Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Assignment Set A. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Biology. Class 12 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 6 Evolution Biology in Class 12 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 6 Evolution in Class 12. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 6 Evolution Class 12 Biology Assignment
Question. Development of different functional structures from a common ancestral form is called
(a) differential evolution
(b) adaptive radiation
(c) non-adaptive radiation
(d) regressive evolution
Answer : B
Question. The process by which different type of finches were evolved in Galapagos islands is a consequence of
(a) adaptive radiation
(b) geographic similarity
(c) geographic dissimilarity
(d) adaptive convergence
Answer : A
Question. The diversity in the type of finches and adaptation to different feeding habits on the Galapagos islands, as observed by Darwin, provides an evidence of
(a) origin of species by natural selection
(b) intraspecific variation
(c) intraspecific competition
(d) interspecific competition
Answer : A
Question. What does presence of homologous organs in different animals indicate?
(a) Different ancestry
(b) Common ancestry
(c) Independent development
(d) Dependent development
Answer : B
Question. Which concept was not included in Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection?
(a) Survival of the fittest
(b) Struggle for existence
(c) Overproduction of offspring
(d) Punctuated equilibrium
Answer : D
Question. What is the difference between natural selection and sexual selection?
(a) Sexual selection occurs during sexual intercourse
(b) Natural selection is a type of sexual selection
(c) Sexual selection is an example of natural selection
(d) Sexual selection occurs within demes
Answer : C
Question. Tendrils of Cucurbita and thorns of Bougainvillea are examples of
(a) vestigial organs
(b) analogous organs
(c) homologous organs
(d) homoplasy
Answer : C
Question. Which one of the following options gives one correct example each of convergent evolution and divergent evolution? 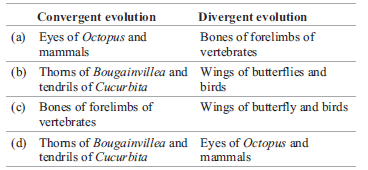
Answer : A
Question. During which period did the first seed plant appear?
(a) Silurian
(b) Devonian
(c) Carboniferous
(d) Cretaceous
Answer : B
Question. The Cenozoic era is often designated as
(a) age of fish
(b) age of reptiles
(c) age of mammals
(d) age of amphibians
Answer : C
Question. In which era Protozoa, sponge and algae originate?
(a) Cenozoic era
(b) Azoic era
(c) Proterozoic era
(d) Mesozoic era
Answer : C
Question. What was the most significant trend in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors?
(a) Shortening of jaws
(b) Binocular vision
(c) Increasing brain capacity
(d) Upright posture
Answer : C
Question. Who used hides to protect their body and buried their dead?
(a) Neanderthal man
(b) Homo habilis
(c) Australopithecus
(d) Dryopithecus
Answer : A
Question. The correct order of evolutionary scale is
(a) Palaeozoic → Archaeozoic → Cenozoic
(b) Archaeozoic → Palaeozoic → Proterozoic
(c) Palaeozoic → Mesozoic → Cenozoic
(d) Mesozoic → Archaeozoic → Proterozoic
Answer : C
Question. First dinosaurs and first egg-laying mammals originated in
(a) Jurassic period
(b) Triassic period
(c) Permian period
(d) Cambrian period
Answer : B
Question. Identify the geographical periods (A, B, C) in the given diagram.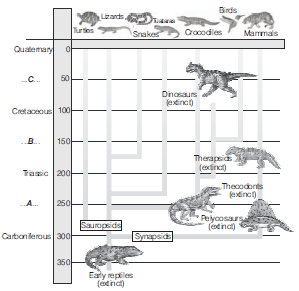
(a) A–Tertiary, B–Jurassic, C–Permian
(b) A–Tertiary, B–Permian, C–Jurassic
(c) A–Permian, B–Jurassic, C–Tertiary
(d) A–Jurassic, B–Tertiary, C–Permian
Answer : C
Question. Choose the incorrectly matched pair.
(a) Reptiles — Thick-shelled eggs which do not dry up
(b) Tyrannosaurus rex — Fish like reptile
(c) Dinosaurs — May be evolved into birds
(d) Continental drift — South America joined North-America
Answer : B
Question. The first viviparous mammals whose fossils are small-sized were like
(a) shrews
(b) monkeys
(c) rats
(d) lobefins
Answer : A
Question. In which epoch, only modern humans prevail?
(a) Pleiostocene
(b) Holocene
(c) Pliocene
(d) Miocene
Answer : B
Question. Which phenomena confined the pouched mammals to Australia they survived because of lack of competition from any other mammals?
(a) Continental origination
(b) Continental shifting
(c) Continental drift
(d) Continental evolution
Answer : C
Question. Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) Ramapithecus – Man-like
(b) Dryopithecus – Ape-like
(c) Fossil of man-like bones were discovered – Ethopia and Tanzania
(d) Australopithecus – Probably lived in Western Africa desert
Answer : B
Question. First human like hominid is known as
(a) Neanderthal man
(b) Homo habilis
(c) Dryopithecus
(d) Homo erectus
Answer : B
Question. Brain (cranial) capacity of Homo habilis was
(a) 750-850 cc
(b) 750-800 cc
(c) 650-800 cc
(d) 550-700 cc
Answer : C
Question. The fossil finding suggest that closest fossil to Homo habilis was
(a) Homo erectus
(b) Homo sapiens
(c) Dryopithecus
(d) Neanderthal man
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following is an extinct animal?
(a) Protopterus
(b) Equus
(c) Archaeopteryx
(d) Columba
Answer : C
Question. Mesozoic era is called the age of
(a) fishes
(b) amphibians
(c) reptiles
(d) birds
Answer : C
Question. The most recent era in geological time scale is
(a) Mesozoic
(b) Cenozoic
(c) Palaeozoic
(d) Proterozoic
Answer : B
Question. The extinct human who lived 10,00,00 to 40,000 years ago, in Europe, Asia and parts of Africa, with short stature, heavy eyebrows, retreating fore heads,large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait and stooped posture was
(a) Homo habilis
(b) Neanderthal human
(c) Cro-Magnon human
(d) Ramapithecus
Answer : B
Question. Homo sapiens, neanderthalensis and Cro-Magnon man, probably originated from
(a) Homo erectus
(b) Homo habilis
(c) Ramapithecus
(d) Proconsul
Answer : A
Question. The difference between Homo sapiens and Homo erectus was
(a) Homo sapiens originated in Africa, while Homo erectus originated in Asia
(b) Homo erectus were much smaller in size than Homo sapiens
(c) Homo erectus stayed in Africa, while Homo sapiens did not
(d) the size of the brain of Homo erectus was smaller than that of Homo sapiens
Answer : D
Question. Who was more intelligent than modern man,cave-dweller, had prominent chin and appeared after neanderthal man?
(a) Erect man
(b) Cro-Magnon man
(c) Hominid tool maker
(d) First ape man
Answer : B
Question. Homo sapiens most likely arose in
(a) India
(b) America
(c) England
(d) Africa
Answer : D
Question. Homo sapiens arose during
(a) ice age between 75000-10000 years ago
(b) continental drift between 75000-10000 years ago
(c) continental drift between 75000-5000 years ago
(d) ice age between 50000-10000 years ago
Answer : A
Question. Stellar distance is measured in :
(a) Kilometer
(b) Light years
(c) Per socond
(d) None
Answer : B
Question. When more than one adaptive radiation appeared to have occurred in an isolated geographical area, it is called as :
(a) Divergent evolution
(b) Convergent evolution
(c) Parallel evolution
(d) Continental drift
Answer : B
Question. Out of the following which is an example of convergent evolution ?
(A) Eyes of octopus and mammals
(B) Flippers of penguins and Dolphins
(C) Sweet potato and potato
(a) A and C
(b) A and B
(c) B and C
(d) A, B and C
Answer : D
Question. What was the food habit of the original variety of Darwin's finches from which many other varieties were developed ?2
(a) Seed eater
(b) Cactus eater
(c) Wood pecker
(d) Fruit eater
Answer : A
Question. What were two main key points of Darwinian theory of natural selection ?
(a) Branching descent
(b) Natural selection
(c) Fitness
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer : D
Question. During evolution the first cellular form of life appeared before how many million years ?
(a) 2000
(b) 400
(c) 100
(d) 50
Answer : A
Question. The biggest dinosour, which appeared during evolution was :
(a) Thecodont
(b) Stegosaurus
(c) Triceratops
(d) Tyrannosaurus rex
Answer : D
Ques. What was the most significant trend in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors?
(a) Shortening of jaws
(b) Binocular vision
(c) Increasing cranial capacity
(d) Upright posture
Answer: C
Ques. The extinct human who lived 1,00,000 to 40,000 years ago, in Europe, Asia and parts of Africa, with short stature, heavy eye brows, retreating fore heads, large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait and stooped posture was
(a) Homo habilis
(b) Neanderthal human
(c) Cro-magnon human
(d) Ramapithecus.
Answer: B
Ques. The most apparent change during the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens is traced in
(a) loss of body hair
(b) walking upright
(c) shortening of the jaws
(d) remarkable increase in the brain size
Answer: D
Ques. There are two opposing views about origin of modern man. According to one view Homo erectus in Asia were the ancestors of modern man. A study of variation of DNA however suggested African origin of modern man. What kind of observation on DNA variation could suggest this?
(a) Greater variation in Asia than in Africa
(b) Greater variation in Africa than in Asia
(c) Similar variation in Africa and Asia
(d) Variation only in Asia and no variation in Africa
Answer: B
Ques. What kind of evidence suggested that man is more closely related with chimpanzee than with other hominoid apes?
(a) Evidence from DNA extracted from sex chromosomes only
(b) Comparison of chromosomes morphology only
(c) Evidence from fossil remains, and the fossil mitochondrial DNA alone
(d) Evidence from DNA extracted from sex chromosomes, autosomes.
Answer: D
Ques. In recent years, DNA sequences (nucleotide sequence) of mtDNA and Y chromosomes were considered for the study of human evolution, because
(a) they are small and therefore, easy to study
(b) they are uniparental in origin and do not take part in recombination
(c) their structure is known in greater detail
(d) they can be studied from the samples of fossil remains.
Answer: B
Ques. According to fossils discovered up to present time origin and evolution of man started from
(a) France
(b) Java
(c) Africa
(d) China.
Answer: C
Ques. Which of the following is closest relative of man?
(a) Chimpanzee
(b) Gorilla
(c) Orangutan
(d) Gibbon
Answer: A
Ques. Which of the following is correct order of the evolutionary history of man?
(a) Peking man, Homo sapiens, Neanderthal man, Cromagnon man
(b) Peking man, Heidelberg man, Neanderthal man, Cromagnon man
(c) Peking man, Neanderthal man, Homo sapiens, Cromagnon man
(d) Peking man, Neanderthal man, Homo sapiens, Heidelberg man
Answer: B
Ques. Homo sapiens have evolved in
(a) Paleocene
(b) Pleistocene
(c) Oligocene
(d) Holocene.
Answer: D
Ques. Character which is closely related to human evolution is
(a) disappearance of tail
(b) reduction in size of jaws
(c) binocular vision
(d) flat nails.
Answer: A
Ques. Who is directly related to man?
(a) Gorilla
(b) Rhesus
(c) Gibbon
(d) Orangutan
Answer: A
Ques. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Australopithecus is the real ancestor of modern man.
(b) Neanderthal man is the direct ancestor of Homo sapiens.
(c) Homo erectus is the ancestor of man.
(d) Cro-magnon man’s fossil has been found in Ethiopia.
Answer: C
Ques. The age of the fossil of Dryopithecus on the geological time scale is
(a) 2.5 × 106 years back
(b) 50 × 106 years back
(c) 75 × 106 years back
(d) 25 × 106 years back.
Answer: A
Ques. Which of the following statements is correct regarding evolution of mankind?
(a) Homo erectus is preceded by Homo habilis.
(b) Neanderthal man and cro-magnon man were living at the same time.
(c) Australopithecus was living in Australia.
(d) None of these
Answer: A
Ques. Common origin of man and chimpanzee is best shown by
(a) binocular vision
(b) chromosome number
(c) dental formula
(d) cranial capacity.
Answer: D
Ques. Which of the following changes for man in the course of evolution is probably useless?
(a) Development of being erect
(b) Development of cranial capacity
(c) Loss of tail
(d) Development of opposable thumb
Answer: C
Ques. Which of the following is the direct ancestor of Homo sapiens?
(a) Australopithecus
(b) H. sapiens neanderthals
(c) Homo erectus
(d) Homo sapiens fossilis
Answer: D
Ques. The first domesticated animal by primitive man was
(a) cat
(b) cow
(c) dog
(d) horse.
Answer: C
Ques. Which one of the following changes involved is irrelevant, in the evolution of man?
(a) Perfection of hand for tool making
(b) Change of diet from hard nuts and hard roots to soft food
(c) Loss of tail
(d) Increase in the ability to communicate with others and develop community behaviour
Answer: B
Question. During natural selection which variety of Bistonbetularia was completely wiped out from England?
(a) White winged moth
(b) Dark winged moth
(c) Both of them
(d) None of them
Answer : D
Question. In which type of natural selection the peak gets higher and narrower ?
(a) Stabilising selection
(b) Directional selection
(c) Disruptive selection
(d) None of these
Answer : A
Question. Fore limbs of whale, bat, cheetah and human are example of :
(a) Analogous organs
(b) Homologous organs
(c) Homoplastic organs
(d) Vestigial organs
Answer : B
Question. Tasmanian Wolf, Tiger Cat, Sugar glider are example of :
(a) Convergent evolution
(b) Adaptive radiation
(c) Australian marsupials
(d) 2 and 3 both
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following statements is true ?
(a) During evolution, the rate of appearance of new form of organisms is linked to the life cycle/life span.
(b) The essence of Darwinian theory is natural selection.
(c) Fitness is based on characteristics which are inherited.
(d) All of them
Answer : D
Question. Hugo de vries called the single step large mutation as :
(a) Mutation
(b) Sports
(c) Micro evolution
(d) Saltation
Answer : D
Question. The industrial melanism phenomenon demonstrate:
(a) Gene mutation
(b) Genetic drift
(c) Natural selection
(d) Migration
Answer : C
Question. Which was absent in Miller's experiment ?
(a) Vacuum pump
(b) Electrodes
(c) Condenser
(d) None
Answer : D
Question. During human evolution the body of which primitive ancestors covered by hairs and walk they walked gorilla and chimpanzee?
(a) Dryopithecus and Cromagnon man
(b) Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus
(c) Ramapithecus and Homo habilis
(d) Java man and Peking man
Answer : B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is the most important pre-condition for adaptive radiation?
Answer : Conditions promoting adaptive radiation are much of the diversity of life originated through episodes of adaptive radiation during periods when ecological space became available for diversification. There are two primary mechanisms through which ecological space can become available. (i) intrinsic changes in organisms. (ii) extrinsic effects, including environmental change and colonisation of isolated landmasses.
Question. How do we compute the age of a rock?
Answer : The age of a rock in years is called its absolute age. It is determined by the natural radioactive decay of certain elements, e.g., uranium, when decays turns into lead. The parent atoms of uranium are converted into daughter atoms of lead over a fixed interval of time. This interval is the decay constant. The ratio of parent-daughter atoms changes in a quantity that can be measured. The radioactive half-life (the amount of time required for one half of the parent atoms to beonverted to daughter atoms) is used to calculate the age of the rock.
Question. When we talk of functional macromolecules (e.g., proteins as enzymes, hormones, receptors, antibodies etc), towards what are they evolving?
Answer : Functional macromolecules are evolving towards creation of a complex organism. There are various evidences that are common to simple and complex forms of lite indicate common ancestry, e.g., histones protein tend to be well preserved among all eukaryotes, from amoebas to blue whale or to humans, with only one or two amino acids different. The genetic code is nearly identical for all known life forms, from bacteria to archaea or animals and plants.
Question. In a certain population, the frequency of three genotypes is as follows Genotypes BB Bb bb Frequency 22% 62% 16% What is the likely frequency of B and b alleles?
Answer : The likely frequency of B = BB + 1 2 Bb
Question. Among the five factors that are known to affect Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, three factors are gene flow, genetic drift and genetic recombination. What are the other two factors?
Answer : The other two factors that affect Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are mutation and natural selection. Mutation is a sudden heritable change in an organism which is generally due to change in the base sequence of the nucleic acid in the organism’s genome. Microbial experiments show that pre-existing advantageous mutations when selected will result in formation of new phenotypes. Over few generations, this would result in speciation. Thus, resulting in changed frequency of genes and alleles. Natural selection is a phenomenon by which organisms possessing heritable variations enabling their better survival reproduce and leave greater number of progeny than their counterpart. It can lead to stabilisation (in which more individuals acquire mean character value), directional change (more individuals acquire value other than the mean character value) or disruption (more individuals acquire peripheral character value at both ends of the distribution curve).
Question. What is founder effect?
Answer : Sometimes, a small number of individuals become isolated from a larger population to form a new population at some distance away from their place of origin. The gene pool of the new population differs from the source population. It is possible that the change in allele frequency is so drastically different in the new sample that they become a different species. The original driftted population becomes founders and this effect is called founder effect.
Question. Who among the Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus was more man like?
Answer : Ramapithecus was more man-like. It walked erect on its hind legs, ate hard nuts and seeds like modern man and had jaws and teeth similar to humans It arose from Dryopithecus, which was considered to be a common ancestor of man and apes. Dryopithecus was more ape-like with same length of arms and legs.
Question. By what Latin name, the first Hominid was known?
Answer : The first hominid was known as Homo habilis. The brain capacities were between 650-800cc. They probably did not eat meat.
Question. Among Ramapithecus, Australopithecines and Homo habilis who probably did not eat meat?
Answer : Homo habilis probably did not eat meat. This creature was the first human like being, with brain capacities between 650-800cc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. State and explain any three factors affecting allele frequency in populations.
Answer : Factors affecting allele frequency in populations are as described below (i) Mutations These are sudden heritable changes which are supposed to be the primary source of genetic variation. They are of following two types (a) Chromosomal Mutations They arise due to changes in chromosome number and changes in structure. (b) Gene Mutations These are changes in gene structure and expression due to addition, deletion, substitution or inversion of nucleotides. (ii) Non-random Mating Repeated mating between individuals of certain selected traits changes the gene frequency, e.g., selection of more brightly coloured male bird by a female bird may increase the gene frequency of bright colour in the next generation. (iii) Gene Flow (Gene Migration) It is the movement of alleles into and out of a gene pool. Breeding of immigrants with the host population adds new alleles to the gene pool of the host population.
Question. Gene flow occurs through generations. Gene flow can occur across language barriers in humans If we have a technique of measuring specific allele frequencies in different population of the world, can we not predict human migratory patterns in pre-history and history? Do you agree or disagree? Provide explanation to your answer.
Answer : Yes, we agree. As the gene flow occurs through geographical barriers over generations, by studying specific allelic frequencies in various populations of the world, we can predict the human migratory patterns in pre-historic and historic era. There have been projects undertaken such as human genographics project. Which uses data from studies on specific genes/chromosomes/mitochondrial DNA to trace the evolutionary history and migratory patterns of humans
Question. How do you express the meaning of worlds like race, breed, cultivars or variety?
Answer : The meaning of the given words are as given below Race It is a classification system used to categorise humans into large and distinct populations or groups by anatomical, cultural, linguistic, geographical, historical and for relegious relationship. Breed It is a specific group of domestic animals or plants having homogenous appearance, homogenous behaviour and other characteristics that distinguish it from other animals or plants of the same species and that were arrived at through selective breeding. Cultivar It is a plant or grouping of plants selected for desirable characteristics that can be maintained by propogation. ‘Cultivar’ stands for ‘cultivated variety’. Variety A variety arises naturally in the plant kingdom and plant grown from its seeds will typically come out true to type.
Question. When we say ‘survival of the fittest’, does it mean that (a) those which are fit only survive (b) those that survive are called fit? Comment.
Answer : In the struggle for existence, the individuals which have more favourable variations will enjoy a competitive advantage over others which have less favourable or unfavourable variations. They are considered fit and thus, will survive and reproduce. Such individuals produce more progeny (with more fit individuals) than others who are less adapted in that environment.
Question. Enumerate three most characteristic criteria for designating a Mendelian population.
Answer : Characteristic criteria for designating a Mendelian population are
(i) Population must be sufficiently large.
(ii) Population must have potentialities for free flow of genetic material among individuals, through sexual reproduction.
(iii) Migration should either be nil or negligible.
Question. ‘Migration may enhance or blurr the effects of selection’ comment.
Answer : The movement of individuals from one place to another is called migration. It can be the movement of individuals to a different populations (i.e., emigration) or movement of individual into a particular population (i.e., cmmigration) Migration may bring in more such alleles, that bestow upon the individuals, such adaptations or traits which are selected by nature. Thus, enhancing the effect of selection. Similarly, emigration may lead to removal of such alleles that confer better adaptations. Immigration may also bring in those alleles which confer the traits that are not selected by nature, i.e., blurr the effects of selection. Hence, it is justifiable to say that ‘Migration may enhance or blurr the effects of selection.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set C |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 6 Evolution which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 12 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 12 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 12 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 12 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 12 Assignments for chapter Chapter 6 Evolution will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 12 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 6 Evolution, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 6 Evolution within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 12 Biology mock tests for Chapter 6 Evolution reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 12 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 6 Evolution yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 12 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 12 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 12 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 6 Evolution assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 12 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 6 Evolution questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 12 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 12 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Evolution from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 6 Evolution Biology Class 12 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 6 Evolution Class 12 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 6 Evolution Class 12
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 6 Evolution Class 12 Biology

