Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Biology. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Biology in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 12 Ecosystem in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology Assignment
Startification : Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in an ecosystem.
Primary Production : Amount of biomas or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis.
Productivity : Rate of biomass production. Its unit is g/m2/year.
Gross Primary Productivity : Rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis.
Net Primary Productivity : Gross primary productivity minus the respiration losses.
Ecosystem : Relationship between living organisms and their abiotic surroundings.
Secondary Productivity : Rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Detritus : Dead leaves, twigs, animal remains etc. constitute detritus.
Detrivore : Organisms who break down detritus into smaller particles. e.g., earthworm.
Ecological succession : The successive and orderly replacement of one community by the other community in an area, over a period of time.
Ecological Pyramids : The sequential graphic representation of an ecological parameter (number/ biomass/energy) depicting different trophic levels in a food chain.
Climax community : The stable and final biotic community that develops at the end of ecological succession and is in perfect harmony with its physical environment.
Pioneer species : The species that invade a bare area at the onset of ecological succession.
Question: A functional unit of nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and also with the surrounding physical
environment is
a) biosphere
b) ecosystem
c) environment
d) None of these
Answer: b
Question: The process by which water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts is called as
a) fragmentation
b) leaching
c) catabolism
d) mineralisation
Answer: b
Question: Biotic components refer to
a) gases produced by industries
b) nutrient-deficient soil
c) living organisms
d) fossil fuels
Answer: c
Question: The process of mineralisation by microorganisms helps in the release of
a) inorganic nutrients from humus
b) both organic and inorganic nutrients from detritus
c) organic nutrients from humus
d) inorganic nutrients from detritus and the formation of humus
Answer: a
Question: Stratification is more pronounced in
a) tropical rainforest
b) deciduous forest
c) temperate forest
d) tropical savannah
Answer: a
Question: Primary productivity depends upon
a) availability of nutrients
b) photosynthetic capacity of plants
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: The green plants in an ecosystem which can trap solar energy to convert it into chemical bond energy are called
a) producer
b) decomposer
c) consumer
d) predators
Answer: a
Question: Fill up the blanks.
I. Herbivores are also called …A…
II. Secondary consumers are eaten by larger …B… .
III. …C… consumer eat the secondary consumers.
IV. A network of many food chains is called a …D… .
Choose the correct option for A, B, C and D.
a) A–secondary consumers, B–top predator, C–Quaternary, D–food web
b) A–primary consumer, B–predators, C–Tertiary consumer, D–food web
c) A–tertiary consumers, B–natural enemies, C–Primary consumer, D–food web
d) A–quaternary consumers, B–alligator, C–Top consumer, D–food web
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following is/are example(s) of detritivore?
a) Millipedes
b) Earthworm
c) Fiddler crabs
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question: Abiotic components refer to
a) non-living physico-chemical factors
b) living physico-chemical factors
c) gases produced by industries
d) living organisms
Answer: a
Question: The organisms which physically and chemically break the complex dead organic remains are known as
a) scavangers
b) decomposers
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) parasites
Answer: b
Question: PAR stands for
a) Photosynthesis Active Reaction
b) Photosynthesis Absorb Radiation
c) Photosynthetically Active Radiation
d) Photosynthetically Active Reaction
Answer: c
Question: The organisms, which attack dead animals are
a) first link of the food chain and are known as primary producers
b) second link the food chain and are herbivorous
c) third link of the food chain and are tertiary consumers
d) present at the starting of food chain and are detritivores
Answer: d
Question: Ecosystems need a constant supply of energy
a) to counteract increasing disorderliness
b) to counteract decreasing disorderliness
c) to synthesise molecules
d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following two organisms are producers?
a) Plants and phytoplanktons
b) Plants and consumers
c) Zooplanktons and phytoplanktons
d) Phytoplanktons and chlorophylls
Answer: a
Question: In what order do a hawk, grass and rabbit form a food chain in a meadow?
a) Hawk → grass → rabbit
b) Grass → hawk → rabbit
c) Rabbit → grass → hawk
d) Grass → rabbit → hawk
Answer: d
Question: …… begins with dead organic matter and saprophytes make the first trophic level. Most appropriate word for filling blank space is
a) Detritus food chain
b) Grazing food chain
c) Complex food chain
d) Normal food chain
Answer: a
Question: Peacock eats a snake and snake eats frog and frog eats insects, while insects eat green plants. The position of peacock is
a) primary producer
b) secondary producer
c) decomposer
d) at the apex of food ecological pyramid
Answer: d
Question: In an ecosystem, organism occupies a specific place in a food chain is called
a) Branching lines
b) Progressive straight line
c) Trophic level
d) Standing crop
Answer: c
Question: The 10% law for energy transfer in food chains was given by
a) Stanley
b) Tansley
c) Lindemann
d) Weismann
Answer: c
Question: In secondary succession, the species that invade depend on
a) the condition of soil
b) availability of water
c) seeds or other propagules
d) All of the above
Ecosystem
Question: A functional unit of nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and also with the surrounding physical
environment is
a) biosphere
b) ecosystem
c) environment
d) None of these
Answer: b
Question: The process by which water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts is called as
a) fragmentation
b) leaching
c) catabolism
d) mineralisation
Answer: b
Question: Biotic components refer to
a) gases produced by industries
b) nutrient-deficient soil
c) living organisms
d) fossil fuels
Answer: c
Question: The process of mineralisation by microorganisms helps in the release of
a) inorganic nutrients from humus
b) both organic and inorganic nutrients from detritus
c) organic nutrients from humus
d) inorganic nutrients from detritus and the formation of humus
Answer: a
Question: Stratification is more pronounced in
a) tropical rainforest
b) deciduous forest
c) temperate forest
d) tropical savannah
Answer: a
Question: Primary productivity depends upon
a) availability of nutrients
b) photosynthetic capacity of plants
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: The green plants in an ecosystem which can trap solar energy to convert it into chemical bond energy are called
a) producer
b) decomposer
c) consumer
d) predators
Answer: a
Question: Fill up the blanks.
I. Herbivores are also called …A…
II. Secondary consumers are eaten by larger …B… .
III. …C… consumer eat the secondary consumers.
IV. A network of many food chains is called a …D… .
Choose the correct option for A, B, C and D.
a) A–secondary consumers, B–top predator, C–Quaternary, D–food web
b) A–primary consumer, B–predators, C–Tertiary consumer, D–food web
c) A–tertiary consumers, B–natural enemies, C–Primary consumer, D–food web
d) A–quaternary consumers, B–alligator, C–Top consumer, D–food web
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following is/are example(s) of detritivore?
a) Millipedes
b) Earthworm
c) Fiddler crabs
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question: Abiotic components refer to
a) non-living physico-chemical factors
b) living physico-chemical factors
c) gases produced by industries
d) living organisms
Answer: a
Question: The organisms which physically and chemically break the complex dead organic remains are known as
a) scavangers
b) decomposers
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) parasites
Answer: b
Question: PAR stands for
a) Photosynthesis Active Reaction
b) Photosynthesis Absorb Radiation
c) Photosynthetically Active Radiation
d) Photosynthetically Active Reaction
Answer: c
Question: The organisms, which attack dead animals are
a) first link of the food chain and are known as primary producers
b) second link the food chain and are herbivorous
c) third link of the food chain and are tertiary consumers
d) present at the starting of food chain and are detritivores
Answer: d
Question: Ecosystems need a constant supply of energy
a) to counteract increasing disorderliness
b) to counteract decreasing disorderliness
c) to synthesise molecules
d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following two organisms are producers?
a) Plants and phytoplanktons
b) Plants and consumers
c) Zooplanktons and phytoplanktons
d) Phytoplanktons and chlorophylls
Answer: a
Question: In what order do a hawk, grass and rabbit form a food chain in a meadow?
a) Hawk → grass → rabbit
b) Grass → hawk → rabbit
c) Rabbit → grass → hawk
d) Grass → rabbit → hawk
Answer: d
Question: …… begins with dead organic matter and saprophytes make the first trophic level. Most appropriate word for filling blank space is
a) Detritus food chain
b) Grazing food chain
c) Complex food chain
d) Normal food chain
Answer: a
Question: Peacock eats a snake and snake eats frog and frog eats insects, while insects eat green plants. The position of peacock is
a) primary producer
b) secondary producer
c) decomposer
d) at the apex of food ecological pyramid
Answer: d
Question: In an ecosystem, organism occupies a specific place in a food chain is called
a) Branching lines
b) Progressive straight line
c) Trophic level
d) Standing crop
Answer: c
Question: The 10% law for energy transfer in food chains was given by
a) Stanley
b) Tansley
c) Lindemann
d) Weismann
Answer: c
Question: In secondary succession, the species that invade depend on
a) the condition of soil
b) availability of water
c) seeds or other propagules
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: The relation between producers and consumers in an ecosystem can be graphically represented in the form of a pyramid called
a) ecological pyramid
b) trophic level
c) Pi chart
d) pyramid of biomass
Answer: a
Question: Primary production is
a) expressed in terms of weight (gm-2) or energy (kcal m-2)
b) the amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: To show how many organisms are present at each level of a food chain, ecologists use a model called
a) an energy flow pyramid
b) pyramid of numbers
c) pyramid of energy
d) food chain/food web pyramid
Answer: b
Question: An inverted pyramid of …A… may occasionally be observed in …B… communities.
a) A–energy, B–grassland
b) A–energy, B–forest
c) A–biomass, B–marine
d) A–biomass, B–grassland
Answer: c
Question: The nature of climax community in ecological succession is most dependent upon
a) climate
b) water
c) soil fertility
d) None of these
Answer: a
Question: The total amount of nutrients like carbon, phosphorus, calcium, etc., present in soil at any time is called
a) standing crop
b) standing state
c) nutrient crops
d) sediment
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following factor is contributing to an overload of the carbon cycle?
a) Photosynthesis
b) Cellular respiration
c) Deforestation
d) Afforestation
Answer: c
Question: In a ……… cycle, the elements returns and is withdrawn from the atmosphere. Most appropriate word to fill the blank is
a) gaseous
b) sedimentary
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Answer: a
Question: What is the reason behind deficit rising in nutrient reservoir?
a) Due to imbalance in the rate of influx
b) Due to imbalance in the rate of efflux
c) Due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: In sedimentary nutrient cycling,
a) the reservoir pool is lithosphere
b) the sedimentary cycles are less perfect
c) the withdrawl from reservoir pool is large
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: Ecological succession is a sequence of series leading from baren land to the ……… .
a) seral community
b) climax community
c) pioneer species
d) benthos
Answer: b
Question: Food chain refers to
a) number of humans forming a chain for food
b) animals gathered near a source of food
c) transfer of energy from producers to consumers
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: What is the medium by which carbon cycle takes place?
a) Through atmosphere
b) Through ocean
c) Through living and dead organisms
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: Phosphorus is needed for the production of
a) DNA and RNA
b) cellular membranes
c) bones and teeth
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following pair is a gaseous type of biogeochemical cycle?
a) Nitrogen and carbon cycle
b) Phosphorus and carbon cycle
c) Nitrogen and sulphur cycle
d) Sulphur and carbon cycle
Answer: a
Question: The relation between producers and consumers in an ecosystem can be graphically represented in the form of a pyramid called
a) ecological pyramid
b) trophic level
c) Pi chart
d) pyramid of biomass
Answer: a
Question: Primary production is
a) expressed in terms of weight (gm-2) or energy (kcal m-2)
b) the amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: To show how many organisms are present at each level of a food chain, ecologists use a model called
a) an energy flow pyramid
b) pyramid of numbers
c) pyramid of energy
d) food chain/food web pyramid
Answer: b
Question: An inverted pyramid of …A… may occasionally be observed in …B… communities.
a) A–energy, B–grassland
b) A–energy, B–forest
c) A–biomass, B–marine
d) A–biomass, B–grassland
Answer: c
Question: The nature of climax community in ecological succession is most dependent upon
a) climate
b) water
c) soil fertility
d) None of these
Answer: a
Question: The total amount of nutrients like carbon, phosphorus, calcium, etc., present in soil at any time is called
a) standing crop
b) standing state
c) nutrient crops
d) sediment
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following factor is contributing to an overload of the carbon cycle?
a) Photosynthesis
b) Cellular respiration
c) Deforestation
d) Afforestation
Answer: c
Question: In a ……… cycle, the elements returns and is withdrawn from the atmosphere. Most appropriate word to fill the blank is
a) gaseous
b) sedimentary
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Answer: a
Question: What is the reason behind deficit rising in nutrient reservoir?
a) Due to imbalance in the rate of influx
b) Due to imbalance in the rate of efflux
c) Due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: In sedimentary nutrient cycling,
a) the reservoir pool is lithosphere
b) the sedimentary cycles are less perfect
c) the withdrawl from reservoir pool is large
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: Ecological succession is a sequence of series leading from baren land to the ……… .
a) seral community
b) climax community
c) pioneer species
d) benthos
Answer: b
Question: Food chain refers to
a) number of humans forming a chain for food
b) animals gathered near a source of food
c) transfer of energy from producers to consumers
d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: What is the medium by which carbon cycle takes place?
a) Through atmosphere
b) Through ocean
c) Through living and dead organisms
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: Phosphorus is needed for the production of
a) DNA and RNA
b) cellular membranes
c) bones and teeth
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following pair is a gaseous type of biogeochemical cycle?
a) Nitrogen and carbon cycle
b) Phosphorus and carbon cycle
c) Nitrogen and sulphur cycle
d) Sulphur and carbon cycle
Answer: a
Question. How do you distinguish between humification and mineralisation?
Answer : Humification is the process of decomposition of soil that leads to accumulation of a dark-coloured amorphous substance called humus. Humus are highly resistant to microbial action and under goes dicomposition at a very slow rate. Mineralisation is the process by which the humus is further degraded by microbes and inorganic nutrients or minerals are released back into the substratum.
Question. Poaching of tiger is a burning issue in today’s world. What implication would this activity have on the functioning of the ecosystem of which the tigers are an integral part?
Answer : Tiger represents an important part of the food web and helps in maintaining the ecological stability. As a carnivore, it keeps a check on the unlimited growth of herbivoresing the and also removes sick or old animlas from the population. It also acts as an indicator of the forest’s health. Saving the tiger means we save the forest. Since, tiger (top carnivore of the food chain) cannot live in places where trees or herbivores, that it hunts, have vanished and in turn secure food and water for all.
Question. In relation to energy transfer in ecosystem, explain the statement ‘‘10kg of deer’s meat is equivalent to 1 kg of lion’s flesh’’.
Answer : In an ecosystem, flow (transfer) of energy is unidirectional. As energy trapped in Ist tropic level, only 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level.
Question. Primary productivity varies from ecosystem to ecosystem. Explain?
Answer : Primary productivity is the rate at which primary producers (plants) capture and store solar radiation to form chemical energy. Primary production depends upon producer (green plant) which are variable in different ecosystem. So, primary productivity varies from ecosystem to ecosystem.
Question. Organisms at a higher trophic level have less energy available. Comment.
Answer : Energy flow in the ecosystem follows the 10% energy flow law, proposed by Lindman. According to this law only 10% of the energy available at each trophic level, gets transferred to the next trophic level, the rest is lost in the environment as heat. As we move to higher trophic levels, the energy available to organisms keeps on decreasing.Thus, the top carnivore gains the lesst energy in a food chain. Heat energy last during Respiration.
Question. The number of trophic levels in an ecosystem are limited. Comment.
Answer : The number of trophic level in an ecosystem are each limited and are not more than 4-5. because the amount of energy flow decreases with successive trophic level as only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next successive level. So rest of the energy is lost in the form of respiration and other vital activities to maintain life. If more trophic levels are present, the residual energy will be limited and decreases to such an extent that it cannot further support any trophic level by the flow of energy. So, the food chain is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels only.
Question. Sometimes due to biotic/abiotic factor the climax remain in a particular seral stage (pre climax) without reaching climax. Do you agree with this statement. If yes give a suitable example.
Answer : Sometimes climax remains in a particular seral stage without reaching to the climax because during ecological succession any change in abiotic and biotic component may affect the particular seral stage, leading to preclimax stage before the climax is achieved. This type of condition occurs presence of seeds and other propagules. This secondarily based area may be invaded by moss or exotic weeds thus exhibiting succession seriously and the climax community is never regenerated. in the case of natural calamities like-fire landslide, floods, change in soil texture.
Question. What is an incomplete ecosystem? Explain with the help of suitable example.
Answer : An ecosystem comprises with biotic and a biotic component. A biotic component include light, air, water, temperature, humidity etc, while biotic factor comprises all living organism. Absence or limited availability of any component (either abiotic or biotic) makes an ecosystem incomplete like the profundal and benthic zone in an aquatic ecosystem.
Question. “The energy flow in the ecosystem follows the second law of thermodynamics.” Explain.
Answer : According to second law of thermodynamics every activity involving energy transformation (According to first law - energy can be transferred and transformed) is accompanied by dissipation of energy as heat and only a part of it is used in building up tissues in an organisms. This trapped energy as biomass is transferred to next trophic level. According to Lindman law only 10% of the stored energy is passed from one trophic level to successive trophic level.
Question. What will happen to an ecosystem if
(a) All producers are removed
(b) All organisms of herbivore level are eliminated and
(c) All top carnivore population is removed
Answer : (a) Removal of all producer reduce primary production in the ecosystem. Hence, no biomass will be available to the successive/higher trophic level or heterotrophic organisms. (b) Elimination of all organisms of herbivore level results into an increase in primary productivity and biomass of producer and carnivorous animal will not survive due to inavailability of food herbivores. (c) Removal of top carnivores also disturb the ecosystem as it will result in huge increase in number of herbivores which will finish plants (producers) creating desertification.
Question. A farmer harvests his crop and expresses his harvest in three different ways.
(a) I have harvested 10 quintals of wheat.
(b) I have harvested 10 quintals of wheat today in one acre of land.
(c) I have harvested 10 quintals of wheat in one acre of land, 6 months after sowing. Do the above statements mean one and the same thing. If your answer is ‘yes’, give reasons. And if your answer is ‘no’ explain the meaning of each expression.
Answer : (a) Farmer's expression for his crop harvestation
(a) he has harvested 10 quintal of wheat,
(b); He has harvested 10 quintals of wheat in one acre of land
(c), six, months after sowing mean one and the same thing. Because crop an artificial ecosystem can be prepared with inclusion of bitoic and abiotic component in a given area. Here abiotic components like water, is given by the farmer, while climatic factor like light, humidity, air is supplied naturally. The living component is wheat plant, which are obtained on harvestation by farmer.
Question. Justify the following statement in terms of ecosystem dynamics. “Nature tends to increase the gross primary productivity, while man tends to increase the net primary productivity”.
Answer : In term of ecsosystem dynamics, flow of energy takes place from one trophic level to the next trophic level and occured in unidirectional way. About 50% of solar energy incident over earth is present in Photosynthetic Active Radiation (PAR) and only 2-10% of this PAR is utilised by green plants to form chemical energy (Gross Primary Productivity) (GPP). Out of 90% of gross primary productivity is lost maximum during respiration and other vital activities. GPP utilised by plants in respiration minus respiration losses is the net primary productivity and is available to the organism of next trophic level (herbivore and decomposers) for consumption. Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. So nature tend to increase gross primary productivity through supporting the large number of plant (producers) in an ecosystem. Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs (human and animals) man tries to increase net primary productivity by cultivating food and other crops which the depend on to fullfil their needs. Formula to genrate NPP is NPP1 GPP – R
Question. Give two examples of artificial or man made ecosystems. List the salient features by which they differ from natural ecosystems.
Answer : Aquarium and farm house, are artificial or man made ecosystem. In artificial ecosystem biotic and abiotic component are maintained artificially like cleaning, feeding and supply of oxygen to fishes in aquarium and irrigation in crop or farm house. While abiotic and biotic component of natural ecosystem are maintained naturally like nutrient cycle, self sutainability, prevention of soil erosion, pollutant absorption and reduction of threat to global warming (ecological servicer), etc.
Question. The biodiversity increases when one moves from the pioneer to the climax stage. What could be the explanation?
Answer : During ecological succession biodiversity increase or changes from pioneer to climax stages. Following are the effects of ecological succession (a) It leads to changes in vegetation that affects food and shelter for various types of animals. (b) As succession proceeds, the numbers and types of plants, animals and decomposers also change. (c) At any time during primary or secondary succession, natural or human induced disturbances (fire, deforestation, etc.) can convert a particular seral stage of succession to an earlier stage. Also such disturbances can create new conditions that encourage some species and discourage or eliminate other species of producer, consumers and decomposers. (d) Over the time, they are succeeded by bigger plants and, ultimately a stable climax forest community is attained. (e) The climax community remains stable if the environment remains unchanged. (f) With time, the xerophytic habitat may gets converted into a mesophytic one.
Question. Name the type of food chains responsible for the flow of larger fraction of energy in an aquatic and a terrestrial ecosystem, respectively. Mention one difference between the two food chains.
Answer. In aquatic system, grazing food chain and in terrestrial ecosystem, detritus food chain is responsible for flow of larger fraction of energy.
| Grazing food chain (GFC) | Detritus food chain (DFC) |
| It starts with green plants called producers as first trophic level. | It begins with dead organic matter and decomposers called saprophytes as first trophic level. Decomposers secrete digestive enzymes that breakdown dead and waste into simple, inorganic materials which are absorbed by them. |
| A much less fraction of energy flows through this type of food chain. | A much large fraction of energy flows through this type of food chain. |
| Energy for food chain comes from sun. | Energy for the food chain comes from organic remain or detritus. |
Question. (a) Name the type of detritus that decomposes faster. List any two factors that enhance the rate of decomposition.
(b) Write the different steps taken in humification and mineralisation during the process of decomposition.
Answer. (a) l Detritus rich in nitrogen decomposes faster. These are water-soluble substances like sugar.
l Factors enhancing rate of decomposition: Warm temperature, moist environment, availability of oxygen.
(b) Humification: Accumulation of dark coloured amorphous substance called humus which is resistant to micorbial action and undergoes decomposition at a very slow rate.
Mineralisation: Humus is further degraded by microbes releasing inorganic nutrients.
Question. Describe the inter-relationship between productivity, gross primary productivity and net productivity.
Answer. Productivity is the rate of biomass production per unit area over a period of time.
Gross primary productivity is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis in an ecosystem.
Net productivity is the gross primary productivity minus respiration losses.
Question. (a) Construct a pyramid of numbers by taking suitable examples for each trophic level in an ecosystem.
(b) Explain why a progressive decline is seen in the population size from the first to the fourth trophic level in the above pyramid.
Answer. (a)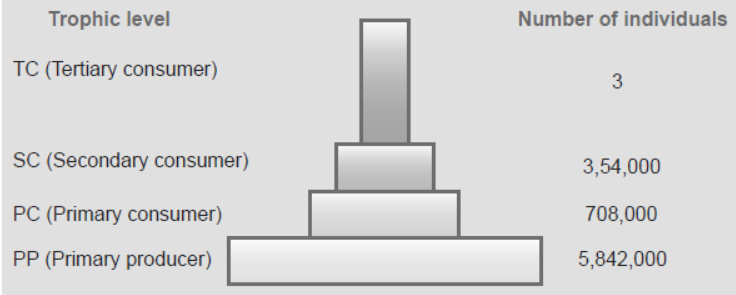
(b) Amount of energy decreases at successive trophic levels resulting into decreasing in number of organisms as per 10% law.
Question. Why is the length of a food chain in an ecosystem generally limited to 3–4 trophic levels?
Explain with an example.
Answer. The amount of energy flow decreases with successive trophic levels as only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next successive level. The energy is lost in the form of respiration and other vital activities to maintain life. If more trophic levels are present, the residual energy will be limited and decreased to such an extent that it cannot further support any trophic level by the flow of energy. So, the food chain is generally limited to 3–4 trophic levels only.
For, e.g.,
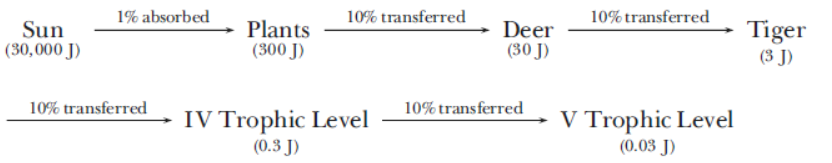
Question. (a) Describe primary succession that occurs on bare rock.
(b) Differentiate between xerarch and hydrarch successions.
Answer. (a)
- Lichens are the pioneer species on a bare area.
- The lichen secretes some acids to dissolve rock and help in weathering and soil formation.
- Later, some small bryophytes invade and hold the small amount of soil.
- The bryophytes are succeeded by herbs, shrubs and ultimately big trees.
- At last, a stable climax forest is formed.
- The xerophytic habitat gets converted into a mesophytic one.
(b)The plant succession is of two types:
(i) Hydrarch succession: The plant succession which takes place in wet area or water, leading to
successional series, progress from hydric to the mesic conditions.
(ii) Xerarch succession: The plant succession which takes place in a dry area, leading to successional
series from xeric to mesic conditions.
Question. Differentiate between primary and secondary succession. Provide one example of each.
Answer. Differences between primary and secondary succession
| Primary Succession | Secondary Succession |
| It begins with areas where no living organisms ever existed. | It begins in areas where natural biotic communities have been destroyed. |
| Establishment of a biotic community is very slow. | Establishment of a biotic community is faster. |
| Example: Newly cooled-lava/barerocks/newly created ponds or reservoir. | Example: Abandoned farm lands/burnt or cut forests/lands that have been flooded. |
Question. (a) State any two differences between phosphorus and carbon cycles in nature.
(b) Write the importance of phosphorus in living organisms.
Answer. (a) Differences between phosphorus and carbon cycles
| Phosphorus cycle | Carbon cycle |
| It is a sedimentary cycle. | It is a gaseous cycle. |
| Atmospheric inputs through rainfall are much smaller. | Atmospheric inputs through rainfall are more. |
| Gaseous exchange of phosphorus between organism and environment is nil. | Gaseous exchange of carbon between organism and environment is much more. |
(b) Phosphorus is a major constituent of biological membranes, nucleic acids and cellular energy transfer system.
Question. Describe the effects of human activities in influencing natural ecosystem cycles with special reference to carbon cycle.
Answer. Human activities have significantly influenced the carbon cycle. Rapid deforestation and massive burning of fossil fuels for energy and transport have significantly increased the rate of release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas which allows the solar radiations to enter but prevent the escape of heat radiations of longer wavelength. The absorbed radiations again come to earth’s surface and heat it up. Thereby increasing the average temperature of surface of the earth, i.e., global warming.
Question. Name the kind of organisms which constitute the pioneer community of xerarch and hydrarch succession, respectively.
Answer. Xerarch succession—Lichens and Hydrarch succession—Phytoplanktons
Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Biology Ecosystem
Question. In an ecosystem based on production of nearly 6 million plants, how many top consumers can be supported ?
(a) 708000
(b) 354000
(c) 3
(d) 30000
Answer : C
Question. In an ecosystem if dry weight of producers is 809 kgm-2. Then what will be the biomass of tertiary consumers
(a) 37 dry weight (Kg m-2)
(b) 11 (Kg m-2)
(c) 15 kg m-2
(d) 1.5 kgm-2
Answer : D
Question. Ecological pyramids show diagramatic representation of ecological parameters like number, biomass and energy. Which is / are limitation of ecological pyramids ?
(a) It does not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels
(b) It does not accomodate a food web
(c) Saprophytes are not given any place in pyramids
(d) All the above
Answer : D
Question. The gradual and fairly predictable changes in the species composition of a given area is called :-
(a) Bioprospecting
(b) Biofortification
(c) Ecological succession
(d) Ecological assessment
Answer : C
Question. All successions whether taking place in water or on land proceeds to which climax community :-
(a) Hydric
(b) Xeric
(c) Mesic
(d) Halophytic
Answer : C
Question. How much amount of carbon is fixed in biosphere through photosynthesis annually
(a) 2 x 1013 kg
(b) 4 x 1013 kg
(c) 5 x 1013 kg
(d) 6 x 1013 kg
Answer : B
Ques. The term ecosystem was coined by
(a) E. Haeckel
(b) E.Warming
(c) E.P. Odum
(d) A. G. Tansley.
Answer: D
Ques. Which one of the following is a characteristic feature of cropland ecosystem?
(a) Absence of weeds
(b) Ecological succession
(c) Absence of soil organisms
(d) Least genetic diversity
Answer: D
Ques. Vertical distribution of different species occupyin different levels in a biotic community is known as
(a) zonation
(b) pyramid
(c) divergence
(d) stratification.
Answer: D
Ques. Which one of the following is not a functional uni of an ecosystem?
(a) Energy flow
(b) Decomposition
(c) Productivity
(d) Stratification
Answer: D
Ques. Which one of the following is one of the characteristics of a biological community?
(a) Stratification
(b) Natality
(c) Mortality
(d) Sex-ratio
Answer: A
Ques. Which of the following is the most stable ecosystem?
(a) Mountain
(b) Ocean
(c) Forest
(d) Desert
Answer: B
Ques. In relation to Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity of an ecosystem, which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Gross primary productivity is always less than Net primary productivity.
(b) Gross primary productivity is always more than Net primary productivity.
(c) Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity are one and same.
(d) There is no relationship between Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity.
Answer: B
Ques. The mass of living material at a trophic level at a particular time is called
(a) net primary productivity
(b) standing crop
(c) gross primary productivity
(d) standing state.
Answer: B
Ques. In an ecosystem the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is termed as
(a) secondary productivity
(b) net productivity
(c) net primary productivity
(d) gross primary productivity.
Answer: D
Ques. Secondary productivity is rate of formation of new organic matter by
(a) consumers
(b) decomposers
(c) producers
(d) parasites.
Answer: A
Ques. The rate of formation of new organic matter by rabbit in a grassland, is called
(a) net productivity
(b) secondary productivity
(c) net primary productivity
(d) gross primary productivity.
Answer: B
Ques. Mass of living matter at a trophic level in an area at any time is called
(a) standing crop
(b) detritus
(c) humus
(d) standing state.
Answer: A
Ques. The biomass available for consumption by the herbivores and the decomposers is called
(a) net primary productivity
(b) secondary productivity
(c) standing crop
(d) gross primary productivity.
Answer: A
Ques. Which one of the following ecosystem types has the highest annual net primary productivity?
(a) Tropical deciduous forest
(b) Temperate evergreen forest
(c) Temperate deciduous forest
(d) Tropical rainforest
Answer: D
Ques. Which of the following is expected to have the highest value (gm/m2/yr) in a grassland ecosystem?
(a) Secondary production
(b) Tertiary production
(c) Gross production (GP)
(d) Net production (NP)
Answer: C
Ques. The rate at which light energy is converted into chemical energy of organic molecules is the ecosystem’s
(a) net secondary productivity
(b) gross primary productivity
(c) net primary productivity
(d) gross secondary productivity.
Answer: B
Ques. Which of the following ecosystem has the highest gross primary productivity?
(a) Mangroves
(b) Rainforest
(c) Grassland
(d) Coral reef
Answer: B
Ques. Maximum solar energy is trapped by
(a) planting trees
(b) cultivating crops
(c) growing algae in tanks
(d) growing grasses.
Answer: C
Ques. A very efficient converter of solar energy with net productivity of 204 kg/m2 or more is the crop
(a) wheat
(b) sugarcane
(c) rice
(d) bajra.
Answer: B
Please refer to the link below for CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set C |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 12 Ecosystem which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 12 Assignments for chapter Chapter 12 Ecosystem will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 12 Ecosystem, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 12 Ecosystem within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Biology mock tests for Chapter 12 Ecosystem reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 12 Ecosystem yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 12 Ecosystem assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 12 Ecosystem questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Ecosystem from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 12 Ecosystem Biology Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 12 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology

