Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Science Periodic classification of elements Sure Shot Questions A. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 10 Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 10 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in Science and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Science prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 10 Science
Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following Pdf for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements in Class 10. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic classification of elements MCQs
Question. Cl, Br and I is a Döberiener’s triad. If the atomic masses of Cl and I are 35.5 and 127 respectively then the atomic mass of Br is
(a) 162.5
(b) 91.5
(c) 81.25
(d) 45.625
Answer. C
Question. According to Mendeléev’s periodic law, the properties of elements are a periodic function of their
(a) atomic numbers
(b) atomic masses
(c) atomic volumes
(d) atomic sizes.
Answer. B
Question. The elements with atomic number 3 to 10 belong to the second period. Identify the most electropositive and the most electronegative element respectively.
(a) F, Li
(b) Li, F
(c) Li, Ne
(d) Ne, Li
Answer. B
Question. According to modern periodic law, the properties of elements are a periodic function of their
(a) atomic masses
(b) atomic volumes
(c) atomic numbers
(d) densities.
Answer. C
Question. Arrange the following atoms in the order of increasing atomic radius : F, Cl, C, O
(a) F, Cl, O, C
(b) C, O, F, Cl
(c) O, C, F, Cl
(d) F, O, C, Cl
Answer. D
Question. Li, Na and K is a Dobereiner triad. The atomic masses of Li and K are 7 and 39 respectively.What is the expected mass of Na?
(a) 7
(b) 18
(c) 23
(d) 39
Answer. C
Question. Element X has a proton number equal to 17.Which of the following statements about X is not correct?
(a) X is a member of Group VII.
(b) X has 7 electrons in the outermost electron shell.
(c) X has three occupied electron shells.
(d) X gains one electron to form X +.
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following statements is correct about elements 19 9A and 37 17B?
(a) A is more electronegative than B.
(b) A forms a positive ion and B forms a negative ion.
(c) A and B have the same number of neutrons.
(d) A and B have the same number of electrons.
Answer. A
Question. Mendeleev peridicted the existence of two elements and named them as eka-silicon and eka-aluminium. Identify the element which took their position at later stage.
(a) Si and Ge
(b) Si and Ga
(c) Ge and Ga
(d) Si and Al
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of the periodic table?
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature.
(b) The number of valence electrons increases.
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(d) The oxides become more acidic.
Answer. C
Question. The correct order of increasing acidic nature of SO2, SiO2, P2O3 and Al2O3 is
(a) SO2 < P2O3 < SiO2 < Al2O3
(b) Al2O3 < SiO2 < SO2 < P2O3
(c) Al2O3 < SiO2 < P2O3 < SO2
(d) SiO2 < SO2 < Al2O3 < P2O3
Answer. C
Question. It was found that the law of octaves was applicable only upto
(a) chlorine
(b) potassium
(c) calcium
(d) argon.
Answer. C
Question. Electronic configurations for four elements
A, B, C and D are given below :
A : 2,1 B : 2,8 C : 2,8,1 D : 2,8,8
Identify the correct statements.
(i) Elements A and B belong to the second period.
(ii) Elements A and C belong to the same group.
(iii) Element C is more reactive than element A.
(iv) Elements C and D belong to the third period
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) All the statements are correct.
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following properties does not match elements of halogen family?
(a) They have seven electrons in their valence shell.
(b) They are diatomic in their molecular form.
(c) They are highly reactive.
(d) They are metallic in nature.
Answer. D
Question. “The properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic numbers”. The statement was given by
(a) N. Bohr
(b) J. W. Dobereiner
(c) D. I. Mendeleev
(d) H. G. J. Moseley.
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following orders of atomic radii is correctly represented?
(a) B > C > N
(b) B > O > C
(c) C > B > N
(d) C > B > O
Answer. A
Question. Which statement about the elements in periodic table is correct?
(a) The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass.
(b) The elements in a period have the same number of outer electrons.
(c) The elements in a group have the same number of occupied electron shells.
(d) The non-metallic characteristic of the elements decreases down a group and increases across a period.
Answer. D
Question. The scientist who showed that the atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass is
(a) Henry Moseley
(b) Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner
(c) John Newlands
(d) Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev.
Answer. A
Question. Silicon is surrounded by the elements of atomic number 6, 13, 15 and 32 in the periodic table, then
(a) the properties of the elements of atomic numbers 6 and 32 will be similar to silicon
(b) the properties of the elements of atomic numbers 13 and 15 will be similar to silicon
(c) the properties of the elements of atomic numbers 6 and 13 will be similar to silicon
(d) the properties of elements of atomic numbers 15 and 32 will be similar to silicon.
Answer. A
Question. An element M forms an ion M –. The electronic configuration of this ion is (2,8).
Which statement is true?
(a) M is in Group VI and Period 2.
(b) M is Group VII and Period 2.
(c) M is in Group VII and Period 3.
(d) M is in Group VI and Period 3.
Answer. B
Question. It was assumed by Newlands that only
(a) 56 elements existed in nature
(b) 57 elements existed in nature
(c) 59 elements existed in nature
(d) 63 elements existed in nature.
Answer. A
Question. The proton numbers of four elements are given below.
| Element | W | X | Y | Z |
| Proton number | 5 | 12 | 15 | 20 |
Which of the following pairs of elements belong to the same group of the periodic table?
(a) W and X
(b) W and Y
(c) X and Z
(d) Y and Z
Answer. C
Question. When Mendeleev started his work, the number of known elements were
(a) 68
(b) 53
(c) 57
(d) 63
Answer. D
Question. The positions of four elements K, L, M and N in the periodic table are shown below :
| Group 13 | Group 14 | Group 15 |
| K – Ga | – L M | – – N |
Which of the following statements are correct?
(I) K, L, M and N are metalloids.
(II) K is a metal while L, M and N are nonmetals.
(III) Among these four elements, K is the smallest in size.
(IV) K is a metal while L and M are metalloids and N is a non‑metal.
(a) II and III
(b) I and III
(c) III and IV
(d) None of these
Answer. B
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic classification of elements Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 83-95, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : In Newlands’ octaves, the properties of lithium and sodium were found to be same.
Reason : Sodium is the eighth element after lithium.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Decreasing order of atomic radii is : Cl > F > O > S.
Reason : Atomic radius increases as the number of energy level increases and decreases as nuclear charge increases.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Increasing order of metallic character is : P < Si < Be < Mg < Na
Reason : Metallic character increases along a period and decreases down a group.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : According to Mendeleev’s periodic law, the properties of elements is the periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Reason : Mendeleev placed some elements with higher atomic mass before the elements with lower atomic mass.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Elements in the same vertical column have similar properties.
Reason : Periodic properties of elements is a function of atomic number.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Group18 is placed at the extreme right of the periodic table.
Reason : It is in accordance with their electronic configuration.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Atomic radius in general decreases along a period.
Reason : In a period, effective nuclear charge decreases.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Number of valence electrons decreases down the group.
Reason : Number of valence electrons increases when we move left to right in a period.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : In Dobereiner’s triad, the three elements present have same gaps of atomic numbers.
Reason : Elements in a triad have similar properties.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Alkali metals do not form dipositive ions.
Reason : After loss of one electron alkali metals achieve stable configuration of noble gas.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Atomic size of As is more than that of P.
Reason : Atomic size decreases along a period.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Down the group, atomic radius increases.
Reason : Electrons are added in new shell.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Atomic size of potassium is greater than that of sodium.
Reason : As we go down the group, atomic radius increases.
Answer. A
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic classification of elements Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
The distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of electrons is known as atomic radius. On moving from left to right along a period, atomic radii decrease because effective nuclear charge increases. For example, the atomic size decreases regularly from Li to F in the second period and from Na to Cl in the third period. It may, however, be noted that in any period, the noble gas has the largest size. On moving down in a group, atomic radii increase.
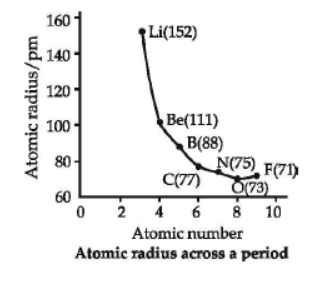
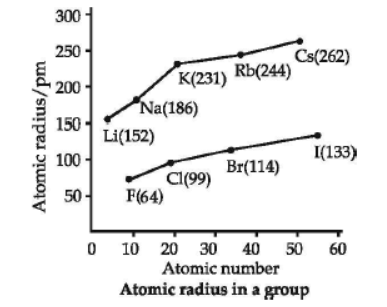
Question. Which of the following has the maximum atomic radius?
(a) Al
(b) Si
(c) P
(d) Mg
Answer. D
Question. The element with the smallest size in group 13 is
(a) gallium
(b) thallium
(c) aluminium
(d) boron.
Answer. D
Question. The atomic radius decreases as we move across a period because
(a) atomic mass increases
(b) atomic number decreases
(c) effective nuclear charge increases
(d) electrons are removed.
Answer. C
Question. In the third period of the periodic table, the element having smallest size is
(a) Na
(b) Ar
(c) Cl
(d) Si
Answer. C
Question. Among O, C, F, Cl, Br, the correct order of increasing atomic radii is
(a) F, O, C, Cl, Br
(b) F, C, O, Cl, Br
(c) F, Cl, Br, O, C
(d) C, O, F, Cl, Br
Answer. A
Case II : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
In 1913, Henry Moseley showed that the atomic number of an element is the more fundamental property than its atomic mass. Accordingly,
Mendeleev’s periodic law was modified and atomic number was adopted as the basis of modern periodic table.
In this periodic table, the elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers. There are 18 vertical columns in the periodic table which constitute 18 groups or families. The groups are numbered as 1, 2, 3, ... upto 18. All the members of a particular group have similar outer shell electronic configuration. There are seven horizontal rows of the periodic table which are known as periods.
Question. All the elements in a period in the periodic table have the same
(a) atomic number
(b) electronic configuration
(c) atomic weight
(d) valence shell.
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following combinations of elements belong to the same group?
(a) N, P, S
(b) Li, Na, K
(c) Na, Mg, Al
(d) O, S, Cl
Answer. B
Question. The atoms of elements belonging to the same group of periodic table have same number of
(a) protons
(b) electrons
(c) neutrons
(d) electrons in outermost shell.
Answer. D
Question. In the periodic table, the element with atomic number 16 will be placed in the group
(a) fourteen
(b) sixteen
(c) thirteen
(d) fifteen.
Answer. B
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
1. The property of an element in the periodic table depends on its, ________.
i) atomic size
ii) atomic mass
iii) electronic configuration
iv) number of protons
2. An element has configuration 2, 8, 1. It belongs to, _________.
i). 1 group and 3rd period
ii). 3 group and 1st period
iii). 1 group and 8th period
iv). 17 group and 3rd period
3. The number of electrons in the valence shell is equal to its ________.
i). atomic mass
ii). group number
iii). period number
iv). atomic volume
4. The non-metallic element present in the third period other than sulphur and chlorine is
i). oxygen
ii). fluorine
iii). nitrogen
iv). phosphorus
5. At the end of each period the valence shell is __________.
i). incomplete
ii). half filled
iii). singly occupied
iv). completely filled
6. The family of elements having seven electrons in the outermost shell is ______.
i). alkali metals
ii). alkaline earth metals
iii). halogens
iv). noble gases
7. Which of the following factors does not affect the metallic character of an element?
i). Atomic size
ii). Ionisation potential
iii). Electronegativity
iv). Atomic radius
8. The family of elements to which potassium belongs is _________.
i). alkali metals
ii). alkaline earth metals
iii). halogens
iv). noble gases
9. The modern periodic table is given by ________
i). Mendeleev
ii). Einstein
iii). Bohr
iv). Mosley
10. Elements belonging to groups 1 to 17 are called __________.
i). noble gases
ii). normal elements
iii). transition elements
iv). inner transition elements
11. A liquid non-metal is ___________.
i). phosphorous
ii). mercury
iii). bromine
iv). nitrogen
12. The first alkali metal is _________.
i). hydrogen
ii). lithium
iii). sodium
iv). francium
13. A purple coloured solid halogen is ________.
i). chlorine
ii). bromine
iii). iodine
iv). astatine
14. Lanthanides and actinides are also called ___________.
i). normal elements
ii). transition elements
iii). noble gases
iv). inner transition elements
15. The family of elements to which calcium belongs is __________.
i). alkali metals
ii). alkaline earth metals
iii). halogens
iv). noble gases
16. The least reactive element in group 17 is ___________.
i). fluorine
ii). chlorine
iii). bromine
iv). iodine
17. The valency of chlorine with respect to oxygen is __________.
i). 1
ii). 3
iii). 5
iv). 7
18. The number of shells in the elements of 3rd period is __________.
i). 1
ii). 2
iii). 3
iv). 0
19. Four elements along a period have atomic number (11, 13, 16 and 17). The most metallic among these has an atomic number of __________.
i). 11
ii). 12
iii). 16
iv). 17
20. Six elements A, B, C, D, E and F have the following atomic numbers (A = 12, B = 17, C = 18, D = 7, E = 9 and F = 11). Among these elements, the element, which belongs to the 3rd period and has the highest ionisation potential, is __________.
i). A
ii). B
iii). C
iv). F
21. A factor that affects the ionisation potential of an element is __________.
i). atomic size
ii). electron affinity
iii). electro-negativity
iv). neutrons
22. The element, which has the highest electron affinity in the 3rd period is _________
i). Na
ii). Mg
iii). Si
iv). Cl
23. The element, which has zero electron affinity in the 3rd period is __________.
i). Al
ii). P
iii). Ar
iv). S
24. The statement that is not true about electron affinity is
i). It causes energy to be released
ii). It causes energy to be absorbed
iii). It is expressed in electron volts
iv). It involves formation of an anion
25. Down a group, the electron affinity __________.
i). increases
ii). decreases
iii). remains same
iv). increases and then decreases
26. Name an element with five electrons in the outer shell.
27. Name an element which tends to lose two electrons.
28. Name an element that would tend to gain two electrons.
29. Name the group having a non metal liquid as well as non metal gas at room temperature.
30. Name the group having element with zero valency.
31. Name the metalloid present in group 14.
32. What is the name given to group of three similar elements by Dobereiner?
33. State "Newlands law of Octaves" for classification of elements.
34. Name the fundamental property used by Mendeleev as the basis of classification.
35. How many groups and periods are there in the Modern periodic table?
36. What was the prediction of Mendeleev regarding the gaps in his periodic table?
37. How is valence of an element determined?
38. What will be the valence of an element having atomic number 16?
39. How does valence vary in going down a group?
40. Why inert gases have zero valences?
41. What would be the valence of an atom containing 8 electrons in its outermost shell?
42. How does the electronegative character of elements vary along a period of the periodic table?
43. The present classification of elements is based on which fundamental property of elements?
44. Among first ten elements in the modern periodic table name the metals present.
45. Metals are on which side of Modern periodic table?
46. State Mendeleev’s periodic law.
47. Name two elements, other than Gallium, whose existence was predicted by Mendeleev.
48. State Modern Periodic law.
49. Write the name given to the vertical columns in a periodic table.
50. What name is given to the horizontal rows in a periodic table?
51. Why does silicon is classified as Metalloid?
52. State two limitations of Newland's law of Octaves
53. Name the scientist who proposed modern periodic law? On which fundamental property of elements it is based?
54. Why could no fixed position be given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s Periodic table?
55. What are metalloids? Give two examples.
56. In group 1 of periodic table three elements X, Y and Z have atomic radii 133 pm , 95pm and 65pm respectively giving a reason, arrange them in the increasing order of their atomic number in the group.
57. In modern periodic table, the isotopes of Chlorine Cl-35 and Cl-37 having different atomic masses will be kept in different slots or they would be assigned same position on the basis of their chemical properties? Give reason in support of your answer.
58. Nitrogen (At no. 7) and Phosphorus (At no. 15) belong to group 15 of the periodic table:-
(i) Write the electronic configuration of the two.
(ii) Predict whether they are metallic or nonmetallic in nature.
59. How and why does the atomic size vary as you go down a group?
60. Why was Dobereiner system of classification of elements into triads not found to be useful?
61. State three merits of Modern periodic table.
62. What are amphoteric oxides? Choose the amphoteric oxide from among the following oxides :– Na2O, ZnO, Al2O3, CO2, H2O
63. Study the variation in the atomic radii of first group elements given below and arrange them in increasing order :– Group I element Na Li Rb Cs K Atomic Radii P.M 86 152 244 262 231
64. An element X has the electronic configuration as 2, 8, 7 :–
(a) What is the atomic number of the element?
(b) What will be the formula of its compound formed with Na?
(c) What is the name given to the family of this element?
65. How do you calculate the valence of the element from its electronic configuration? What is the valence of Mg with atomic number 12 and sulphur with atomic number 16? How does the valence vary in going down in a group?
66. Atomic radii of the elements of the period II are as follows:– Period II elements : Be B O N C Li Atomic Radius : 111 88 66 74 77 152
(i) Arrange them in decreasing order of their atomic radii.
(ii) How does the atomic size vary on moving from left to right in a period? Explain why?
(iii) How will the tendency to lose electrons will vary on moving from left to right in this period II?
67. Oxygen (O, 8) and sulphur (S, 16) belong to group 16 of the periodic table:-
(i) Write the electronic configuration and valence of these two elements?
(ii) Which among these will be more electronegative? Why?
68. Two elements ‘A’ and ‘B’ belong to group 1 and 2 respectively in the same period. Compare them with respect to :–
(a) Number of valence electrons. (b) Valency
(c) Metallic character (d) Size of atom
(e) Formulae of their oxides.
69. What is periodicity?
70. Who showed for the first time that there is periodicity in properties of elements?
71. Are the properties of elements placed in a group same?
72. Give reason for the need of classification of elements.
73. Hydrogen can be placed in group 1 and group 7 of periodic table. Why?
74. Name two elements whose properties were correctly predicted by Mendeleev. Mention their present day name.
75. State Mendeleev's periodic law. Why did he leave gaps in his periodic table?
76. An element Z is of second group of the periodic table. Write the formula of its oxide.
77. Noble gases did not find a place in Newland's Octaves. Explain.
78. Give formula for the following:
(i) bromide of element X of second group.
(ii) oxide of element Y of third group.
(iii) chloride of element Z of fourth group.
79. How many elements are present in (i) Second period (ii) Six period
80. Name (i) A Non metal solid at room temperature (ii) A Metal liquid at room temperature
81. Arrange the following elements in the decreasing order of metallic character.
(i) Si, Be, Mg, Na, P
(ii) B, Al, Mg, K
82. How in modern periodic table position of elements in groups and periods is decided?
83. Why metallic character decreases across a period and increases down a group?
84. Among the elements of second period ‘Li’ to ‘Ne’ pick out the element.
(i) with the largest atomic radius
(ii) that is the most reactive non metal
(iii) that is the most reactive metal
(iv) which is a metalloid.
85. Elements A, B, C, D, E have following electronic configurations-
A: 2,3
B: 2,8,3
C: 2,8,5
D: 2,8,7
E: 2,8,8,2
(i) Which of these belong to same group?
(ii) Which of these belong to same period?
Please click the link below to download CBSE Class 10 Science Periodic classification of elements Sure Shot Questions A.
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. Also download Class 10 Science Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements is free

