NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Social Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Social Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 4 Agriculture is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 4 Agriculture Class 10 Social Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 4 Agriculture in Class 10. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 4 Agriculture NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography for Chaper 4 Agriculture
Major crops and cliatic conditions.
Key Points
1. Rice is a commercial crop in Haryana and Punjab, but in Odisha, it is a subsistence crop.
2. Plantation is a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
3. Important plantation crops in India- tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, banana, etc.
4. Rice is the staple food crop of a majority of the people in India. Our country is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China.
5. In states like Assam, West Bengal and Odisha, three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are Aus, Aman and Boro.
6. Wheat is the second most important cereal crop. It is the main food crop, in north and north-western part of the country.
7. Maize is a crop which is used both as food and fodder.
8. Jowar, bajra and ragi are the important millets grown in India. Though, these are known as coarse grains, they have very high nutritional value.
9. Jowar is the third most important food crop with respect to area and production.
10. India is the largest producer as well as the consumer of pulses in the world.
11. India is the second largest producer of sugarcane only after Brazil.
12. groundnut production in the world- China (1st),lndia (2nd) and in rapeseed production Canada - 1st, China- 2nd and India - 3rd in the world.
13. In 2020 China-1st and lndia- 2nd in tea production in the world.
14. In 2013, India was the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables in the world after China.
15. Crop Rotation- Growing different crops on a piece of land to increase the productivity and fertility of land.
16. Slash and burn farming/Shifting cultivation-farmers clear apatch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
After decrease of soil fertilityfarmers shift and clear a freash patch of land for cultivation.
17. White revolution- To improve the breeds of animals for the growth in milk production with the use of modern technology.lt is also called Operation Flood.
18. Green Revolution- Based on the Uses of HYV seeds.Modern technology,fertilisers,pesticides,insecticides to increase production especially Wheat production.
19. Jute is known as the golden fibre.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Short Answer Type Questions
Question. The three major cropping seasons of India are:
(a) Aus, Aman and Boro
(b) Rabi, Kharif and Zaid
(c) Baisakh, Paus and Chait
(d) None of the above
Answer. B
Question. Kharif crops are grown:
(a) with the onset of monsoon and harvested in September-October
(b) with the onset of winter and harvested in summer
(c) with onset of Autumn and harvested in summer
(d) None of the above
Answer. A
Question. A short season between the rabi and kharif season is known as:
(a) Aus
(b) Boro
(c) Zaid
(d) None of the above
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following is known as golden fibre?
(a) Cotton
(b) Jute
(c) Hemp
(d) Silk
Answer. B
Question. What are the two important beverage crops of India?
Answer. coffee and tea
Question. Define shifting cultivation?
Answer. A person uses a piece of land, only to abandon or alter the initial use a short time later.
Question. Which is the leading sugarcane producer state of India?
Answer. Uttar Pradesh
Question. Name two major tea-producing states of India.
State whether the following statements are True or False:
Answer. Assam and West Bengal.
Question. A system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area is called shifting agriculture.
Answer. False
Question. Punjab is major producer of the maize in India.
Answer. False
Question. PDS system launched by government of India ensure subsidised prices for food grains to poor in rural areas.
Answer. True
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Short/Long Answer Type Questios
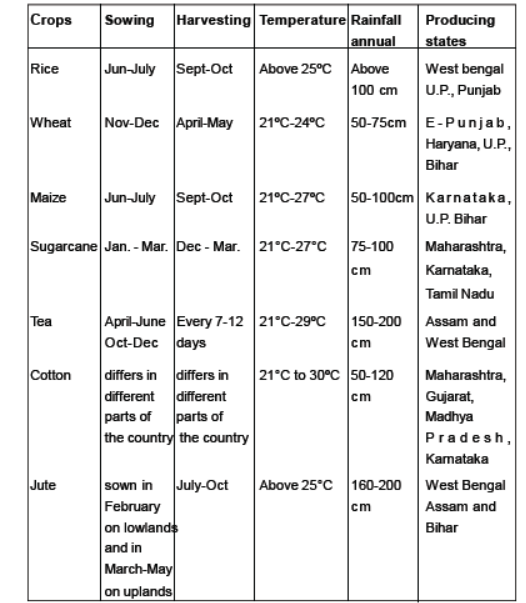
Question. Explain the favourable temperature, rainfall and soil conditions required for the growth of tea. Name the leading tea producing states.
Answer. (a) Climate: grow well in tropical and subtropical ( hot and humid) climate.
(b) Soil Type: deep fertile well drained soil which is rich in humus and organic matter.
(c) Rainfall: 150 to 300 cm annual. High humidity and frequent showers evenly distributed throughout the year
(d) Assam and West Bengal
Question. What are the Geographical conditions required for rice growth. Name the major areas of its production.
Answer.
(a) Climate: Paddy is a tropical crop and grows well in the wet monsoon.
(b) Temperature: Above 25°C, coupled with heavy humidity.
(c) Rainfall: above 100 cm. It requires heavy rainfall in summer and irrigation in areas of less rainfall.
(d) Areas of Cultivation: plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic region. Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan. With the help of irrigation.
Question. Which is the second most important cereal crop? What are the Geographical conditions required for its growth. Name the major areas of its production.
Answer. (a) Wheat is the second most important cereal crop .
(b) Soil Type: Alluvial soil and black soil
(c) Temperature: Cool growing season and bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
(d) Rainfall: 50 to 75 cm of annual rainfall
(e) Areas of Cultivation: the Ganga-Sutlej plain in the north-west and black soil region of Deccan. Wheat producing states are Punjab,Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Source Based Questions
Read the following passage and answer the questions at the end.
The Green Revolution based on the use of package technology and the White Revolution (Operation Flood) were some of the strategies initiated to improve the lot of Indian agriculture. But, this too led to the concentration of development in few selected areas. Therefore, in the 1980s and 1990s, a comprehensive land development programme was initiated, which included both institutional and technical reforms. Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire and disease, establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies and banks for providing loan facilities to the farmers at lower rates of interest were some important steps in this direction.
Question. Which movements played an important role in improving Indian agriculture?
Answer. The Green Revolution and the White Revolution played an important role in improving agriculture
Question. What was the negative impact of Green Revolution?
Answer. The impact of Green Revolution was concentrated in few areas.
Question. What are the steps taken by government to imrove Indian agriculture?
Answer. Crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire and disease, establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies etc.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Sustained uses of land without compatible techno-institutional changes have hindered the pace of agricultural development. Inspite of development of sources of irrigation most of the farmers in large parts of the country still depend upon monsoon and natural fertility in order to carry on their agriculture. For a growing population, this poses a serious challenge. Agriculture which provides livelihood for more than 60 per cent of its population, needs some serious technical and institutional reforms. Thus, collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari, etc. were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after Independence. ‘Land reform’ was the main focus of our First Five Year Plan. The right of inheritance had already lead to fragmentation of land holdings necessitating consolidation of holdings.
Question. What was the main focus of the ‘First Five Year Plan’?
Answer. Its main focus was on ‘Land reforms’.
Question. What was the serious challenge for the growing population?
Answer. The serious challenge was that inspite of development of sources of irrigation most of the farmers in large parts of the country still depend upon monsoon and natural fertility in order to carry on their agriculture.
Question. Agriculture provided livelihood to how much population?
Answer. Agriculture provided livelihood to 60% of the population.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Multiple choice questions.
Question. Which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area?
(a) Shifting Agriculture
(b) Plantation Agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Intensive Agriculture
Answer: (b) Plantation Agriculture
Question. Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
(a) Rice
(b) Gram
(c) Millets
(d) Cotton
Answer: (b) Gram
Question. Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
(a) Pulses
(b) Jawar
(c) Millets
(d) Sesamum
Answer: (a) Pulses
Question. Which one of the following is announced by the government in support of a crop?
(a) Maximum support price
(b) Minimum support price
(c) Moderate support price
(d) Influential support price
Answer: (b) Minimum support price
2. Answer the following questions in 30 words.
Question. Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
Answer: Tea is an important beverage crop. This grows well in tropical or sub tropical climates, and deep and fertile well-drained soil, which is rich in humus and organic matter. Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate all throughout the year.
Question. Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
Answer: Rice is a staple food crop of India. It grows in the plains of north and north-east India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. It is also grown with the help of irrigation in Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh.
Question. Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
Answer: The various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government for the benefit of farmers are:
- Minimum Support Price policy
- Crop insurance against drought, flood, fire etc.
- Subsidy on power and fertilizers
- Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme
Question. The land under cultivation has got reduced day by day. Can you imagine its consequences?
Answer: A declining area of land under cultivation coupled with increasing population have many consequences. These are
- Food shortage
- Unemployment and loss of livelihood for farmers
- Rise in price of food grains
- Shortage of supply of raw material for agro- industries
- Adverse affect on agricultural export
3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
Question. Suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Answer: Various initiatives taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production are:
- Consolidation of land holdings
- Abolition of Zamindari
- Land Reform was the main focus of our ‘First Five Year Plan’.
- The Green Revolution was initiated in India in the 1960's to increase food production.
- The White Revolution or Operation Flood launched in 1970, which is a project of the National Dairy and initiated to improve the lot of Indian agriculture.
- Minimum Support Price policy and provision for crop insurance
- Grameen Banks, Kissan Credit Card, and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme are also some of the reforms bought by Indian Government.
Question. How did the partition of the country in 1947 affect the jute industry?
Answer: Jute: It is known as the golden fibre. Jute grows well on well-drained fertile soils in the flood plains where soils are renewed every year. High temperature is required during the time of growth. It is used in making gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets, and other artifacts. Due to its high cost, it is losing the market to synthetic fibres and packing materials, particularly the nylon.
Question. Describe the impact of globalization on Indian agriculture.
Answer: Raw cotton and spices were important export items from India during the colonial time. Indian farmers revolted in Champaran against the British government being forced to grow indigo in place of foodgrains in 1917. Thus, globalization has had its boons and banes for Indian agriculture. Post liberalization, after 1990s Indian farmers face new challenges in the form of competition from highly subsidized agriculture of developed nations. This prompts, the need for making Indian agriculture successful and profitable by improving the conditions of small and marginal farmers, countering the negative effects of Green Revolution, developing and promoting organic farming, bio-technology in food production and diversifying cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops.
Question. Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Answer: The geographical conditions required for growth of rice are as follows:
- It is a kharif crop and requires hot and humid climate for cultivation.
- Temperature above 25°C and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm are favorable for growth of rice.
- Rich alluvial soils of the floodplains and deltaic areas are ideal for rice cultivation.
- Cheap labour as most of the farming involves manual labour.
- Rice requires abundant rainfall or good water supply through irrigation during its growing season in June- July.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Very Short Answer Questions
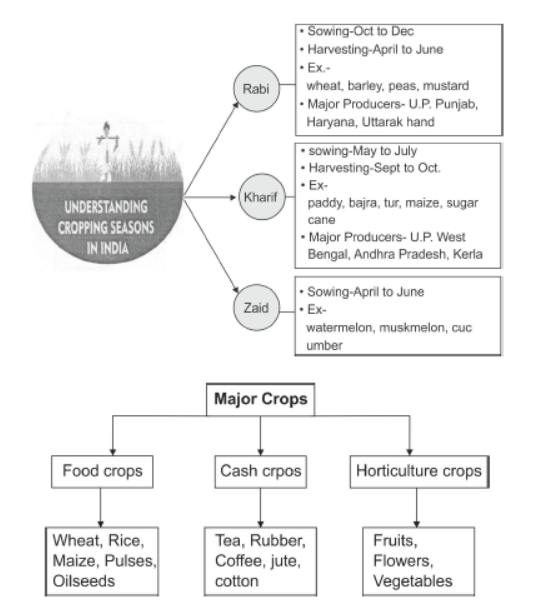
Question. Which main cropping patterns are followed in India?
Answer. India has three cropping seasons—rabi, kharif and zaid.
Question. When are rabi crops grown?
Answer. Grown in from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June.
Question. Name the important plantation crops grown in India.
Answer. In India, tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, banana are important plantation crops.
Question. Which factors are playing an important role in development of plantation?
Answer. A well developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets.
Question. Which crops are grown in rabi season?
Answer. Wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard, etc. are grown in rabi season.
Question. Which institutional reforms were introduced for farmers?
Answer. Collectivisation, consolidation of land holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari, etc.
Question. Which two revolutions, revolutionized Indian agriculture?
Answer. The Green Revolution based on the use of package technology and the White Revolution were some of the strategies initiated to improve the Indian agriculture.
Question. Which schemes were introduced by government for the benefit of farmers?
Answer. Kissan Credit Card (KCC), Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) are some schemes introduced by government of India for the benefit of the farmers.
Question. When are kharif crops grown?
Answer. Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September or October.
Question. Why is India called an ‘agrarian’ country?
Answer. Two thirds of India’s population are engaged in agricultural activities. Agriculture is a primary activity.
Question. Which fibre is known golden fibre?
Answer. Jute.
Question. In which regions is Jute grown?
Answer. West Bengal, Bihar, Assam, Odisha and Meghalaya are the major jute producing states of India.
Question. Why is jute losing its importance?
Answer. Due to its high cost, it is losing market to synthetic fibres and packing materials, particularly the nylon.
Question. Which are the important kharif crops?
Answer. The important kharif crops grown during this season are paddy (rice), maize, jowar, bajara, tur, moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean.
Question. What is Zaid Season?
Answer. In between the rabi and kharif seasons, there is a short season during the summer month known as ‘zaid’ season.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Short Answer Questions
Question. What is ‘slash and burn’ agriculture?
Answer. (i) In this agriculture, farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other crops to sustain their families.
(ii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iii) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
Land productivity in this type of agriculture is low, as the farmers do not use fertilisers or any modern inputs.
Question. Describe the three cropping seasons of India.
OR
Describe any three main features of Rabi crop season and Kharif crop season.
Answer. (1) Rabi season:
(a) Crops sown in winters and harvested in summers.
(b) Some of the important rabi crops are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard.
(c) States growing rabi crops are: Punjab, Haryana, Himachal, Jammu and Kashmir,Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh.
(2) Kharif season:
(a) Crops grown with the onset of monsoons and harvested in September or October.
(b) Important Kharif growing states are: Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra.
(c) Crops grown during this season are: rice, maize, jowar, bajra, tur, moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean.
(3) Zaid season:
(a) It falls in between the rabi and kharif seasons.
(b) It’s a short season during the summer months.
(c) Major crops grown are: watermelon, muskmelon, cucumbers, vegetables and fodder crops.
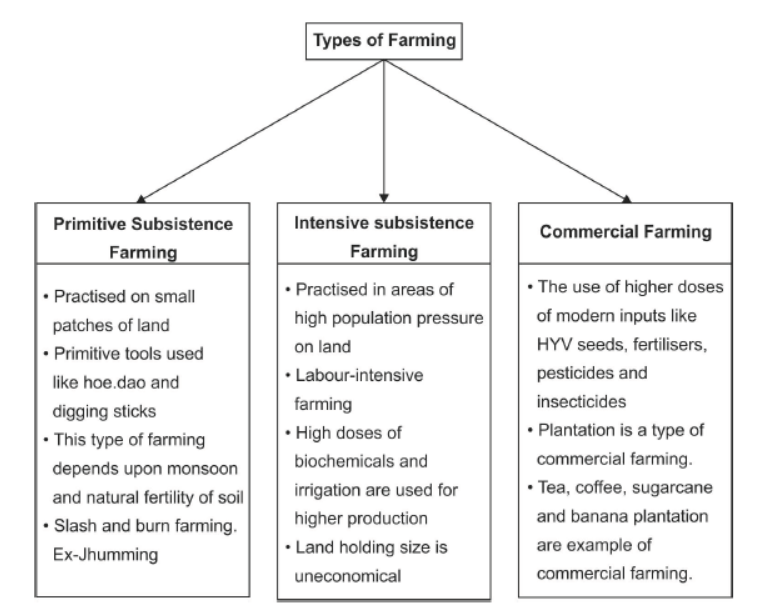
Question. What is primitive subsistence farming?
Answer. (i) It is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools.
(ii) This type of farming depends upon the monsoons and natural fertility of the soil.
(iii) It is also called ‘slash and burn’ agriculture.
Question. What do you understand by ‘Bhoodan’ and ‘Gramdan’?
Answer. Some poor landless villagers demanded some land for their economic well-being. Vinoba Bhave could not assure but promised to talk to the government regarding that. Suddenly Shri Ram Chandra Reddy, stood up and offered 80 acres of land to be distributed among 80 landless villagers. This act was known as ‘Bhoodan’. Similarly, some zamindars, owners of many villages, offered to distribute some villages among the landless. It was known as ‘Gramdan’. This Gramdan & Bhoodan movement was initiated by Vinoba Bhave. It is also known as the ‘Bloodless Revolution’.
Question. What is ‘Jhumming’?
Answer. ‘Jhumming’ is slash and burn agriculture, practised in north eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya,Mizoram and Nagaland, etc. This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes only.
Question. Why do we need technical and institutional reforms in agriculture?
Answer. Inspite of development of sources of irrigation, most of the farmers in large parts of the country still depend upon monsoon and natural fertility in order to carry on their agriculture. For a growing population, this poses a serious challenge. Agriculture needs some serious technical and institutional reforms.
Question. Differentiate between commercial farming and plantation farming.
Answer.
| Commercial farming | Plantation farming |
| In this type of farming, crops are grown only for commercial purposes. |
In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area. |
| Farmers make use of higher doses of modern inputs, HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides, etc. |
Labour is employed to work in large tracts of land, using capital intensive devices. |
| E.g.: Rice is a commercial crop in Haryana and Punjab. |
E.g.: Tea Gardens produce tea, and coffee plantations produce coffee. |
Question. How is commercial farming practised in India?
OR
What is the main characteristic of commercial farming?
Answer. (i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the production of a commercial crop.
(ii) In this type of farming, High Yielding Variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, etc. are used to obtain higher productivity.
(iii) The degree of commercialisation varies from one region to another.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Long Answer Questions
Question. Give some main characteristics of coffee crop.
Answer.
- India produces about 4 per cent of the world’s coffee production.
- Indian coffee is known in the world for its good quality.
- The Arabica variety, initially brought from Yemen, is produced in the country.
- Initially, its cultivation was introduced on the Baba Budan Hills in Karnataka and even today its cultivation is confined to Nilgiri in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Indian coffee variety is in great demand all over the world.
Question. “The declining share of agriculture in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a matter of serious concern in India”. Support the statement with any five reasons.
Answer. Agriculture has been the backbone of the Indian economy though its share in the Gross Domestic Product has registered a dealing travel from 1951 onwards; yet its share in providing employment and livelihood to the population continues to be as high as 63 per cent in 2001.
Establishment of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), agricultural universities, veterinary services and animal breeding centres, horticulture development, research and development in the field of meteorology and weather forecast, etc. were given priority for improving Indian agriculture.
Indian farmers are facing a big challenge from international competition and our government is going ahead with reduction in the public investment in agriculture sector particularly in irrigation, power, rural roads, market and mechanisation.
Question. Why has Indian agriculture started a declining trend in food production? Explain.
Answer. (i) Indian farmers are facing a big challenge from international competition.India is producing lots of food and commercial crops but its products are not able to compete with the developed countries since subsidized agriculture is practised in those countries.
(ii) There is reduction in the public investment in agriculture sector particularly in power production, making of rural roads, market and mechanisation of farming.
(iii) Subsidy on fertilizers has also decreased since the cost of production has increased.
(iv) Agricultural products which are imported have low prices because of low import duty, giving competition to Indian farmers.
Question. “Irrigation has changed the cropping pattern of many regions in India.” Analyse the statement.
Answer. (i) Well-developed irrigation facilities have lessened the dependency of peasants on monsoon by ensuring regular supply of water.
(ii) Major shift- The development of proper irrigation facility has enabled peasants to grow the water-intensive and commercial crop.
(iii) The development of tube wells, irrigation pumps in the farming land has enabled peasants to irrigate a large plot of land.
The following are the effects of developing proper irrigation facilities:
(i) This has resulted in brininess of the earth.
(ii) It has increased productivity.
(iii) The development of irrigation facilities has resulted and aided in changing the cropping pattern. for instance, rice, which was earlier grown in Northeastern India because heavy rainfall favourably helped the production of rice.Now production of rice can be seen in the areas of low rainfall such as Punjab, Haryana and parts of Rajasthan.
Question. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming.
Answer.
| Primitive Subsistence | Intensive Subsistence |
| It is practised on small patches of land. | It is practised on comparatively bigger land holdings. |
| Primitive tools like hoe, dao and diggingsticks, and family community labour are used. | Modern inputs like HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides, etc., to obtain higher productivity are used. |
| In this type of farming, farmers depend on the monsoons and natural fertility of the soil. |
In intensive subsistence, irrigation facilities like tubewells and canal irrigation is used. |
Question. Name the two most important cereal crops in India. Describe the conditions required to grow these two crops.
Answer. Rice and Wheat
1. Rice:
(i) Temperature: It is a kharif crop which requires high temperature, and high humidity. This means monthly temperature of about 25° C with minor variation during the sowing, growing and harvesting season, is suitable for the growth of the plant.
(ii) Rainfall: Rice needs abundant rainfall, i.e., more than 100 cm. It can grow in areas with less rainfall, but with assured irrigation. Rice is grown in Punjab and Haryana with the help of irrigation.
(iii) Soil: Rice can grow in a variety of soils including silts, loams and gravels, but it is grown best in alluvial soil with a sub-soil of impervious clay. Areas of production: Rice is cultivated in almost all the states of India, but most of its cultivation is concentrated in the river valleys,deltas of rivers and the coastal plains.
The main rice producing states are West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab,Odisha, Karnataka, Assam and Maharashtra.
2. Wheat:
(i) Temperature: Cool and moist weather is required during growth, and warm and dry climate during ripening is needed.
(ii) Rainfall: 50-70 cm rainfall is required. Rainfall is necessary and beneficial, 15 days after sowing, and 15 days before ripening. A few winter showers or assured irrigation ensures a bumper harvest
(iii) Soil: Light loamy soil is required. It can also be grown in black soil. Important producers: Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh are the main producers of wheat.
Question. Explain four technological reform initiatives taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Answer. Technological reforms:
(i) Green Revolution in agriculture and White Revolution in milk were introduced.
(ii) Tractors, harvesters, threshers and tubewells, etc., and technological devices were introduced.
(iii) For better production, fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides were also produced.
(iv) The government also announced the minimum support price, which checks the exploitation of farmers by speculators and middlemen.
Question. Suggest the initiatives taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Answer. (i) The right of inheritance has led to fragmentation of landholdings. Therefore, collectivisation, consolidation of landholdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari, etc. were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after independence.
(ii) The Green Revolution based on the use of package technology and White Revolution were initiated to improve the Indian agriculture.
(iii) Land development programme was initiated, which included provision for crop insurance against famine, flood, cyclone, fire and disease, establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies, etc.
(iv) Kissan credit cards, Personal Accident Insurance scheme were introduced for the benefit of farmers.
(v) Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers are run on the radio and television.
(vi) To check the exploitation of farmers by speculators and middlemen, the government announces minimum support price, remunerative and procurement prices for important crops.
Project Work
2. On an outline map of India show wheat producing areas.
3. Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
1. The two staple food crops of India.
2. This is the summer cropping season of India.
3. Pulses like arhar, moong, gram, urad contain…
4. It is a coarse grain.
5. The two important beverages in India are…
6. One of the four major fibers grown on black soils.
Answer:
1. Rice and Wheat
2. Kharif
3. Protein
4. Jowar
5. Coffee, Tea
6. Cotton
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Water Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Power Sharing |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Federalism |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Popular Struggles and Movements |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Challenges to Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Print Culture and Modern World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money And Credit |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalization And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Social Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 4 Agriculture of Social Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 4 Agriculture Class 10 chapter of Social Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 4 Agriculture NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Social Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Social Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Social Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Social Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 4 Agriculture Class 10 Social Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 Agriculture Social Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 4 Agriculture have been answered by our teachers

