Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Science Our Environment Sure Shot Questions B. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 10 Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 10 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in Science and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Science prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 10 Science
Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following Pdf for Chapter 15 Our Environment in Class 10. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) A food chain is always straight.
(b) Producers belong to second trophic levels.
(c) Top carnivore are fourth order consumers.
(d) Consumers obtain organic nutrients from outside as food.
Answer. A
Question. Select the mismatched pair.
(a) Crop field – Natural ecosystem
(b) Garden – Man made ecosystem
(c) Temperature – Abiotic factor
(d) Grass – Transducer
Answer. B
Question. DDT was accidently added to the water of a lake. All the organisms in it would be affected by DDT. Which of the following organisms would be affected the most?
(a) Man
(b) Birds living in the lake
(c) Fish living in the lake
(d) Aquatic plants in the lake
Answer. A
Question. The thinning of ozone layer was first observed in
(a) 1980s
(b) 1950s
(c) 1940s
(d) 1990s.
Answer. A
Question. Ozone layer is essential because it absorbs most of the
(a) infrared radiations
(b) solar radiations
(c) ultraviolet radiations
(d) both (a) and (b).
Answer. C
Question. Burning of waste substances usually in anaerobic conditions at high temperature of about 670°C is called
(a) land filling
(b) composting
(c) incineration
(d) none of these.
Answer. D
Question. Select the odd one out.
(a) Tomato leaves
(b) Wood
(c) Synthetic polymers
(d) Lime juice
Answer. C
Question. Complete the given analogy. Non-biodegradable : _________ :: Biodegradable : Livestock wastes
(a) Cotton
(b) Grass
(c) Glass
(d) Orange peel
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following groups contain nonbiodegradable substances only?
(a) Flowers, crops, plastic
(b) Plastic, polythene bags, aluminium cans
(c) Grass, wood, glass
(d) Fruit and vegetable peels, grass, wood
Answer. C
Question. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Food we eat is digested by various enzymes in our body.
(b) Non-biodegradable substances are not broken down by biological processes.
(c) All enzymes have same action on each substance.
(d) Plastics cannot be broken down by the action of bacteria and other saprophytes.
Answer. B
Question. Minamata disease is due to
(a) MIC gas
(b) methyl mercury
(c) lead nitrate
(d) cobalt chloride.
Answer. D
Question. According to Charles Elton, which is not correct?
(a) Carnivores at the top of the pyramid.
(b) Producers at the top of the pyramid.
(c) Energy trapping is high at the top of the pyramid.
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following statements regarding solid wastes is correct?
(a) Change in the packaging technology has resulted in generation of lot of solid wastes.
(b) Dumping of solid wastes could reduce the fertility of the soil leading to reduction in crop yield.
(c) Accumulation of solid waste could cause increased incidents of disease in a locality.
(d) All of these.
Answer. D
Question. Incineration and pyrolysis are two methods of waste disposal done at high temperature. The two differs from each other as in later
(a) aerobic burning occurs
(b) chemical energy and chemical constituents are recovered
(c) ashes are the end products
(d) medical wastes are burnt with clinkers as the end product.
Answer. B
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Case Based Questions
Case I : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
Various components of an ecosystem maintain a balance in nature. Disturbance in any component of the environment cause an imbalance. One of the main environmental problem caused by human activities is global warming. Global warming is a phenomenon caused by the increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere resulting due to enhanced greenhouse effect.
Question. Refer to the given pie chart showing the contribution of different gases to global warming.
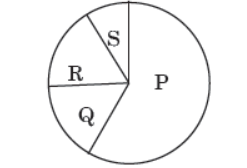
Identify gases P, Q, R and S and select the incorrect statement regarding them.
(a) P could be a gas that increases in atmosphere due to excessive use of fossil fuel.
(b) Q could be a gas produced by complete combustion of biomass.
(c) R could be synthetic gaseous compounds used as refrigerants in air conditioners and refrigerators.
(d) S could be a gas produced by combustion of nitrogen rich fuel.
Answer. B
Question. What could not be a source of gas Q given in the above pie chart?
(a) Flooded paddy field
(b) Cattle
(c) Jet fuel
(d) Marshes
Answer. C
Question. If there is no CO2 in the atmosphere, then what will be the most likely consequence of this on the temperature of earth?
(a) The temperature remain unchanged as it depends upon the oxygen content of the atmosphere.
(b) The temperature would increase as less greenhouse gases will be absorbed by CO2.
(c) The temperature would decrease as CO2 is the principal greenhouse gas.
(d) None of these
Answer. C
Question. Study carefully the following figure representing greenhouse effect.
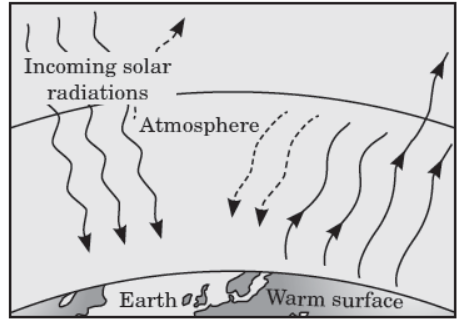
Select the correct statement regarding this.
(a) Much of the long wavelength infrared radiations re-radiated by the earth’s surface are absorbed by the atmospheric greenhouse gases.
(b) CO2, CH4, CFCs and N2O are the gases which are responsible for greenhouse effect.
(c) The atmosphere is transparent to the incoming short-wavelength radiations and is translucent to the long-wavelength infrared radiations.
(d) All of these
Answer. D
Question. Greenhouse effect is due to
(a) accumulation of O3 and depletion of CO2
(b) accumulation of both O3 and CO2
(c) accumulation of CO2 and depletion of O3
(d) presence of green plants on the earth.
Answer. C
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Assertion And Reason Based MCQs
For question, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : The burning of substances at higher temperature to form ash is called incineration.
Reason : Incineration greatly reduces the volume of waste.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : If pesticide is present in water bodies then fish eating birds accumulate maximum amount of DDT in their bodies.
Reason : Pesticides are not metabolised within bodies of living organisms and get concentrated at each trophic level leading to bioaccumulation.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Using jute bags while shopping is more environment friendly as compared to polythene bags.
Reason : Jute is biodegradable whereas polythene bag is non-biodegradable.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : A food chain comprises of producers and consumers.
Reason : Consumers can be herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : We live in troposphere.
Reason : Our atmosphere extends beyond troposphere also.
Answer. B
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. We often use the word environment. What does it mean?
Answer. Environment can be defined as the physical or biological world where an organism lives. Literally speaking, an, organism’s immediate surrounding constitutes its environment which includes both biotic and abiotic components around it.
Question. Why is lake considered to be a natural ecosystem?
Answer. Lake is an ecosystem where living organisms grow, reproduce and interact among each other as well as with abiotic components and carry out other activities in nature by themselves without any human interference, therefore it is referred to as a natural ecosystem.
Question. The following organisms form a food chain. Which of these will have the highest concentration of non-biodegradable chemicals?
Name the phenomenon associated with it.
Insects, Hawk, Grass, Snake, Frog
Answer. Among the following organisms of the food chain, hawk being top consumer is present at topmost trophic level, hence will have the highest concentration of non-biodegradable chemicals due to a phenomenon known as biomagnification.
Question. In a food chain, if 10,000 joules of energy is available to the producer, how much energy will be available to the secondary consumer to transfer it to the tertiary consumer?
Answer. According to ten percent law, 10% of the energy of producer will be available to primary consumer, and 10% of this energy will be available to secondary consumer (100J) and so on.

Question. Why is excessive use of CFCs a cause of concern?
Answer. CFCs or chlorofluorocarbons are potent compounds that release active chlorine in the atmosphere which reacts with ozone molecules present there to convert them to oxygen.This results in thinning of ozone layer. Hence, excessive use of CFCs is a cause of concern.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Differentiate between food chain and food web.
Answer. Differences between food chain and food web are:
| Food chain | Food web |
| It is the single straight pathway process in which one organism consumes the other. | It is number of food chains interconnected at various trophic levels. |
| Each organism of higher trophic level receives food from single type of organisms of lower trophic level. | Each organism of higher trophic level receives food from number of alternative organisms of the lower trophic level. |
| It does not add adaptability in organism. | It increases adaptability in organism. |
| Only the members of one trophic level compete for obtaining the same food. | Competition is among members of different species. It is less severe as a number of alternate foods are available. |
| Presence of separate or isolated food chains adds to instability of the ecosystem | Presence of food webs increases the stability of the ecosystem. |
Question. Why only 4 or 5 trophic levels are present in each food chain?
Answer. The quantum of available energy in a food chain successively gets decreased at each trophic level. There is only 10% flow of energy from one trophic level to the next higher level. Second law of thermodynamics says that transformation of energy from one form to the other is inefficient and involves dissipation of unavailable energy. This loss of energy at successive trophic levels restricts the size of food chain in an ecosystem to maximum 4 to 5 steps. Hence, only 4 to 5 trophic levels are present in each food chain.
Question. Write three characteristics of energy transfer in the biosphere?
Answer. The following are the characteristics of energy transfer in the biosphere: (any three)
(i) Energy is supplied by the sun and it is not created in the biosphere. Energy is only converted from one form to another in the biosphere.
(ii) The flow of energy is unidirectional.
(iii) There is loss of energy as we go from one trophic level to the next in an ecosystem. At each transfer, generally 80-90% of energy is lost as heat in accordance with second law of thermodynamics.
Question. Mention the advantages of paper bags over plastic bags.
Answer. The advantages of paper bags over plastic bags are :
(i) Paper bags can be recycled as they are biodegradable Their recycling does not produce poisonous gases like recycling of plastic bags.
(ii) Once discarded, paper bags can be recycled again easily, while plastic bags cannot be recycled easily as they clog machines and complicate the recycling processes.
(iii) Plastic bags kill thousands of marine animals every year as some animals confuse plastic bags with jellyfish which block the entrance to the stomach. Paperbags are a healthy, safe alternative to hazardous plastic bags.
(iv) Paper bags are finding favour with all consumers, government and even the environmentalists.
Question. What will happen if all the deers are removed from the given food chain?
Plants → Deer → Tigers
Answer. From the given food chain, if the deers are removed, the population of plants will increase as deers are herbivores and feed on plants whereas the population of tiger (that consume deer) will decrease, as food available for tiger would be less.
Question. (a) From the following group of organisms create a food chain which is most advantageous for human beings in terms of energy.
Hawk, Rat, Cereal plant, Goat,Snake, Human being
(b) State the possible disadvantage if the cereal plant is growing in soil rich in pesticides.
(c) Construct a food web using the organisms mentioned above.
Answer. (a) A food chain which is most advantageous for human beings in terms of energy is:
Cereal plant → Human being
(b) If the cereal plant is growing in soil rich in pesticides, then these pesticides would be absorbed by growing plants along with water and minerals, when animals eat these cereal plants, these poisonous chemical pesticides go into their bodies through food. This increase in concentration of harmful pesticides in the body of living organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification. Pesticides are lethal to non-target species also. The extensive use of pesticides in agriculture can change the community of microorganisms living in soil.
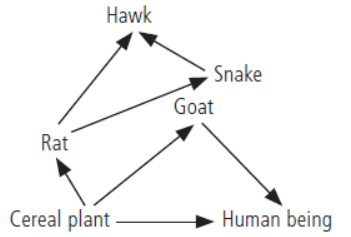
Question. Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer. Yes, the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level will be different for different trophic levels, e.g., removal of all the producers (T1) will adversely affect all the types of consumers including herbivores and carnivores, while the removal of all the herbivores will adversely affect only the carnivores but there will be increase in the number of the producers.
No, Removal of all the organisms of any trophic level will always adversely affect the ecosystem, e.g., the removal of lions and tigers (top carnivores) will cause rapid increase in deer population, which will lead to rapid consumption of vegetation resulting in scarcity of vegetation and population crash of deer.
Question. Study the given food chain anddiscuss the effect of removal of any one of the trophic level from it.
Grasses → Deers → Lions
Answer. In the above food chain, if all the lions are removed,
the population of deer will increase since there would not be any lion to kill them and to keep the deer population under control. This will lead to high consumption of grasses (producers) and may even eliminate them and if the deer population is removed instead of lions, it will lead to decrease of lion population since there will not be any prey. The lions may even resort to other preys such as domestic animals or man to survive. If the deer and lion operate in other food chains in a food web, then the removal of any one of them will lead to disruption of the food web and will cause disturbance in the ecosystem. In addition if the grasses (producers) are removed, then all life will come to an end. If there is no grass, there will be no herbivores. If there are no herbivores, then there will be no carnivores. Therefore, ultimately all organisms will die.
Question. “Our food grains such as wheat and rice, the vegetables and fruits and even meat are found to contain varying amounts of pesticide residues.”
State the reason to explain how and why it happens.
Answer. Pesticides are poisonous chemical substances which are sprayed over crop plants to protect them from pests and diseases. These chemical pesticides mix up with soil and water. From soil and water, these pesticides are absorbed by the growing plants along with water and other mineral’s. When herbivorous animals feed on these plants the poisonous pesticides enter their bodies through the food chain. Similarly, when the carnivorous animals eat these herbivores, the pesticides get transferred to their bodies. Therefore, the plant products such as food grains, vegetables and fruits as well as meat of animals contain varying amounts of pesticide residues depending upon the trophic level they occupy in a food chain.
Question. Write two harmful effects of using plastic bags on the environment. Suggest alternatives to the usage of plastic bags.
Answer. Two harmful effects of using plastic bags on the environment:
(i) Plastic bags are non-biodegradable substances which are not acted upon by microbes. So, they cannot be decomposed and therefore persist in the environment for a long time causing harm to the soil fertility and quality.
(ii) Plastic bags choke drains which result in waterlogging, that allows breeding of mosquitoes and hence leads to various diseases.Jute bags and cloth bags are the alternatives to the polyethene bags.
Question. What do you mean by acid rain? Give some effective measures to control it.
Answer. Any precipitation or deposition having a pH lower than 5.6 is called acid rain. Acid rain occurs by the emission of sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen that react with rain
water and form acids.
Following measures can be taken to prevent and control acid rain:
(i) Acid rain is mainly caused due to air pollution. Air pollution can be reduced by using pollution-controlling equipment, such as scrubber.
(ii) Other sources for the generation of electricity, such as nuclear fuel or solar power can be used instead of using fossil fuel to reduce the release of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur.
(iii) Cleaner fuels, such as LPG, CNG, etc., could be used in automobiles.
(iv) Use of neutralising agents such as powdered lime stone can be sprayed over areas that are prone to acid rain.
Question. Give suitable mechanism(s) for waste management in fertiliser industries.
Answer. Industries involved in making inorganic fertilisers such as urea, potash, etc., cause air and water pollution by releasing harmful and toxic chemicals in air and water during the synthesis of the chemical fertilisers.
Measures required to be adopted for the management of these wastes are :
(i) The release of various pollutants directly in the air should be controlled and minimised by removing particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from foul air before its emission in the source.
(ii) The effluents should be treated and then discharged into the environment. Before discharging them in the water source they should be converted into less harmful, non-toxic materials.
Question. What efforts have been made at international level for mitigating global change?
Answer. Initiatives for mitigating global change are: Montreal Protocol (16 September 1987) : A landmark international agreement to protect the stratospheric ozone by agreeing to limit the production and use of ozone depleting substances to half the level of 1986 and helping the developing countries to implement use of alternatives to CFCs.
Helsinki Declaration (May, 1989) : Montreal Protocol was ratified by 82 nations at Helsinki. They pledged to phase out CFCs by 2000.
Kyoto Protocol (December, 1997) : International conference held in Kyoto, Japan obtained commitments from different countries for developing alternatives to oxygen depleting substances (ODS) and reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions at a level 5% below 1990 level by 2008-2012. Beijing Protocol (1999) – The protocol lays down steps to reduce emission of CFCs and other ozone depleting substances. It separates the efforts to be made by developing and developed countries.
Question. What will be the consequence of absence of decomposers in an ecosystem?
Answer. In absence of decomposers, recycling of materials will not occur in biosphere. It is due to the reason that decomposers break down the complex organic substances like dead organisms, garbage, etc. into simple inorganic compounds, which go into the soil and used again by plants. From plants they enter the biosphere through food chain.
Question. State the consequences of stratospheric zone depletion.
Answer. Stratosphere contains ozone layer which absorbs harmful UV radiations of the sun, protecting the living beings on earth from health consequences of stratospheric zone (ozone) defetion are:
(i) Cancers: UV radiations damage skin cells causing increase in incidences of skin cancer and skin ageing.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Length of food chains in an ecosystem is generally limited to three or four trophic levels. Why?
Answer. Energy flow is always unidirectional, moving successively through trophic levels. Solar energy is received and trapped by autotrophs which passes it to primary, secondary and tertiary consumers. During energy transfer from one trophic level to successive trophic level, 90% of energy is lost and only 10% energy reaches the next trophic level, (Lindemann’s 10% law). Thus, after three or four trophic levels, negligible amount of energy is left to be passed to the next trophic levels. That is why length of food chains is limited to three or four trophic levels only. According to 10% law: If a producer produces 1000 KJ energy, then T2 level (second trophic level) will get 100 KJ, T3 will get 10 KJ of energy, T4 will get 1 KJ and for T5 0.1 KJ energy will be left. More number of trophic levels will get further decreased amount of energy which is neither economical, nor feasible. Thus in nature, length of food chains is generally limited to three or four trophic levels.
Question. Name the wastes which are generated in your house daily. What measures would you take for their disposal?
Answer. The types of waste generated in a house are—
(i) Kitchen wastes like vegetable and fruit peel, rind, used tea leaves.
(ii) Empty milk pouches, polythene bags, empty cartons, etc.
(iii) Waste paper (newspaper, paper bags, packing paper).
(iv) Used tooth picks and ear buds.
(v) Dust and other sweepings.
Measures for household waste disposal–
At an individual’s end following measures should be taken:
(i) Reuse of maximum possible materials
(ii) Separation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes
(iii) Biodegradable wastes should be used for composting
(iv) Non-biodegradable wastes should be disposed off at suitable places from where municipal authorities can pick them up and dispose properly and scientifically.
ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS SET – 2
OUR ENVIRONMENT
1. Which one of the following is an artificial ecosystem?
(a) Pond
(b) Crop field
(c) Lake
(d) Forest
2. In a food chain, the third trophic level is always occupied by
(a) carnivores
(b) herbivores
(c) decomposers
(d) producers
3. An ecosystem includes
(a) all living organisms
(b) non-living objects
(c) both living organisms and non-living objects
(d) sometimes living organisms and sometimes non-living objects
4. In the given food chain, suppose the amount of energy at fourth trophic level is 5 kJ, what will be the energy available at the producer level?
Grass →Grasshopper →Frog →Snake →Hawk
(a) 5 k J
(b) 50 k J
(c) 500 k J
(d) 5000 k J
5. Accumulation of non-biodegradable pesticides in the food chain in increasing amount at each higher trophic level is known as
(a) eutrophication
(b) pollution
(c) biomagnification
(d) accumulation
6. Depletion of ozone is mainly due to
(a) chlorofluorocarbon compounds
(b) carbon monoxide
(c) methane
(d) pesticides
7. Organisms which synthesise carbohydrates from inorganic compounds using radiant energy are called
(a) decomposers
(b) producers
(c) herbivores
(d) carnivores
8. In an ecosystem, the 10% of energy available for transfer from one trophic level to the next is in the form of
(a) heat energy
(b) light energy
(c) chemical energy
(d) mechanical energy
9. Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several types of organisms belonging to a lower trophic level constitute the
(a) food web
(b) ecological pyramid
(c) ecosystem
(d) food chain
10. Flow of energy in an ecosystem is always
(a) unidirectional
(b) bidirectional
(c) multi directional
(d) no specific direction
11. Excessive exposure of humans to U V-rays results in
(i) damage to immune system
(ii) damage to lungs
(iii) skin cancer
(iv) peptic ulcers
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
12. In the following groups of materials, which group (s) contains only non-biodegradable items?
(i) Wood, paper, leather
(ii) Polythene, detergent, PVC
(iii) Plastic, detergent, grass
(iv) Plastic, bakelite, DDT
(a) (iii)
(b) (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
13. Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
(a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b) Dufficient food supply
(c) Polluted air
(d) Water
14. Which of the statement is incorrect?
(a) All green plants and blue green algae are producers
(b) Green plants get their food from organic compounds
(c) Producers prepare their own food from inorganic compounds
(d) Plants convert solar energy into chemical energy
15. Which group of organisms are not constituents of a food chain?
(i) Grass, lion, rabbit, wolf
(ii) Plankton, man, fish, grasshopper
(iii) Wolf, grass, snake, tiger
(iv) Frog, snake, eagle, grass, grasshopper
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d)
(i) and (iv)
16. The percentage of solar radiation absorbed by all the green plants for the process of photosynthesis is about
(a) 1 %
(b) 5 %
(c) 8 %
(d) 10 %
17. In the given below Figure the various trophic levels are shown in a pyramid. At which trophic level is maximum energy available?
(a) T4
(b) T2
(c) T1
(d) T3
18. What will happen if deer is missing in the food chain given below? Grass → Deer → Tiger
(a) The population of tiger increases
(b) The population of grass decreases
(c) Tiger will start eating grass
(d) The population of tiger decreases and the population of grass increases
19. The decomposers in an ecosystem
(a) convert inorganic material, to simpler forms
(b) convert organic material to inorganic forms
(c) convert inorganic materials into organic compounds
(d) do not breakdown organic compounds
20. If a grass hopper is eaten by a frog, then the energy transfer will be from
(a) producer to decomposer
(b) producer to primary consumer
(c) primary consumer to secondary consumer
(d) secondary consumer to primary consumer
21. Disposable plastic plates should not be used because
(a) they are made of materials with light weight
(b) they are made of toxic materials
(c) they are made of biodegradable materials
(d) they are made of non-biodegradable materials
22. Why is improper disposal of waste a curse to environment?
23. Write the common food chain of a pond ecosystem.
24. What are the advantages of cloth bags over plastic bags during shopping?
25. Why are crop fields known as artificial ecosystems?
26. Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances. Cite examples.
27. Suggest one word for each of the following statements/ definitions
(a) The physical and biological world where we live in
(b) Each level of food chain where transfer of energy takes place
(c) The physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind and soil of an ecosystem
(d) Organisms which depend on the producers either directly or indirectly for food
28. Explain the role of decomposers in the environment?
29. We do not clean ponds or lakes, but an aquarium needs to be cleaned. Why?
30. Indicate the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Why is it unidirectional? Justify.
31. What are decomposers? What will be the consequence of their absence in an ecosystem?
32. Suggest any four activities in daily life which are eco-friendly.
33. Give two differences between food chain and food web.
34. Name the wastes which are generated in your house daily. What measures would you take for their disposal?
35. Suggest suitable mechanism (s) for waste management in fertiliser industries.
36. What are the by-products of fertiliser industries? How do they affect the environment?
37. Explain some harmful effects of agricultural practices on the environment.
38. ACTIVITY BASED QUESTION: Given below is the pictorial representation of a terrestrial food chain and a marine chain. Observe them carefully and answer the questions
given in the worksheet.
♦ Fill in the blank in the terrestrial food chain (Blank no. 1). Why is the rat given this term?
♦ Can the rat come at a lower position in the terrestrial food chain? Give reasons for your
answer.
♦ Fill up the blank no. 2. Write one common feature of all organisms that are placed at this
level in a food chain.
♦ What will be the fate of this terrestrial food chain if all the rats were removed?
♦ Will the food chains be affected if the animals at the top carnivore level were removed?
Give reasons for your answer.
39. Name four biotic and four abiotic components observed in this area.
40. Will this place be called a natural ecosystem or an artificial ecosystem? Give reasons for your answer.
41. List four producers and four consumers present in this area.
42. Construct one food chain that operates in this area. Identify the producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers (if any) in the food chain.
43. Write any two points of environmental concern that have arisen in the area due to human intervention.
44. Instruction: Read the clues given below and fill up the blocks with appropriate word/term to compete the crossword puzzle given below: One 'word' has been done for you.
The Clues
Across:
3 This principle is useful in solar cooker but can be harmful on earth (5, 5, 6)
5 Element used to make solar cells
6 A black surface ____________ heat.
7 This fossil fuel mode industrial revolution possible
8 A green house gas
10 High rise structures constructed on rivers to produce hydro electricity.
Down:
1. Its construction, on River Ganga, was opposed
2. Clean Fuel (abbreviation)
3. Bio-gas is commonly called
4. Nuclear power generation is based on this process
9. This energy is converted to electrical energy in a thermal power plant
Please click the link below to download CBSE Class 10 Science Our Environment Sure Shot Questions B.
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Chapter 15 Our Environment designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. Also download Class 10 Science Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment is free

