Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Biology. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Biology in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 12 Ecosystem in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology Assignment
Startification : Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in an ecosystem.
Primary Production : Amount of biomas or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis.
Productivity : Rate of biomass production. Its unit is g/m2/year. Gross Primary Productivity : Rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. Net
Primary Productivity : Gross primary productivity minus the respiration losses.
Ecosystem : Relationship between living organisms and their abiotic surroundings.
Secondary Productivity : Rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Detritus : Dead leaves, twigs, animal remains etc. constitute detritus.
Detrivore : Organisms who break down detritus into smaller particles. e.g., earthworm.
Ecological succession : The successive and orderly replacement of one community by the other community in an area, over a period of time.
Ecological Pyramids : The sequential graphic representation of an ecological parameter (number/ biomass/energy) depicting different trophic levels in a food chain.
Climax community : The stable and final biotic community that develops at the end of ecological succession and is in perfect harmony with its physical environment.
Question. Amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants is represented or expressed in terms of :-
(a) Weight (g-2) - g-2 yr-1
(b) Energy (Kcal m-2) - Kcal m-2 / yr-1
(c) Fresh weight
(d) Dry weight
Answer : D
Question. In an aquatic ecosystem which type of food chain is major conduit for energy flow is
(a) GFC
(b) Parasitic food chain
(c) DFC
(d) Both 1 and 3
Answer : A
Question. The gradual and fairy predictable changes in the species composition of a given area is not characterised by :-
(a) Increase in number of species
(b) Increase in number of individuals of species
(c) Increase in biomass
(d) Decrease in niche specialisation
Answer : D
Question. About succession, which of the following statement is correct :-
(a) In xerosere, xeric conditions progress to hydric conditions
(b) In hydrosere, mesic environment progress to hydric conditions
(c) In hydrosere, hydric environment progress to mesic conditions
(d) Abandoned farm lands show primary succession
Answer : C
Question. During decomposition, humification leads to accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance called humus. Which of the following is correct regarding humus ?
(a) Susceptible to microbial action
(b) Undergoes decomposition at an extremely high rate
(c) Colloidal in nature
(d) It promote compaction of soil
Answer : C
Question. About flow of food energy by the process of eating and being eaten, which of the following is incorrect
(a) In an aquatic ecosystem, GFC is major conduit for energy flow
(b) In terrestrial ecosystem, DFC major conduit for energy flow
(c) In predator food chain there is increase in size of organism with trophic level
(d) DFC can never be connected with GFC
Answer : D
Question. Mass of the living material at a particular time called as the standing crop. Biomass of a species is expressed in terms of ............. is more accurate
(a) Fresh weight
(b) Dry weight
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Kcal m-2/yr-1
Answer : B
Ques. Which one of the following processes during decomposition is correctly described?
(a) Catabolism – Last step in the decomposition under fully anaerobic condition
(b) Leaching – Water soluble inorganic nutrients rise to the top layers of soil
(c) Fragmentation – Carried out by organisms such as earthworm
(d) Humification – Leads to the accumulation of a dark coloured substance humus which undergoes microbial action at a very fast rate.
Answer: C
Ques. The breakdown of detritus into smaller particles by earthworm is a process called
(a) humification
(b) fragmentation
(c) mineralisation
(d) catabolism.
Answer: B
Ques. The slow rate of decomposition of fallen logs in nature is due to their
(a) anaerobic environment around them
(b) low cellulose content
(c) low moisture content
(d) poor nitrogen content.
Answer: D
Ques. Plant decomposers are
(a) monera and fungi
(b) fungi and plants
(c) protista and animalia
(d) animalia and monera.
Answer: A
Ques. Which of the following acts as “nature’s scavengers”?
(a) Insects
(b) Microorganisms
(c) Man
(d) Animals
Answer: B
Ques. If we completely remove the decomposers from an ecosystem, its functioning will be adversely affected, because
(a) mineral movement will be blocked
(b) the rate of decomposition will be very high
(c) energy flow will be blocked
(d) herbivores will not receive solar energy.
Answer: A
Ques. The primary producers of the deep-sea hydrothermal vent ecosystem are
(a) green algae
(b) chemosynthetic bacteria
(c) blue-green algae
(d) coral reefs.
Answer: B
Ques. Most animals that live in deep oceanic waters are
(a) tertiary consumers
(b) detritivores
(c) primary consumers
(d) secondary consumers.
Answer: B
Ques. If 20 J of energy is trapped at producer level, then how much energy will be available to peacock as food in the following chain?
Plant → Mice → Snake → Peacock
(a) 0.02 J
(b) 0.002 J
(c) 0.2 J
(d) 0.0002 J
Answer: A
Ques. Which of the following is a primary consumer in maize field ecosystem?
(a) Grasshopper
(b) Wolf
(c) Phytoplankton
(d) Lion
Answer: A
Ques. When man eats fish which feeds on zooplanktons which have eaten small plants, the producer in this chain is
(a) small plants
(b) fish
(c) man
(d) zooplankton.
Answer: A
Ques. Identify the possible link “A” in the following food chain.
Plant → Insect → Frog → “A” → Eagle
(a) Rabbit
(b) Wolf
(c) Cobra
(d) Parrot
Answer: C
Ques. Of the total incident solar radiation the proportion of PAR is
(a) about 70%
(b) about 60%
(c) less than 50%
(d) more than 80%.
Answer: C
Ques. Which one of the following animals may occupy more than one trophic levels in the same ecosystem at the same time?
(a) Sparrow
(b) Lion
(c) Goat
(d) Frog
Answer: A
Ques. Which one of the following types of organisms occupy more than one trophic level in a pond ecosystem?
(a) Fish
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Frog
(d) Phytoplankton
Answer: A
Ques. Consider the following statements concerning foodchains.
A. Removal of 80% tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation.
B. Removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deers.
C. The length of food chains is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to energy loss.
D. The length of food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels.
Which two of the above statements are correct?
(a) A, D (b) A, B
(c) B, C (d) C, D
Answer: C
Ques. Bamboo plant is growing in a fir forest then what will be the trophic level of it?
(a) First trophic level (T1)
(b) Second trophic level (T2)
(c) Third trophic level (T3)
(d) Fourth trophic level (T4)
Answer: A
Ques. Which is the reason for highest biomass in aquatic ecosystem?
(a) Nano plankton, blue green algae and green algae
(b) Sea grass and slime moulds
(c) Benthic and brown algae
(d) Diatoms
Answer: C
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Why green plants are not found beyond a certain depth in the ocean?
Answer. Beyond a certain depth in the ocean, sunlight is not able to penetrate. Due to which green plants cannot photosynthesise and thus, do not survive.
Question. Why is an earthworm called a detritivore?
Answer. This is because earthworm breaks down detritus into smaller particles.
Question. “Man can be a primary as well as a secondary consumer.” Justify this statement.
Answer. Man has a varied diet. When on vegetarian diet, they are primary consumers and when on nonvegetarian diet, they are secondary consumers.
Question. Define mineralisation.
Answer. It is the process in which the humus is degraded by certain microbes and thus inorganic nutrients are released in the soil.
Question. Mention the role of pioneer species in primary succession on rocks.
Answer. The pioneer species invade a bare area and pave way for other species.
Question. Under what conditions would a particular stage in the process of succession revert back to an earlier stage?
Answer. Natural or human induced disturbances like fire, deforestation, etc.
Question. What is detritus?
Answer. Dead organic matter or remains of plant such as leaves, bark, flower and dead remain of animals, including faecal matter constitute detritus.
Question. Name the pioneer species:
(i) on a bare rock
(ii) in a water body
Answer. (i) Lichens
(ii) Phytoplanktons
Question. State what does ‘standing crop’ of a trophic level represent.
Answer. Standing crop represents the mass of living material (biomass) at a particular time.
Question. List any two ways of measuring the standing crop of a trophic level.
Answer. Standing crop is measured as the biomass or the number of plant in a unit area.
Question. Write a difference between net primary productivity and gross productivity.
Answer. Gross productivity (GPP) is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis.
Net primary productivity (NPP) is the available biomass for the consumption by heterotrophs.
GPP − R = NPP
Question. How is ‘stratification’ represented in a forest ecosystem?
Answer. Stratification in the vertical distribution of species at different levels. Trees occupy top vertical strata, shrubs the second layer and herbs/ grasses occupy the bottom layers.
Question.Name the basic requirement of any ecosystem to function and sustain properly.
Answer. A constant input of solar energy is the ultimate source of all energy and requirement of any ecosystem to function and sustain properly.
Question. What is detritus?
Answer. Dead organic matter or remains of plant such as leaves, bark, flower and dead remain of animals, including faecal matter constitute detritus.
Question. What is net primary productivity?
Answer. The amount of energy or biomass remaining in a producer after meeting the cost of its respiration and is passed on to next trophic level is called the net primary productivity.
Question. Why is the rate of assimilation of energy at the herbivore level called secondary productivity?
Answer. It is because the biomass available to the consumer for consumption is a resultant of the primary productivity from plants.
Short Answer Questions
Question. What would happen to the successive trophic levels in the pyramid of energy, if the rate of reproduction of phytoplanktons was slowed down? Suggest two factors which could cause such a reduction in phytoplankton reproduction.
Answer. If the rate of reproduction of phytoplanktons slows down then the net primary productivity decrease. As a result, flow of energy will also decrease in the successive trophic level.
The following two factors cause reduction in phytoplankton reproduction:
(i) Less water availability
(ii) Less nutrient availability.
Question. What are the shortcomings of ecological pyramids in the study of ecosystem?
Answer. The ecological pyramid assumes a simple food chain and does not accommodate food webs.
Thereby, it does not take into account the fact that species may belong to two or more trophic levels at a time. Also saprophytes despite their vital role in ecosystem are given no place in the ecological pyramids.
Question. How does primary succession start in water and lead to the climax community? Explain.
Answer. Primary succession in water
• The pioneer species are phytoplanktons.
• The phytoplanktons are replaced by free-floating angiosperms.
Question. What could be the reason for the faster rate of decomposition in the tropics?
Answer. The rate of decomposition is regulated by climatic factors like temperature and soil moisture as they have an effect on the activities of soil microbes. The tropics with its hot and humid climatic condition provides an environment which is ideal for the microbes to speed up the process of decomposition.
Question. Name the pioneer and the climax species in a water body. Mention the changes observed in the biomass and the biodiversity of the successive seral communities developing in the water body.
Answer. Pioneer species — Phytoplanktons
Climax species — Forest or trees
Biomass will be gradually increased and phytoplanktons are replaced by free-floating angiosperms then by rooted hydrophytes followed by different seral communities thus, biodiversity also increases.
Question. Define decomposition and describe the process and products of decomposition.
Answer. Steps in Decomposition
(i) Fragmentation: The process of breaking down of detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, e.g., as done by earthworm (= farmer’s friend).
(ii) Leaching: The process by which water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts is called leaching.
(iii) Catabolism: The enzymatic process by which bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus to simpler inorganic substances is called catabolism.
Decomposition produces a dark coloured nutrient rich substance called humus which on degradation releases CO2, water and other nutrients in the soil.
Question. Explain the function of ‘reservoir’ in a nutrient cycle. List the two types of nutrient cycles in nature.
Answer. The function of the reservoir is to meet the deficit of nutrients which occurs due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux.
The two types of nutrient cycles are:
(i) Gaseous, and (ii) Sedimentary
Question. Differentiate between a detritivore and a decomposer giving an example of each.
Answer. Differences between detritivore and decomposer
| Detritivore | Decomposer |
| They are organisms which feed on detritus and break them into smaller particles, e.g., earthworm. | They are organisms which by secreting enzymes break down complex organic matter into inorganic substances, e.g., some bacteria and fungi. |
Question. Apart from plants and animals, microbes form a permanent biotic component in an ecosystem.
While plants have been referred to as autotrophs and animals as heterotrophs, what are microbes referred to as? How do these microbes fulfil their energy requirements?
Answer. Microbes are referred to as heterotrophs and saprotrophs. They fulfil their energy requirement by feeding on dead remains of plants and animals through the process of decomposition.
Question. Construct a grazing food chain and detritus food chain using the following, with 5 links each:
Earthworm, bird, snake, vulture, grass, grasshopper, frog, decaying plant matter.
Answer. Grazing food chain:
Grass→ Grasshopper→ Frog→ Snake→ Vulture
OR
Grass→ Grasshopper→ Bird→ Snake→ Vulture
Detritus food chain:
Decaying plant matter→ Earthworm→ Bird→ Snake→ Vulture
Question. “It is possible that a species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.” Explain with the help of one example.
Answer. For example, sparrow is an omnivore. When it eats seeds, fruits or any other plant products, it occupies the primary trophic level. Whereas, when it eats worms and any other insect, it occupies the secondary trophic level. Thus, it occupies more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem.
Question.Justify the importance of decomposers in an ecosystem.
Answer. Decomposers which are heterotrophic organisms, mainly fungi and bacteria, break down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water and nutrients. They meet their energy and nutrient requirements by degrading dead organic matter or detritus. These are also known as saprotrophs. Decomposers secrete digestive enzymes that breakdown dead and waste materials into simple, inorganic materials, which are subsequently absorbed by them.
Question. What would happen to the successive trophic levels in the pyramid of energy, if the rate of reproduction of phytoplanktons was slowed down? Suggest two factors which could cause such a reduction in phytoplankton reproduction.
Answer. If the rate of reproduction of phytoplanktons slows down then the net primary productivity decrease. As a result, flow of energy will also decrease in the successive trophic level.
The following two factors cause reduction in phytoplankton reproduction:
(i) Less water availability
(ii) Less nutrient availability.
Long Answer Questions
Question. What are the limitations of ecological pyramids?
Answer. Limitations of ecological pyramids:
(i) It never takes into account the same species belonging to
(ii) It assumes a simple food chain, which never exists in nature. It does not accommodate a food web.
(iii) In spite of the vital role played by saprophytes/decomposers, they are not given any position in ecological pyramids.
Question. Describe the components of an ecosystem.
Answer. An ecosystem consists of two types of components, i.e., biotic or living and abiotic or non-living.
There are three main types of biotic components on the basis of mode of obtaining their food—producers, consumers and decomposers.
(i) Producers (autotrophs): They are photosynthetic or autotrophic plants that synthesise their own organic food from inorganic raw materials with the help of solar radiations. Common producers are algae, plants and photosynthetic bacteria. Phytoplanktons are the producers of aquatic ecosystems.
(ii) Consumers (heterotrophs): They are animals which feed on other organisms or producers for obtaining their nourishment. Common consumers are deer, goat, etc.
(iii) Decomposers: They are saprotrophs which obtain nourishment from organic remains. They release digestive enzymes to digest the organic matter. Common decomposers are detritivores, e.g., earthworm. Abiotic component of ecosystem consists of non-living substances and factors which are as follows:
(a) Temperature (b) Light
(c) Wind (d) Humidity
(e) Precipitation (f) Water, etc.
Question. Define ecological succession. Give three differences between seral stages and climax community during succession.
Answer. The sequential, gradual and predictable changes in the species composition in an area are called succession or ecological succession.
Table 14.13: Differences between seral stages and climax community
Question. (a) Name the type of detritus that decomposes faster. List any two factors that enhance the rate of decomposition.
(b) Write the different steps taken in humification and mineralisation during the process of decomposition.
Answer. (a) O Detritus rich in nitrogen decomposes faster. These are water-soluble substances like sugar.
O Factors enhancing rate of decomposition: Warm temperature, moist environment, availability of oxygen.
(b) Humification: Accumulation of dark coloured amorphous substance called humus which is resistant to micorbial action and undergoes decomposition at a very slow rate.
Mineralisation: Humus is further degraded by microbes releasing inorganic nutrients.
Question. (a) Colonisation of a rocky terrain is a natural process. Mention the group of organisms which invade this area first. Give an example.
(b) Over the years, it has been observed that some of the lakes are disappearing due to urbanisation. In absence of human interference, depict by making a flow chart, how do the successional series progress from hydric to mesic condition.
(c) Identify the climax community of hydrarch and xerarch succession.
Answer. (a) Pioneer species invade the area first. For example, lichen
(b) Phytoplankton – (hydr→ic) Submerged plant stage → Submerged free floating plant stage → Reed swamp stage → Marsh – meadow stage → Scrub stage → Forest stage (Mesic condition)
(c) Forest is the climax community for both successions.
Question. (a) With suitable examples, explain the energy flow through different trophic levels. What does each bar in this pyramid represent?
(b) Write any two limitations of ecological pyramids.
Answer. (a) In an ideal energy pyramid, the primary producers use only 1% of the energy in the sunlight available to them. The subsequent trophic levels pass on 10% of the energy received from previous trophic level to the next trophic level.
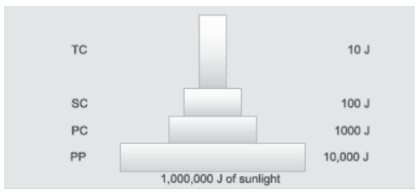
Each bar or level in the pyramid represents the amount of energy transferred to the next trophic level.
(b) (i) It does not take into account the same species belonging to two trophic levels.
(ii) It assumes simple food chain and not food web.
(iii) Saprophytes are not considered. (Any two)
Question. (a) Describe primary succession that occurs on bare rock.
(b) Differentiate between xerarch and hydrarch successions.
Answer. (a) Refer to Basic Concepts Poiiin). 14
(b) (i) Hydrarch succession: The plant succession which takes place in wet area or water, leading to successional series, progress from hydric to the mesic conditions.
(ii) Xerarch succession: The plant succession which takes place in a dry area, leading to successional series from xeric to mesic conditions.
Question. (a) Draw a simplified model of phosphorus cycling in a terrestrial ecosystem.
(b) Write the importance of such cycles in ecosystems.
Answer. (a)
(b) Such cycles recycle nutrients again and again and maintain the balance in ecosystem.
Question. Describe the process of decomposition of detritus under the following heads: Fragmentation; leaching; catabolism; humification and mineralisation.
Answer. The process of breaking down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like—, water
and nutrients is called decomposition. The raw material for decomposition is called detritus.
They are dead remains of plants and animals.
Steps in decomposition:
(a) Fragmentation: The process of breaking down of detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, e.g., as done by earthworm.
(b) Leaching: The process by which water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
(c) Catabolism: The enzymatic process by which degraded detritus is converted into simple inorganic substances is called catabolism.
(d) Humification: The process of accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance called humus, that is, highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate.
(e) Mineralisation: The process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes and release inorganic nutrients is called mineralisation.
Question. (a) What is meant by ecological succession? Explain how it occurs.
(b) What properties distinguish a pioneer community from a climax community?
Answer. (a)
- The sequential, gradual and predictable changes in the species composition in an area are called succession or ecological succession.
- It mainly focuses on changes in vegetation that in turn affect types of animals.
- The entire sequence of communities that successively changes in a given area are called sere(s).
- The individual transitional communities are termed as seral stages or seral communities.
- The community that is in near equilibrium with the environment is called a climax community.
- The species that invade a bare area are called pioneer species.
- The changes that occur in successive seral stages to reach a climax community are:
(i) changes in the diversity of species of organisms.
(ii) increase in the total biomass.
(iii) increase in the number of species and organisms.
(b) Differences between pioneer community and climax community
| Pioneer community | Climax community |
| The species which invade a bare area or land to initiate succession is called pioneer community. | The last or final stage in a succession constitute the climax community. |
| The pioneer species have high reproductive rate. | The climax species have low reproductive rate. |
| The pioneer species have short life span. | The climax species have long life span. |
| They are replaceable. | They are stable and not replaced. |
Question. Fill in the missing stages in the given primary hydrarch succession.
Phytoplankton→ (a)→ (b)→ (c)→ Submerged free-floating→
(d) Forest plant stage
What is common between hydrarch and xerarch succession?
Answer. (a) Reed-swamp stage
(b) Submerged plant stage
(c) Marsh-meadow stage
(d) Scrub stage
Both the hydrarch and xerarch lead to mesic conditions of forest.
Question. Describe the process of decomposition of detritus under the following heads: Fragmentation; leaching; catabolism; humification and mineralisation.
Answer. The process of breaking down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like—, water and nutrients is called decomposition. The raw material for decomposition is called detritus.
They are dead remains of plants and animals.
Steps in decomposition:
(a) Fragmentation: The process of breaking down of detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, e.g., as done by earthworm.
(b) Leaching: The process by which water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
(c) Catabolism: The enzymatic process by which degraded detritus is converted into simple inorganic substances is called catabolism.
(d) Humification: The process of accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance called humus, that is, highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate.
(e) Mineralisation: The process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes and release inorganic nutrients is called mineralisation.
Question. (a) Draw a ‘pyramid of numbers’ of a situation where a large population of insects feed upon a very big tree. The insects in turn, are eaten by small birds which in turn are fed upon by big birds.
(b) Differentiate giving reason, between the pyramid of biomass of the above situation and the pyramid of numbers that you have drawn.
Answer. 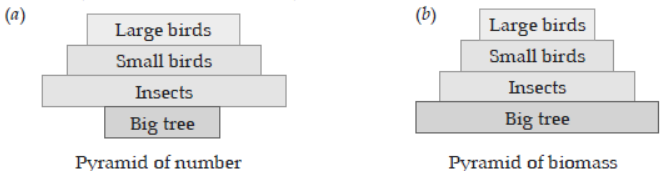
The pyramid of biomass is upright at the first two trophic levels because the biomass of a single tree is much more than total population of insects. Whereas, the pyramid of number is inverted at the first two trophic levels because the number of insects is much more than the number of trees.
Question. (a) What is a trophic level in an ecosystem? What is ‘standing crop’ with reference to it?
(b) Explain the role of the ‘first trophic level’ in an ecosystem.
(c) How is the detritus food chain connected with the grazing food chain in a natural ecosystem?
Answer. (a) The specific places occupied by an organism in the food chain is called trophic level.
Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time which is called as the standing crop.
(b) The first trophic level is comprised by the producers which trap solar energy to convert it into chemical bond energy of food. They serve as food for subsequent trophic levels.
(c) The organisms of the detritus food chain (DFC) are the prey to the grazing food chain (GFC) organisms. The dead remains of GFC are decomposed into simple inorganic materials. These materials are then absorbed by DFC organisms.
Question. (a) Differentiate between primary and secondary ecological successions.
(b) Explain the different steps of xerarch succession occurring in nature.
Answer. (a) Primary succession: It begins in areas where no living organisms ever existed. Therefore, the establishment of a biotic community is very slow, e.g., newly cooled lava, bare rock, newly created pond or reservoir.
Secondary succession: It begins in areas where natural biotic communities have been destroyed, e.g., abandoned farm lands, buried or cut forests. Since soil is available, it is a faster process.
(b) Xerarch Succession in Nature:
- Lichens are the pioneer species on a bare area.
- The lichen secretes some acids to dissolve rocks and help in weathering and soil formation.
- Later, some small bryophytes invade and hold the small amount of soil.
- The bryophytes are succeeded by herbs, shrubs and ultimately big trees.
- At last, a stable climax forest is formed.
- The xerophytic habitat gets converted into a mesophytic one.
Question. Describe the advantages for keeping the ecosystems healthy.
Answer. By keeping the ecosystem healthy we can take advantage of the ecosystem services which are the products of ecosystems.
Following are the economic and environmental goods that we obtain from the ecosystem. They
(i) Purify air and water
(ii) Mitigate drought and floods
(iii) Cycle nutrients
(iv) Generate fertile soil
(v) Provide wildlife habitat
(vi) Maintain biodiversity
(vii) Pollinate crops
(viii) Provide storage site for carbon
(ix) Provide aesthetic, cultural and spiritual value
(x) Provide stable food chain
(xi) Provide economically useful forest products
(xii) Provide sustainable biological legacy to future generations.
Question. What will happen to an ecosystem if
(a) All producers are removed;
(b) All organisms of herbivore level are eliminated; and
(c) All top carnivore population is removed.
Answer. (a) Reduction in primary productivity. No biomass available for consumption by higher trophic levels/heterotrophs and hence heterotrophs also die of starvation.
(b) Increase in primary productivity and biomass of producers. Carnivore population will subsequently dwindle due to food shortage.
(c) Increase in number of herbivores which leads to over-grazing by herbivores, finally resulting in desertification.
Please refer to attached file for CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set C |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 12 Ecosystem which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 12 Assignments for chapter Chapter 12 Ecosystem will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 12 Ecosystem, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 12 Ecosystem within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Biology mock tests for Chapter 12 Ecosystem reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 12 Ecosystem yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 12 Ecosystem assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 12 Ecosystem questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 12 Ecosystem Biology Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology

