NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Social Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Social Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Class 10 Social Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity in Class 10. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
Democracy And Diversity
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics for Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity
Before you Read
Apartheid: A policy or system of segregation or discrimination on ground of race.
Racisim: Discrimination one the basis of colour of skin.
Homogenous Society : A society that has similar kinds of people especially where there are no significant ethnic difference.
Migrants: Any body who shift from oen region to another region whithin the country or another country for work or other economica opportunities.
African-American: The descendants of Africans who were brought into America as slaves between the 17th century and easly 19th century.
Civil Rights Movements: It refers to a set of events and reforms movements aimed at abolishing legal racial discriminations against African-American.
Overlapping: Social divisions takes place when some social difference overlaps with other differences.Overlapping social differences create possiblities of dep social divisions and tensions.
Cross Cutting: Cross-cutting social diffrences are easier to accommodate.
The Black Power: The black power movement emerged in 1966 and lasted till 1975, which was a more militant anti-racist movement, advocating even violence if necessary to end racism in the US.
Politics of Social Division
- Social divisions lead to political divisons that result in conflicts and violence.
- Effect of social divisons on voting behaviour.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics for Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Consider the following statements which of the statements is/are correct?
(A) Social divisons take place when social difference overlap.
(B) It is possible that a person can have multiple identities.
(C) Social division exist in ony big countries like India.
(a) A, B and C are correct
(b) A and B are correct
(c) B and C are correct
(d) Only C is corrects
Answer. B
Question. In dealing with social division which one of the following statement is not correct about democracy?
(a) Due to political competition in a democracy, social division get reflected in polities.
(b) In a democracy, it is possible for communities to voice their grievances in a peaceful manner.
(c) Democracy is the best way to accommodate social diversity.
(d) Democracy always leads to disintegration of society on the basis of social divisions.
Answer. D
Question. Fill in the blanks :
(i) _____ social differences create possiblities of deep social divisons and tensions.
(ii) _____ scial differences do not usually lead to conflicts.
(iii) Racism is the _____ on the basis of colour skin.
(iv) Any body who shift from one region to another region within the country or another country for work or other economic opportunities is called ____ .
(v) The main religion of people in Northern Ireland is ____ .
Answer. 1. Overlapping,
2. Cross-Cutting,
3. Discrimination,
4. Migrant
5. Roman Catholic
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics for Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Assertion-Reason Questions
The following questions consist of two statements — Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question. Assertion (A) : The assertion of social diversities in a country need not be seen as a source of danger.
Reason (R) : In a democracy, political expression of social divisions is very normal and can be healthy.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion (A) : All kinds of social differences are not based on accident of birth.
Reason (R) : Some of the differences are based on our choices.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion (A) : Every social difference does lead to social division.
Reason (R) : Social differences divide similar people from one another , but they also unite very different people.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion (A) : As long as people in Northern Ireland saw themselves as only Catholic or Protestant, their differences were difficult to reconcile.
Reason (R) : It is much easier if the people see that their identities are multiple and are complementary with the national identity.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion (A) : Social divisions of one kind or another exist in not every country.
Reason (R) : Even those countries such as Germany and Sweden, that were once highly Homogeneous, are undergoing rapid change with influx of people from other parts of the world.
Answer. D
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics for Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Source Based Questions
Read the Passage and Answer the Questions
''I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the colour of their skin but by the content of their character. Let freedom ring. And when this happens and when we allow freedom ring— when we let it ring from every village and hamlet, from every state and every city, we will be able to speed up that day when all of God's children— black men and white men, Jews and Gentiles Protestants and Catholics — will be able to join hands and sing in the words of the old
Negro Spritual : 'Free at last! free at last! Thank God Almighty, we are free at last!'' I have a dram that one day this nation will rise up and live out a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed : we hold these truths to be self evident : That all men are created equal.
Questions
Question. Which social division is mentioned in the passage ?
Answer. Social Divisions : Social division in USA between the Blacks and White, jews and Genetiles and Protestants and Catholics.
Question. What are the aspiration and anxieties mentioned in the passage.
Answer. Aspiration and Anxieties : Aspire that all human beings must be free and there should be no discrimination on the basis of colour or creed. He dream that his children would live in such society.
Question. Do you see a relationship between the expressions of the passage and incident in Mexico olympics mentioned in this chapter.
Answer. Relationship between speech (expression) and incident in Mexico
Olympic — Medal ceremony
Protest against Black povert
Question. Write the words of old Negro spiritual.
Answer. Old Negro spiritual words — free at last! Thank God ......... Created equal''
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Every social difference does not lead to social division. Social differences divide similar people from one another , but they also unite very different people . People belonging to different social groups share differences and similarities cutting across the boundaries of their groups . In the instance above, Carlos and Smith were similar in one way (both were African-American) and thus different from Norman who was white . But they were also all similar in other ways – they were all athletes who stood against racial discrimination. It is fairly common for people belonging to the same religion to feel that they do not belong to the same community, because their caste or sect is very different. It is also possible for people from different religions to have the same caste and feel close to each other . Rich and poor persons from the same family often do not keep close relations with each other for they feel they are very different. Thus , we all have more than one identity and can belong to more than one social group . We have different identities in different contexts .
Question. How were Smith, Carlos and Norman similar to each other?
Answer. They were all athletes who stood against racial discrimination.
Question. Why do people belonging to the same religion feel that they do not belong to the same community?
Answer. Because their caste or sect is very different.
Question. Why every social difference does not lead to social division?
Answer. Social differences divide similar people from one another, but they also unite very different people.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Take the case of Northern Ireland that we referred above. The region of the United Kingdom has been for many years the site of a violent and bitter ethno-political conflict. Its population is divided into two major sets of Christianity : 53 percent are protestants and 44 percent are Roman Catholics. The catholics were represented by Nationalist parties who demanded that Northern Ireland be Unified with the Republic of Ireland, a predominantly catholic country. The protestants were represented by Unionists who wanted to remain with the U.K. Which is predominantly protestants. Hundreds of civillians, militants and security forces were killed in the fight between unionists and Nationalists and between the security forces fo the UK and the Nationalists. it was only in 1998, that the UK government and the Nationalist reached a peace treaty after, which the latter suspended their armed struggle.
In Yugoslavia, the story did not have a happy ending. Political competition along religious ending ethnic lines led to the disintegration of Yugoslavia into six independent countries.
Questions
Question. What is the main religion of people in Northern Ireland?
Answer. Roman Catholic is the main religions of the people in Nothern Ireland
Question. Who represented catholics ?
Answer. Nationalist Parties.
Question. What was the result of political competition along religious and ethnic lives in Yugoslavia ?
Answer. Disintegretion of Yugoslavia into Six independent countries.
Question. Which is the main religion in the U.K ?
Answer. Protestants.
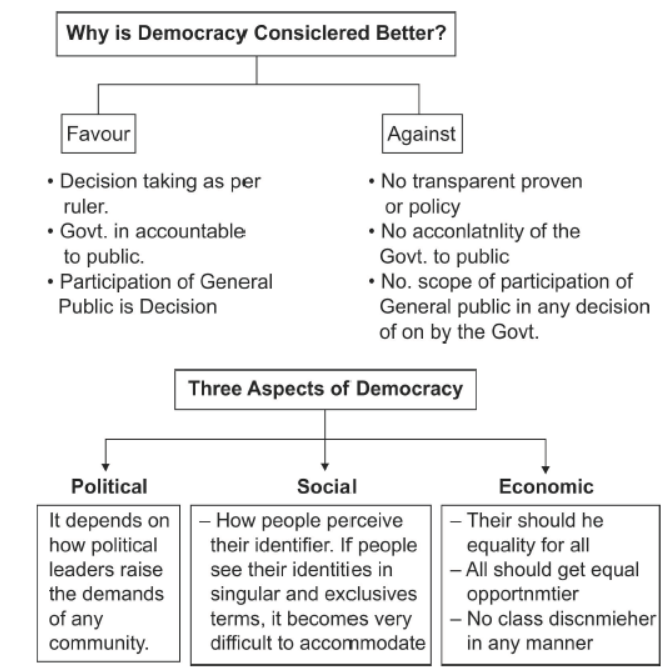
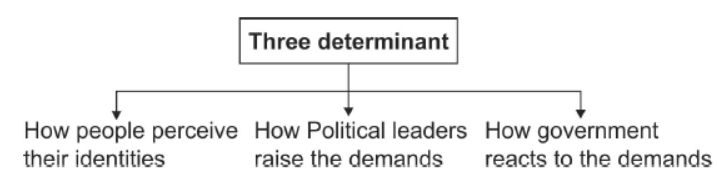
Question. Discuss three factors that determine the outcomes of politics of social divisions.
Answer. Three factors which determine the outcomes of politics of social divisions:
• The people's perception of their identities: When this is singular, the accommodation of other identities becomes difficult.
• Representation of a community by political leaders: While representing a community, if politicians raise demands that are constitutional, then it is easier to accommodate those demands.
• The government's reaction: If the reasonable demands of a community are suppressed by the government, then it leads to social divisions, which in turn threaten the integrity of the country.
Question. When does a social difference become a social division?
Answer. A social difference becomes a social division when it overlaps with some other social difference. For example, the Whites were rich and powerful and the Blacks were poor and homeless and discriminated against. When one kind of social difference becomes more important than the other, then it leads to division.f
Question. How do social divisions affect politics? Give two examples.
Answer. • Democracy involves competition among various political parties.
• Political parties tend to exploit some existing social divisions. This can turn social divisions into political divisions and lead to serious conflict, violence or even disintegration.
• Northern Ireland is an example of how social divisions can affect politics.
• The population of Northern Ireland comprised of 53 percent Protestants and 44 percent Roman Catholics.
• The Nationalist parties represented the Catholics. They demanded Northern Ireland to be unified with Republic of Ireland.
• The Unionists represented the Protestants and wanted to remain with UK.
• A bloody war took place between Unionists and Nationalists in which hundreds of civilians, militants and security men were killed.
• It was only in 1998, that the UK government and the Nationalists reached a peace treaty after which the violence ended.
• In Yugoslavia too, political parties competed on the lines of ethnic and religious divisions.
• But unlike Northern Ireland, Yugoslavia could not save itself from disintegration. The disintegration of Yugoslavia led to the formation of six independent countries.
Question. _______________Social differences create possibilities of deep social divisions and tensions. __________social differences do not usually lead to conflicts.
Answer. Overlapping social differences create possibilities of deep social divisions and tensions. Cross-cutting social differences do not usually lead to conflicts.
Question. In dealing with social divisions which one of the following statements is NOT correct about democracy?
(a) Due to political competition in a democracy, social divisions get reflected in politics.
(b) In a democracy it is possible for communities to voice their grievances in a peacefuI manner.
(c) Democracy is the best way to accommodate social diversity.
(d) Democracy always leads to disintegration of society on the basis of social divisions.
Answer. (d) Democracy always leads to disintegration of society on the basis of social divisions.
Explanation: In a democracy, political expression of social divisions is very normal and can be healthy. This allovvs various disadvantaged and marginal social groups to express their grievances and get the government to attend to these. Expression of various kinds of social divisions in politics often results in their cancelling one another out and thus reducing their intensity.
Question. Consider the following three statements.
A. Social divisions take place when social differences overlap.
B. It is possible that a person can have multiple identities.
C. Social divisions exist in only big countries like India. Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) A, B and C I
(b) A and B
(c) B and C
(d) Only C
Answer. (b)A and B
Question. Arrange the following statements in a logical sequence and select the right answers by using the code given below.
A. But all political expression of social divisions need not be always dangerous.
B. Social divisions of one kind or the other exist in most countries.
C. Parties try to win political support by appealing to social divisions.
D. Some social differences may result in social divisions.
(a) D,B,C,A
(b) D,B,A,C
(c) D,A,C,B
(d) A,B,C,D
Answer. (a)D,B,C,A
Question. Among the following, which country suffered disintegration due to political fights on the basis of religious and ethnic identities?
(a) Belgium
(b) lndia
(c) Yugoslavia
(d) Netherlands
Question. Discuss three factors that determine the outcomes of politics of social divisions.
Answer. Three factors are crucial in deciding the outcome of politics of social divisions-
Firstly, the outcome depends on how people perceive their identities. If people see their identities in singular and exclusive terms, it becomes too difficult to accommodate. As long as people in Northern Ireland saw themselves as only Catholic or Protestant, chances of reconciliation were slim. It is much easier if people realize they have multiple identities that are complementary with the national identity. Most Belgians now feel that they are Belgians first and then Dutch or German speakers.
Secondly, it depends on how political leaders raise the demands of any community. The demands of a community ought to be within a constitutional framework. These demands should not be at the cost of other communities. In Sri Lanka, the demand for 'only Sinhala' was at the cost of the Tamil community.
Thirdly, it depends on how the government reacts to demands of different groups. The governments of Belgium and Sri Lanka reacted differently to the demands. While Belgian leaders were ready to accommodate all groups, in Sri Lanka, the demands of the minority were suppressed in the name of national unity. Attempts of forced integration can lead to disintegration.
Question. When does a social difference become a social division?
Answer • When one social difference overlaps with another, social divisions take place.
• In USA, the difference between African-Americans and Whites becomes a social division because most blacks are poor, homeless, unemployed and discriminated against.
• In India, the Dalits are often landless and poor. They have to face discrimination and injustice.
• Such differences often make people feel that they belong to different communities.
Question. How do social divisions affect politics? Give two examples.
Answer. • Democracy involves competition among various political parties.
• Political parties tend to exploit some existing social divisions. This can turn social divisions into political divisions and lead to serious conflict, violence or even disintegration.
• Northern Ireland is an example of how social divisions can affect politics.
• The population of Northern Ireland comprised of 53 percent Protestants and 44 percent Roman Catholics.
• The Nationalist parties represented the Catholics. They demanded Northern Ireland to be unified with Republic of Ireland.
• The Unionists represented the Protestants and wanted to remain with UK.
• A bloody war took place between Unionists and Nationalists in which hundreds of civilians, militants and security men were killed.
• It was only in 1998, that the UK government and the Nationalists reached a peace treaty after which the violence ended.
• In Yugoslavia too, political parties competed on the lines of ethnic and religious divisions.
• But unlike Northern Ireland, Yugoslavia could not save itself from disintegration. The disintegration of Yugoslavia led to the formation of six independent countries.
Question. _______________Social differences create possibilities of deep social divisions and tensions. __________social differences do not usually lead to conflicts.
Answer. Overlapping social differences create possibilities of deep social divisions and tensions. Cross-cutting social differences do not usually lead to conflicts.
Question. In dealing with social divisions which one of the following statements is NOT correct about democracy?
(a) Due to political competition in a democracy, social divisions get reflected in politics.
(b) In a democracy it is possible for communities to voice their grievances in a peacefuI manner.
(c) Democracy is the best way to accommodate social diversity.
(d) Democracy always leads to disintegration of society on the basis of social divisions.
Answer. (d) Democracy always leads to disintegration of society on the basis of social divisions.
Explanation: In a democracy, political expression of social divisions is very normal and can be healthy. This allovvs various disadvantaged and marginal social groups to express their grievances and get the government to attend to these. Expression of various kinds of social divisions in politics often results in their cancelling one another out and thus reducing their intensity.
Question. Consider the following three statements.
A. Social divisions take place when social differences overlap.
B. It is possible that a person can have multiple identities.
C. Social divisions exist in only big countries like India. Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) A, B and C I
(b) A and B
(c) B and C
(d) Only C
Answer. (b)A and B
Question. Arrange the following statements in a logical sequence and select the right answers by using the code given below.
A. But all political expression of social divisions need not be always dangerous.
B. Social divisions of one kind or the other exist in most countries.
C. Parties try to win political support by appealing to social divisions.
D. Some social differences may result in social divisions.
(a) D,B,C,A
(b) D,B,A,C
(c) D,A,C,B
(d) A,B,C,D
Answer. (a)D,B,C,A
Question. Among the following, which country suffered disintegration due to political fights on the basis of religious and ethnic identities?
(a) Belgium
(b) lndia
(c) Yugoslavia
(d) Netherlands
Answer. (b)Yugoslavia
Question. Read the following passage from a famous speech by Martin Luther King Jr. in 1963. Which social division is he talking about? What are his aspirations and anxieties? Do you see a relationship between this speech and the incident in Mexico Olympics mentioned in this chapter?
"I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the colour of their skin but by the content of their character. Let freedom ring. And when this happens, and when we allow freedom ring-when we let it ring from every village and every hamlet, from every state and every city, we will be able to speed up that day when all of God's children-black men and white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics-will be able
to join hands and sing in the words of the old Negro spiritual: 'Free at last! Free at last! Thank God Almighty, we are free at last!' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: 'We hold these truths to be self-evident: that all men are created equal'."
Answer. • The social division referred by Martin Luther King Jr. in this speech is the colour of the skin.
• His aspirations are that his children should not be judged by the colour of their skin but by their character. He wants equality for all - black men, white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics. He dreams that one day his nation (USA) will accept the truth that all men are created equal.
• Yes, there is a relation between the Mexico Olympics incident mentioned in the chapter and Martin Luther King's speech. Both highlight the fact that African-Americans were discriminated against in the United States of America.
The Black American athletes, Tommie Smith and John Carlos had tried to draw international attention towards the racial discrimination in the United States. Martin Luther King has also made a reference to this racial discrimination in his speech.
(b)Yugoslavia
Question. Read the following passage from a famous speech by Martin Luther King Jr. in 1963. Which social division is he talking about? What are his aspirations and anxieties? Do you see a relationship between this speech and the incident in Mexico Olympics mentioned in this chapter?
"I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the colour of their skin but by the content of their character. Let freedom ring. And when this happens, and when we allow freedom ring-when we let it ring from every village and every hamlet, from every state and every city, we will be able to speed up that day when all of God's children-black men and white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics-will be able
to join hands and sing in the words of the old Negro spiritual: 'Free at last! Free at last! Thank God Almighty, we are free at last!' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: 'We hold these truths to be self-evident: that all men are created equal'."
Answer. • The social division referred by Martin Luther King Jr. in this speech is the colour of the skin.
• His aspirations are that his children should not be judged by the colour of their skin but by their character. He wants equality for all - black men, white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics. He dreams that one day his nation (USA) will accept the truth that all men are created equal.
• Yes, there is a relation between the Mexico Olympics incident mentioned in the chapter and Martin Luther King's speech. Both highlight the fact that African-Americans were discriminated against in the United States of America.
The Black American athletes, Tommie Smith and John Carlos had tried to draw international attention towards the racial discrimination in the United States. Martin Luther King has also made a reference to this racial discrimination in his speech.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics for Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What does ‘Black Power’ mean?
Answer. Black Power was a movement that emerged in 1966 to end racism in USA.
Question. What is the origin of social difference?
Answer. Accident of birth.
Question. What kind of social differences do we normally face in our society?
Answer. People around us are male or female, tall or short, have different kinds of complexions, have different physical abilities or disabilities.
Question. Which are social groups formed on the basis of our choice?
Answer. Some people are atheists, they don’t believe in God or any religion. Some people choose to follow a religion other than the one in which they were born. These differences are based on our choices.
Question. Who were the two US athletes who won medals in 1968 Mexico Olympics?
Answer. Tommie Smith and John Carlos.
Question. How did they protest in medal ceremony?
Answer. They received their medals wearing black socks and no shoes to represent Black Poverty.
Question. On which factor does the outcome of politics of social division depend?
Answer. The outcome depends on how people perceive their identities. If people see their identities in singular and exclusive terms, it becomes very difficult to accommodate.
Question. Is there any country which is homogenous at present?
Answer. Truly homogenous countries are either islands (Iceland, Japan etc.,) geographically, isolated (Scandinavia) or politically isolated (North Korea). The rest are artificially formed to become nation states (Germany, Italy, Armenia).
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics for Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Short Answer Questions
Question. ‘The assertion of social diversities in a democratic country is very normal and can be healthy.’ Justify the statement with argument.
Answer. Assertion of social diversities in a country need not to be seen as a source of danger because in a democratic country every person and a community has the right to state their views and opinions. This is very normal and healthy in a democracy. This allows the less privileged and marginal groups to express their grievances and concerns and can get the government to attend these. This only leads to the strengthening of democracy.
Question. What was black power movement?
Answer. ‘African-American’, ‘Afro-American’, ‘Black American’ or ‘Black’ are the terms used to refer mainly to the descendants of Africans who were brought into America as slaves between the 17th and early 19th century. The Black Power Movement emerged in 1966 and lasted till 1975, which was a militant anti-racist movement, advocating even violence, if necessary, to end racism in the US.
Question. On what basis are social differences created?
Answer. (i) Based on accident of birth:
(a) Normally, we don’t choose to belong to one community. We belong to it simply because we were born into it.
(b) We all experience social differences based on accident of birth in our everyday lives.
(ii) Based on physical abilities or disabilities:
(a) There is discrimination based on gender; some are tall or short, have different kinds of complexions or have different physical abilities or disabilities.
(b) All kinds of social differences are not based on accident of birth.
(iii) Differences based on choices:
(a) Some people are atheists, they do not believe in God or any religion.
(b) While some people choose to follow a religion other than the one in which they were born into.
(c) Most of us choose what to study, which occupation to take up and which games or cultural activities to take part in.
All these lead to the formation of social groups that are based on our choices.
Question. “Every social difference does not lead to social division.” Explain the statement.
Answer.
- Social differences divide similar people from one another, but they also unite very different people.
- People belonging to different social groups share differences and similarities cutting across the boundaries of their groups.
- It is fairly common for people belonging to the same religion to feel that they do not belong to the same community, because their caste or sect is different.
- It is also possible for people from different religions to have the same caste and feel close to each other.
- Rich and poor persons from the same family, often do not keep close relations with each other because they feel they are different.
Question. The combination of politics and social division is very dangerous and explosive. Do you agree? Support the answer with suitable examples.
Answer. Social divisions and politics really make a very explosive combination.
- We have seen the case of Sri Lanka, where preference is given to Sinhalese, dejecting the Tamils in the society as well as politics, which led to revolt and ultimately a civil war, which is creating disturbance in the country.
- In Northern Ireland, the Catholics were represented by Nationalist parties who wanted to join the Republic of Ireland.
- The Protestants were represented by Unionists, who wanted to remain with the United Kingdom. This led to conflict between them and hundreds of civilians, militants and security forces were killed.
- In Yugoslavia, the political competition along religious ending ethnic lines led to the disintegration of Yugoslavia into six independent countries.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Water Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Power Sharing |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Federalism |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Popular Struggles and Movements |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Political Parties |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Challenges to Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Print Culture and Modern World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money And Credit |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalization And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity is available on our website for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Social Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity of Social Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Class 10 chapter of Social Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Social Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Social Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Social Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Social Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Class 10 Social Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity Social Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity have been answered by our teachers

