Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Assignment Set B. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Biology. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Biology in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Class 12 Biology Assignment
Anticodon : A sequence of three nitrogenous bases on tRNA which is complementary to the codon on mRNA.
Transformation : The phenomenon by which the DNA isolated from one type of a cell, when introduced into another type, is able to express some of the properties of the former into the latter.
Transcription : The process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA into RNA.
Translation : The process of polymerisation of amino-acids to form a polypeptide as dictated by mRNA.
Nucleosome : The structure formed when negatively charged DNA is wrapped around positively charged histone octamer.
DNA Polymorphism : The variations at genetic level, where an inheritable mutation is observed.
Satellite DNA : The repetitive DNA sequences which form a large portion of genome and have high degree of polymorphism but do not code for any proteins.
Operon : A group of genes which control a metabolic pathway.
Exons : The regions of a gene which become part of mRNA and code for different regions of proteins.
Introns : The regions of a gene which are removed during the processing of mRNA.
Euchromatin : The region of chromatin which is loosely packed and transcriptionally active.
Heterochromatin : The chromatin that is more densely packed, stains dark and is transcriptionally inactive.
Capping : Adding of methyl guanosine triphosphate to the 5´ end of hnRNA.
Splicing : The process in eukaryotic genes in which introns are removed and the exons are joined together to form mRNA.
Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. A transcription unit in DNA is defined primarily by three regions in DNA. These regions are
(a) Promoter, regulator and structural gene
(b) Promoter, structural gene and terminator
(c) Promoter, regulator and terminator
(d) Promoter, regulator and operator gene
Answer : B
Question. At which of the following levels, regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes donot occur
(a) Transcription level
(b) Processing level
(c) Transport of ribosomal subunits from nucleus to cytoplasm level
(d) Translation level
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is not a goal of HGP
(a) Identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes
(b) Store this information in database
(c) Restrict the related technologies so that other sector donot benefited with it
(d) Address the ethical, legal and social issues
Answer : C
Question. The human genome project was coordinated by
(a) U.S. department of energy
(b) National institute of health
(c) Sanger centre
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following organism was not used as model organism is human genome project
(a) Arabidopsis
(b) Caenorhabdities elegans
(c) Rice
(d) Hyacinthus orientalis
Answer : D
Question. Regarding to salient features of human genome select out the incorrect one
(a) Human genome contains 3164.7 million nucleotide bases
(b) Human genome contain 30,000 genes
(c) y-chromosome has largest number of genes
(d) 1.4 million locations are associated with SNPs
Answer : C
Question. If an inheritable mutation is observed in a population at high frequency, it is referred as
(a) DNA polyploidy
(b) DNA polymorphism
(c) DNA redundancy
(d) Sequence annotation
Answer : B
Question. Due to high degree of polymorphism, size of VNTR varies in size from
(a) 0.1 - 2 kb
(b) 0.1 - 2000 kb
(c) 0.1 - 20 kb
(d) 0.1 - 200 kb
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Adenine pairs with thymine through two H-bonds.
(b) Adenine pairs with thymine through one H-bond.
(c) Adenine pairs with thymine through three H-bonds.
(d) Adenine does not pair with thymine.
Answer: A
Question. Purines found both in DNA and RNA are
(a) cytosine and thymine
(b) adenine and thymine
(c) adenine and guanine
(d) guanine and cytosine.
Answer: C
Question. The association of histone H1 with a nucleosome indicates that
(a) DNA replication is occurring
(b) the DNA is condensed into a chromatin fibre
(c) the DNA double helix is exposed
(d) transcription is occurring.
Answer: B
Question. In sea urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in this DNA are
(a) G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
(b) G 8.5%, A 50%, T 24.5%
(c) G 34%, A 24.5%, T 24.5%
(d) G 17%, A 16.5%, T 32.5%.
Answer: A
Question. What are the structures called that give an appearance as ‘beads-on-string’ in the chromosomes when viewed under electron microscope?
(a) Genes
(b) Nucleotides
(c) Nucleosomes
(d) Base pairs
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following does not follow the central dogma of molecular biology?
(a) Pea
(b) Mucor
(c) Chlamydomonas
(d) HIV
Answer: D
Question. The 3′ - 5′ phosphodiester linkages inside a polynucleotide chain serve to join
(a) one DNA strand with the other DNA strand
(b) one nucleoside with another nucleoside
(c) one nucleotide with another nucleotide
(d) one nitrogenous base with pentose sugar.
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following statements about the particular entity is true ?
(a) Centromere is found in animal cells, which produces aster during cell division.
(b) The gene for producing insulin is present in every body cell.
(c) Nucleosome is formed of nucleotides.
(d) DNA consists of core of eight histones.
Answer: B
Question. In the DNA molecule,
(a) the proportion of adenine in relation to thymine varies with the organism
(b) there are two strands which run antiparallel- one in 5′ → 3′ direction and other in 3′ → 5′
(c) the total amount of purine nucleotides and pyrimidine nucleotides is not always equal
(d) there are two strands which run parallel in the 5′ → 3′ direction.
Answer: B
Question. Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it?
(a) Guanine, Adenine - Purines
(b) Adenine, Thymine - Purines
(c) Thymine, Uracil - Pyrimidines
(d) Uracil, Cytosine - Pyrimidines
Answer: B
Question. One turn of the helix in a B-form DNA is approximately
(a) 2 nm
(b) 20 nm
(c) 0.34 nm
(d) 3.4 nm.
Answer: D
Question. Antiparallel strands of a DNA molecule means that
(a) one strand turns clockwise
(b) one strand turns anti-clockwise
(c) the phosphate groups of two DNA strands, at their ends, share the same position
(d) the phosphate groups at the start of two DNA strands are in opposite position (pole).
Answer: D
Question. Which one of the following makes use of RNA template to synthesise DNA?
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) RNA polymerase
(c) Reverse transcriptase
(d) DNA dependant RNA polymerase
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following hydrolyses internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain?
(a) Lipase
(b) Protease
(c) Endonuclease
(d) Exonuclease
Answer: C
Question. The following ratio is generally constant for a given species:
(a) A + G / C + T
(b) T + C / G + A
(c) G + C / A + T
(d) A + C / T + G.
Answer: C
Question. In a DNA percentage of thymine is 20% then what will be percentage of guanine?
(a) 20%
(b) 40%
(c) 30%
(d) 60%
Answer: C
Question. Length of one loop of B-DNA
(a) 3.4 nm
(b) 0.34 nm
(c) 20 nm
(d) 10 nm.
Answer: A
Question. DNA is mainly found in
(a) nucleolus
(b) nucleus only
(c) cytoplasm only
(d) none of these.
Answer: B
Question. In prokaryotes, the genetic material is
(a) linear DNA without histones
(b) circular DNA without histones
(c) linear DNA with histones
(d) circular DNA with histones.
Answer: B
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Calculate the length of the DNA of bacteriophage lambda that has 48502 base pairs.
Answer. Distance between two consecutive base pairs = 0.34 × 10–9 m
The length of DNA in bacteriophage lambda = 48502 × 0.34 × 10–9 m
= 16.49 × 10–6 m
Question. Write the function of RNA polymerase II.
Answer. RNA polymerase II transcribes precursor of mRNA or hnRNA.
Question. Mention the carbon positions to which the nitrogen-s base and the phosphate molecule are respectively linked in the nucleotide given below:
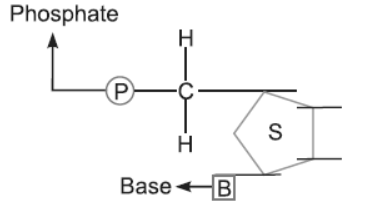
Answer. Nitrogenus base is linked to first carbon.
Phosphate is linked to fifth carbon.
Question. How is repetitive/satellite DNA separated from bulk genomic DNA for vari-s genetic experiments?
Answer. By density gradient centrifugation.
Question. State which human chromosome has
(i) the maximum number of genes and
(ii) the one which has the least number of genes?
Answer. (i) Chromosome-1
(ii) Y-Chromosome
Question. Given below is a schematic representation of a lac operon in the absence of an inducer. Identify ‘a’ and ‘b’ in it.
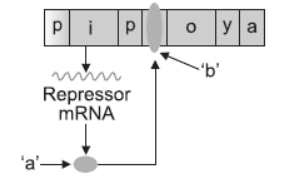
Answer. a–Repressor
b–Repressor b-nd to the operator and prevents transcription of structural genes.
Question. Mention the contribution of genetic maps in human genome project.
Answer. Genetic maps have played an important role in se-encing of genes, DNA fingerprinting, tracing human history, chromosomal location for disease associated se-ences (Any one).
Question. What are ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the nucleotide with purine represented below?
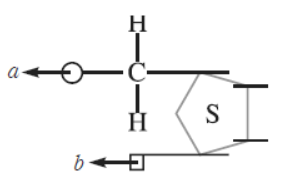
Answer. ‘a’ is phosphate gr-p and ‘b’ is purine (adenine/guanine).
Question. Name the negatively charged and positively charged components of a nucleosome.
Answer. In a nucleosome, the negatively charged component is DNA and positively charged component is histone octamer.
Question. Why is lactose considered an inducer in lac operon?
Answer. Lactose binds to repressor and prevents it from binding with the operator, as a result RNA polymerase binds to promoter–operator region to transcribe the structural genes.
Question. Mention the two additional processing which hnRNA needs to undergo after splicing so as to become functional.
Answer. Capping and tailing.
Question. At which ends do ‘capping’ and ‘tailing’ of hnRNA occur, respectively?
Answer. Capping occurs at 5′-end and tailing occurs at 3′-end.
Question. In a nucleus, the number of RNA nucleoside triphosphates is 10 times more than the number of DNA nucleoside triphosphates, still only DNA nucleotides are added during the DNA replication, and not the RNA nucleotides. Why?
Answer. DNA polymerase is highly specific to recognise only deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates.
Therefore it cannot hold RNA nucleotides.
Question. What is cistron?
Answer. A cistron is a segment of DNA coding for a polypeptide.
Short Answer Questions
Question. A DNA segment has a total of 2,000 nucleotides, -t of which 520 are adenine containing nucleotides. How many purine bases this DNA segment possesses?
Answer. [A] = [T]
A + T = 520 + 520
= 1040
Total number of nucleotides = 2000
∴ G + C = 2000 – 1040
= 960
G = 960/2
= 480
∴ Total number of purines (A + G) = 520 + 480
= 1000.
Question. Following are the features of genetic codes. What does each one indicate?
Stop codon; Unambiguous codon; Degenerate codon; Universal codon.
Answer. Stop codon does not code for any amino acid and terminates the synthesis of polypeptide chain.
Unambiguous codon: one codon codes for one amino acid only.
Degenerate codon: some amino acid are coded by more than one codon.
Universal codon: Genetic code is same for all organisms (bacteria to humans).
Question. Discuss the role of enzyme DNA ligase plays during DNA replication.
Answer. DNA ligase joins or seals the discontinuous DNA fragments.
Question. Mention the role of ribosomes in peptide bond formation. How does ATP facilitate it?
Answer. There are two sites in the large subunit of the ribosome, for subsequent amino acids to bind to and thus, be close enough to each other for the formation of a peptide bond. The ribosome also acts as a catalyst for the formation of peptide bond 23S rRNA in bacteria is a ribozyme. Amino acids become activated by binding with its tRNA in the presence of aminoacyl tRNA synthetase and ATP.
Question. Describe the structure of a nucleosome.
Answer. Packaging of DNA in eukaryotes
- Roger Kornberg (1974) reported that chromosome is made up of DNA and protein.
- Later, Beadle and Tatum reported that chromatin fibres look like beads on the string, where beads are repeated units of proteins.
- The proteins associated with DNA are of two types— basic proteins (histones) and acidic non-histone chromosomal (NHC) proteins.
- The negatively charged DNA molecule wraps ar-nd the positively charged histone proteins to form a structure called nucleosome.
- The nucleosome core is made up of f-r types of histone proteins—H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 occurring in pairs.
- 200 bp of DNA helix wrap ar-nd the nucleosome by 1¾ turns, plugged by H1 histone protein.
- Repeating units of nucleosomes form the chromatin in nucleus, which is a thread-like structure.
- The chromatin is packed to form a solenoid structure of 30 nm diametre.
- Further supercoiling forms a looped structure called the chromatin fibre.
- These chromatin fibres further coil and condense at metaphase stage of cell division to form chromosomes. Packaging of chromatin at higher level re-ires NHC proteins.
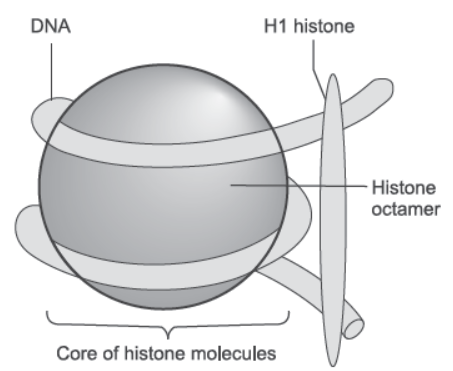
Question. Draw a schematic diagram of a part of d-ble stranded dinucleotide DNA chain having all the f-r nitrogen-s bases and showing the correct polarity.
Answer. 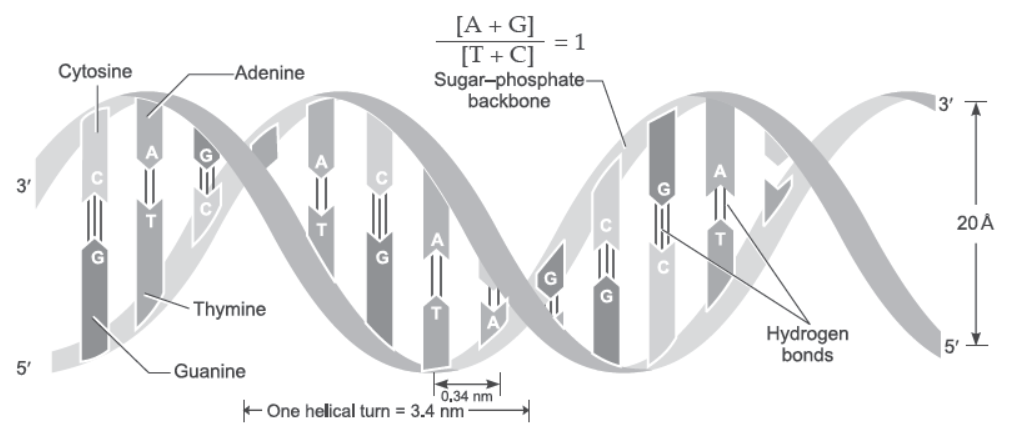
Question. Alth-gh a prokaryotic cell has no defined nucleus, yet DNA is not scattered thr-gh-t the cell. Explain.
Answer. DNA is negatively charged and has positively charged histone proteins. These help DNA to be held in a place in large loops called nucleoid.
Question. Draw the structure of a tRNA charged with methionine.
Answer.
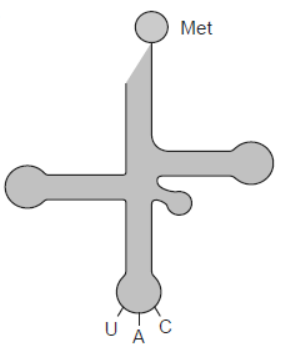
Question. Explain the role of 35S and 32P in the experiments conducted by Hershey and Chase.
Answer. Viruses grown in the medium containing 32P contained radioactive DNA but not radioactive protein because DNA contains phosphorus but proteins do not contain phosphorus. Similarly,viruses grown on radioactive sulphur contained radioactive protein but not radioactive DNA because DNA does not contain sulphur.
Question. Recall the experiment done by Frederick Griffith, Avery, Macleod annd McCarty, where DNA was speculated to be the genetic material. If RNA, instead of DNA was the genetic material,w-ld the heat killed strain of Streptococcus have transformed the R-strain into virulent strain? Explain y-r answer.
Answer. RNA is more labile and prone to degradation (owing to the presence of 2′–OH gr-p in its ribose).
Hence heat-killed S-strain may not have retained its ability to transform the R-strain.
Question. How do histones ac-ire positive charge?
Answer. Histones are rich in the basic amino acid residues lysines and arginines, which carry positive charges in their side chains. Therefore, histones are positively charged.
Question. How are the structural genes inactivated in lac operon in E. coli? Explain.
Answer. The regulator gene produces repressor which when free, binds to the operator region of the operon and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes.
Question. Draw a labelled schematic diagram of a transcription unit.
Answer.
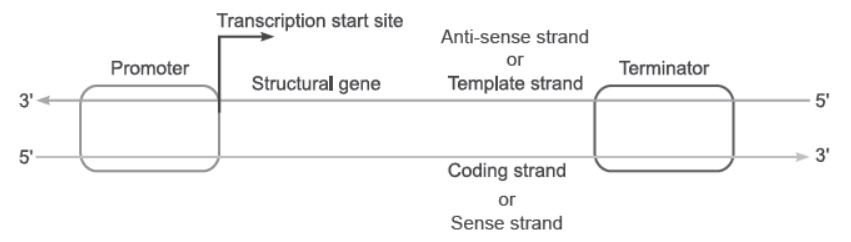
Question. How are the structural genes activated in the lac operon in E. coli?
Answer. Lactose acts as the inducer that binds with repressor protein that cannot bind to operator and hence frees the operator gene. RNA polymerase freely moves over the structural genes, transcribing lac mRNA, which in turn produces the enzymes responsible for the digestion of lactose.
Question. State the difference between the structural genes in a transcription unit of prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Answer. Differences between structural genes of prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
(i) Polycistronic Monocistronic
(ii) No split genes present. The coding sequence Split genes present. The coding sequence is
is not interrupted. interrupted to form exon and intron.
Question. (i) Name the scientist who suggested that the genetic code should be made of a combination of three nucleotides.
(ii) Explain the basis on which he arrived at this conclusion.
Answer. (i) George Gamow.
(ii) He proposed that there are four bases and 20 amino acids So, there should be atleast 20 different genetic codes for these 20 amino acids.
The only possible combinations that would meet the requirement is combinations of 3 bases that will give 64 codons.
Question. Protein synthesis machinery revolves ar-nd RNA but in the c-rse of evolution it was replaced by DNA. Justify.
Answer. Since RNA was unstable and prone to mutations, DNA evolved from RNA with chemical modifications that makes it more stable.
DNA has d-ble stranded nature and has complementary strands. These further resist changes by evolving a process of repair.
Question. Explain the two factors responsible for conferring stability to double helix structure of DNA.
Answer. Factors responsible for conferring stability to double helix structure are presence of hydrogenbonds, the plane of one base pair stacks over the other, complementary presence of thymine in place of uracil.
(B) (C)
Question. (a) (A) — DNA → mRNA → Protein
Look at the above se-ence and mention the events (A), (B) and (C).
(b) What does Central Dogma state in Molecular Biology? How does it differ in some viruses?
Answer. (a) A—DNA replication, B—Transcription, C—Translation
(b) Central Dogma in Molecular Biology states that information flows in the order
DNA → RNA → Proteins
It differs in some viruses as the flow of information is in reverse direction, that is, from DNA to RNA.
Question. Retrovirus do not follow central dogma. Comment.
Answer. Genetic material of retrovirus is RNA. At the time of synthesis of protein, RNA is reverse transcribed to its complementary DNA first, then transcriped to RNA and proteins. Hence,retrovirus are not known to follow central dogma.
Question. What are satellite DNA in a genome? Explain their role in DNA fingerprinting.
OR
Explain the significance of satellite DNA in DNA fingerprinting technique.
Answer. A small stretch of DNA sequence that repeats many a time, shows a high degree of polymorphism and forms a bulk of DNA in a genome called satellite DNA.
(i) They do not code for any proteins.
(ii) They form large part of the human genome.
(iii) They show high degree of polymorphism and are specific to each individual.
Question.
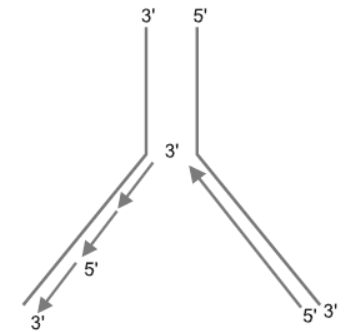
Why do you see two different types of replicating strands in the given DNA replication fork?
Explain. Name these strands.
Answer. The DNA-dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerisation only in one direction i.e., 5′→3′.
Therefore, in one strand with polarity 3′→5′ continuous replication takes place whereas the other strand with polarity 5′→3′ carries out discontinuous replication.
The strand with polarity 3′→5′ is called leading strand and the strand with polarity 5′→3′ is called lagging strand.
Question. (a) List the two methodologies which were involved in human genome project. Mention how they were used.
(b) Expand ‘YAC’ and mention what was it used for.
Answer. The two methodologies involved in human genome project are:
(a) (i) Expressed Sequence Tags: Identifying all the genes that are expressed as RNA
(ii) Sequence Annotation: Sequencing the whole set of genome coding or non coding sequences and later assigning different region with functions.
(b) ‘YAC’ stands for Yeast Artificial Chromosome. It is used as a cloning vectors.
Question. Name indicating their functions, a few additional enzymes, other than DNA polymerase and ligase, that are involved in the replication of DNA with high degree of processivity and accuracy.
Answer. (i) Helicase: opens the helix
(ii) Topoisomerases: removes the supercoiling of DNA relieves the tension due to unwinding
(iii) Primase: synthesises RNA primer
(iv) Telomerase: to synthesises the DNA of telomeric end of chromosomes.
Question. State the dual role of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates during DNA replication.
OR
Write the dual purpose served by Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in polymerisation.
Answer. (i) Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates act as substrates for polymerisation.
(ii) These provide energy from its two terminal phosphates for polymerisation reaction.
Question. A template strand is given below. Write down the corresponding coding strand and the mRNA strand that can be formed, along with their polarity.
3′ ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC 5′
Answer. Coding strand: 5′ TACGTACGTACGTACGTACGTACG 3′
mRNA strand: 5′ UACGUACGUACGUACGUACGUACG 3′
Question. The base se-ence of one strand of DNA is TACTAGGAT.
(i) Write the base se-ence of the RNA got after transcription of the given se-ence.
(ii) What is the distance maintained between the two consecutive pairs of bases in the DNA molecule?
(iii) Who contributed the base complementary rule?
Answer. (i) AUGAUCCUA.
(ii) 3.4 Å or 0.34 nm.
(iii) Chargaff contributed the base complementary rule.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproductive Health Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproductive Health Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health and Disease Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health and Disease Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Microbes in Human Welfare Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Microbes in Human Welfare Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and its Applications Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and its Applications Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity and Conservation Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity and Conservation Assignment Set B |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 12 Assignments for chapter Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Biology mock tests for Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Biology Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Class 12 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 5 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Class 12 Biology

