Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Assignment Set B. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Biology. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Biology in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Class 12 Biology Assignment
POINTS TO REMEMBER
Acrosome : A small, sheathy structure at the end of a sperm.
Blastula : A stage of embryogendesis which comes after morula and has a hollow fluid filled space called blastocoel.
Endometrium : Innermost glandular layer lining the uterine cavity.
Foetus : An advanced stage of embryo within the uterus.
Gestation Period : A period between fertilisation of ovum and the birth of a baby.
Hymen : A thin membrane partially covering the vaginal aperture.
Implantation : Fixing of embryo/fertilized egg in uterus. It leads to pregnancy.
Menarche : The beginning of first menstruation in female on attaining puberty.
Menopause : Permanent cessation of menstrual cycle in female. It occurs between the age 45 to 50 years in human female.
Oogenesis : Formation and development of ova in ovary.
Ovulation : Process of release of mature ovum (Secondary oocyte) from the ovary.
Parturition : Process of delivery of the foetus (Child birth).
Puberty : A stage at which immature reproductive system of boy or girl becomes mature.
Scrotum : A muscular pouch which houses two testes.
Spermiation : A process by which spher matozora are released from the sominiferous tubules.
Spermatogenesis : Process of formation of sperm from malegerm. cell in the testes.
VSA
1. Failure of testes to descend into scrotal sacs leads to sterility. Why?
2. Both vaccine and colostrum produce immunity. Name type of immunity produced by these.
3. How many sperms will be produced from 10 primary spermatocytes and how many eggs will be produced from 10 primary oocytes?
4. The spermatogonial cell has 46 chromosomes in human male. Give the number of chromosomes in -
(a) Primary spermatocyte (b) Spermatid
5. In ovary which structure transforms as corpus luteum and name the hormone secreted by corpus luteum?
6. "Each and every coitus does not results in fertilisation and pregnancy". Justify the statement.
Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction
Question. Find out 'A' and 'B' respectively :
(a) Uterus, Ovary
(b) Ovary, Uterus
(c) Oviduct, Ovary
(d) Seminal vesicle, Uterus
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following can be used as an emergency contraceptives to avoid possible pregnancy :
(a) Progestogens
(b) IUD within 72 hours
(c) Diaphrams
(d) 1 and 2
Answer : D
Question. During the first two months of pregnancy the basic structures are formed. During this period, the developing stage is called as :
(a) Infant
(b) Foetus
(c) Child
(d) Embryo
Answer : D
Question. Which is not correct about amnion ?
(a) It acts as a shock absorber
(b) It provides a fluid medium to the developing embryo.
(c) It takes part in the formation of human placenta
(d) None of the above
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statement is not correct ?
(a) Cleavage divisions are rapid
(b) Cleavage divisions are asynchronous
(c) Cleavage divisions are repeated mitotic divisions.
(d) Approximately one month after fertilisation, the blastocyst embedded itself in the thickened wall of the uterus.
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following set is correct ?
(a) Ovarian follicle - Estrogen
(b) Corpus luteum - Progesterone & Estrogen
(c) Placenta - HCG hormone
(d) All of the above
Answer : D
Question. Which pair is correct ?
(a) Progesterone ® Steroid Estrogen ® Protein
(b) Progesterone & Estrogen ® Protein
(c) Progesterone & Estrogen ® Steroid
(d) Progesterone ® Protein Estrogen ® Steroid
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following method of contraception is effective only upto a maximum period of six months following parturition ?
(a) Cortus interruptus
(b) Lactational amenorrhea
(c) Periodic abstinance
(d) Condoms
Answer : B
Ques. Select the correct sequence for transport of sperm cells in male reproductive system.
(a) Testis → Epididymis → Vasa efferentia → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Inguinal canal → Urethra → Urethral meatus
(b) Testis → Epididymis → Vasa efferentia → Rete testis → Inguinal canal → Urethra
(c) Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis → Vasa efferentia → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra → Urethral meatus
(d) Seminiferous tubules → Vasa efferentia → Epididymis → Inguinal canal → Urethra
Answer: C
Ques. Which of the following depicts the correct pathway of transport of sperms?
(a) Rete testis → Efferent ductules → Epididymis → Vas deferens
(b) Rete testis → Epididymis → Efferent ductules → Vas deferens
(c) Rete testis → Vas deferens → Efferent ductules → Epididymis
(d) Efferent ductules → Rete testis → Vas deferens → Epididymis
Answer: A
Ques. The shared terminal duct of the reproductive and urinary system in the human male is
(a) urethra
(b) ureter
(c) vas deferens
(d) vasa efferentia.
Answer: A
Ques. The Leydig’s cells as found in the human body are the secretory source of
(a) progesterone
(b) intestinal mucus
(c) glucagon
(d) androgens.
Answer: D
Ques. If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will not be transported from
(a) testes to epididymis
(b) epididymis to vas deferens
(c) ovary to uterus
(d) vagina to uterus.
Answer: A
Ques. The testes in humans are situated outside the abdominal cavity inside a pouch called scrotum. The purpose served is for
(a) maintaining the scrotal temperature lower than the internal body temperature
(b) escaping any possible compression by the visceral organs
(c) providing more space for the growth of epididymis
(d) providing a secondary sexual feature for exhibiting the male sex.
Answer: A
Ques. Sertoli cells are found in
(a) ovaries and secrete progesterone
(b) adrenal cortex and secrete adrenaline
(c) seminiferous tubules and provide nutrition to germ cells
(d) pancreas and secrete cholecystokinin.
Answer: C
Ques. Vasa efferentia are the ductules leading from
(a) testicular lobules to rete testis
(b) rete testis to vas deferens
(c) vas deferens to epididymis
(d) epididymis to urethra.
Answer: B
Ques. Seminal plasma in human males is rich in
(a) fructose and calcium
(b) glucose and calcium
(c) DNA and testosterone
(d) ribose and potassium.
Answer: A
Ques. Secretions from which one of the following are rich in fructose, calcium and some enzymes?
(a) Male accessory glands
(b) Liver
(c) Pancreas
(d) Salivary glands
Answer: A
Ques. Seminal plasma in humans is rich in
(a) fructose and calcium but has no enzymes
(b) glucose and certain enzymes but has no calcium
(c) fructose and certain enzymes but poor in calcium
(d) fructose, calcium and certain enzymes.
Answer: D
Ques. Male hormone is produced in the testis by cells of
(a) Sertoli
(b) epithelial
(c) spermatocytes
(d) Leydig.
Answer: D
Ques. Location and secretion of Leydig’s cells are
(a) liver-cholesterol
(b) ovary-estrogen
(c) testis-testosterone
(d) pancreas-glucagon.
Answer: C
Ques. Hysterectomy is surgical removal of
(a) vas deferens
(b) mammary glands
(c) uterus
(d) prostate gland.
Answer: C
Ques. The part of Fallopian tube closest to the ovary is
(a) isthmus
(b) infundibulum
(c) cervix
(d) ampulla.
Answer: B
Ques. Bartholin’s glands are situated
(a) on the sides of the head of some amphibians
(b) at the reduced tail end of birds
(c) on either side of vagina in humans
(d) on either side of vas deferens in humans.
Answer: C
Ques. Meiotic division of the secondary oocyte is completed
(a) prior to ovulation
(b) at the time of copulation
(c) after zygote formation
(d) at the time of fusion of a sperm with an ovum.
Answer: D
Ques. The difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation is
(a) in spermiogenesis spermatids are formed, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed
(b) in spermiogenesis spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation spermatids are formed
(c) in spermiogenesis spermatozoa from Sertoli cells are released into the cavity of seminiferous tubules, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed
(d) in spermiogenesis spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation spermatozoa are released from Sertoli cells into the cavity of seminiferous tubules.
Answer: D
Ques. Which of the following layers in an antral follicle is acellular?
(a) Stroma
(b) Zona pellucida
(c) Granulosa
(d) Theca interna
Answer: B
Question. Differentiate between major structural changes in the human ovary during the follicular and luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
Answer : Differences between follicular and luteal phases of mentrual cycle
| Follicular phase | Luteal phase |
| During this, primary follicles grow to become fully mature Graafian follicle. | During this, remaining part of Graafian follicle transforms into corpus luteum. |
| Endometrium regenerates through proliferation. | Endometrium further thickens secreting progesterone for implantation after fertilisation. If fertilisation does not occur, corpus luteum degenerates. |
Question. What is the number of chromosomes in the following cells of a human female?
(i) Primary oocyte (ii) Ootid
(iii) Secondary oocyte (iv) Follicle cells
Answer : (i) 46 (ii) 23
(iii) 23 (iv) 46
Question. Corpus luteum in pregnancy has a long life. However, if fertilisation does not take place it remains active only for 10−12 days. Why?
Answer : This is because of a neural signal given by the maternal endometrium to its hypothalamus in presence of a zygote to sustain the gonadotropin (LH) secretion, so as to maintain the corpus luteum as long as the embryo remains there. In the absence of a zygote, therefore, the corpus luteum degenerates.
Question. Why does corpus luteum secrete large amount of progesterone during luteal/secretory phase of the menstrual cycle?
Answer : The hormone progesterone is essential for the maintenance of endometrium of the uterus. It maintains the endometrial lining of uterus so that the foetus may get implanted in the uterus. So,corpus luteum secretes large amounts of progesterone during the luteal phase of menstrual cycle.
Question. Mention the fate of corpus luteum and its effect on the uterus in absence of fertilisation of the ovum in a human female.
Answer : In the absence of fertilisation, corpus luteum degenerates and this causes disintegration of the endometrium of ovary, leading to menstruation.
Question. Explain the events that follow up to fertilisation when the sperms come in contact with the ovum in the fallopian tube of a human female.
Answer : The secretion of the acrosome help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida and the plasma membrane. This induce the completion of second meiotic division of the secondary oocyte, forming second polar body and a haploid ovum. Soon the haploid nucleus of the sperm and that of the ovum fuse together to form a diploid zygote.
Question. Differentiate between menarche and menopause.
Answer : Menarche is the beginning of menstrual cycle at puberty. It starts at the age of 13−15 years. Menopause is the cessation of menstrual cycle. It happens around 50 years of age.
Question. Mention the target cells of luteinising hormone in human males and females. Explain the effect and the changes which the hormone induces in each case.
Answer : The target cells of luteinising hormone (LH) in males are the Leydig cells and in females are the mature growing follicles.
LH in males stimulates the Leydig cells (interstitial cells) of testes to synthesise and secrete androgens which in turn stimulate the process of spermatogenesis. LH in females stimulate the ovulation (release of ovum) and transformation of Graafian follicle into corpus luteum to secrete progesterone which prepares the endometrium to receive and implant blastocyst.
Question. Write the effect of the high concentration of LH on a mature Graafian follicle.
Answer : In high conventration of LH, the mature Graafian follicle ruptures to release the secondary oocyte or ovum from the ovary by the process of ovulation.
Question. After implantation interdigitation of maternal and foetal tissues takes place. Identify the tissues involved and justify their role.
Answer : After implantation interdigitation of maternal and foetal tissues results in formation of structural and functional unit between embryo and maternal body called placenta.
It facilitates supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo, removal of carbon dioxide and excretory material and also acts as an endocrine tissue and produces hormones like HCG, hPL,estrogen, progesterone and relaxin.
Question. What are the events taking place in the ovary and uterus during follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
Answer : (i) The primary follicles grow and become fully mature Graafian follicles.
(ii) Secretion of estrogen hormone.
(iii) Endometrium of uterus regenerates through proliferation.
Question. Name two hormones that can be found only in the blood of a pregnant woman. Mention the source organ/tissue that secretes each of them.
Answer : Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)—Placenta.
Human placental lactogen (hPL)—Placenta.
Relaxin (towards the end of pregnancy)—Ovary.
Question. Write the function of each one of the following:
(i) (Oviducal) Fimbriae (ii) Oxytocin
Answer : (i) Collection of ovum released by ovary.
(ii) Cause uterine contraction for parturition; promotes milk ejection.
Question. State the fate of trophoblast of a human blastocyst at the time of implantation and that of the inner cell mass immediately after implantation.
Answer : The trophoblast layer gets attached to the endometrium, and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo.
Question. Placenta acts as an endocrine tissue. Justify.
Answer : Placenta produces several hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estrogens, progesterones that are essential to maintain pregnancy. This way placenta acts as an endocrine tissue.
Question. (i) Where do the signals for parturition originate from in humans?
(ii) Why is it important to feed the newborn babies on colostrum?
Answer : (i) Signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus the placenta which induce uterine contractions. This is called as foetal ejection reflex. (Any one)
(ii) Colostrum contains antibodies (IgA), to (passively) immunise the baby.
Question. State the role of oxytocin in parturition. What triggers its release from the pituitary?
Answer : Oxytocin acts on uterine muscle and cause stronger uterine contraction. This leads to expulsion of the foetus or baby out of uterus.
Question. When and where do chorionic villi appear in humans? State their functions.
Answer : Chorionic villi appear after implantation on the trophoblast. It becomes interdigitated with uterine tissue to form the placenta and increases the surface area for exchange of materials between the mother and the embryo.
Question. Why is breast-feeding recommended during the initial period of an infant’s growth? Give reasons.
OR
Medically it is advised to all young mothers that breast feeding is the best for their newborn babies. Do you agree? Give reasons in support of your Answer :
Answer : The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called colostrum. It contains several antibodies (IgA) absolutely essential, to develop passive immunity in the new-born babies. It also contains nutrients such as calcium, fats, lactose. Breast feeding also develops a bond between mother and child.
Question. What stimulates pituitary to release the hormone responsible for parturition? Name the hormone.
Answer : The signal from the fully developed foetus and placenta or the foetal ejection reflex induces mild uterine contraction. The hormone released is oxytocin.
Question. Women experience two major events in their life time, one at menarche and the second at menopause. Mention the characteristics of both the events.
Answer : Menarche represents the beginning of menstrual cycle which is an indication of attainment of sexual maturity. Menopause, on the other hand, refers to the cessation of menstruation which in turn means stoppage of gamete production, i.e., it marks the end of reproductive or fertile life of the female.
Question. (i) Draw a sectional view of seminiferous tubule of a human. Label the following cells in the seminiferous tubule:
(a) Cells that divide by mitosis to increase their number.
(b) Cells that undergo Meiosis I.
(c) Cells that undergo Meiosis II.
(d) Cells that help in the process of spermiogenesis.
(ii) Mention the role of Leydig cells.
OR
Draw a labelled sectional view of seminiferous tubule of a human male.
Answer :
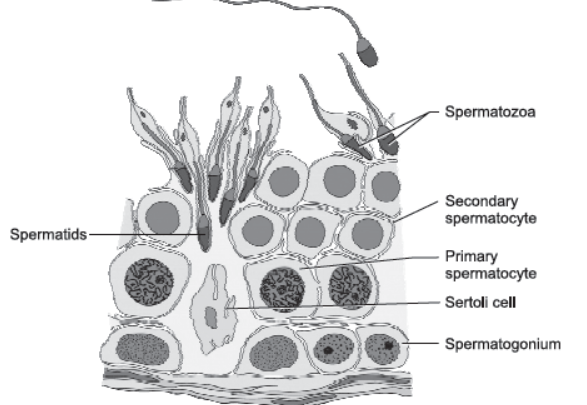
(a) Cells that divide by mitosis to increase their number—Spermatogonia
(b) Cells that undergo Meiosis I—Primary spermatocytes
(c) Cells that undergo Meiosis II—Secondary spermatocytes
(d) Cells that help in the process of spermiogenesis—Sertoli cells
(ii) Role of Leydig cells: They synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called androgens.
Question. Name the source of gonadotropins in human females. Explain the changes brought about in the ovary by these hormones during menstrual cycle.
OR
Describe how the changing levels of FSH, LH and progesterone during menstrual cycle induce changes in the ovary and the uterus in human female.
Answer : Gonadotropins (LH and FSH) are secreted by the anterior lobe of pituitary gland.OO Gonadotropins (LH and FSH) increase gradually during the follicular phase (proliferative phase) of menstrual cycle and stimulate follicular development as well as secretion of estrogen by the growing follicles.
OO LH and FSH attain a peak level in the middle of the cycle (about 14th day) and rapid secretion of LH induces rupture of Graafian follicle followed by ovulation (release of ovum).
OO LH stimulates transformation of Graafian follicle into corpus luteum.
Question. When and where do chorionic villi appear in humans? State their function.
Answer : Chorionic villi appear after implantation on the trophoblast.
It becomes interdigitated with uterine tissue to form the placenta and increases the surface area for exchange of materials between the mother and the embryo.
Question. (i) How is placenta formed in the human female?
(ii) Name any two hormones which are secreted by it and are also present in a non-pregnant woman.
Answer : (i) The chorionic villi and uterine tissue become interdigitated with each other and jointly form a structural and functional unit called placenta.
(ii) Estrogen and progestogens.
Question. It is commonly observed that parents feel embarrassed to discuss freely with their adolescent children about sexuality and reproduction. The result of this parental inhibition is that the children go astray sometimes.
(i) Explain the reasons that you feel are behind such embarrassment amongst some parents to freely discuss such issues with their growing children.
(ii) By taking one example of a local plant and animal, how would you help these parents to overcome such inhibitions about reproduction and sexuality?
Answer : (i) The reasons behind this embarrassment are illiteracy, their conservative attitude, misconceptions, social myths and generation gap.
(ii) It can be seen in animals such as honey bee and plants such as orchid ophrys flower that sexual attraction is a natural phenomenon. The male honey bee assumes the petal of orchid as its female partner and pseudocopulates with it. So, sexuality is a natural phenomenon and parents should speak to their children about it.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set C |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 12 Assignments for chapter Chapter 2 Human Reproduction will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 2 Human Reproduction, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 2 Human Reproduction within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Biology mock tests for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 2 Human Reproduction yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 2 Human Reproduction assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 2 Human Reproduction questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Biology Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Class 12 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Class 12 Biology

