option.
I. Political Parties are a necessary condition for a democracy.
II. Political Parties help the government to make policies.
III. Political Parties justify or oppose the representative governments.
Options
(a) Only I
(b) Both I and II
(c) Both II and III
(d) All of these
Answer: D
Question. ‘Political Faction’ means a group of individuals within a political party that share a .............Identify.
(a) Balanced view
(b) Common political purpose
(c) Regional and communal diversities
(d) Ideal political structure
Answer: B
Question. Why can’t modern democracies exist without political parties? Identify the reason from the given options.
(a) As the utility of government will remain uncertain in nature.
(b) Loss of Accountability towards people.
(c) State responsibility will lead to national integration.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following describes representative democracy? Identify the best suitable option depicting the same from the following.
(a) It is not a common form of democracy in the modern age.
(b) It involves direct participation.
(c) It involves indirect participation through elected representatives.
(d) It was the most prevalent form of democracy in the Colonial era.
Answer: C
Question. Why does large society need representative democracies? With reference to the above context, infer the appropriate option.
(a) To form a responsible government.
(b) To form an ideal form of government.
(c) To gather public opinions.
(d) To resolve issues of minority communities.
Answer: A
Question. Why is the existence of Political Party necessary for a democracy? Choose the correct options from the following.
(a) Political Parties helps to develop public opinion.
(b) No independent candidate can make any promise to the people.
(c) Independent elected representatives are only responsible for their own constituency.
(d) Political Parties helps to inculcate insecurity among the people.
Answer: A
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties Short Answer Type Questions
Question. State any two advantages of the multi-party system.
In what way is an alliance different from a coalition government?
Answer: The advantages of multi-party system are
(i) This system allows a variety of interests and opinions to enjoy political representation.
(ii) Under this system, the choice of the voter is not limited to two candidates only. It gives a voter enough scope to make intelligent choice.
In the following ways, alliance is different from coalition
| Alliance | Coalition Government |
| When several parties join hands for the purpose of contesting elections, it is called an alliance or a front, e.g. the National Democratic Alliance. |
When no single party gets a majority in the election and he government is formed by two or more parties coming together, it is referred to as a coalition government. |
Question. What is meant by ‘defection’ in democracy? Explain.
Answer: Defection in democracy is a political phenomena. It means moving of a person from one party to another party for some personal benefit. It happens when a legislature, after having been elected from a particular party leaves it and joins in other party.
Anti-Defection Law was formulated to prevent elected MLA’s and MP’s from changing parties. Now the law states that if any MLA or MP changes parties, he or she will lose seat in the legislature. The new law has brought percentage of defection down and has made dissent even more difficult.
Question. What do you know about Communist Party of India?
Answer: The Communist Party of India (CPI) was formed in 1925 and believes in Marxism, Leninism, Secularism and Democracy. It opposed the forces of secessionism and communalism. It accepts parliamentary democracy as a means of promoting the interests of working class, farmers and the poor.
It became weak after the split in the party in 1964 that led to the formation of Communist Party of India (Marxist). It had significant presence in Kerala, West Bengal, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. Its support base had gradually declined over the years.
Question. Why has India adopted a Multi-party system? Explain.
Answer: India adopted a Multi-party system because
• As India is a vast and diverse country, the multi-party system was needed to accommodate the vast population.
• The social and geographical diversity of India could not be represented by two or three parties.
• The multi-party system in India evolved over a long time, depending on the nature of society, its social, regional division, its history of politics and its system of elections.
• Multi-party system ensures a healthy competition between different parties and prevents dictatorship of a single party. Indian Constitution declares India as a democratic country. Multi-party system fulfils this criteria and provides chance for proper growth of the nation.
Question. Write a short note on Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP).
Answer: Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) was founded by Kanshi Ram in 1984. It seeks to represent Bahujan Samaj, which includes Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), OBCs and religious minorities.
It gets inspiration from the ideas and teachings of Sahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Periyar Ramaswami Naicker and BR Ambedkar. It stands for the cause of securing the interests and welfare of the dalits and oppressed people.
It has its main base in Uttar Pradesh and substantial presence in neighbouring states like Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Delhi and Punjab.
Question. When was the Communist Party of India (Marxist) formed? Mention the ideologies of the party.
Answer: The Communist Party of India (Marxist) Party was formed in 1964.
Ideologies of Communist Party of India (Marxist) are
• The party believes in Marxism-Leninism. It supports socialism, secularism and democracy and opposes imperialism and communalism.
• The party accepts democratic elections as a useful and helpful means for securing the objective of socio-economic justice in India.
• The party is critical of the new economic policies that allow free flow of foreign capital and goods into the country.
Question. It is true that meaningful choice is not given to the voters? Discuss.
Answer: Yes, it is true that meaningful choice is not given to the voters as often political parties do not offer them. In order to offer meaningful choice, parties must be significantly different from each other. In recent years, there has been a decline in the ideological differences among parties in most parts of the world. In our country, the differences among all the major parties on the economic policies have reduced. Those who actually want different policies, have no option available to them. Sometimes, people can’t even elect very different leader either because the same set of leaders keep shifting from one party to another.
Question. How are political parties recognised as regional and national parties in India? Explain with examples.
Answer: In India, there are both national and regional parties.
The parties that are present in only one of the federal units are called regional or state parties. On the other hand parties that are present in several or all units of the federation are known as national parties.
Hence, the political parties are recognised as regional and national parties on the following basis
• A party that secures at least 6% of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a state and wins at least two seats, is recognised as a State or Regional party. For example, Janata Dal (Secular), Telugu Desam Party.
• A party that secures at least 6% of the total votes in Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four states and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha , is recognised as a National party. For example, India National Congress, Bharatiya Janata Party etc.
Question. What is the difference between national and regional party?
Answer: The differences between national and regional party are
| National Party | Regional Party |
| It influences the whole country. |
Its influence is limited and region-based. |
| It takes national as well as international issues. |
It is interested in promoting regional/state interest only. |
| It has to secure at least 6% of the total votes in the Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in 4 states and win at least 4 seats in the Lok Sabha. |
It has to secure at least 6% of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a state and win at least 2 seats in the State Assembly. |
Question. Expain the three components of ‘political party’.
Answer: A political party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government.
The three components of political party are
(i) The Leaders Every political party has some prominent leaders who formulate policies and programmes of the party and choose candidates for contesting elections.
(ii) The Active MembersThey are involved in different committees of the party and participate directly in their activity.
The three components of political party are
(i) The Leaders Every political party has some prominent leaders who formulate policies and programmes of the party and choose candidates for contesting elections.
(ii) The Active Members They are involved in different committees of the party and participate directly in their activity.
Question. What is the role of the opposition party in a democracy?
Answer: The opposition party plays a very important role in a democracy as
• It acts as pressure group.
• It mobilises the government.
• It keeps a check on the working of the ruling party.
• It puts different views in the Parliament and criticise the government for its failures or wrong policies.
• It watches over the ruling party to prevent the government from being authoritarian and restrict its powers.
• It also have the right to audit the government’s spending.
• The opposition parties outside the legislature draw media’s attention and publish their criticism of government policy in the newspapers.
Question. “Nearly every one of the state partes wants to get an opportunity to be a part of one or the other national level coalition.” Support this statement with arguments.
Answer: Nearly every one of the state parties wants to get an opportunity to be a part of one or the other national level coalition because
• The members of the state party get a chance of being included in the cabinet or the council of ministers.
• State parties get an opportunity and a platform to express their views and ideology at the national level.
• It helps in strengthening of federalism and democracy, and thus bringing diversity in the parliament.
Question. Give any two merits and demerits of one-party system.
Answer: Merits of one-party system are
(i) Strong and Stable Government Since there is no opposition party, government is strong and cannot be removed or voted out of power.
(ii) Less Expensive Since there is only one party and one candidate of the party, not much money is spent on the election.
Demerits of one-party system are
(i) Undemocratic Government can become dictatorial.
(ii) No Choice It gives no choice to the voters.
Question. How do money and muscle power play an important role in elections? Explain.
Answer: Money and muscle power play an important role in elections in the following ways
• Role of money and muscle power in parties especially during elections is growing. Parties tend to nominate those candidates who have or can raise money.
• Rich people and compaines who give funds to the parties tend to have influence on the policies and decisions of the party.
• In some cases, parties support criminals who can win elections due to their power.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties Long Answer Type Questions
Question. “The political parties are necessary for democracy.” Justify the statement.
Or What is the necessity of a political party for a democracy?
Answer: The political parties are necessary as modern democracies cannot exist without political parties. Without existence of parties, following situations may occur
• Every candidate in the elections will be independent.
No one will be able to make any promises to the people about any major policy changes.
• The government may be formed, but its utility will remain ever uncertain. Elected representatives will be accountable to their constituency for what they do in the locality. But no one will be responsible for how the country will be run.
• The Panchayat elections are non-party based elections to the Panchayat in many states of India. Although, the parties do not contest formally, it is generally noticed that the village gets split into more than one group, each of which puts up a ‘panel’ of its candidates. This creates need for the political party.
• The rise of political parties is directly linked to the emergence of representatives democracies. As societies became large and complex, they needed some agency to gather different views on various issues and to present these to the government.
• Society needs a mechanism to support or restrain the government, make policies, justify or oppose them.
Political parties fulfil these needs of every representative government.
Question. Describe any five features of Bharatiya Janata Party.
Answer: Bharatiya Janata Party was formed in 1980. This party has originated from the Bharatiya Jana Sangh, which was formed in 1951 by Shyama Prasad Mukherjee.
The main features of this party are
• It wants to build a strong modern India by drawing inspiration from India’s ancient culture and values and Deendayal Upadhyaya’s ideas of integral humanism and Antyodaya.
• Cultural nationalism or Hindutva is an important element in BJP’s conception of Indian nationhood and politics.
• It has passed law for full territorial and political integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India.
• It claims a uniform civil code for all people living in the country irrespective of religion.
• It wants to ban on religious conversions. The party wants to get an anti-conversion law to stop religious conversion in the country.
Question. Identify and list the symbols of the following political parties with their states.
(i) Shiromani Akali Dal
(ii) Samajwadi Party
(iii) AIADMK
(iv) All India Trinamool Congress
(v) Rashtriya Janata Dal
Answer:
| Party | Place | Symbol |
| (i) Shiromani Akali Dal | Punjab | Balanced Scales or Weighing Balance |
| (ii) Samajwadi Party | Uttar Pradesh | Bicycle |
| (iii) AIADMK | Tamil Nadu | Two Leaves |
| (iv) All India Trinamool Congress |
West Bengal | Flower and Grass |
| (v) Rashtriya Janata Dal | Bihar | Lantern |
Question. Define ‘Political Party’. Describe any four main challenges faced by the Indian political parties.
Answer: A political party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government.
The four challenges faced by the Indian political parties are
(i) The first challenge is lack of democracy within parties. All over the world, there is a tendency in political parties towards the concentration of powers in one or few leaders at the top. Parties do not keep membership registers, do not hold organisational meetings and do not conduct internal elections regularly.
(ii) The second challenge is dynastic succession where the top positions of a party are always enjoyed by members of one particular family. This trend is harmful for other members of the party as well as for democracy. This tendency is present in some measures all over the world.
(iii) The third challenge is about the growing role of money and muscle power in parties which is specially observed during elections. Rich people and companies who give funds to the parties always dominate the policies and decisions of the party.
(iv) The fourth challenge is that usually parties do not seem to offer a meaningful choice to the voters. In our country, the difference among all the major parties on the economic policies have reduced. Sometimes, the same set of leaders keep shifting from one party to another, thus people have no option available to them.
Question. Describe the efforts to reform political parties in India.
Answer: The efforts that have been made to reform political parties in India are
• The Constitution was amended to prevent elected MLAs and MPs from changing parties by introducing Anti Defection law. Defection is changing party allegiance from the party on which a person got elected to a different party.
The law says that if any MLA or MP changes parties he will lose the seat in the legislature. This new law has helped bring defection down.
• The Supreme Court passed an order to reduce the influence at money and criminal. Now, it is mandatory for every candidate who contests elections to file an affidavit giving details of his property and criminal cases pending against him.
• The Election Commission passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organisational elections and file their income tax returns.
Some effort that have to be made to reform political parties are
• A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of political parties. It should be made compulsory for political parties to maintain a register of its members to hold open elections to follow its own Constitution, etc.
• It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a minimum number of tickets, about one-third to women candidates.
• There should be state fundings for elections. The government should give parties money to support their election expenses.
Question. Describe any five functions of political party.
Or Describe the role of political parties in modern democracy.
Answer: The functions and role of political parties in modern democracy are
(i) Political parties put forward different policies and programmes and the voters choose from them.
(ii) Political parties play a decisive role in making laws for our country by making debate and passing law for people.
(iii) Political parties form and run government by recruiting leaders, train them and make them ministers to run the government.
(iv) Political parties shape public opinion by raising and highlighting important issues.
(v) Political parties provide people access to government machinery and welfare schemes implemented by governments. Parties have to be responsive to people’s needs and demands otherwise people can reject those parties in the next elections.
Question. Define the Two-Party system. Explain its advantages and disadvantages.
Answer: When two major parties exist in the country and the power generally changes between them (as in USA and England), the system is known as the two-party system.
Advantages of Two-Party system are
• It provides political stability to the country.
• This kind of party system discourages radical minor parties.
• This kind of party system is better than multi-party system as it is easier to govern.
• It is easier for voters to choose between only two political parties.
Disadvantages of Two-Party system are
• Two-party system offers limited options to the people.
• This system creates inconsistent governing.
• These systems donot effectively tackle the issues faced by the minority or other sections of the society.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties Case Based Questions
1. Read the cases/sources and answer the following questions.
Source A Dissatisfaction with Political Parties Political parties need to face and overcome these challenges in order to remain effective instruments of democracy. The first challenge is lack of internal democracy within parties.
All over the world there is a tendency in political parties towards the concentration of power in one or few leaders at the top. Parties do not keep membership registers, do not hold organisational meetings and do not conduct internal elections regularly. Ordinary members of the party do not get sufficient information on what happens inside the party.
Question. To what extent political parties are different in our country?
Answer: In our country the difference among all major parties has reduced remarkably. In economic field the different parties have little choice to differ. People even can not find better candidate to vote for, as leaders keep shifting from one party to another.
Question. Evaluate the reasons for lack of internal democracy within political parties.
Answer: The reason for lack of internal democracy within political parties arises due to the concentration of power in one or few leaders in the party. As a result these leaders take all the important decisions regarding the party’s activity. Personal loyalty to these leaders becomes necessary for all the party workers.
Source B Dynastic Succession Money and Muscle Power The second challenge of dynastic succession is related to the first one. Since most political parties do not practice open and transparent procedures for their functioning, there are very few ways for an ordinary worker to rise to the top in a party. Those who happen to be the leaders are in a position of
unfair advantage to favour people close to them or even their family members. In many parties, the top positions are always controlled by members of one family.
Question. To what extent dynastic succession control democracy?
Answer: Dynastic succession controls democracy in the following ways
• Sometimes top positions in a political party is controlled by a family members of a particular family.
Even the people who doesn’t have adequate experience and popular support becomes the leader.
• Most political parties do not practice open and transparent procedures for their functioning, etc.
This is not good for democracy and hampers the basic idea that citizens should be able to participate in decision making.
Source C Minimal Choice for Voters
The fourth challenge is that very often parties do notseem to offer a meaningful choice to the voters. In order to offer meaningful choice, parties must be significantly different. In recent years there has been a decline in the ideological differences among parties in most parts of the world.
For example, the difference between the Labour Party and the Conservative Party in Britain is very little. They agree on more fundamental aspects but differ only in details on how policies are to be framed and implemented.
2. Read the case/source given and answer the following questions.
Muhammad Yunus is a famous economist of Bangladesh. He received several International honours for his efforts to promote economic and social development for the benefit of the poor. He and the Grameen Bank started, jointly received the Nobel Peace Prize for the year 2006.
In February 2007, he decided to launch a political party and contest in the parliamentary elections. His objective was to foster proper leadership, good governance and build a new Bangladesh. He felt that only a political party different from the traditional ones would bring about new political culture.
His party would be democratic from the grassroots level. The launching of the New party, called Nagarik Shakti (Citizens’ Power), has caused a stir among the Bangladeshis. While many welcomed his decision, some did not like it.
‘‘Now I think Bangladesh will have a chance to choose between good and bad and eventually have a good government,’’ said Shahedul Islam, a government official. ‘‘That government, we hope, would not only keep itself away from corruption but also make fighting corruption and black money a top priority.’’
But leaders of traditional political parties who dominated the country’s politics for decades were apprehensive. ‘‘There was no debate (over him) winning the Nobel, but politics is different—very challenging and often controversial,’’ said a senior leader of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party. Some others were highly critical. They asked why he was
rushing into politics. ‘‘Is he being planted in politics by mentors from outside the country,’’ asked one political observer.
Question. If you were the one to begin this political party, how would you defend it?
Answer: If I were one of them to begin this political party, I would try to develop direct interaction with the people living in the countryside and in towns.
Regular meetings of the party members, seminars, workshops, etc would have been adopted to win the confidence of the people. I would bring about a totally new political culture, more democratic and more transparent.
Question. Do you agree with the statements and fears expressed by various people?
Answer: I agree with the statement of a government official, Shahedul Islam that the launch of the new party may change the political culture of the country. But I do not agree with the view points of a senior leader of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party. He expressed his fear about the capability of Muhammad Yunus in the field of politics.
Question. How do you want this new party organised to make it different from other parties?
Answer: I think, people like Muhammad Yunus when established a political party, it should be democratic from very grassroots level. This party should fight against corruption and the problem of black money in the country which dominated the country, as H.
Yunus is a respected personality with a great vision.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Water Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Power Sharing |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Federalism |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Popular Struggles and Movements |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Challenges to Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Print Culture and Modern World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money And Credit |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalization And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Social Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 6 Political Parties of Social Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 6 Political Parties Class 10 chapter of Social Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 6 Political Parties NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Social Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Social Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Social Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Social Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 6 Political Parties Class 10 Social Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 6 Political Parties Social Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 6 Political Parties have been answered by our teachers

