Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Environmental Issues Assignment Set A. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Biology. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Biology in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 16 Environmental Issues in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Class 12 Biology Assignment
Question. Positive pollution of soil is due to
(a) reduction in soil productivity
(b) addition of waste to soil
(c) excessive use of fertilizers
(d) all of the above
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following metal pollution causes sterility in human beings?
(a) Mercury
(b) Arsenic
(c) Manganese
(d) Chromium
Answer : C
Question. Deforestation causes
(a) soil erosion
(b) soil pollution
(c) noise pollution
(d) air pollution
Answer : A
Question. Nitrogen oxides, produced from the emission of automobiles and power plants, are the source of fine air borne particles which lead to
(a) photochemical smog
(b) dry acid deposition
(c) industrial smog
(d) wet acid deposition
Answer : A
Question. Formation of non-functional methaemoglobin causes blue-baby syndrome. This is due to
(a) excess of arsenic concentration in drinking water
(b) excess of nitrates in drinking water
(c) deficiency of iron in food
(d) increased methane content in the atmosphere
Answer : B
Question. Pollution from animal excreta and organic waste from kitchen can be most profitably minimized by
(a) storing them in underground storage tanks
(b) using them for producing biogas
(c) vermiculture
(d) using them directly as biofertilizers
Answer : C
Question. Which one of the following statement pertaining to pollutants is correct?
(a) DDT is a non-biodegradable pollutant
(b) Excess fluoride in drinking water causes osteoporosis hardening of bones, stiff joints
(c) Excess cadmium in drinking water causes black foot disease
(d) Methylmercury in water may cause "Itai Itai" disease
Answer : A
Question. In the environment, ozone is known for its
(a) Harmful effects
(b) Useful effects
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Inert nature
Answer : C
Question. Which one of the following statement is true?
(a) The greater the BOD of waste water, more is its polluting potential.
(b) The greater the BOD of waste water, less is its polluting potential.
(c) The lesser the BOD of waste water, more is its polluting potential.
(d) The lesser the BOD of waste water, less is its polluting potential.
Answer : A
Question. The two gases making the highest relative contribution to the greenhouse gases are
(a) CO2 and CH4
(b) CH4 and N2O
(c) CFCand N2O
(d) CO2 and N2O
Answer : A
Question. DDT residues are rapidly passed through food chain causing biomagnification because DDT is
(a) moderately toxic
(b) non-toxic to aquatic animals
(c) water soluble
(d) lipo soluble
Answer : D
Question. Scrubber is one of the device used to remove air pollutants. Which of the following gaseous pollutant can be remove through it -
(a) NOx
(b) SO2
(c) CO
(d) CO2
Answer : B
Question. The Bharat Stage-III norms of Automobiles are applicable throughout the country from -
(a) 1 October 2005
(b) 1 October 2010
(c) 1 October 2009
(d) 1 October 2012
Answer : B
Question. All automobiles and fuel petrol and diesel - were to have met the Euro-IV emission specification in 13 highly polluted cities of India from -
(a) 1 April 2002
(b) 1 April 2005
(c) 1 April 2010
(d) 1 April 2012
Answer : C
Question. Unlike domestic sewage, waste water from industries like petroleum, paper manufacturing, metal extractions and processing etc. are often important source of water pollution. Out of these heavy metals are -
(a) Elements with density < 5 g/cm3
(b) Elements with density < 5 g/cm2
(c) Elements with density > 5g /cm3
(d) Elements with density > 5g/ cm2
Answer : C
Question. Biomagnification - an increase in concentration of toxic substances at successive trophic levels, is well known for -
(a) DDT
(b) Mercury
(c) CO
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer : D
Question. According to CPCB particulate size £ 2.5 micrometer are responsible for cousing greatest harm to human health. They can cause various harms except -
(a) Breathing and Respiratory symptoms
(b) Respiratory Irritation
(c) Inflammation and damage to lungs
(d) Lack of sleep
Answer : D
Question. The unique idea of integrated organic farming was executed by-
(a) Ramesh Chandra Dagar
(b) Ahmed Khan
(c) Amrita Devi
(d) Sunderlal Bahuguna
Answer : A
Question. Green house effect leads to deleterious changes in the environment and resulting in odd climatic changes. Which among the following is not the control measure of it -
(a) Cutting down the use of fossil fuel
(b) Improving efficiency of energy usage
(c) Increasing deforestration
(d) Slowing down the human population
Answer : C
Question. The thickness of the ozone in a column of air from ground to top of the atmosphere is measured in terms of -
(a) Decibel
(b) Dobson
(c) Deby
(d) Dalton
Answer : B
Question. Harmful effects of air polluntants depends on -
(a) Concentration of pollutants
(b) Duration of exposure
(c) Organism
(d) All the above
Answer : D
Question. In India, the Air (prevention and control of pollution) act, came in to force in -
(a) 1972
(b) 1981
(c) 198
(d) 1992
Answer : B
Question. Cl atoms released from CFC show degradation of ozone in which layer of atmoshpere -
(a) Trophosphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Ionosphere
(d) Thermosphere
Answer : B
Question. Which among the following is not the influence of UV-B on human health -
(a) Aging of skin
(b) Inflammation of cornea
(c) Cancer of skin
(d) Depigmentation
Answer : D
Question. Realising the significance of participation by local communities, the goverment of India in 1980s has introduced the concept of -
(a) Integrated Forest Management [IFM]
(b) Joint forest management [JFM]
(c) National Forest Policy
(d) Chipko movement
Answer : B
Ques. Which of the following is pollution related disorder?
(a) Silicosis
(b) Pneumonicosis
(c) Fluorosis
(d) Leprosis
Answer: C
Ques. Which of the following is the use of lichens in case of pollution?
(a) They promote pollution.
(b) Lichens are not related with pollution.
(c) They treat the polluted water.
(d) They act as bioindicators of pollutions.
Answer: D
Ques. The supersonic jets cause pollution by the thinning of
(a) O2 layer
(b) O3 layer
(c) CO2 layer
(d) SO2 layer.
Answer: B
Ques. Carbon monoxide is a pollutant because
(a) reacts with haemoglobin
(b) makes nervous system inactive
(c) it reacts with O2
(d) it inhibits glycolysis.
Answer: A
Ques. How carbon monoxide, emitted by automobiles, prevents transport of oxygen in the body tissues?
(a) By forming a stable compound with haemoglobin
(b) By obstructing the reaction of oxygen with haemoglobin
(c) By changing oxygen into carbon dioxide
(d) By destroying the haemoglobin
Answer: A
Ques. The Taj Mahal is threatened due to the effect of
(a) oxygen
(b) hydrogen
(c) chlorine
(d) sulphur dioxide.
Answer: D
Ques. The toxic effect of carbon monoxide is due to its greater affinity for haemoglobin as compared to oxygen approximately by
(a) 200 times
(b) 1000 times
(c) 2 times
(d) 20 times.
Answer: A
Ques. Sounds above what level are considered hazardous noise pollution?
(a) Above 80 dB
(b) Above 30 dB
(c) Above 150 dB
(d) Above 120 dB
Answer: D
Ques. Ultraviolet radiations from sunlight causes a reaction that produces
(a) fluorides
(b) carbon monoxide
(c) sulphur dioxide
(d) ozone.
Answer: D
Ques. Most hazardous metal pollutant of automobile exhausts is
(a) mercury
(b) cadmium
(c) lead
(d) copper.
Answer: C
Ques. Which one is not a pollutant normally?
(a) Hydrocarbon
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Carbon monoxide
(d) Sulphur dioxide
Answer: B
Ques. Acid rain is due to increase in atmospheric concentration of
(a) ozone and dust
(b) CO2 and CO
(c) SO3 and CO
(d) SO2 and NO2.
Answer: D
Ques. Major aerosol pollutant in jet plane emission is
(a) sulphur dioxide
(b) carbon monoxide
(c) methane
(d) fluorocarbon.
Answer: D
Ques. Acid rains are produced by
(a) excess NO2 and SO2 from burning fossil fuels
(b) excess production of NH3 by industry and coal gas
(c) excess release of carbon monoxide by incomplete combustion
(d) excess formation of CO2 by combustion and animal respiration.
Answer: A
Ques. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) may not be a good index for pollution for water bodies receiving effluents from
(a) domestic sewage
(b) dairy industry
(c) petroleum industry
(d) sugar industry.
Answer: C
Ques. A lake which is rich in organic waste may result in
(a) increased population of aquatic organisms due to minerals
(b) drying of the lake due to algal bloom
(c) increased population of fish due to lots of nutrients
(d) mortality of fish due to lack of oxygen.
Answer: D
Ques. The highest DDT concentration in aquatic food chain shall occur in
(a) phytoplankton
(b) seagull
(c) crab
(d) eel.
Answer: B
Ques. A river with an inflow of domestic sewage rich in organic waste may result in
(a) an increased production of fish due to biodegradable nutrients
(b) death of fish due to lack of oxygen
(c) drying of the river very soon due to algal bloom
(d) increased population of aquatic food web organisms.
Answer: B
Ques. Eutrophication of water bodies leading to killing of fishes is mainly due to non-availability of
(a) essential minerals
(b) oxygen
(c) food
(d) light.
Answer: B
Ques. Increase in concentration of the toxicant at successive trophic levels is known as
(a) biotransformation
(b) biogeochemical cycling
(c) biomagnification
(d) biodeterioration.
Answer: C
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : Secondary succession takes place in recently denuded area.
Reason : It is caused due to baring of an area.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Excess of nitrates in drinking water are harmful for infants.
Reason : Nitrates are responsible for blue baby syndrome.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Water pollutants are measured by BOD.
Reason : If BOD is more, the water is polluted.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Methane, component of green house gases, contributing to global warming is about 20 percent.
Reason : Introduction of multi-point fuel injection engines in automobiles has decreased methane content in the exhausts.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Eutrophication shows increase in productivity in water.
Reason : With increasing eutrophication, the diversity of the phytoplankton increases.
Answer : B
Short Answer Questions
Question. (a) Name any two places where it is essential to install electrostatic precipitators. Why it is required to do so?
(b) Mention one limitation of the electrostatic precipitator.
Answer. (a) It is essential to install electrostatic precipitators in thermal power plants and smelters to remove particulate matter.
(b) Limitation of the electrostatic precipitator:
(i) particulate matter less than 2.5 micrometres are not removed.
(ii) velocity of air between plates must be low enough to allow the dust to fall.
(iii) it cannot work without electricity. (Any one)
Question. (a) Why are the colourful polystyrene and plastic packaging used for protecting the food,considered an environmental menace?
(b) Write about the remedy found for the efficient use of plastic waste by Ahmed Khan of Bangalore.
Answer. (a) The colourful polystyrene and plastic packaging are non-biodegradable and non-ecofriendly.
(b) The remedy was found by developing polyblend, which is a fine powder of recycled modified plastic. Polyblend is mixed with bitumen to lay roads. This enhanced the water repellent property of bitumen and enhanced the life of roads.
Question. How does an algal bloom cause eutrophication of a water body? Name the weed that can grow in such a eutrophic lake.
Answer. Algal bloom in the lake or any other water body forms a scum. The scum depletes the oxygen in the water leading to foul smelling of the water body. The oxygen depletion affects the aquatic life adversely resulting in the death of fish and ultimately the eutrophic lake itself dies. Water hyacinth grows in such a eutrophic lake.
Question. (a) Name the green house gases that cause global warming.
(b) Which of them has caused ozone hole and how?
Answer. (a) CO2, CH4, N2O, chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs
(b) Ozone degradation has increased due to chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs are refrigerants which react with UV in stratosphere to release chloride atoms. Chloride atoms act as catalyst to degrade ozone and release molecular oxygen. CFCs have permanent and continued effect as chloride atoms are not consumed.
Question. Explain the relationship between green house gases and global warming.
Answer. Greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4, N2O, CFCs) allow the solar radiations to enter but prevent the escape of heat radiations of longer wavelength. The absorbed radiations again come to earth’s surface and heat it up. Increase in the level of these greenhouse gases allow the heat waves to reach earth but prevent their escape and thus the earth becomes warm. There is gradual continuous increase in average temperature of earths’ surface leading to global warming.
Question. Explain the relationship between CFCs and ozone in the stratosphere.
Answer. UV rays act on CFCs and release chlorine. These chlorine atoms act on ozone to release O2, resulting in ozone layer depletion.
Question. Name any one of the green house gases and its possible source of production on a large scale.
What are the harmful effects of it?
Answer. CO2 and Methane. CO2 levels are increasing due to burning of fossil fuel leading to global warming.
Question. How do chlorofluorocarbons destroy ozone layer?
Answer. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) break down in the presence of UV rays and produce active chlorine.
The chlorine atoms break down ozone into molecular O2, thereby depleting ozone layer.
Question. What is joint forest management? How can it help in conservation of forests?
Answer. Joint Forest Management (JFM) is a programme initiated by the Government of India in 1980 where government works closely with the local communities for protecting and managing forests.By this programme forests are conserved by locals in a sustainable manner as locals are also benefited with forest products like fruits, gum, rubber, medicines, etc.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Explain any three remedial measures to overcome the acute air pollution in our cities.
Answer. (i) Electrostatic precipitators to remove paritculate matter present in the exhaust from thermal power plant.
(ii) Scrubber to remove SO2 from the exhaust of thermal power plant.
(iii) Alternative sources of energy in place of petrol.
(iv) Lead-free petrol or diesel.
(v) Catalytic convertors - to reduce lead pollution.
(vi) Use of CNG.
(vii) Use of low sulphur petrol and diesel.
(viii) Phasing out of old vehicles and stringent enforcement of pollution level norms.
Question. (i) State the consequence if the electrostatic precipitator of a thermal plant fails to function.
(ii) Mention any four methods by which the vehicular air pollution can be controlled.
Answer. (i) Particulate matter will pollute the air.
(ii) Vehicular pollution can be controlled by:
In 1990’s Delhi ranked 4th among 41 most polluted cities of the world. A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) was filed in the Supreme Court.
- All buses of Delhi were converted to run on CNG by the end of 2002 as per the directives of the Supreme Court.
- Advantages of CNG over diesel/petrol:
(a) CNG burns most efficiently without leaving any unburnt remnant behind.
(b) CNG is cheaper than petrol or diesel.
(c) CNG cannot be siphoned off by thieves and adulterated like petrol or diesel.
- Some other steps to reduce vehicular pollution:
(a) Phasing out of old vehicles.
(b) Use of unleaded petrol.
(c) Use of low-sulphur petrol and diesel.
(d) Use of catalytic converters in vehicles.
Question. How does an electrostatic precipitator work to remove particulate pollutants released from the thermal power plants?
Answer. Electrostatic precipitator (ESP)
- It is an electrical device used to remove particulate matter present in the exhaust of thermal power plant.
- More than 99% particulate matter can be removed by this method.
- ESP has electrode wires and a stage of collecting plates.
- Electrode wires are provided with an electric current of several thousand volts, which produces a corona that releases electrons.
- These electrons attach to dust particles and give them a negative charge within a very small fraction of a second.
- Collecting plates are earthed so that they attract charged dust particles.
- The velocity of air passing through plates is slow enough to allow the dust particles to fall.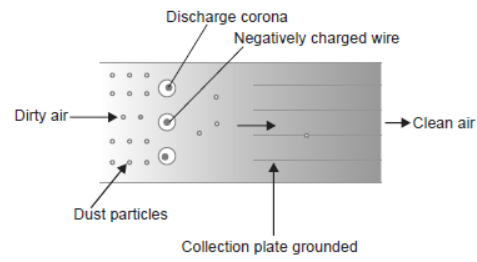
Question. By the end of 2002 the public transport of Delhi switched over to a new fuel. Name the fuel. Why is this fuel considered better? Explain.
Answer. The fuel was CNG or compressed natural gas. CNG is considered better because of the following reasons:
(i) CNG burns more efficiently unlike diesel or petrol.
(ii) Very little of it is left unburnt.
(iii) It cannot be adulterated.
(iv) It is cheaper than petrol or diesel.
Question. Write any three ways by which noise pollution affects the human body adversely. List any three steps that should be followed in order to reduce noise pollution.
Answer. Effects of noise pollution are: sleeplessness, increased heart beat, altered breathing pattern,damaged hearing ability and damaged ear drum (Any three)
Steps to be followed to reduce noise pollution:
(i) Following of stringent laws laid down in relation to noise level.
(ii) Delimitation of horn free zones around hospitals and schools.
(iii) To adopt permissible sound level of crackers and loudspeakers.
(iv) Adhereing to time limit for loudspeakers beyond which it cannot be played.
(v) Use of sound absorbent material in industries.
(vi) Muffling of noise. (Any three)
Question. Explain accelerated eutrophication. Mention any two consequences of this phenomenon.
Answer. Accelerated eutrophication is nutrient enrichment of water bodies due to human activities like passage of sewage.
Consequences are:
(i) Large amount of nutrients in water causes excessive growth of planktonic algae (called algal bloom) which impart characteristic colour to water bodies.
(ii) Depletion of oxygen content of water leading to the death of the aquatic organisms.
Question. Eutrophication is the natural aging of a lake. Explain.
Answer. Eutrophication is the natural aging of a lake by biological enrichment of its water. In a young lake, the water being cold and clear, does not support much life. But with time, streams draining into the lake introduce nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which encourage the growth of aquatic organisms. As the lake’s fertility increases, plant and animal life begins to develop and organic remains begin to be deposited on the lake’s bottom. Over the centuries, as silt and organic debris pile up, the lake grows shallower and warmer. Now, the warm water organisms replace those that live in a cold environment. Marsh plants take root in the shallows and begin to fill in the original lake basin. Eventually, the lake develops large masses of floating plants (bog), finally converting into land.
Question. Explain the cause of algal bloom in a water body. How does it affect an ecosystem?
OR
How does algal bloom destroy the quality of a fresh water body? Explain.
Answer. Domestic sewage and industrial effluents contains nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus which favour the excessive growth of planktonic (free-floating) algae.
Its harmful effects cause:
(i) sharp decline in dissolved oxygen content in the water.
(ii) deterioration of water quality and causes mortality of aquatic life forms.
(iii) distinct odour from the water bodies.
Question. Why is the concentration of toxins found to be more in the organisms occupying the highest trophic level in the food chain in a polluted water body? Explain with the help of a suitable example.
Answer. The concentration of toxic materials like heavy metals and pesticides increase at each trophic level of a food chain and is more in organisms of highest trophic level due to their accumulation at each trophic level. For example, when DDT was used to control mosquitoes in a lake of USA, 800 times more DDT was found in the phytoplanktons than in the water of the lake. Zooplanktons had about 13 times more DDT than phytoplanktons. It was also observed that the fishes population had 9–40 times more DDT than zooplanktons and fish eating birds had 25 times more DDT than fish.
Question. Explain the causes of global warming. Why is it a warning to mankind?
Answer. Causes of global warming:
(i) Deforestation
(ii) Rise in the concentration of greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4, CFCs, N2O).
(iii) Burning of fossil fuels
(iv) Rise in industrial wastes and pollutants.
Global warming is a warning to mankind because:
(i) Rise in temperature is leading to increased melting of polar ice-caps as well as of other places like the Himalayan snow caps. This will result in a rise in sea level that can submerge many coastal areas.
(ii) Deleterious changes in the environment results in odd weather and climate changes, e.g.,El Nino effect.
Question. Discuss the following:
(i) Chipko Movement
(ii) Scrubber
(iii) Radioactive wastes.
Answer.
(i) Chipko Movement: Chipko movement (Hug the Trees Movement) was an organised resistance to the destruction of forests. It started in 1974 in Reni village of Garhwal. A contractor was allowed to cut trees in a forest near the village. When the contractor’s workers appeared, the women of the village reached the forest quickly and clasped the tree trunks with their arms, preventing the workers from cutting down the trees. Mr. Sunder Lal Bahuguna, a Gandhian activist and philosopher was the leader of Chipko Movement.
(ii) Scrubber:
- It is used to remove gases like sulphur dioxide from industrial exhaust.
- The exhaust is passed through a spray of water or lime.
- Water dissolves gases and lime reacts with sulphur dioxide to form a precipitate of calcium
sulphate and sulphide.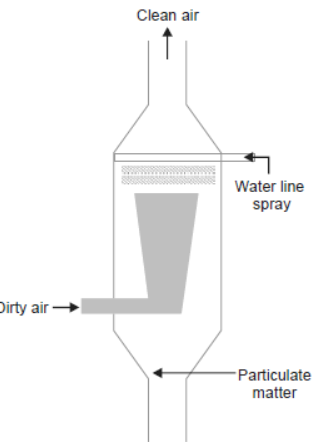
(iii) Radioactive wastes: Radioactive wastes such as uranium, are used as fuel in the atomic power plant. The accidental leakage and disposal of radioactive wastes are the most serious problems. All safety measures for this purpose should be strictly enforced. Highlevel radioactive wastes generate a lot of heat and thus require cooling, as well as special protective shield during handling and transport. Radiation, that is given off by nuclear wastes is extremely harmful to the organisms, because it causes mutation at a very high rate. At high doses, nuclear radiation is lethal but at lower doses, it creates various disorders, the most frequent of all being cancer. Therefore, nuclear waste is an extremely potent pollutant and has to be dealt with utmost caution.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set C |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 16 Environmental Issues which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 12 Assignments for chapter Chapter 16 Environmental Issues will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 16 Environmental Issues, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 16 Environmental Issues within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Biology mock tests for Chapter 16 Environmental Issues reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 16 Environmental Issues yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 16 Environmental Issues assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 16 Environmental Issues questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Biology Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Class 12 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Class 12 Biology

