Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Assignment Set B. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Biology. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Biology in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 Biology Assignment
Bacteriophage : A virus that infects bacteria.
Bioreactor : A large vessel in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products under optimal conditions such as temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen. Stirring type bioreactors are commonly used.
Biotechnology : It deals with techniques of using live organisms (Microbes, plants animals) or components for benefit to humans.
According to EFB (European Federation of Biotechnology) : Biotechnology in the integration of natural science and organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services.
Cloning Vectors : A small, self-replicating DNA molecule into which foreign DNA is inserted. It replicates inside the host cell. The vectors that may be used in genetic engineering are plasmids, bacteriophages, animal, plant, virus, YACS and BACs and insome yeasts.
Features of cloning vector: Origin of replication (Ori), selectable marker and cloning sites are the features that are required to facilitate cloning into a vector.
(a) Origin of Replication (Ori) : This is a sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells. This sequence is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.
(b) Selectable Marker : It is a gene which helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants from transformants (having recombinant DNA) by selectively permitting the growth of transformants. The process through which a piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium is called transformation. The genes encooling resistance to antibiotics are considered useful selectable marker for E.coli.
Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Biology Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Question. DNA cannot pass through cell membrane as it is :
(a) hydrophilic
(b) hydrophobic
(c) lipophilic
(d) All the above
Answer : A
Question. Which type of bioreactor is usually cylindrical or with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the contents?
(a) Sparged tank bioreactor
(b) Stirred tank bioreactor
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer : B
Question. In PCR-technology primer is a :
(a) Small chemically synthesized oligonucleotide that are complementary to region of DNA
(b) Large chemically synthesized oligonucleotide that are identical to region of DNA
(c) Small segment of RNA
(d) None of these
Answer : A
Question. In gel electrophoresis the DNA fragment separate according to their size through sieving effect, which is provided by :
(a) Agarose gel
(b) Nylone membrane
(c) Polyethylene glycol
(d) Ethidium Bromide
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following method of vectorless gene transfer is suitable for plants ?
(a) Biolistics method
(b) Micro injection
(c) Liposome mediated
(d) Electroporation
Answer : A
Question. The linking of antibiotic resistant gene in the plasmid vector become possible with the enzyme :
(a) Restriction endonuclease
(b) DNA ligase
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) RNA polymerase
Answer : B
Question. In gel electrophoresis, separated bands of DNA are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel pieces, This step is known as :
(a) Blotting
(b) Elution
(c) Cloning
(d) Tagging
Answer : B
Question. If the plasmid in the bacteria dose not have any insert then the colonies produce :
(a) Blue colour in the presence of X-gal
(b) No colour in the presence of X-gal
(c) Blue colour in the absence of X-gal
(d) None of the above
Answer : A
Question. The normal E-coli cell carries resistance gene against:
(a) Ampicillin
(b) Chloramphenicol
(c) Tetracycline
(d) None of the above
Answer : D
Question. Ti plasmid is present in :
(a) E.coli
(b) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(c) Agrobacterium orifaciens
(d) Vibrio cholerae
Answer : B
Question. Apart from DNA in the bacterial nucleoid, there is a circular extrachromosomal DNA in a bacterial cell called :
(a) Plasmid
(b) Mesosomes
(c) Chromosome
(d) None of these
Answer : A
Question. The DNA molecule to which the gene of interest is integrated for cloning is called
(a) template
(b) carrier
(c) transformer
(d) vector.
Answer: D
Question. The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of
(a) selectable markers
(b) ligases
(c) restriction enzymes
(d) probes.
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following is a case of wrong matching?
(a) Somatic – Fusion of two hybridization diverse cells
(b) Vector DNA – Site for tRNA synthesis
(c) Micropropagation – In vitro production of plants in large numbers
(d) Callus – Unorganised mass of cells produced in tissue culture
Answer: B
Question. Which one of the following techniques made it possible to genetically engineer living organisms?
(a) Recombinant DNA techniques
(b) X-ray diffraction
(c) Heavier isotope labelling
(d) Hybridization
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following are used in gene cloning?
(a) Nucleoids
(b) Lomasomes
(c) Mesosomes
(d) Plasmids
Answer: D
Question. Manipulation of DNA in genetic engineering became possible due to the discovery of
(a) restriction endonuclease
(b) DNA ligase
(c) transcriptase
(d) primase.
Answer: A
Question. The bacteria generally used for genetic engineering is
(a) Agrobacterium
(b) Bacillus
(c) Pseudomonas
(d) Clostridium.
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following is related to genetic engineering?
(a) Heterosis
(b) Mutation
(c) Plastid
(d) Plasmid
Answer: D
Question. Genetic engineering is possible, because
(a) we can cut DNA at specific sites by endonucleases like DNase I
(b) restriction endonucleases purified from bacteria can be used in vitro
(c) the phenomenon of transduction in bacteria is well understood
(d) we can see DNA by electron microscope.
Answer: B
Question. When scientists make an animal superior by view of genotype, introducing some foreign genes in it, is called
(a) immunization
(b) genetic engineering
(c) tissue culture
(d) biotechnology.
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following organelles is related with genetic engineering?
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Plasmids
(c) Golgi bodies
(d) Lysosomes
Answer: B
Question. Identify the wrong statement with regard to restriction enzymes.
(a) Each restriction enzyme functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence.
(b) They cut the strand of DNA at palindromic sites.
(c) They are useful in genetic engineering.
(d) Sticky ends can be joined by using DNA ligases.
Answer: D
Question. Choose the correct pair from the following.
(a) Ligases - Join the two DNA molecules
(b) Polymerases - Break the DNA into fragments
(c) Nucleases - Separate the two strands of DNA
(d) Exonucleases - Make cuts at specific positions within DNA
Answer: A
Question. The sequence that controls the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector, is termed
(a) selectable marker
(b) Ori site
(c) palindromic sequence
(d) recognition site.
Answer: B
Question. In gel electrophoresis, separated DNA fragments can be visualized with the help of
(a) acetocarmine in bright blue light
(b) ethidium bromide in UV radiation
(c) acetocarmine in UV radiation
(d) ethidium bromide in infrared radiation.
Answer: B
Question. Following statements describe the characteristics of the enzyme restriction endonuclease. Identify the incorrect statement.
(a) The enzyme recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA.
(b) The enzyme cuts DNA molecule at identified position within the DNA.
(c) The enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands.
(d) The enzyme cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone at specific sites on each strand.
Answer: C
Question. A selectable marker is used to
(a) help in eliminating the non-transformants, so that the transformants can be regenerated
(b) identify the gene for a desired trait in an alien organism
(c) select a suitable vector for transformation in a specific crop
(d) mark a gene on a chromosome for isolation using restriction enzyme.
Answer: A
Question. Given below are four statements pertaining to separation of DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis. Identify the incorrect statements.
(i) DNA is negatively charged molecule and so it is loaded on gel towards the anode terminal.
(ii) DNA fragments travel along the surface of the gel whose concentration does not affect movement of DNA.
(iii) Smaller the size of DNA fragment larger is the distance it travels through it.
(iv) Pure DNA can be visualized directly by exposing UV radiation.
Choose correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (i), (iii) and (iv) (b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv) (d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following is commonly used as a vector for introducing a DNA fragment in human lymphocytes?
(a) Retrovirus
(b) Ti plasmid
(c) λ phage
(d) pBR322
Answer: A
Question. The DNA fragments separated on an agarose gel can be visualised after staining with
(a) acetocarmine
(b) aniline blue
(c) ethidium bromide
(d) bromophenol blue.
Answer: C
Question. In genetic engineering, which of the following is used ?
(a) Plasmid
(b) Plastid
(c) Mitoch ondria
(d) E.R.
Answer. A
Question. Introduction of foreign gene for improving genotype is called
(a) tissue culture
(b) vernalization
(c) genetic engineering
(d) eugenics
Answer. C
Question. An example of gene therapy is
(a) production of injectable hepatitis B vaccine.
(b) production of vaccines in food crops like potatoes which can be eaten.
(c) introduction of gene for adenosine deaminase in persons suffering from Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency (SCID).
(d) production of test tube babies by artificial insemination and implantation of fertilized eggs.
Answer. C
Question. What is the first step in the Southern blot technique?
(a) Denaturation of DNA on the gel for hybridization with specific probe.
(b) Production of a group of genetically identical cells.
(c) Digestion of DNA by restriction enzyme.
(d) Denaturation of DNA from a nucleated cell such as the one from the scene of crime.
Answer. C
Question. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology was discovered by
(a) Karry Mullis
(b) Saiki et al
(c) Craig Venter
(d) Maxam and Gilbert
Answer. A
Question. After 4 PCR cycles how many DNA molecules are formed from one DNA template molecule ?
(a) 4
(b) 32
(c) 16
(d) 8
Answer. C
Question. Human Genome Project (HGP) is closely associated with the rapid development of a new area in biology called as
(a) biotechnology
(b) bioinformatics
(c) biogeography
(d) bioscience
Answer. B
Question. Identify the correct match for the given apparatus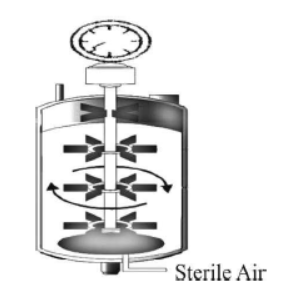
Apparatus Function
(a) Gene gun Vectorless direct gene transfer
(b) Column chromatograph Separation of chlorophyll pigments
(c) Stirred tank bioreactor Carry out fermentation process
(d) Respirometer Finding out rate of respiration
Answer. C
Question. Genes of interest can be selected from a genomic library by using
(a) Restriction enzymes
(b) Cloning vectors
(c) DNA probes
(d) Gene targets
Answer. C
Assertion Reason Questions
Directions : These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following five responses.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
(e) If the Assertion is incorrect but the Reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : Plasmids are extrachromosomal DNA.
Reason : Plasmids are found in bacteria and are useful in genetic engineering.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion: Plasmids are single-stranded extra chromosomal DNA.
Reason: Plasmids are usually present in eukaryotic cells.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion: Clones are produced by sexual reproduction.
Reason: These are prepared by group of cells descended from many cells or by inbreeding of a heterozygous line.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : In recombinant DNA technology human genes are often transferred into bacteria (prokaryotes) or yeast (eukaryote).
Reason : Both bacteria and yeast multiply very fast to form huge population which expresses the desired gene.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Agrobacterium tumefaciens is popular in genetic engineering because this bacterium is associated with the roots of all cereal and pulse crops.
Reason : A gene incorporated in the bacterial chromosomal genome-gets automatically transferred to the crop with which the bacterium is associated.
Answer. D
Case-based MCQs
I. Read the following and answer questions from given below :
Restriction endonuclease was isolated for the first time by W. Aber in 1962 in bacteria. Restriction endonucleases cut the DNA duplex at specific points therefore they are also called as molecular scissors or biological scissors. Three types of restriction endonucleases are Type I, Type II and Type III. Restriction endonuclease EcoR I recognises the base sequence GAATTC in DNA duplex and cut strands between G and A.
Question. Restriction endonucleases are also called as molecular or biological scissors because :
(A) They cleave base pairs of DNA only at their terminal ends.
(B) They cleave one or both the strands of DNA.
(C) They act only on single stranded DNA.
(D) None of these.
Answer : B
Question. Only type II restriction enzymes are used in gene manipulation because :
(A) ATP is not required for cleaving.
(B) It consists of three different subunits.
(C) It makes cleavage or cut in both the strands of DNA molecule.
(D) Both (A) and (C).
Answer : D
Question. Restriction endonuclease was isolated for the first time from a :
(A) Plant cell
(B) Animal cell
(C) Prokaryotic cell
(D) Germinal cell
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following ions are used by restriction endonucleases for restriction?
(A) Mg²+ ions
(B) Mn2+ ions
(C) Na+ions
(D) K+ions
Answer : A
Question. Which type of restriction endonucleases is used mostly in genetic engineering?
(A) Type I
(B) Type II
(C) Type III
(D) Type IV
Answer : B
II. A schematic representation of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) up to the extension stage is given below.
Question. Name the process ‘a’
(A) Termination
(B) Annealing
(C) Denaturation
(D) Extension
Answer : C
Question. PCR technique is best for :
(A) DNA synthesis
(B) Protein amplification
(C) DNA amplification
(D) DNA ligation.
Answer : C
Question. Identify ‘b’
(A) Termination
(B) Annealing primer
(C) Denaturation
(D) Extension
Answer : B
Question. Which among the following is not an application of PCR ?
(A) ELISA
(B) Diagnosis of pathogens
(C) DNA fingerprinting
(D) In palaeontology.
Answer : B
Question. How many DNA duplex is obtained from one DNA duplex after 3 cycles of PCR?
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 8
(D) 16
Answer : C
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How is copy number of the plasmid vector related to yield of recombinant protein?
Answer. The recombinant DNA can multiply as many times as the copy number of the vector plasmid thereby determining the yield of recombinant protein. So, higher the copy number of plasmid vector, higher the copy number of gene and consequently, protein coded by the gene is produced in high amount.
Question. Mention the uses of cloning vector in biotechnology.
Answer. Cloning vectors are used for transferring fragments of foreign DNA into a suitable host. They are also used to select recombinants from non-recombinants.
Question. What is the function of restriction enzyme?
Answer. To cut DNA at specific site.
Question. What are palindromes?
Answer. Palindromes are group of letters (sequences) that read same both in forward and backward direction.
Question. What is recombinant DNA?
Answer. Recombinant DNA is the DNA formed by combining DNAs from two different organisms.
Question. Would you choose an exonuclease, while producing a recombinant DNA molecule?
Answer. No, as exonuclease acts on the free ends of linear DNA molecule. Therefore, instead of producing DNA fragments with sticky ends, it will shorten or completely degrade the DNA fragment containing the gene of interest and the circular plasmid (vector) will not get cut as it lacks free ends.
Question. What does H in ‘d’ and III refer to the enzyme Hind III?
Answer. (i) The first letter ‘H’ indicates the genus of the organism from which the enzyme was isolated, H = genus Haemophilus.
(ii) The fourth letter d indicates the particular strain used to produce the enzyme,d = strain Rd.
(iii) The Roman numerals denoted the sequence in which the restriction endonuclease enzyme from that particular genus, species and strain of bacteria have been isolated-III, i.e., third restriction endonuclease to be isolated from this species.
Question. Restriction enzymes should not have more than one site of action in the cloning site of a vector. Comment.
Answer. If the restriction enzymes have more than one recognition site in a vector, then the vector itself will get fragmented on treatment with the restriction enzymes.
Question. What does ‘competent’ refer to in competent cells used in transformation experiments?
Answer. DNA being a hydrophilic molecule can not pass through cell membranes. Therefore, the bacteria should be made competent to accept the DNA molecules.
Competent means bacterial cells, on treatment with chemicals likeCaCl2, are made capable of taking up foreign DNA.
Question. What is the significance of adding proteases at the time of isolation of genetic material (DNA)?
Answer. Proteases degrade the proteins present inside a cell (from which DNA is being isolated).
If the proteins are not removed from DNA preparation then they could interfere with any downstream treatment of DNA.
Question. While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Answer. If denaturation of double-stranded DNA does not take place then primers will not be able to anneal (joining) to the template. Hence, no extension will take place and after are there will be no amplification.
Question. Name a recombinant vaccine that is currently being used in vaccination program.
Answer. Hepatitis-B recombinant vaccine (engerix) is used for vaccination of hapatitis virus.
Question. Do biomolecules (DNA and protein) exhibit biological activity in anhydrous conditions?
- Thinking Process
Water is critical not only for the correct folding of proteins but also for the maintenance of the structure of DNA and protein.
Answer. Biomolecules (DNA, and protein) exhibit change in biological activity in anhydrous conditions, In non-aqueous or anhydrous conditions the rigidity of protein and DNA increases due to the weakening of hydrogen bond strength.
It results into the change in overall free energy, which is the combined effects of the exposure of the interior polar and non-polar groups and their interaction with water.
In absence of aqueous condition, the free energy change is negative, which is responsible for the denaturation of biomolecules.
Increasing strength of hydrogen-bond causes water to primarily bond with itself and not to be available for the hydrating structure of proteins or DNA, or for dissolving ions.
On the other hand, if the water-water hydrogen bond strength reduces then the exchange mechanisms operating within the cell, such as hydrogen bonded water chains within and between proteins and DNA, will become non-operational. It will further leads to the denaturation.
Question. What modification is done on the Ti-plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to convert it into a cloning vector?
- Thinking Process
T-DNA is the only essential part required to make Ti-plasmid a cloning vector.
Answer. The plasmid is disarmed by deleting the tumour inducing genes in the plasmid. So, that it become an effective cloning vector. The modified tumour inducing (Ti) plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens will no longer remain pathogenic to the plants but still deliver genes of interest into a variety of plants.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is meant by gene cloning?
Answer. Gene cloning refers to a process in which a gene of interest is ligated to a vector. The recombinant DNA thus produced is introduced in a host cell by transformation.
Each cell gets one DNA molecule and when the transformed cell grows to a bacterial colony, each cell in the colony has a copy of the gene. This is gene cloning.
Question. Both a wine maker and a molecular biologist who had developed a recombinant vaccine claim to be biotechnologists. Who in your opinion is correct?
Answer. In my opinion both of them are correct. As biotechnology is a very wide area which deals with techniques of using a ‘natural’ organism (or its parts) as well as genetically modified organism to produce and processes useful for mankind.
A wine maker employs a strain of yeast to produce wine by fermentation (a natural phenomenon), while the molecular biologist has cloned gene for the antigen (that is used as vaccine) in an organism which allows the production of the antigen in large amount.
Question. A recombinant DNA molecule was created by ligating a gene to a plasmid vector. By mistake, an exonuclease was added to the tube containing the recombinant DNA. How does this affect the next step in the experiment,i.e., bacterial transformation?
- Thinking Process
Bacterial transformation is the process by which bacterial cells take up naked DNA molecules (exogenous or foreign DNA).
Answer. The experiment will not likely to be affected as recombinant DNA molecule is circular and closed, with no free ends. Hence, it will not be a substrate for exonuclease enzyme which removes nucleotides from the free ends of DNA.
Question. Restriction enzymes that are used in the construction of recombinant DNA are endonucleases which cut the DNA at ‘specific’-recognition sequence?
What would be the disadvantage if they do not cut the DNA at specific-recognition sequence?
Answer. If the restriction enzymes would cut DNA at random sites instead of at specific sites, then the DNA fragments obtained will not have ‘sticky ends’. In the absence of sticky ends, construction of recombinant DNA molecule would not be possible.
Question. A plasmid DNA and a linear DNA (both are of the same size) have one site for a restriction endonuclease. When cut and separated on agarose gel electrophoresis, plasmid shows one DNA b and, while linear DNA shows two fragments. Explain.
Answer. When a plasmid DNA and a linear DNA having one site for a restriction endonuclease are cut and separated, plasmid shows one DNA band, while linear DNA shows two band because of difference in their basic structure.
Plasmid is a circular DNA molecule and when cut with these enzyme, it becomes linear but does not get fragmented due to presence of only one restriction site, whereas a linear DNA molecule gets cut into two fragment.
Question. How does one visualise DNA on an agarose gel?
Answer. A compound called ethidium bromide stains DNA, which on exposure with ultra-violet, (uv) radiation gives orange light band of DNA. Hence, DNA fragments appear as orange band in the presence of ethidium bromide and UV light.
Question. A plasmid without a selectable marker was choosen as vector for cloning a gene. How does this affect the experiment?
Answer. In a gene cloning experiment, first a recombinant DNA molecule is constructed, where the gene of interest is ligated to the vector (the step would not be affected) and introduced inside the host cell (transformation).
Since, not all the cells get transformed with the recombinant/plasmid DNA, in the absence of selectable marker, it will be difficult to distinguish between transformants and non-transformant, because role of selectable marker is in the selection of transformants.
Question. A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in an agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed.
What could be the reason?
Answer. The reasons are as follows
(i) DNA sample that was loaded on the gel may have got contaminated with nuclease (exo or endo both) and completely degraded.
(ii) Electrodes were put in opposite orientation in the gel assembly that is anode towards the wells (where DNA sample is loaded). Since, DNA molecules are negatively charged, they move towards anode and hence, move out of the gel instead of moving into the matrix of gel.
(iii) Ethidium bromide was not added at all or was not added in sufficient concentration and so DNA was not visible.
Question. Describe the role of CaCl2 in the preparation of competent cells?
Answer. CaCl2 is known to increase the efficiency of DNA uptake to produce transformed bacterial cells. The divalent Ca+2 ions create transient pores on the bacterial cell wall by which the entry of foreign DNA is facilitated into the bacterial cells.
Question. What would happen when one grows a recombinant bacterium in the bioreactor but forget to add antibiotic to the medium in which the recombinant is growing?
Answer. In the absence of antibiotic, there will be no pressure on recombinants to retain the plasmid (containing the gene of our interest). Since, maintaining a high copy number of plasmids is a metabolic burden to the microbial cells, it will thus tend to loose the plasmid.
Question. How does a restriction nuclease function? Explain.
Answer. Restriction nuclease cuts DNA at specific sites. Nucleases are of two types exonuclease and endonuclease.
Exonuclease cuts DNA at the ends, whereas endonuclease cuts at specific sites within DNA.
Question. Explain the work carried out by Cohen and Boyer that contributed immensely in biotechnology.
Answer. Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer in 1972 constructed the first recombinant DNA. They isolated the antibiotic resistance gene by cutting out a piece of DNA from the plasmid of a bacterium which was responsible for conferring antibiotic resistance. The cut piece of DNA was then linked with the plasmid DNA of Salmonella typhimurium and transferred to E. coli for transformation.
Question. A vector is engineered with three features which facilitate its cloning within the host cell. List the three features and explain each one of them.
Answer. (i) Origin of replication/ori site—From here the replication starts (and any piece of DNA when linked, can be made to replicate within the host cell).
(ii) At least two Selectable markers—Helpful in identifying and eliminating non-transformants.
(iii) Unique Restriction sites for more than one restriction enzymes—The foreign DNA links to this region of the plasmid.
Question. How is DNA isolated in purified form from a bacterial cell?
Answer. DNA, a genetic material is isolated in purified form by treating the bacterial cells with the enzymes such as lysozyme to remove the cell wall. The RNA thus released can be removed by treating them with ribonuclease and enzyme proteases is added to remove proteins. Finally, chilled ethanol is added to precipitate the purified DNA.
Question. What is meant by gene cloning?
Answer. Gene cloning refers to a process in which a gene of interest is ligated to a vector. The recombinant DNA thus produced is introduced in a host cell by transformation. Each cell gets one DNA molecule and when the transformed cell grows to a bacterial colony, each cell in the colony has a copy of the gene.
Question. Is there any difference between recombinant DNA and recombinant protein? Support your answer.
Answer. rDNA is the plasmid vector containing the foreign DNA whereas recombinant protein is the product of transgenic gene in the host body or cell.
Question. (a) Mention the difference in the mode of action of exonuclease and endonuclease.
(b) How does restriction endonuclease function?
Answer. (a) Exonuclease removes nucleotides from the ends of DNA whereas endonuclease cuts at specific positions within DNA at specific positions.
(b) Restriction endonuclease recognises and cuts specific palindromic nucleotide sequences in the DNA.
Question. Where and why do we use Taq polymerase enzyme when it works exactly as DNA polymerase?
Answer. In PCR, because it is a thermostable DNA polymerase enzyme, is isolated from bacteria Thermus aquaticus from hot water springs, and it does not get denatured at high temperature which is required during PCR and works as normal DNA polymerase enzyme (whereas the normal DNA polymerase gets denatured at high temperature).
Question. Name the most commonly used bioreactor and describe its working.
Answer. The most commonly used bioreactor is stirred-tank bioreactor.A stirred-tank bioreactor is usually cylindrical and have a stirrer which mixes the reactor contents evenly and makes oxygen available throughout the bioreactor. Optimum conditions of temperature, pH and foam control are provided.
Question. Describe the role of CaCl2 in preparation of competent cells.
Answer. CaCl2 is known to increase the efficiency of DNA uptake to produce transformed bacterial cells.The divalent Ca2+ ions supposedly create transient pores in the bacterial cell wall, by which the entry of foreign DNA is facilitated into the bacterial cells.
Question. What is the significance of adding proteases at the time of isolation of genetic material (DNA)?
Answer. Role of proteases is to degrade the proteins present inside a cell (from which DNA is being isolated). If the proteins are not removed from DNA preparation then they could interfere with any downstream treatment of DNA.
Question. Write the use of the following in biotechnology.
(a) Chilled ethanol (b) Microinjection
(c) Bioreactor (d) Plasmid
Answer. (a) It is added to precipitate the purified DNA to isolate it.
(b) It is used to inject the foreign gene into a host cell, directly.
(c) It is the set up to culture large volumes of transgenic bacteria to get large quantities of the product protein.
(d) It is the vector to transform a foreign gene.
Question. Write the role of ‘ori’ and ‘restriction’ site in a cloning vector pBR322.
Answer. ori is the site where replication starts. This site is responsible for controlling the copy number of linked DNA. If we want to produce many copies of target DNA, we should clone in a vector whose ori supports high copy number.
Restriction site is the site of ligation of alien/foreign DNA in the vector, in one of the two antibiotic resistance site or coding sequence of a-galactosidase.
Question. What does ‘competent’ refer to in competent cells used in transformation?
Answer. Competent means bacterial cells which by various methods like treatment with CaCl2 are made capable of taking up foreign DNA.
Question. Name the source organism from which Ti plasmid is isolated. Explain the use of this plasmid in biotechnology.
Answer. Ti plasmid is isolated from Agrobacterium tumifaciens. Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens has been modified into a cloning vector, which is not pathogenic to plants but still is able to use the mechanisms to deliver genes of interest into plants.
Question. Why is Agrobacterium tumifaciens a good cloning vector? Explain.
Answer. Agrobacterium tumifaciens is a soil bacterium which causes disease in many dicot plants. It is able to deliver a piece of DNA known as T-DNA, to transform the normal cells into tumour cells and direct these tumour cells to produce the chemicals required by the pathogen. The tumour inducing (Ti) plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens has now been modified into a cloning vector which is no more pathogenic to the plants but still deliver genes of interest into a variety of plants.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. For selection of recombinants, insertional inactivation of antibiotic marker has been supercoded by insertional inactivation of a marker gene
coding for a chromogenic substrate. Give reasons.
Answer. In selection of recombinants due to inactivation of antibiotics, the transformed cells are first plated on the antibiotic plate which has not been insertionally inactivated (i.e., ampicillin) and incubated overnight for growth of transformants.
For selection of recombinants, these transformants are replica-plated on second antibiotic (say, tetracycline) plate (which got inactivated due to insertion of gene). Non-recombinants grow on both the plates (one carrying ampicillin and the other carrying tetracycline) while recombinants will grow only on ampicillin plate.This entire exercise is
labourious and takes more time (two overnight incubation) as well.
However, if we choose insertional inactivation of a marker that produces colour in the presence of a chromogenic compound, we can distinguish between the recombinants and non-recombinants on a single medium plate (containing one antibiotic and the chromogenic compound) after overnight growth.
Question. Describe the role of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in transforming a plant cell.
Answer. A soil-inhabiting, plant pathogenic bacterium, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, infects broad-leaved crops including tomato, soyabean, sunflower and cotton, but not the cereals. It causes tumours called crown galls.
Tumour formation is induced by its plasmid, which is, therefore called Ti-plasmid (Ti for tumour inducing). The Ti-plasmid integrates a segment of its DNA, termed T-DNA,
into the chromosomal DNA of its host plant cells. The T-DNA causes tumours. As gene transfer occurs without human effort, the bacterium is known as natural genetic engineer of plants.
Plant molecular biologists have started using Ti-plasmids as vectors to transfer foreign genes of interest into the target plant cells. They use a version of the plasmid from which tumour forming gene has been eliminated. The transformed bacteria do not cause disease, but still deliver genes of interest into a variety of plants.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set C |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 12 Assignments for chapter Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Biology mock tests for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Biology Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 Biology

