NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Social Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Social Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy Class 10 Social Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy in Class 10. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy
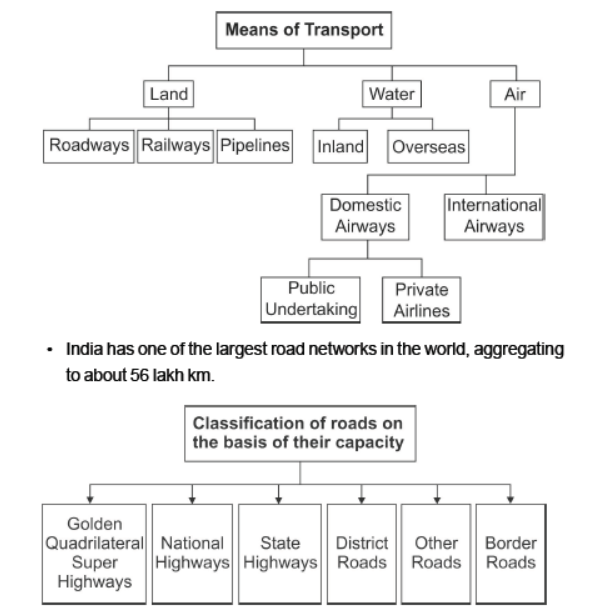
Lifelines of National Economy
Points to remember:
Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways
• A Six lane Super Highway which connects Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai-and Delhi.
• The North South corridors linking Srinagar (Jammu & Kashmir) and Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu).
• The East-West corridor connecting Silcher (Assam) and Porbander (Gujrat).
• The major objective of these Super Highways is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India.
• These highway projects are being implemented by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI).
National Highways
• It link extreme parts of the country.
• These are primary road systems.
• These are laid and maintained by the Central Public works Department (CPWD) Railways
• Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
• It also makes it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business,sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
• It has been a great integrating force along with accelerating the development of industry and agriculture.
• The Indian Railways is now reorganized into 16 zones.
Problems-
• Travelling without ticket.
• Theft and damaging of railway property.
• Pulling the chain unnecessarily.
• Late running of trains.
Pipelines
• In the past these were used to transport water to cities and industries.
• Now are being used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products,and natural gas from oil.
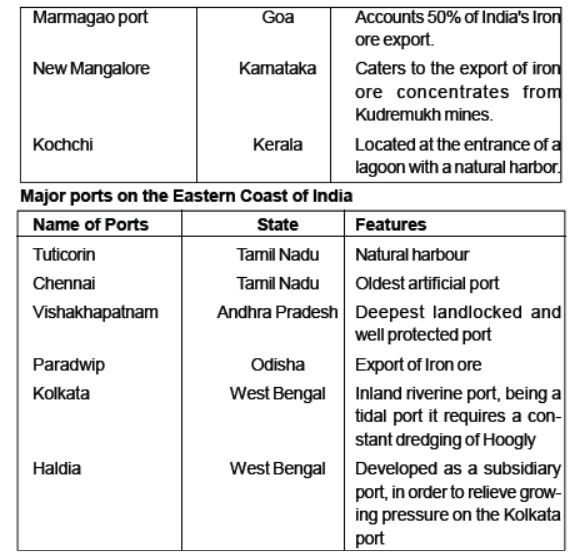
Major ports on the Western Coast of India
Airways
• Fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of transportation.
• It can cover very difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense forests and along oceanic stretches with great ease.
• Very helpful for North-Eastern states.
• The air transport was nationalized in 1953.
• Air India provides International air services while Indian airlines provide domestic services.
• It is also used to provide relief during any natural calamities. Problems
• Expensive
• Dependent on seasonal conditions
International Trade
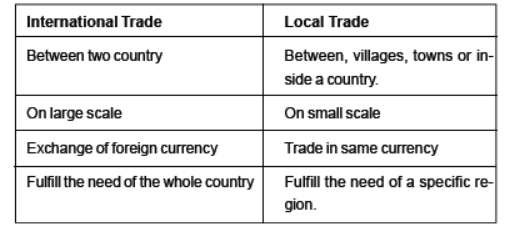
• The exchange of goods among people, states and countries is referred to as trade.
• Trade between two countries is called International trade.
• All the countries are dependent on international trade as availability of resources are regional and its distribution is unequal.
• Import and Export are the component of the trade.
• The balance of trade of a country is the difference between its export and import.
• When the value of export exceeds the value of imports it is called a favourable balance of trade.
• On the contrary if the value of import exceeds the value of export, it is termed as unfavourable balance of trade.
Transport and communications are supplementary to each otner
• Efficiency of transportation and communication converted the world into a global village.
• Connection of local and foreign trade accelerated the development of economy of the world.
• Lives of the people become more comfortable.
Tourism as a Trade
• More than 15 million people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
• It promotes national integration and provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
• Helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage.
• Foreign tourists visit India for heritage tourism, eco tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, medical tourism and business tourism.
• Thus it also increases the national income in foreign exchange.
Important Airports of India
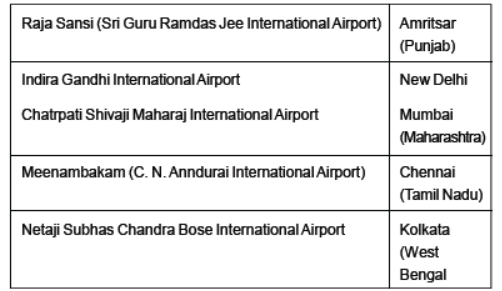
Rajiv Gandhi International Airport Hyderabad (Telangana)
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. Which one of the following states is not connected with the H.V.J. pipeline?
a. Madhya Pradesh
b. Gujarat
c. Maharashtra
d. Uttar Pradesh
Answer. C
Question. Identify the industry:
(1) Industry in India has grown substantially over the last three decades.
(2) 15 million people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
(3) The industry promotes national integration, provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
A. Paper
B. Information and technology
C. Tourism
D. Films
Answer. C
Question. Which one of the following is not the means of mass communication?
A. Cards and envelopes
B. Radio
C. Newspaper
D. Films
Answer. A
Question. Difference between the total value of exports and imports is called.
A. Balance of Payment
B. Balance of Trade
C. Surplus Budget
D. Deficit Balance
Answer. B
Question. The people who make the products come to the consumers by transportation are called ______________ .
A. Businessman
B. Retailers
C. Traders
D. Industrialists
Answer. C
Question. Complete the following table with appropriate terms in place of (a).
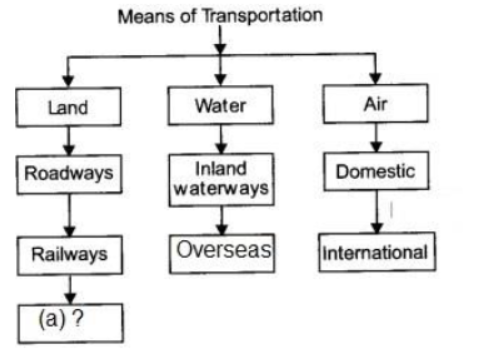
A. Pipeline
B. Unmetalled Road
C. Metalled Road
D. Super Highways
Answer. A
Question. Identify the port:
(1) It is located on the Western Coast.
(2) It is the premier iron ore exporting sea port of the country
A. Kochi
B. Marmagao Port
C. Visakhapatnam
D. Haldia
Answer. B
Question. Narrow Gauge railway line is found in
A. the Northern Plains
B. the hilly areas of Darjeeling, Shillong and Ooty
C. deserts of Rajasthan
D. the Central Highlands
Answer. B
Question. Match the following roads from column A with the organisations responsible for their construction and maintenance from column B:
Column A (Types of Road ) Column B (Organisation)
(a) Super Highways (i) Zila Parishad
(b) National Highways (ii) State Public Works Department
(c) State Highways (iii) Central Public Works Department
(d) District Roads (iv) National Highway Authority of India
A. (a)-iii,(b)-iv,(c)-ii,(d)-i
B. (a)-iii(b)-ii(c)-iv,(d)-i
C. (a)-iv,(b)-i(c)-ii,(d)-iii
D. (a)-iv,(b)-iii,(c)-ii,(d)-i
Answer. D
Question. …………….. is the extreme south-western port located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbour.
A. Kochi
B. Kolkata
C. Haldia
D. Tuticorin
Answer. A
ASSERTION AND REASONING
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable A. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
B. Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
C. (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
D. (A) is wrong but (R) is correct
Question. ASSERTION (A): No country can survive without international trade.
REASON (R): Resources are not space bound.
Answer. C
Question. ASSERTION (A): Road transportation in India faces a number of problems.
REASON (R): Roads are unmetalled, their network is adequate.
Answer. A
Question. ASSERTION (A):Transport and communications are called lifeline of our economy.
REASON (R): transport and communications do not help in easy movement of goods and materials between countries.
Answer. C
Question. ASSERTION (A): Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
REASON (R): It is a fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
Answer. A
Question. ASSERTION (A): Mass communication promotes national integration and provides entertainment.
REASON (R): It strengthens democracy in the country by providing news to the masses. They feel attached to the country and a feeling of Nationalism arises in them.
Answer. A
Source Based Questions
1. Read the extract and answer the following questions-
For a long time, trade and transport restricted to a limited space. With the development in science and technology the area of influence of trade and transport expanded far and wide. Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
Today, India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity and . linguistic and socio-cultural plurality. Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc. have been
contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways. The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy. It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life.
Question. Which one of these is responsible for expansion of area of influence of trade?
(a) Development of science and technology
(b) Developed communication system
(c) Both
(d) None of these
Answer. C
Question. Which one of the following is not responsible for the socio-economic progress of India?
(a) Population
(b) Railways
(c) Radio
(d) Internet
Answer. A
Question. What do you understand by the term 'large village' used in the paragraph?
Answer. With the help of efficient and fast moving transport and communication the countries all over the world are connected very closely to form like a large village
Question. Write a summary of the given paragraph in your own word.
Answer. Students will do by their own
1. Multiple choice questions
Question. Which two of the following extreme locations are connected by the east-west corridor?
(a) Mumbai and Nagpur
(b) Silcher and Porbandar
(c) Mumbai and Kolkata
(d) Nagpur and Siligudi
Answer: (b) Silcher and Porbandar
Question. Which mode of transportation reduces trans- shipment losses and delays?
(a) Railways
(b) Roadways
(c) Pipeline
(d) Waterways
Answer: (c) Pipeline
Question. Which one of the following states is not connected with the H.V.J. pipeline?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Gujarat
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer: (b) Maharashtra
Question. Which one of the following ports is the deepest land-locked and well-protected port along the east cost?
(a) Chennai
(b) Paradwip
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Vishakhapatnam
Answer: (d) Vishakhapatnam
Question. Which one of the following is the most important modes of transportation in India?
(a) Pipeline
(b) Railways
(c) Roadways
(d) Airways
Answer: (b) Railways
Question. Which one of the following terms is used to describe trade between two or more countries?
(a) Internal trade
(b) International trade
(c) External trade
(d) Local trade
Answer: (b) International trade
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
Question. State any three merits of roadways.
Answer: Merits of roadways:
- Road transport required much less capital investment than the railways in terms of construction costs.
- Roads can go through dissected and undulating land areas and through steep mountains.
- Roads provide door-to-door or warehouse-to- warehouse service.
Question. Where and why is rail transport the most convenient means of transportation?
Answer: In the northern India, rail transport is the most convenient mode of transportation. This is because this region has vast alluvial and level lands that are good for laying tracks, and huge population and high agricultural productivity, making rail transport a profitable venture.
Question. What is the significance of the border roads?
Answer: Border roads are strategically important as they improve accessibility to areas like the northern and northeastern borders, which have a difficult terrain.
Question. What is meant by trade? What is the difference between international and local trade?
Answer: Trade is the movement of goods and services between regions for economic gain. Trade between two or more countries is termed as international trade, while trade occurring in a region within the same country is called local trade.
3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
Question. Why are the means of transportation and communication called the lifelines of a nation and its economy?
Answer: The means of transportation and communication are called the lifelines of a nation and its economy due to the following reasons:
- They help in the production and movement of goods and services.
- Various means of communication help us in interacting with other in all the parts of the world, and have brought the world closer.
- Railways help us in conducting various activities like business, touring, and transportation of goods over longer distances.
- Air transport provides the fastest, most comfortable mode of transport.
- Pipelines are used for transporting crude oil and petroleum, and natural gas to refineries and fertilizer factories.
- Water transport is the cheapest means of transport.
These means of transport and communication help in the development of the country. Therefore, they are called the lifelines of a nation and its economy.
Question. Write a note on the changing nature of the international trade in the last fifteen years.
Answer: (i) The means of transportation and communication are called the lifelines of a nation and its economy due to the reasons given below:
• The means of transportation and communication help in the production and movement of goods and services.
• Transport helps in the development of communication . Various means of communication help us in interacting with other in all the parts of the world It has brought the world closer.
• Transport like railways help us in conducting various activities like business, sight seeing, pilgrimage and transportation of goods over longer distances.
• Pipelines are used for transporting crude oil and natural gas to refineries and factories.
• Water provide the cheapest means of transport and is useful for international trade.
• Air transport provides the fastest, most comfortable mode of transport.
Thus, it is clear that there are many advantages of transportation and communication.
These means help in the development of the country. So they are called the lifelines of a nation and its economy.
(ii) The changing nature of the international trade for India, in the last fifteen years, has been impressive. Exchange of information and knowledge has surpassed exchange of goods and commodities. Through its advanced software knowledge and excellence in the field of information technology, India has emerged as a viable contender at the international level and is earning huge amounts of foreign exchange through the same. Tourism too has added to India's upgraded position in international trade. In 2004, there was a 23.5% increase in foreign tourist arrivals as against the number in 2003. Thus, international trade for India has undergone a cognisable change in the past fifteen years.
Quiz Drive
1. Northern terminal of the North-south corridor.
2. The name of National Highway No.2.
3. The headquarter of the southern railway zone.
4. The rail gauge with a track width of 1.676 m.
5. The southern terminal of the National Highway No.7.
6. A Riverine Port.
7. Busiest railway junction in Northern India.
Answer:1. Srinagar
2. Sher-Shah Suri Marg
3. Chennai
4. Broad gauge
5. Kanyakumari
6. Kolkata Port Trust
7. Mughalsarai
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Objective Questions
Question. What type of trade is carried in cities, towns and villages?
(a) State level trade
(b) Local trade
(c) District level trade
(d) None of these
Answer: B
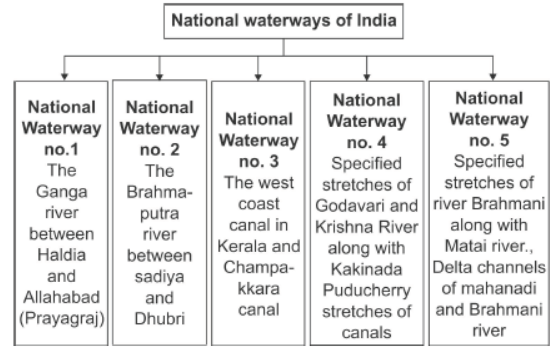
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the National Waterways and their length.
(a) NW-1 – 1620 km
(b) NW-2 – 205 km
(c) NW-3 – 891 km
(d) NW-4 – 588 km
Answer: A
Question. Match the following.
| Column A | Column B |
| A. National Highways | 1. Central Public Works Department |
| B. State Highways | 2. Border Roads Organisation |
| C. Rural Roads | 3. State Public Works Department |
| D. Border Roads | 4. Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana |
Codes
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 1 3 4 2
(c) 4 2 3 1
(d) 3 4 1 2
Answer: B
Question. .................... is the type of communication service in India that is largest in the world.
(a) Telecom Network
(b) Postal Network
(c) Television Network
(d) Radio Network
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct ?
(a) Roads can be built in uneven surface like hills and mountains.
(b) The National Highway 1 is also known Sher-Shah Suri Marg.
(c) The total distance of Atal Tunnel is 9.02 km.
(d) The first train was started in 1954 in India.
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following corridors links Srinagar and Kanniyakumari? Identify the correct option.
(a) North- South Corridor
(b) East- West Corridor
(c) North- East Corridor
(d) South-West Corridor
Answer: A
Question. Which two of the following extreme locations are connected by the East-West Corridor?
(a) Mumbai and Nagpur
(b) Silchar and Porbander
(c) Mumbai and Kolkata
(d) Nagpur and Siligudi
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following is an autonomous agency responsible for management of National Highways in India?
(a) Border Roads Organisation
(b) National Highway Authority of India
(c) Central Public Works Department
(d) None of the above
Answer: B
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the major sea port and their location.
(a) Kandla – Goa
(b) Marmagao – Mumbai
(c) Tuticorin – Tamil Nadu
(d) Paradwip – West Bengal
Answer: C
Question. Which mode of transportation reduces trans-shipment losses and delays?
(a) Railways
(b) Roadways
(c) Pipeline
(d) Waterways
Answer: C
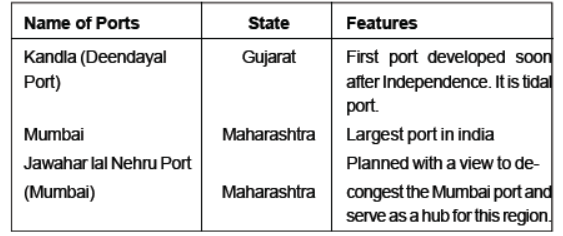
Question. Which of the following was the first port developed soon after Independence to use the volume of trade on the Mumbai Port?
(a) Kandla
(b) Kochi
(c) Marmagao
(d) Tuticorin
Answer: A
Question. Identify the name of the National waterways with the help of given clues.
• The total distance of the waterways is 991 km.
• It covers distance between Sadiya to Dhubri.
• It is located on the Brahmaputra river.
(a) NW-1
(b) NW-2
(c) NW-3
(d) NW-4
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following is the largest Public Sector Undertaking in the country?
(a) Airways
(b) Roadways
(c) Waterways
(d) Railways
Answer: D
Question. The trade between two countries is called
(a) International trade
(b) National trade
(c) Community trade
(d) None of these
Answer: A
Question. Match the following.
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Kolkata Port | 1. Biggest Port |
| B. Visakhapatnam Port | 2. Oldest Artificial Port |
| C. Chennai Port | 3. Deepest Landlocked and well- protected port |
| D. Mumbai Port | 4. Tidal and Inland riverine port |
Codes
A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 3 2 1 4
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 4 1 2 3
Answer: C
Question. Which of the following is the Northernmost international airport in India?
(a) Raja Sansi International Airport
(b) Indira Gandhi International Airport
(c) Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport
(d) Meenam Bakkam International Airport
Answer: A
Question. Identify the port through the given features.
• It is the deepest landlock port.
• It is well protected port for exporting iron-ore.
• It is located in Andhra Pradesh.
(a) Tuticorin port
(b) Vishakhapatnam port
(c) Paradip port
(d) Kandla port
Answer: B
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Assertion-Reason MCQs
Directions Each of these questions contains two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, any one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Question. Assertion (A) Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
Reason (R) It is a fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) Trade is considered as the economic barometer of the country.
Reason (R) Trading helps largely in developing countries like India. Advancement of Trade is an index to its economic prosperity.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) Tourism promotes national integration.
Reason (R) Millions of people are directly engaged in tourism industry.
Answer: B
Question. Assertion (A) Transport and Communications are called lifelines of our economy.
Reason (R) Transport and Communications do not help in easy movement of goods and materials between countries.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion (A) The Himalayan mountainous regions are unfavourable for the construction of railway lines.
Reason (R) The Himalayan mountainous regions have high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
Answer: A
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Case Based MCQs
Read the case/source given and answer questions that follow by choosing the correct option.
Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India. Railways also make it possible for people to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
Apart from an important means of transport the Indian Railways have been a great integrating force for more than 150 years.
Railways in India bind the economic life of the country as well as accelerate the development of the industry and agriculture. The Indian Railway is now reorganised into 16 zones.
The distribution pattern of the Railway network in the country has been largely influenced by physiographic, economic and administrative factors. The Northern plains with their vast levell and, high population density and rich agricultural resources provided the most favorable condition for their growth.
However, a large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges across their wide beds posed some obstacles. In the hilly terrains of the peninsular region, railway tracts are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels.
Question. Why Indian railway network is mostly concentrated in Ganga Plains? Choose the most suitable option:
(a) Due to concentration of Industries.
(b) Due to topographical uniformity and high density of population.
(c) Due to high agricultural production.
(d) Due to lack of economic opportunities.
Answer: B
Question. Why is the Indian Railways called the lifeline of the country? With reference to the above context, infer the appropriate option.
(a) Railways in India bind the economic life of the country.
(b) It is the largest public undertaking in the country.
(c) Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
(d) All of the above
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following factors are responsible for distribution pattern of railways network in the country? Identify the correct option:
(a) Topographical factors
(b) Economic and administrative factors
(c) Social factors
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: D
Question. Assertion (A) Rail Transport is the most convenient means of transportation in the Northern Plains.
Reason (R) The Northern Plains are densely populated, which enables the maximum number of people to utilise this means of transport.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and Rare true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer: A
Question. Why is it essential to develop a unigauge system of railways in our country? Identify the correct option.
(a) It will lead to reduction in trans-shipment.
(b) Because it has larger capacity.
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) It will bring administrative convenience.
Answer: C
Question. When was the first railway line opened in India?
Choose the correct option from the following.
(a) 1803
(b) 1823
(c) 1853
(d) 1854
Answer: C
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Short Answer Type Questions
Question. State the ways by which means of transport and communication help the growth of industries in India.
Answer: The ways by which means of transport and communication help the growth of industries in India are
• Transport facilities are required to transport raw materials from their source region to industrial locations.
• Final products from industries also require transport facilities for their transportation to market.
• Communication lines supply required information about various industries.
• Means of transport and communication also help in reduction of regional imbalances resulting in balanced regional development.
Question. Classify communication services into two categories?
Explain main features of each.
Answer: Communication services are classified into personal communication and mass communication.
Features of Personal communication are
• In personal communication, people can express their thoughts and share with others.
• Letters, e-mails, SMSs, telephone and mobile phone facilities including STD and ISD services are examples of personal communication.
Features of mass communication are
• Mass communication provides entertainment and creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies.
• It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazine, books and films.
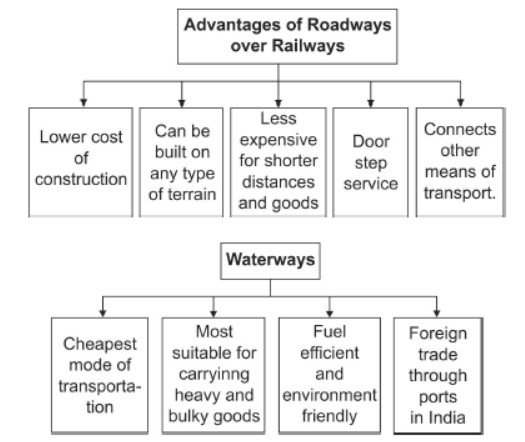
Question. “Roadways have an edge over Railways.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer: Roadways still have an edge over the railways in India because
• Construction cost of roads is much lower than railway lines.
• Roads can be constructed easily in hilly terrains and undulating topography than railways.
• Roadways act as a feeder to other modes of transport, as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
• Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
• Road transport provides door-to-door service thus, the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
Question. Why are metalled roads better than unmetalled roads? What is the role of border roads and national highways in transportation?
Or Explain the importance of ‘Border Roads’ for India.
Answer: Metalled roads are better than unmetalled roads because they have a waterproof coating on their upper surface, this makes them usable in all seasons. On the other hand,
unmetalled roads are difficult to use in the rainy season, as their upper surface becomes uneven due to absorption of rain water.
Importance of border roads is
• They have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain.
• These roads help in the economic development of the border areas of the country.
Role of National Highways is
• National Highways link important parts of the country like state capitals and commercial centres.
• They enable fast and efficient movement of goods in areas connected to them.
Question. “Rail transport suffers from certain problems in India.”
Support the statement with examples.
Answer: Rail transport suffers from certain problems which are
• The infrastructure of railways is poor. For example, the tracks are old and outdated which cause many serious railway accidents. This also leads speed reduction and cause delay in arrival of trains on stations.
• Another major problem that is being faced in India is that a large number of passengers travel without purchasing tickets. Indian railways have to bear a huge loss every
year on account of travelling without tickets.
• The incidence of railway accidents in our country is greater as compared to other countries of the world. Accidents occur due to the errors and negligence of the employees.
Question. Explain any two merits and two demerits of pipelines transport.
Answer: Merits of pipelines transport are
(i) There are no trans-shipment losses or delays in transportation of materials.
(ii) Their construction has made inland locations of refineries like Barauni and Mathura and gas based fertiliser plants viable.
Demerits of pipelines transport are
(i) Initial costs of laying pipelines are very high, particularly oil and gas pipelines which have to be laid underground.
(ii) Leakage in pipes or damage to the pipeline might pollute soil and contaminate ground water, damaging the environment.
Question. How has the world been converted into a global village? Explain.
Answer: The world has been converted into a global village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport and communication facilities in the following ways
• Daily flights to different countries and improved technology to develop fast means of transportation has connected the countries.
• Computer and internet facilities supported by satellite services have made the world a small village wherein an information can be reached at almost instantly.
• Every country is well-linked with the rest of the world through various means of transport and communication.
• Means of transportation such as railways, airways, waterways and means of communication such as newspapers, radio, television, cinema, internet, etc have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways.
Question. Explain any four characteristics of Kandla sea port.
Answer: The four characteristics of Kandla sea port are
(i) It was the first port developed soon after independence.
(ii) It was developed to reduce the volume of traffic on Mumbai port.
(iii) It is a tidal port.
(iv) It caters to the convenient handling of exports and imports of highly productive granary and industrialised belts including Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Question. “Distribution of roads is not uniform in India.”
Support the statement with examples.
Answer: It is true that the distribution of roads is not uniform in India. For example,
• Density of roads (length of roads per 100 square km of area) varies from Jammu and Kashmir (UT), which has the lowest density of road to Kerala, which has the highest density of roads in the country.
• The density of road is high in most of the Northern states and major Southern states. It is low in the Himalayan region, North-Eastern region, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan due to their topography.
• Nature of terrain and the level of economic development are the main determinants of density of roads. Construction of roads is easy and cheaper in the plain areas while it is difficult and costly in hilly and plateau areas.
Question. Explain any four merits and two demerits of air transport.
Answer: Merits of air transport are
(i) Air transport is the fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport.
(ii) It can cover very difficult terrains with great ease.
(iii) It makes access to far-flung and remote or otherwise inaccessible areas easier and quicker.
(iv) It provides transport services to offshore oil and gas exploration activities.
Demerits of air transport are
(i) Air transport is a very costly means of transportation.
(ii) Places not having airports or helipads are not covered by it.
Question. Distinguish between a major port and a minor port.
Answer: Differences between a major and a minor port are
| Major Port | Minor Port |
| Major ports are bigger ports compared to minor ports. There are about 12 major ports in India. | In India, there are 200 minor ports in operation. |
| Major ports mostly deal with international trade. |
Minor ports, on the other hand, deal with the coastal trade along with fishing. |
| Major ports are controlled and managed by Port Trusts and Central Government. |
Minor ports are the responsibility of State Governments. |
| Mumbai, Chennai and Kandla are examples of major ports. |
Dwarka, Porbandar and Okha are some of the examples of minor ports. |
Question. What has necessitated the need for transport? Is it right to say that efficient means of transport are prerequisites for fast development? Justify.
Or ‘‘Efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for fast development of the country.’’ Support the statement with examples.
Answer: The need for transport has been necessitated due to the need for movement of goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations or market. Some
people are engaged in facilitating these movements. These are known to be traders who make the products come tothe consumers by transportation.
Efficient means of transport are prerequisite for fast development because more development of goods and services are not enough. The goods need to be transported
from one place to another in proper time for their distribution and consumption.
Question. Explain briefly the advantages that result in using waterways as a mode of transport for heavy and bulky goods.
Answer: Advantages/features of using waterways as mode of transport for heavy and bulky goods are
• Waterways are the cheapest means of transport and most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
• They are fuel-efficient and environment-friendly mode of transport.
• Heavy and bulky goods being exported or imported are easier for trans-shipment from waterways to ships on the coast, as the waterways lead to ports.
Question. Why is air transport more popular in the North- Eastern part of the country? Give three reasons.
Or “Airways is the most preferred mode of transport in North-Eastern states of India.” Give three reasons to prove this preference.
Answer: Air transport or airways is the most preferred mode of transport in the North-Eastern states in India because
(i) Big and wide rivers are present in the North Eastern states, due to which rail or road bridges over them are difficult and costly to construct.
(ii) This area has dissected relief features, preventing durable construction of rail and road links.
(iii) Dense forests in this region create many difficulties in construction of railway lines and roads.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Classify the roads according to their capacity and describe the role of each.
Answer: In India, roads are classified in six classes according to their capacity as
• Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways This super highway links India’s four largest metropolitan cities, i.e. Delhi-Kolkata- Chennai-Mumbai.
North-South and East-West corridor are part of this.
These highways reduce time and distance between mega cities.
• National Highways These are primary road systems that link important parts of the country.
• State Highways These roads link a state capital with its district headquarters. These are constructed by State Public Works Department.
• District Roads These roads connect the district headquarters with other places of the district.
• Rural Roads These roads, also known as other roads, link rural areas and villages with towns.
• Border Roads These roads are constructed along the international border of India by Border Road Organisation. It has improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain.
Question. Explain the importance of railways as a means of transport.
Answer: The importance of Indian Railways as a means of transport is
• Railways are considered as the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
Daily a lot of commuters and office goers travel through railways.
• Railways provides cheap mode of transport to all. It is cheaper as compared to other modes of transport like airways.
• Railways help to conduct various activities, viz, business, sightseeing, pilgrimage, transportation of goods over long distances etc. Through these activities railways add more revenue to the economy of a country.
• Railways bind the economic life of our country by accelerating the development of the industry and agriculture.
• The Indian Railways is the largest public sector undertaking in the country which is the biggest employer in India.
Question. Classify any five ports of India according to their types and main purpose.
Answer: The ports of India according to their types and main purpose are
(i) Chennai Port (Tamil Nadu)
• Type of Port It is one of the oldest artificial ports in India.
• Purpose It is made for trade and cargo
(ii) Haldia Port (West Bengal)
• Type of Port It is a subsidiary port to relieve pressure on Kolkata port.
• Purpose It is made for decongesting Kolkata port.
(iii) Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Maharashtra)
• Type of Port It is specialised in handling
container shipments.
• Purpose It is made for decongesting Mumbai port and serve as a hub for the region.
(iv) Kandla Port (Gujarat)
• Type of Port It is a tidal port.
• Purpose It was developed after independence to ease the volume of trade on Mumbai port.
(v) Kochi Port (Kerala)
• Type of Port It is a natural port located at the entrance of a lagoon.
• Purpose It specialised in handling container shipments.
Question. Explain the importance of means of transport as a prerequisite for the development of a country.
Answer: Efficient means of transport are prerequisite for fast development because more development of goods and services are not enough alone.
The importance of means of transport is
• Transportation offers numerous opportunities within the employment sector. Traffic control, pilots, captains, delivery services and drivers are some of the jobs that are provided through this industry. Thus, it also helps the country to reduce unemployment ratio.
• High quality transport links ensure that communities can access basic services, facilities and employment opportunities. The connectivity provided by such links promotes social inclusion. It can also reduce social isolation and enhance quality of life.
• Transport facilities are also required to transport raw materials from their source region to industrial locations such as transportation of coal to iron and steel industry.
• Final products from industries also require transport facilities for their transportation to market so that consumers are able to buy them.
• Availability of transport services i.e. roadways, railways and waterways (wherever there is scope) help in increasing trade, connect the areas and facilitate movement of people. This helps in the development of a country.
Question. “International trade is considered the economic barometer of a country.” Justify the statement with arguments.
Answer: International trade is considered the economic barometer of a country because
• As the resources are limited no country can survive without international trade.
• Goods or resources possessed by one country are required by other and vice-versa. These differences create conditions for international trade.
• Foreign trade has helped India to improve its productivity of manufactured goods. International trade contributes to India’s economic growth, raising income levels of people.
• In recent years, exchange of information and knowledge has benefitted in greater exchange of goods across states and countries.
• India has emerged as a software giant at the international level and it is earning large foreign exchange through the export of information technology.
Question. The pace of change in the communication sector has been rapid in modern times.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer: The pace of change in communication sector has been rapid in modern times as a result of which the long distance communication has become easier without physical
movement of the communicator or receiver. For example,
• The advanced communication meant to save our time and money as well. Personal communication and mass communication including television, radio, press, films etc, are the major means of communication.
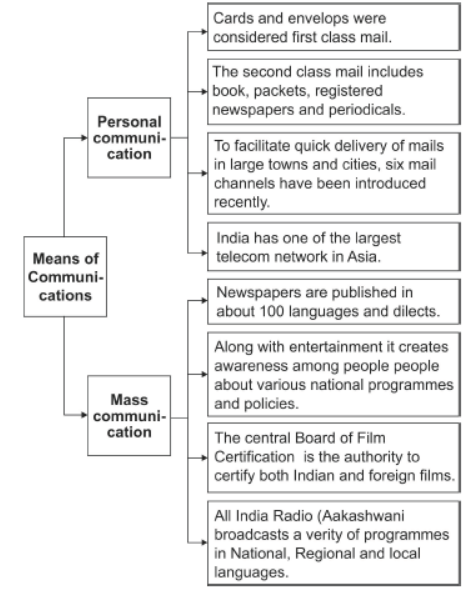
• The Indian postal network handles parcels as well as personal written communication. It also deals with first class mails (e.g. cards, envelopes) and second-class mails
(e.g. books packets, periodicals, registered newspapers) which are carried by different means of transport. To facilitate quick delivery of mails in large towns and cities,
six mail channels namely Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical Channel have been introduced recently.
• The use of mobile phones has also provided boost to the communication sector in the modern times.
Question. Explain the importance of roadways as a means of transport.
Answer: The importance of roadways as a means of transport is
• Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
• Road transport also provides door-to-door service, thus, the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
• Road transport links other modes of transport like between railway stations, air and sea ports.
• National and state highways help in linking the extreme parts of the state and country. Through roads the entire country is connected.
• People can go from one place to another in search of jobs, businesses, tourism etc and goods can be transported due to proper linking of roads. Thus, road ways are a very important means of transportation.
Question. Describe any five points of importance of mass communication.
Or Write any three importance of means of mass communication.
Answer: Importance of mass communication is
(i) Mass communication is required to spread the flow of information upto the grassroot level. Therefore, government has made special provision to extend 24 hours STD facility to every village in the country.
(ii) All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people spread over different parts of the country.
(iii) Doordarshan broadcasts a variety of programmes for entertainment, educational programmes to sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
(iv) India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually for providing information.
(v) India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short films, video feature films and video short films for entertainment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Case Based Questions
1. Read the case/source given and answer the following questions.
The distribution pattern of the Railway network in the country has been largely influenced by Physiographic, economic and administrative factors.
The Northern plains with their vast level land, high population density and rich agricultural resources provided the most favourable condition for their growth.
However, a large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges across their wide beds posed some obstacles.
In the hilly terrains of the peninsular region, railway tracts are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels.
The Himalayan mountainous regions too are unfavourable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
Likewise, it was difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plain of Western Rajasthan, swamps of Gujarat, forested tracks of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Jharkhand. The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gaps or passes (Ghats).
In recent times, the development of the Konkan railway along the West coast has facilitated the movement of passengers and goods in this most important economic region of India. It has also faced a number of problem such as sinking of track in some stretches and landslides.
Question. Although, the railways have become more important in our national economy still this transport is facing a number of problems.Why? State any two reasons.
Answer: It is true that railways have become more important in our national economy but still this transport is facing a number of problems which are
• Many passengers travel by trains without tickets.
This incurs heavy loss of rail budget.
• People stop the trains, pull the chain unnecessarily and this causes heavy damage to the railway.
Question. Which factors are largely responsible to influence the railway network in India? Write any one merit of railways.
Answer: Factors which are largely responsible to influence the railway network in India are physiographic, economic and administrative factors.
An advantage or merit of railways is that they make it possible to conduct many activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
Question. Why is it difficult to construct railway lines in the Peninsular region and Himalayan region?
Answer: It is difficult to construct railway lines in the Peninsular region and Himalayan region because
• The Peninsular region and the Himalayan region are hilly and mountainous regions. Peninsular region has undulating topography where railway tracts are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels.
• On the other hand the Himalayas have high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
2. Read the cases/sources given and answer the following questions.
Source A Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways The government has launched a major road development project linking Delhi–Kolkata– Chennai–Mumbai and Delhi by six-lane Super Highways. The North–South corridors linking Srinagar (Jammu and Kashmir) and Kanniya kumari (Tamil Nadu), and East-West Corridor connecting Silchar (Assam) and Porbander (Gujarat) are part of this project. The major objective of these Super Highways is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India. These highway
projects are being implemented by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI).
Question. To what extent do you agree that India needs a number of National Highways? Give only one
reason. Discuss the role of National Highways.
Answer: I agree with that India needs a number ofNational Highways because India is a vast country and National Highways link extreme parts of the country with each other. Role of National Highways is
• National Highways link important parts of the country like state capitals and commercial sectors.
• They enable fast and efficient movement of goods in areas connected to them.
Source C State Highways
Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as State Highways. These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (PWD) in State and Union Territories.
Question. What is the Golden Quadrilateral? To what extent do you agree that Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways are important for our country? Give only one aspect.
Answer: Golden Quadrilateral comprises of the National Highways connecting Delhi-Mumbai-Chennai- Kolkata by a 6-lane Super Highway.
I agree with that Golden Quadrilateral SuperHighways are important for our country because these highways reduce time and distance between mega cities of India.
Source B National Highways
National Highways link extreme parts of the country. These are the primary road systems and are laid and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD). A number of major National Highways run in North-South and East–West directions. The historical Sher-Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway No. 1, between Delhi and Amritsar.
Question. Evaluate the importance of the State Highways.
Answer: Importance of the State Highways is
• State Highways are constructed within a state to provide better connectivity of roads and places.
• These highways link a state capital with different district headquarters.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Water Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Power Sharing |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Federalism |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Popular Struggles and Movements |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Challenges to Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Print Culture and Modern World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money And Credit |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalization And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Social Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy of Social Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy Class 10 chapter of Social Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Social Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Social Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Social Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Social Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy Class 10 Social Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy Social Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy have been answered by our teachers

