Please refer to CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Money and Credit. Download HOTS questions and answers for Class 10 Social Science. Read CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit below and download in pdf. High Order Thinking Skills questions come in exams for Social Science in Class 10 and if prepared properly can help you to score more marks. You can refer to more chapter wise Class 10 Social Science HOTS Questions with solutions and also get latest topic wise important study material as per NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and pattern for Class 10
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Class 10 Social Science HOTS
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following high order thinking skills questions with answers for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit in Class 10. These HOTS questions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
HOTS Questions Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Class 10 Social Science with Answers
Summary
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit
Question : Because money acts as an intermediary in a transaction,it is referred to as _____.
(a) Unit of account
(b) Standard of deferred payment
(c) Medium of exchange
(d) Store of value
Answer : C
Question : Which among the following issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government ?
(a) State Bank of India
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Commercial Bank of India
(d) Union Bank of India
Answer : B
Question : Which of the following statement best describes a demand deposit?
(a) The cash held by people which can be used as and when they require is called demand deposit.
(b) The cash deposited in a bank which can be withdrawn on demand is called demand deposit.
(c) The order to a bank to pay a certain sum from the drawer’s account is called demand deposit.
(d) The currency approved by international bodies to carry out trade practices is called demand deposit.
Answer : B
Question : Who has the authority to issue the following currency note ?
(a) Central Government
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Union Bank of India
(d) State Bank of India
Answer : B
Question : Which one of the following is the name given to a substitute of cash and cheque?
(a) Credit card
(b) Coin
(c) Currency
(d) Demand deposit
Answer : A
Question : Which one of the following is other name of organised credit?
(a) Informal credit
(b) Formal credit
(c) Cooperative credit
(d) None of the above
Answer : B
Question : Since money act as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called __________.
Choose the correct option:
(a) Medium of exchange
(b) Balance
(c) Cash deposits
(d) Withdrawals
Answer : A
Question : Major portion of the deposit is used by banks for ___________. Choose the correct option:
(a) Extending loan
(b) Interest
(c) Deposits
(d) Loan
Answer : A
Question : Presently banks in India, hold about ____ per cent of their deposits as cash.
(a) 35
(b) 30
(c) 20
(d) 15
Answer : D
Question : Mohan produces ice cream and wants to sell it to people.
He also requires sugar to make ice cream, so he wishes to buy sugar. Now, Mohan is unable to find a person who will exchange sugar for ice cream. Which of the following terms
explain the problem that Mohan is facing?
(a) Lack of trade expertise
(b) Double coincidence of wants
(c) Irrational consumer behavior
(d) Future expectations
Answer : B
Question : Identify the correct option with regard to money from the following options:
(a) currency
(b) value
(c) transfer
(d) barter
Answer : A
Question : A porter making pots, wants to exchange pots for wheat.
Luckily, he meets a farmer who has wheat and is willing to exchange it for the pots. What is this situation known as?
Select the appropriate option:
(a) Incidence of wants
(b) Double coincidence of wants
(c) Barter system of wants
(d) None of the above
Answer : B
Question : Which among the following issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government?
(a) State Bank of India
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Commercial Bank of India
(d) Union Bank of India
Answer : B
Question : Which among the following statements is true regarding banks?
(a) Banks mediate between those who want to sell one commodity in exchange of other commodity.
(b) Banks use a major proportion of deposits to invest in mutual funds.
(c) Banks charge a lower interest rates on loan than the interest rate they offer on deposits.
(d) Banks use the deposits to fulfil loan requirements of the people.
Answer : D
Question : Which of the following statements best describes a debttrap?
(a) When a person takes a loan and is unable to repay, the loan, he or she has to sell portion of the land and it worsens the persons situation is known as a debt trap.
(b) When a person takes loan for production process, earns good profit, returns the credit and again takes loan in the next production cycle, the person is in a debt trap.
(c) When a person takes loan from unorganized sector, the person is in a debt trap.
(d) When a person takes loan from a bank, the person is in a debt trap as the banks charge a very high interest rate on loans.
Answer : A
Question : Who has the authority to issue the following currency note ?

(a) Central Government
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Union Bank of India
(d) State Bank of India
Answer : B
Question : Modern forms of money include:
(a) silver coins
(b) copper coins
(c) paper notes
(d) gold coins
Answer : C
Question : In rural areas, farmers take credit for
(a) Health
(b) Education
(c) Crop production
(d) Fodder
Answer : D
Question : Study the picture and answer the question that follows:
Which of the following aspect best signifies the above image?
(a) Medium of exchange
(b) Cheque Payments
(c) Loan Certificate
(d) None of the above
Answer : A
Question : Study the picture and answer the question that follows:

Which of the following best signifies the above image?
(a) Bank Cheque
(b) Bank Draft
(c) Terms of Credit
(d) Letters of Payment
Answer : A
Question : Identify the relation between a trader and a farmer:
(a) A trader provides farm inputs on the condition that the farmer will sell his crop produce to him at higher prices so that he could sell it at medium prices in the market.
(b) A trader provides farm inputs on the condition that the farmer will sell his crop produce to him at lower prices so that he could sell it at higher prices in the market.
(c) A trader provides farm inputs on the condition that the farmer will sell his crop produce to him at medium prices so that he could sell it at higher prices in the market.
(d) A trader provides farm inputs on the condition that the farmer will sell his crop produce to him at higher prices so that he could sell it at lower prices in the market.
Answer : B
Question : Choose the correctly-matched pair about Chit Fund:
(a) Chit fund comes under organised credit.
(b) Chit fund comes under unorganised credit.
(c) Chit fund comes under discounted coupon.
(d) Chit fund comes under formal credit.
Answer : B
Question : Which of the following is a reason for using money to buy goods and services?
(a) Money can be easily exchanged for any good or service a person wants.
(b) Money is more valuable than any good or service a person wants.
(c) Money cannot be put to any other use apart from transaction.
(d) Money is less valuable than any good or service a person wants so people easily give money for the goods and services.
Answer : A
Question : Which of the following statement is true of banks?
(a) Banks mediate between those who want to sell one commodity in exchange of other commodity
(b) Banks use a major proportion of deposits to invest in mutual funds.
(c) Banks charge a lower interest rates on loan than the interest rate they offer on deposits.
(d) Banks use the deposits to fulfil loan requirements of the people.
Answer : D
Question : A system where goods are exchanged for other good is called ______.
(a) barter system
(b) flexible exchange system
(c) fluctuating system
(d) rational trade system
Answer A
Question : What are electronic banking services?
(a) ATM
(b) Debit Card
(c) Credit Card
(d) All of the above.
Answer : D
Question : Modern form of money is linked with which system?
(a) Accounts system
(b) Finance system
(c) Banking system
(d) None of the above.
Answer : C
Question : Which among the following is not a feature of informal source of credit?
(a) It is supervised by the Reserve Bank of India.
(b) Rate of interest is not fixed.
(c) Terms of credit are very flexible.
(d) Traders, employers, friends, relatives, etc. provide informal credit source.
Answer : A
Question : Which of the following is not a feature of Self Help Groups (SHGs)?
(a) It consists of 15-20 members or more.
(b) Here, members pool their savings which acts as collateral.
(c) Loans are given at nominal rate of interest.
(d) It is an informal source of credit.
Answer : D
Question : Identify the correct statement with regard to money:
(a) Money is based on double coincidence of wants.
(b) Money is based on single coincidence of wants.
(c) Money is based on double or single coincidence of wants.
(d) Money is based on double and single coincidence of wants.
Answer : B
Question : Which among the following is the name given to a system wherein goods were exchanged without using money?
(a) Goods system
(b) Exchange system
(c) Barter system
(d) No-money system
Answer : C
Question : What is the name given to a new medium of exchange that was developed to solve the problem of similar wants?
(a) Capital
(b) Cost
(c) Rent
(d) Money
Answer : D
Question : Which among the following is included in modern forms of money?
(a) Currency notes and coins
(b) Cowrie shells and stones
(c) Gold and silver coins
(d) Grains and cattle
Answer : A
Question : Major portion of the deposits is used by banks for:
(a) setting up new branches
(b) paying taxes
(c) extending loans
(d) none of the above
Answer : C
Question : Deposits in bank accounts withdrawn on demand are called:
(a) Demand deposits
(b) Fixed deposits
(c) Recurring deposits
(d) Withdrawal deposits
Answer : A
Question : Which of the following is the most important function of money?
(a) Used in banking transactions
(b) Payment of loans
(c) Medium of exchange
(d) Stock market exchange
Answer : C
Question : Identify which of the following is not true regarding the inconvenience of Barter Exchange:
(a) Lack of double coincidence of want
(b) Absence of divisibility
(c) Difficulty in storing wealth
(d) Availability of money as a medium of exchange.
Answer : D
Question : Raghav has surplus money, so he opens a bank account and deposits in it. Whenever he needs money, he can go to his bank and withdraw from there. What is the name given
to this kind of deposit with the banks?
(a) Demand deposit
(b) Term deposit
(c) Fixed deposit
(d) Surplus deposit
Answer : A
Question : Which of the following statement best describes a demand deposit?
(a) The cash held by people which can be used as and when they require is called demand deposit.
(b) The cash deposited in a bank which can be withdrawn on demand is called demand deposit.
(c) The order to a bank to pay a certain sum from the drawer's account is called demand deposit.
(d) The currency approved by international bodies to carry out trade practices is called demand deposit.
Answer : B
Question : A paper that instructs a bank to pay a specific amount from a person’s account to another person in whose name the paper is issued is called a ______.
(a) demand deposit
(b) time deposit
(c) bond
(d) cheque
Answer : D
Question : A person can withdraw money by issuing a cheque. Which one among the following statements is true about cheque?
(a) Loan taken by the bank.
(b) Loan taken by the depositor from the bank.
(c) Paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount.
(d) Paper valid to withdraw money.
Answer : C
Question : Which among the following statements is correct with regard to banks and borrowers?
(a) Banks give loans and charge rent on loan amount from the borrowers.
(b) Banks give loans and charge wages on loan amount from the borrowers.
(c) Banks give loans and charge interest on loan amount from the borrowers.
(d) Banks give loans and charge money on loan amount from the borrowers.
Answer : C
Question : Ram and Shyam are small farmers. Ram has taken credit of ` 20,000 at 1.5% per month from a trader while Shyam has taken the same amount credit at 8% per annum from a bank. Who is better off?
(a) Ram is better because he has to do no paperwork.
(b) Shyam is better because his interest payment is less.
(c) Ram is better because he has not paid any collateral.
(d) Both Ram and Shyam are equal so no one is better off.
Answer : B
Question : Identify the correct essential feature of barter system:
(a) Money can easily be used to exchange any commodity.
(b) It is based on double coincidence of wants.
(c) It is generally accepted as a medium of exchange of goods.
(d) It acts as a measure and store of value.
Answer : B
Question : Higher cost of borrowing for the farmers means a larger part of the _____________of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
(a) collateral
(b) expenses
(c) earnings
(d) none of these
Answer : C
Question : Match the following:

Options:
(a) I-3, II-1, III-2
(b) I-3, II-2, III-1
(c) I-1, II-2, III-3
(d) I-2, II-1, III-3
Answer : A
Question : Informal sector loans are given by
(a) Traders
(b) Employers
(c) Relatives and friends
(d) All of the above
Answer : D
Question : Formal sources of credit do not include:
(a) banks
(b) money lenders
(c) cooperatives
(d) none of these
Answer : B
Question : Who supervises the functioning of formal source of loans?
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(b) State Bank of India
(c) Central Bank of India
(d) Informal money lenders.
Answer : A
Question : Match the following:
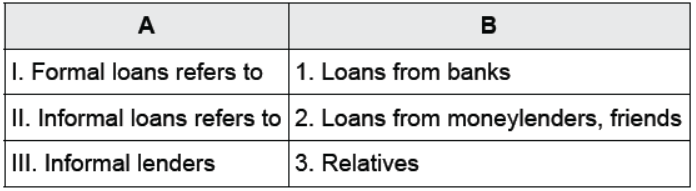
Options:
(a) I-2, II-1, III-3
(b) I-3, II-1, III-2
(c) I-1, II-2, III-3
(d) I-1, II-2, III-3
Answer : C
Question : Poor households in urban areas take loans from ____ sources.
(a) formal
(b) informal
(c) direct
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer : D
True / False
Question : Money eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants. (True/False)
Answer : True
Question : Transactions are made in money because it eliminates the inconvenience of barter system of exchange.
Answer : True
Fill in the Blanks
Question : Majority of the credit needs of the __________households are met from informal sources.
Answer : Poor
Question : The share of formal sector credit is ___________for thericher households as compared to the poor households inIndia.
Answer : higher
Question : Absence of ___________as a guarantee is a major cause that prevents poor people from obtaining loans from formal sector sources, such as commercial banks.
Answer : collateral
Question : ______ help the borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
Answer : SHGs
Question : __________costs of borrowing increase the debt-burden.
Answer : High
One Word Answer Type Questions
Question : Who can refuse the payment made in rupee in India ?
Answer : No one.
Question : What kind of economy is suitable for barter system ?
Answer : Backward economy.
Question : Which are the major sources of credit for rural India ?
Answer : Banks, cooperative societies and moneylenders.
Question : What are the modern forms of money — currency and deposits associated with ?
Answer : Modern banking system.
Question : What is the main function of money ?
Answer : The medium of exchange.
Question : Which are the modern forms of money ?
OR
What are the modern forms of money ?
Answer : Currency (paper notes and coins) and demand deposits withdrawable by cheques.
Question : What is the major source of credit for poor household in urban areas ?
Answer : Informal source of credit.
Question : Who issues currency in India ?
Answer : The Reserve Bank of India.
Question : What things can be used as collateral ?
Answer : Land, building, jewellery, vehicle, livestock, deposits with banks etc.
Question : Who legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment for settling transactions in India ?
Answer : The Indian law.
Question : What are the formal sources of cheap loans for rural people ?
Answer : Banks and cooperative societies (or cooperatives) etc.
Question : Name two objects that were used as money before the introduction of coins.
Answer : Grains and cattle.
Rewrite the Statement
Question : In a SHG most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by a non-government organization.
Answer : In a SHG most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by members.
Question : The law legalizes the use of rupee as a medium of payment that can be refused in settling transactions in India.
Answer : The law legalizes the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
Question : Since money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called a store of value.
Answer : Since money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called a medium of exchange.
Question : A cheque is a paper instructing the person to pay a specific amount in the person’s account from the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Answer : A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Question : The Government of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
Answer : The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
Assertion and Reasoning Based Questions
Mark the option which is most suitable:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertion : Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves.
Reason : Banks in India these days hold about 15 per cent of their deposits as cash.
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
Reason : The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small scale industries, to small borrowers etc.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
Reason : The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : The terms of deposit are same for all credit arrangements.
Reason : Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country's development.
Answer : (d) A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertion : Credit would be useful if does not depends on the risk involved in a situation.
Reason : The chance of benefitting from credit is highest in agriculture sector.
Answer : (c) A is true but R is false.
Question : Assertion : Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country's development.
Reason : Banks and cooperatives give loans on a lesser interest rate than the informal sector.
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Money eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants.
Reason : Money serves as a medium of exchange.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Mark the option which is most suitable :
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Question : Assertion : If credit would be useful or not depends on the risk involved in a situation.
Reason : The chance of benefitting from credit is highest in agriculture sector.
Answer : (c) Whether credit would be useful or not depends on the risks in the situation and whether there is some support, in case of loss.
Question : Assertion : In India, no individual can refuse to accept a payment made in rupees.
Reason : Rupee is the legal tender in India.
Answer : (a) The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
Question : Assertion : Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, deposits with banks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid. Reason : Collateral is given as the lender can sell the collateral to recover the loan amount if the borrower fails to repay the loan.
Answer : (a) Property such as land titles, deposits with banks, livestock are some common examples of collateral used for borrowing. In case of failure of repayment of loan, the lender can sell the collateral to recover the loan amount.
Question : Assertion : Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves.
Reason : Banks in India these days hold about 15 per cent of their deposits as cash.
Answer : (b) Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves because they use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans as there is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities.
Question : Assertion : The modern currency is used as a medium of exchange; however, it does not have a use of its own.
Reason : Modern currency is easy to carry
Answer : (b) The modern currency is used as a medium of exchange because it is accepted and authorised as a medium of exchange by a country’s government.
Data Based Questions
Question : Prakash is a small farmer and grows groundnuts in his three acres of land. He takes a loan from the moneylender to meet the expenses of cultivation, hoping that his harvest would help repay the loan. But the failure of crops makes loan repayment impossible. He has to sell a portion of his land to repay the loan. Credit, instead of helping Prakash improve his earnings, leaves him worse off.
Identify the situation in which Prakash falls into.
(a) Debt trap
(b) Insolvent
(c) Bankrupt
(d) None of these
Answer : (a) Debt trap
Question : Rahul wants to sell sugar and buy wheat. He has to look for a person who wants sugar and has wheat to sell. In contrast, if in an economy, where money is used, Rahul who wants to sell sugar only has to look for a buyer for his sugar. The money which he will get can be used to purchase the wheat or any other commodity in the market. Since money is used in the exchange process, identify the function of money discussed here.
(a) Store of value
(b) Standard of deferred payment
(c) Medium of exchange
(d) Double coincidence of wants
Answer : (c) Medium of exchange
Question : Anupam takes a loan of ₹ 5 lakh from a bank for his production needs. He utilizes the money efficiently, makes a profit, and repays the loan with interest on time as per the credit terms. Identify the role of credit here.
(a) Negative role, by helping him to increase his income.
(b) Positive role, by helping him to increase his income.
(c) Negative role, by helping him to create liability on him.
(d) None of the above
Answer : (b) Positive role, by helping him to increase his income.
Very Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit
Question : Why one cannot refuse a payment made in rupees in India?
Answer : One cannot refuse a payment made in rupees in India because rupee is officially accepted as medium of exchange. This currency is authorised by the government of the country.
Question : What is debt trap?
Answer : A debt trap is a situation in which a debtor has to take more debts to pay back the previously secured loans and their interest liability.
Question : Befor the introduction of modern coins, what was used as money ?
Answer : Before the introduction of modern coins, a variety of objects like grains and cattle, metals such as gold, silver, copper (coins) were used as money.
Question : What difficulties of barter system has the money removed ?
Answer : Money has removed the difficulty of the double coincidence of wants and lack of a standard method of payment inherent in the barter system.
Question : How is modern currency different from the one used earlier?
Answer : Modern currency is made of paper notes and coins unlike gold, silver or copper coins used earlier.
Question : What is meant by double coincidence of wants?
OR
What do you mean by double coincidence of wants ?
Answer : It refers to a situation in the barter system wherein both parties agree to buy and sell each other's commodities such that what one desires to sell is exactly what the other one wishes to buy.
Question : What are the two benefits of cooperatives ?
Answer : (i) Cooperatives help their members to acquire credit at reasonable terms.
(ii) It save the members from the exploitation of informal sources of credit like moneylenders.
Question : Who supervises the credit activities of informal sources in India ?
Answer : There is no organisation which supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector.
Question : What is the meaning of ‘barter system’?
Answer : The exchange of goods, property, services, etc. for other goods, etc. without using money is known as ‘barter system’.
Question : Why did Salim need credit?
Answer : Salim needed credit to purchase the raw materials for the manufacture of shoes.
Question : Why did Swapna need credit?
Answer : Swapna needed credit to meet the expenses of cultivation.
Question : Give the reason why transactions are made in money.
Answer : A person holding money can easily exchange it for commodity or service that he/she might want.
Question : Why do people in rural areas demand for credit?
Answer : They demand for credit for crop production.
Question : Why did Swapna sell a portion of her land?
Answer : Swapna did this in order to repay the loan.
Question : Name two objects that were used as money before the introduction of coins.
Answer : Grains and cattle.
Question : What are the modern forms of money?
Answer : The modern forms of money include currency – paper notes and coins.
Question : What are the modern forms of money?
Answer : The modern forms of money include currency – paper notes and coins.
Question : What is money?
Answer : is something that can act as a medium of exchange in transactions.
Question : When is crucial for the country’s development?
Answer : Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country is development.
Question : What is necessary to reduce the dependence on informal sources of credit in rural areas?
Answer : It is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending in the rural areas.
Question : What is the chief feature of the modern currency?
Answer : The modern currency is without any use of its own.
Question : Why are deposits in the banks called demand deposits?
Answer : Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Question : Which segment of the society depends on the formal sources?
Answer : The poor have to depend on the formal sources.
Question : Mention one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans.
Answer : Absence of collateral is one of the major reason which prevents the poor from getting bank loans.
Question : What is the major source of revenue for the commercial banks?
Answer : Their major source of revenue is the difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors.
Question : What do banks do with the money we deposit there?
Answer : Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. They use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans.
Question : ho can issue currency in India other than RBI?
Answer : As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency other than RBI.
Question : Why do people deposit money in the bank?
Answer : People deposit their money in the banks because banks pay interest on their deposits. In this way, people's money is safe with the banks and it also earns an amount as interest.
Question : Prove with an argument that there is a great need to expand formal sources of credit in rural India.
Answer : There is a need to expand formal sources of credit in rural India because there is no organisation which supervises the credit activities of the lenders in the informal sector. They
lend at a higher interest rate and use unfair means to get their money back.
Question : Why should cheap and affordable credit be available for everyone?
Answer : Cheap and affordable credit should be available for all so that all individuals can engage themselves in economic activities which in turn will lead to the economic development of the country.
Question : What are demand deposits?
OR
What is demand deposit?
Answer : People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Question : What are the two benefits of banks?
Answer : (i) Banks accepts deposits from people and pay an amount of interest to people for the same.
(ii) Banks only keep some of the cash with themselves and use the rest to give loans to people who need it for different economic activities.
Question : What is money ?
Answer : Money is anything which is generally acceptable as a medium of exchange.
Question : Why do people prefer transactions with money?
Answer : A person having money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she wants.
Question : Why is money called a medium of exchange?
Answer : Money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process that is why it is called a medium of exchange.
Question : Name some transactions in which money is used.
Answer : Paying school fees, buying of books, purchase of petrol, food articles, paying doctors fee etc. are some of the transactions in which money is used.
Question : Why did Swapna sell a portion of her land?
Answer : Swapna did this in order to repay the loan.
Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit
Question : “Most of the poor households still depend on the informal sector for loans, both in rural and urban areas of India”. Support the statement with three examples.
Answer : (i) Banks are not present everywhere in rural India. Even when they are present, getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources.
(ii) Bank loans require proper document and collateral. Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans.
(iii) Informal lenders such as moneylenders, on the other hand, know the borrowers personally and hence are often willing to give a loan without collateral. The borrowers can, if necessary, approach the moneylenders even without repaying their earlier loans.
Question : Which government body supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India? Explain its functioning.
Or
Who supervises the functioning of banks? In what ways is the supervision done?
Answer : (i) The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
(ii) The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
(iii) The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, to small borrowers, etc.
(iv) Periodically banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Question : Mention three limitations of the barter system.
Answer : The three limitations of the barter system are:
(i) Lack of double coincidence of wants. It means, both the parties have to agree to sell and buy each others’ commodities.
(ii) Valuations of all the goods cannot be done easily.
(iii) There are certain products which cannot be divided.
Question : What are the benefits that you can get by depositing your extra money in the banks?
Answer : (i) Safety
(ii) Earn interest
(iii) Can make payments easily through cheques.
Question : In what ways does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of banks? Why is this necessary?
Answer : (i) The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
(ii) The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
(iii) The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, to small borrowers, etc.
(iv) Periodically banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Question : What is the role played by the banks in the economic development of a country?
Answer : The banks play an important role in an economy of a country. They give interest on the money deposited by the people. Thus they add to the income of the family. Many families survive on the bank interest. The banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money. Banks provide cheap loans to a large number of people. They boost the industry also by providing cheap loans to industrialists. Banks are the backbone of the country’s trade. Banks employ a large number of people and as such they solve the problem of unemployment to a great extent.
Question : What is credit? What is its importance?
Answer : Credit refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrowers with money, goods and services in return for the promise of future payments.
Importance of credit
(i) In some situation, credit helps to increase earnings and therefore the person is better off than before.
(ii) We can understand it with an example. Salim obtains credit to meet the working capital needs of production. The credit helps him to meet the ongoing expenses of production, complete production on time and thereby increase his earnings. Thus, credit plays a rival and positive role in this situation.
Question : Look at a 10-rupee note. What is written on top? Can you explain this statement?
Answer : A ten-rupee note has “Reserve Bank of India” written on the top, followed by a statement “Guaranteed by the Central Government”. It is a promissory note and can only be issued by the Reserve Bank of India which supervises all money- related functions in the formal sector in India. The statement on the ten rupee note relates to this idea that the RBI is the central organ in the working of money- related activities.
Question : What according to you can reduce the dependence of the poor households on informal sources of credit? Suggest ways to avert this situation.
Answer : The poor households in rural India is bound to lead a very hard life. The reason is that they don’t have their own land or any property with them. They work as landless labourers in the field of big farmers. Whenever they need money, they seek the help of moneylenders, who charge much higher interest on loans. Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of earning of the borrowers is used to repay the loan and they have less income left for themselves. This dependence of theirs can be reduced only when the following steps will be taken:
(i) Education should be spread in rural areas.
(ii) The government should assist them in improving their condition.
(iii Poor people belonging to rural areas should be made self-sufficient so that they may have a decent life.
Question : Differentiate between formal and informal sources of credit. Explain problems faced by borrowers of loan from informal sources.
Answer :
Question : Which government body supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India? Explain its functioning.
Answer : (i) The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
(ii) The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
(iii) The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, to small borrowers, etc.
(iv) Periodically banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Question : Why is cheap and affordable credit important for the country’s development? Explain three reasons.
Answer : Cheap and affordable credit is important for the country’s development because of the following reasons:
(i) This would lead to higher incomes and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(ii) They could grow crops, do business, set up small scale industries etc.
(iii) They could set up new industries or trade in good. All these lead to the country’s development.
Question : What would the lender do in case the borrower fails to repay the loan?
Or
Why do lender ask for collateral while lending?
Answer : If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to obtain payment.
Question : What are demand deposits? What are their advantages?
Answer : People deposit extra cash with the bank by opening a bank account in their name. Banks accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount of interest. People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Question : Why are transactions made in money? Explain with suitable examples.
Answer : Everyone prefers to receive payments in money and then exchange the money for things they want. For example, take the case of a blacksmith. He wants to sell tools in the market and buy rice. The blacksmith will first exchange tools that he has produced for money and then exchange the money for rice.
The transactions are made in money because a person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she wants.
Question : In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower. Explain.
Answer : At times repayment of the loan becomes difficult and credit instead of improving the earnings, pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very difficult and painful. This situation is called debt-trap. Then the borrower is forced to give up his collateral or asset used as the guarantee to the lender.
Question : Explain any two features each of formal sector loans and informal sector loans.
Answer : Formal Sector Loans
(i) It provides loans at a fixed rates and terms.
(ii) It gives loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries to small borrowers etc.
Informal Sector Loans
(i) Rates of interest are not fixed. Moneylenders can charge whatever interest rate they choose.
(ii) There is no one to stop them from using unfair means to get their money back.
Question : Why is it necessary for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas? Explain.
Answer : Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers. Hence, it is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
While formal sector loans need to expand, it is also necessary that everyone receives these loans. At present, it is the richer households who receive formal credit whereas the poor have to depend on the informal sources. So, it is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that the poor can benefit from the cheaper loans.
Question : Throw light on the various sectors of the economy.
Answer : People obtain loan from various sources. The various types of loans can be grouped as formal sector loans and informal sector loans.
Formal sector: It Includes banks and cooperatives. The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loan. The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance. Similarly, the RBI sees that these banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, to small borrowers etc. Periodically banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending and to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Informal sector: It includes moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends etc. There is no one to supervise their credit activities. It can charge whatever interest rate they choose. There is no one to stop them from using unfair means to get their money back.
Question : How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants? Explain with an example of your own.
Answer : (i) In a barter system, commodities are exchanged with commodities without the use of money. But in this type of exchange, both parties have to agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities. This is called double coincidence of wants.
(ii) Money solves the problem of double coincidence of wants by acting as a medium of exchange. The transactions are made in money because a person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she wants.
(iii) Suppose an ice-cream vendor wants a bicycle but the bicycle manufacturer wants clothes, and not ice-creams. In such a situation the vendor can use money to obtain a bicycle. In the same way, the bicycle manufacturer too will use money to buy clothes.
Question : Analyse the role of credit for development.
Answer : (i) Credit refers to an agreement in which lender supplies the borrowers with money, goods and services in return for the promise of future payments.
(ii) Whether credit will be useful or not, depends upon the risks in the situation and on whether there is some support in case of loss.
(iii) When a borrower takes a loan from the bank for increasing the production of goods and he/she is able to increase it and pay the loan back to the bank within the given time limit, then credit has played a positive role in making him/her wealthy.
Long Questions for Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit
Question : What is the idea behind forming the Self Help Groups or the SHGs? Explain the functioning of the Self Help Group or the SHGs?
Answer : Self-Help Groups consist of certain members who pool their savings and constitute a fund which is further used in making finance and advances to other members. A typical Self-Help Group has 15 to 20 members. The members pool their savings and after some time, it becomes a large amount which is used to give loans to the needy ones at a very nominal rate of interest. This helps to reduce the functioning of informal sectors of credit.
After a year, if such a group is regular in its savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank. Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members. Loans are provided for releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs as buying seeds, fertilisers, raw materials, for acquiring assets like sewing machine, handlooms, cattle, etc. Important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members. The group decides the purpose, amount, interest to be charged, repayment schedule etc. Non-repayment is taken seriously. Because of this feature, banks are willing to lend loan especially to the poor women when organised in SHG.
SHGs are becoming popular for the following reasons:
(i) They help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(ii) They can get timely loans for variety of purposes and at a reasonable interest rate.
(iii) They are building blocks of the organisation of the rural poor.
(iv) It helps women to become self-reliant.
(v) The regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on various social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence etc.
Question : Study the diagram given below and answer the following questions:
(i) Which are the two major sources of credit for rural households in India?
(ii) Which one of them is the most dominant sources of credit for rural households?
(iii) Why is it the most dominant source of credit? Give two reasons.
Answer : (i) Moneylenders and cooperative societies are the two major sources of credit for rural households in India.
(ii) Moneylenders are the most dominant sources of credit for rural households.
(iii) Moneylenders are the most dominant sources of credit for rural households because
(a) Rural households need not to produce certificate of their earning or documents of their employment while borrowing money from the money lenders.
(b) Neither they have to show any property or assets as collateral (security or guarantee)
Question : What is credit? Why is there a need for credit in rural areas?
Answer : Credit refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment. There is a need for credit in rural areas for the following reasons.
(i) In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production.
(ii) crop production involves considerable costs on seeds fertilisers, pesticides, water electricity, repair of equipment, etc.
(iii) Farmers usually takes crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest.
(iv) Rural people also take loans for starting small business and for the marriage of their daughters.
Question : Grameen Bank of Bangladesh has done a great job in the rural areas of the country. Which values according to you is it able to support?
Answer : Grameen Bank of Bangladesh was started in the 1970s as a small project. But soon it achieved grand success in removing poverty from the country. It helps the poor to meet their credit needs at reasonable rates. Almost all of the borrowers are women who belong to poorest sections of the society. These borrowers have proved themselves very reliable. They use the money in a number of income generating activities and thus empower themselves and their families.
The values that Grameen Bank of Bangladesh supports are:
(i) Removal of poverty.
(ii) Women empowerment.
(iii) Self-sufficiency.
Question : “Whether credit would be useful or wet, it depends on the situations”. Give two different examples in support of this statement.
Answer : We can give examples of Salim and Swapna in support of this statement.
(i) Salim is a shoe manufacturer. He obtains credit to meet the working capital needs of production. The credit helps him to meet the ongoing expenses of production, complete production on time and thereby increase his earnings. Credit, plays a vital and positive role in this situation.
(ii) Swapna is a small farmer and grows groundnuts in her three acres of land.
She takes a loan from the moneylender to meet the expenses of cultivation, hoping that her harvest would help repay the loan. But the failure of crops makes loan repayment impossible. She has to sell a portion of her land to repay the loan. Credit, instead of helping Swapna improve her earnings, leaves her worse off. She falls into a debt trap.
Question : In India, about 80 per cent of farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(a) Why might banks be unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b) What are the other sources from which the small farmers can borrow?
(c) Explain with an example how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmer.
(d) Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
Answer : (a) Banks might be unwilling to lend to small farmers because small farmers usually lack proper documents and collateral or asset.
(b) The other sources from which the small farmers can borrow are moneylenders, relatives or friends, self-help groups and cooperative banks.
(c) The terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmer if he has a bad crop, and is forced to either surrender his collateral (if he borrowed from a bank) or sell off a part of his land (if he borrowed from the informal sector), in order to repay his loan.
(d) Self-help groups and cooperative banks do not require collateral as a guarantee; hence, they can provide cheap credit to the small farmers.
Question : How does the use of money make exchange of things easier? Explain with examples.
Answer : (i) Money means wealth around which the whole economic activities of every country move. Money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process and therefore it is called a medium of exchange.
(ii) In our day to day transactions, goods are being bought and sold with the use of money. At times we do exchange services with money.
(iii) Use of money has made things easier to exchange as we can exchange it for any commodity we need.
(iv) The transactions are made in money because a person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she wants.
(v) Thus, the main function of money in an economic system is to facilitate the exchange of goods and services. Without exchange of money nobody can fulfil his all needs and requirements.
Question : What is the role of SHGs? What are the reasons of its growing popularity?
Or
What are Self-Help Groups? Describe, in brief, their functioning.
Answer : Self-Help Groups consist of certain members who pool their savings and constitute a fund which is further used in making finance and advances to other members. A typical Self-Help Group has 15 to 20 members. The members pool their savings and after some time, it becomes a large amount which is used to give loans to the needy ones at a very nominal rate of interest. This helps to reduce the functioning of informal sectors of credit.
After a year, if such a group is regular in its savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank. Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members. Loans are provided for releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs as buying seeds, fertilisers, raw materials, for acquiring assets like sewing machine, handlooms, cattle, etc. Important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members. The group decides the purpose, amount, interest to be charged, repayment schedule etc. Non-repayment is taken seriously. Because of this feature, banks are willing to lend loan especially to the poor women when organised in SHG.
SHGs are becoming popular for the following reasons:
(i) They help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(ii) They can get timely loans for variety of purposes and at a reasonable interest rate.
(iii) They are building blocks of the organisation of the rural poor.
(iv) It helps women to become self-reliant.
(v) The regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on various social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence etc.
Question : Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
Answer : We need to expand the formal sources of credit to increase the income of the weaker sections of the society and stop the exploitation of these people by the usurious practices of informal sources of credit, like moneylenders. These informal sources of credit, like moneylenders, charge a very high rate of interest on the loans provided by them to the weaker sections of the society, like to the small farmers and agricultural labourers in rural areas, and small businessmen, labourers, small artisans etc. in urban areas who are their prime borrowers. This high interest rate leaves such people with lesser incomes. If these weaker people lose this loan amount or any part of it due to any reason, they have to compensate it either by selling their assets or collateral or take new loans to pay back old loans. This puts them in debt trap. The informal sources don't keep proper records which may also become a source of exploitation for weaker sections. Expansion of formal sources of credit like banks and cooperatives are required to be expanded both in rural and urban areas to stop such exploitation of weaker sections and increase their income so that their standard of living may improve.
Question : How can the formal sector loans be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers? Suggest any five measures.
Answer : People obtain loans from various sources:
The various sources of loans are categorised into:
(i) Formal sector loans.
(ii) Informal sector loans.
The formal sector loans are given by banks and cooperatives. Poor people and workers get much of their loans from the informal sector, which is not only exploitative, but also charges a very high interest rate. These make the poor people and workers to fall into the trap of poverty. The informal lenders include moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends etc. The measures to make formal sector loans beneficial for poor farmers and workers are:
(i) The formal sector like banks and cooperatives should lend more to poor people and workers, particularly in rural areas.
(ii) The formal sector should provide cheap and affordable credit.
(ii) The formal sector should ensure that every one has access to loans.
(iv) Providing assistance to Self Help Groups.
(v) There should be more number of cooperatives and banks in rural areas.
Question : What steps do you think are necessary for banks to extend credit facilities to the poor sections of the society ?
Answer : Following steps are necessary for the expansion of credit facilities to the poor sections of the society :
(i) The banking facilities must be expanded to every corner of the country whether urban or rural, so that the banking facilities can cover all the families.
(ii) An awareness campaign must be run continuously so that the poor sections can become aware of the banking facilities.
(iii) Poor sections must be encouraged to open bank accounts and deposit money no matter how small that may be. This will develop a kind of banking habit among them. For this
purpose, a bit higher interest rate may be offered to them.
(vi) Credit facility with softer terms must be designed for the poor sections.
(v) Process of credit must be made simpler for them.
(vi) Banks must provide as much as possible loans to cooperatives and self-help groups.
(vii) RBI must take steps to regularise the practices of informal sector.
Case Study for Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit
Question : Read the extract and answer the questions that follow:
There is an interesting mechanism at work here. Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. For example, banks in India these days hold about15 per cent of their deposits as cash. This is kept as provision to pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money from the bank on any given day. Since, on any particular day, only some of its many depositors come to withdraw cash, the bank is able to manage with this cash. Banks use the ma'or portion of the deposits to extend loans. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. We shall read more about this in the following sections. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people. In this way, banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers). Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits. The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income. A large number of transactions in our day to-day activities involve credit in some form or the other. Credit (loan) refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment.
(i) What do you understand by the term credit?
Answer : Credit (loan) refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment.
(ii) Who will mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers)?
Answer : Bank will mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers).
(iii) What does bank do with the deposits of public?
Answer : Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.
Creating Based Questions for Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit
Question : Fill in the blanks to complete the paragraph.
The money that people can withdraw from a bank as and when they require is termed as ______ deposits. These deposits have the essential characteristic of _____ and as they serve as a _______. People can also use other methods of making payment or withdrawing money from the banks. The payer who has an account with a bank can make a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to another person. This paper is known as a _____.
Answer : The money that people can withdraw from a bank as and when they require is termed as demand deposits. These deposits have the essential characteristic of money and as they serve as a medium of exchange. People can also use other methods of making payment or withdrawing money from the banks. The payer who has an account with a bank can make a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person's account to another person. This paper is known as a cheque.
Question : Fill in the blanks with appropriate information.
In a ______ system, people exchange _____ for goods. This requirement of exchange leads to a problem of ______. ______ resolves such a problem in an economy by serving as an intermediary in an ______ process and so is known as a ______.
Answer : In a barter system, people exchange goods for goods. This requirement of exchange leads to a problem of double coincidence of wants. Money resolves such a problem in an economy by serving as an intermediary in an exchange process and so is known as a medium of exchange.
Question : In Karnataka, Ugadi, beginning of the New Year according to Hindu Lunar calendar, is celebrated at a large scale. It is the time of the year when people heavily shop. It is three months from ugadi, and Rajshekhra, a silk saree manufacturer, has received a large order for sarees from a large seller. However, Rajshekhra does not have the huge amount of money available to carry out the production. Devise a plan for Rajshekhra to resolve the issue.
Answer : Rajshekhra can request his raw material supplier to supply the material to him for which Rajshekhra will make the payment at a later date. Rajshekhra can also demand some advance payment from the saree seller and promise him to deliver the order on requested time. Also, Rajshekhra can borrow a sum from a bank or a cooperative society to carry out manufacturing.
Question : In a small village, farmers are very prosperous as their lands are highly fertile. However, the farmers tend to keep their money at home and the cases of robbery are high in the village. What could be changed to improve the situation of the village?
Answer : The solution to the farmers' problem in this village is the development of a bank. Since the process of development of a bank may take longer, the farmers can come together to form a cooperative banking society in the village to ensure the safety of their money. Farmers can pool their resources which can be used to provide agricultural loans and loans for other activities such as construction of houses. Forming a cooperative bank will not only keep the farmers' funds safe, but also ensure credit availability to farmers when in need.
Question : Credit can push a borrower into a situation from which recovery is very difficult. What information can you infer from this statement?
Answer : Sometimes, the borrowers may not be able to repay the borrowed money due to failure of business. In such cases, they may have to borrow more money to continue with the business activity or to repay the loan. Such a situation is called a debt trap and coming out of the situation can be very difficult for the borrower.
Questions :
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Resources and Development |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Resources and Development in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Water Resources |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Water Resources in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Agriculture |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Agriculture in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Minerals & Energy Resources |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Minerals & Energy Resources in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Manufacturing Industries |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Manufacturing Industries in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Lifelines of National Economy |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Lifelines of National Economy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Power Sharing |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Power Sharing in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Federalism |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Federalism in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Democracy and Diversity in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Democracy and Diversity |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Gender Religion and Caste |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Gender Religion and Caste in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Popular struggles and Movements in hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Popular Struggles and Movements |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Political Parties in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Political Parties |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Outcomes of Democracy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Outcomes of Democracy |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Challenges to Democracy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Challenges to democracy |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs Rise of Nationalism in Europe in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs Nationalism in India in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Nationalism in India |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs The Making of a Global World in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs The Making of a Global World |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs The Age of Industrialization in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs The Age of Industrialization |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs Print Culture and the Modern World in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Print culture and the Modern World |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Development in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Development |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Sectors of the Indian Economy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Sectors of the Indian Economy |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Money and Credit |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Money and Credit in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Globalisation and the Indian Economy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Globalization and the Indian Economy |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Consumer Rights |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Consumer Rights in Hindi |
HOTS for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Social Science Class 10
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to develop the Social Science Class 10 HOTS. If you download HOTS with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Class 10 test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. High Order Thinking Skills questions practice of Social Science and its study material will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. You can easily download and save all HOTS for Class 10 Social Science also from www.studiestoday.com without paying anything in Pdf format. After solving the questions given in the HOTS which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Social Science in the HOTS so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Social Science MCQ Test for the same chapter
You can download the CBSE HOTS for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the HOTS issued by CBSE for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit have been made available here for latest academic session
HOTS stands for "Higher Order Thinking Skills" in Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Class 10 Social Science. It refers to questions that require critical thinking, analysis, and application of knowledge
Regular revision of HOTS given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, HOTS questions are important for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Class 10 Social Science exams as it helps to assess your ability to think critically, apply concepts, and display understanding of the subject.

