Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Science Periodic Classification Of Elements. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 10 Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 10 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in Science and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Science prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 10 Science
Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following Pdf for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements in Class 10. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Dobereiner’s Triads
Dobereiner observed that when elements were arranged into groups of three in the order of their increasing atomic masses, the atomic mass of the middle element was the arithmetic mean of rest of the two.
Limitation
Could be applied only to limited number of elements.
Newlands’ Law of Octaves
Newlands found that every eighth element has chemical properties when they are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses.
Limitations
* Could be valid up to calcium only
* Newlands assumed that only56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered. Mendeleev's Periodic Classification Mendeleev‟s Periodic Law states that the properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses.
Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
* Mendeleev left some blank spaces for undiscoveredelements.
* Mendeleev predicted the discovery of some elements and named them as eka-boron, eka-aluminium and eka-silicon.
* Noble gases discovered later could be placed without disturbing the existing order.
Limitations of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
* Position of Hydrogen- Could not assign a correct position to hydrogen as hydrogen resembles alkali metals as well as halogens
* Position of Isotopes- Isotopes are placed in same position though they have different atomic masses
* Separation of chemically similar elements while dissimilar elements are placed in the same group. Modern Periodic Classification Modern Periodic Law states that properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Groups in Modern Periodic Table:
Group 1 Alkali metals
Group 2 Alkaline earth metals
Groups 3 to 12 Transition elements
Group 13 Boron family
Group 14 Carbon family
Group 15 Nitrogen family
Group 16 Oxygen family
Group 17 Halogens
Group 18 Noble gases
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic classification of elements Objective Questions
Question. Two elements X and Y belong to group 1 and 2 respectively in the same period. The formulae of this oxides are
(a) XO, YO
(b) X2O, YO
(c) X2O, Y2O
(d) XO, YO2
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following has maximum non-metallic character?
(a) F
(b) Br
(c) Cl
(d) I
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following is not the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
Isotopes of an element
(a) show same atomic mass
(b) show same atomic number
(c) occupy same position in the Periodic Table
(d) show same chemical properties
Answer : A
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic classification of elements Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How many triads could Döbereiner identify from the existing elements then?
Answer : Döbernier could identify only three triads.
Question. What was the basis of classification of elements made by Newlands?
Answer : Newlands arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic masses.
Question. On what basis did Mendeleev classified the element?
Answer : Mendeleev arranged the elements on the basis of their increasing atomic mass and similarity of chemical properties.
Question. State Mendeleev’s Periodic Law.
Answer : The properties of elements are the Periodic Function of their atomic masses.
Question. What is the formula of oxide and hydride of Group I elements?
Answer : Oxide formula → R2O
Hydride formula → RH.
‘R’ represents element.
Question. Write the atomic numbers of two elements ‘X’ and ‘Y’ having electronic configurations 2, 8, 2 and 2, 8, 6 respectively.
Answer. Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 2
Atomic number is 2 + 8 + 2 = 12
Similarly,
Electronic configuration of Y = 2, 8, 6
Atomic number is 2 + 8 + 6 = 16
Question. State the Modern periodic law of classification of elements.
Answer. Modern periodic law states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Question. N, O, F cannot be classified as Döbereiner’s triad. Why?
Answer. Although the atomic mass of O (16 u) is approximately an average (16.5 u) of the atomic masses of N (14 u) and F
(19 u), i.e., (14 + 19)/2 = 16.5 but they cannot be regarded as a Döbereiner’s triad because their properties are altogether different.
Question. Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his periodic table? (any two)
Answer. Germanium, Scandium.
Question. Name two elements which show same kind of chemical reactivity as sodium.
Answer. Lithium (Li) and potassium (K) both belong to the same group as sodium (Na), So, they will show the same chemical properties as sodium.
Question. What is the location of metals and non-metals in the Modern Periodic Table?
Answer : Metals are placed on the left side and non-metals are placed on the right side of the Periodic Table.
Question. What is common among all the elements present in one period?
Answer : All the elements in same period show same number of shells e.g., all elements in period 3, show 3 electron shells each.
Question. What is atomic size?
Answer : The radius of an atom, i.e., the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an atom is called atomic size.
The atomic radius is measured in picometre. (1 pm = 10–12 m)
Question. What happens to the size of atom as we move from left to right in a period.
Answer : Ans. The atomic size in a period decreases as we move from left to right.
Question. How do you think the tendency to lose electrons will change in a group?
Answer : Down the group, the effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons decreases, hence they can easily lose electrons.
Question. What are noble gases/inert gases?
Answer : The element which is inactive, does not react with any other element and it has its outermost shell completely filled are called inert gases or noble gases.
e.g., He, Ne, Ar, Xe.
Question. An element ‘X’ belongs to II group and 2nd period. Write the atomic number and name of element.
Answer : K L ∴ Atomic Number = 4
2, 2 Element = Beryllium
Question. An element ‘P’ belongs to group = 2 and period = 3, state whether it is a metal or nonmetal and nature of its oxides.
Answer : Group 2 = Metals
Nature of oxide = Basic oxide
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic classification of elements Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Choose from the following :
4Be, 9F, 19K, 20Ca
(i) The element having one electron in the outermost shell.
(ii) Two elements of the same group.
Answer. The electronic configurations of the given elements are :
4Be = 2, 2
9F = 2, 7
19K = 2, 8, 8, 1
20Ca = 2, 8, 8, 2
(i) Potassium (K) has one electron in its outermost shell.
(ii) Be and Ca have two electrons in their outermost shells hence, they belong to same group.
Question. What is meant by periodicity of properties of elements? Why are the properties of elements placed in the same group of the periodic table similar?
Answer. When elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers, elements with similar chemical properties are repeated at definite intervals. This is known as periodicity of properties of elements.
Elements placed in the same group of the periodic table have similar properties because they have same number of outermost electrons and hence, show same valency. Thus, they all will form similar type of compounds.
Question. Rewrite the following statements after correction, if necessary
(i) Elements in the same period have equal valency.
(ii) The metallic character of elements in a period increases gradually on moving from left to right.
Answer. (i) Elements in the same group have equal valency
(ii) The metallic character of elements in a period decreases gradually on moving from left to right.
Question. In the Modern Periodic Table, the element calcium (atomic number = 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21 and 38. Which of these elements have physical and chemical properties resembling those of calcium and why?
Answer. From the given data, the electronic configuration of
different elements can be written as :
Calcium (20) = 2, 8, 8, 2
Element with atomic number 12 = 2, 8, 2
Element with atomic number 19 = 2, 8, 8, 1
Element with atomic number 21 = 2, 8, 8, 3
Element with atomic number 38 = 2, 8, 18, 8, 2
It can be easily seen that elements with atomic numbers 12 and 38 have two electrons in their outermost shell thus, they belong to same group as that of calcium. So, they will show the physical and chemical properties resembling those of calcium.
Question. Carbon (atomic number = 6) and silicon (atomic number = 14) are elements in the same group of the periodic table. Give the electronic arrangements of the carbon and silicon atoms and state the group in which these elements occur.
Answer. Electronic arrangement of carbon : 2, 4
Electronic arrangement of silicon : 2, 8, 4
Both C and Si belong to group 14.
Question. From the list of the elements given below, select three elements which form a Döbereiner’s triad. F, Mg, Ca, Br, Li, Rb, Cl, Sr, I.
Answer. Cl, Br and I form a Döbereiner’s triad because atomic mass of Br is approximetly equal to the average of the atomic mass of Cl and I. Although Mg, Ca and Sr have similar properties but the atomic mass of Ca (40 u) is not an average of the atomic masses of Mg (24.31 u) and Sr (87.62 u). Therefore, these elements do not constitute a Döebereiner’s triad.
Question. What physical and chemical properties of elements were used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table? List two observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law.
Answer : The physical property used was the atomic mass of an element.
The chemical property used was the nature of oxide and hydride formed i.e. similarity in chemical properties were used by Mendeleev. The two observations that posed challenge in Mendeleev Periodic Law were:
(i) Arranging elements according to the increasing order of atomic mass could not be maintained. Chemical properties do not depend on atomic mass.
(ii) Isotopes were not given any place in the table as they have different atomic mass but same chemical properties.
Question. Two elements A and B belong to the 3rd period of Modern Periodic Table and are in group 2 and 13 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form.
(a) Number of electrons in their atoms
(b) Size of their atoms
(c) Their tendencies to loose electrons
(d) The formula of their oxides
(e) Their metallic characters
(f) The formula of their chlorides
Answer. Electronic configuration of A = 2, 8, 2 i.e., Mg Electronic configuration of B = 2, 8, 3 i.e., Al
| Characteristics | A | B |
| No. of electrons in their atoms | 12 | 13 |
| Size of their atoms | Bigger | Smaller |
| Tendency to loose electrons | More | Less |
| Formula of their oxides | AO | B2O3 |
| Metallic character | More | Less |
| Formula of their chlorides | ACl2 | BCl3 |
Question. An element X has a total of 31 nucleons, out of which 16 are neutrons.
(a) Write the electronic configuration of an atom of element X.
(b) Determine the group and period number of element X.
(c) Give the formula of the ion formed by element X.
Answer. (a) Number of protons = 31 – 16 = 15
Number of electrons = 15
Electronic configuration = 2,8,5
(b) Element X has five valence electrons.
Hence, element X is from Group V.
Element X has three occupied shells.
Hence, element X is in Period 3.
(c) Formula of the ion formed by X = X 3–
Question. (a) Consider three elements Na, Cl, Ar and answer the following.
(i) Discuss their metallic and non-metallic character.
(ii) Discuss the acid-base character of their oxides.
(b) The element with atomic number 14 is hard and forms acidic oxide and a covalent halide.To which of the categories does the element belong?
Answer. (a) The electronic configurations of these elements are
Na : 2, 8, 1 ; Cl : 2, 8, 7 and Ar : 2, 8, 8
(i) Sodium has only 1 electron in its valence shell which it can lose easily. Therefore it is a typical metal, chlorine has seven electrons in its outermost shell, it can easily accept one electron to get noble gas configuration, hence it is a typical non-metal. Ar is a noble gas.
(ii) The oxide of Na i.e. Na2O dissolves in water to form NaOH which is a strong base. The oxide of chlorine i.e. Cl2O7 dissolves in water to give HClO4 which is a strong acid.
Ar does not form any oxides.
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
Cl2O7 + H2O → 2HClO4
Hence, both metallic character of the elements and basic character of oxides decreases from left to right across a period.
(b) Non-metal, because it forms acidic oxide and covalent halide which are characteristics of non-metals.
Question. In the table given below, some of the elements of the periodic table with atomic numbers from 3 to 18 are given. These are represented by letters, which are not the usual symbols of the elements.
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| A | E | G | |||||
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| B | C | D | F |
(a) Which of these
(i) is an alkaline earth metal?
(ii) are alkali metals?
(iii) is an element with valency 4?
(b) If A combines with F, what would be the formula of the resulting compound?
(c) What is the electronic arrangement of G?
Answer. (a) (i) C is an alkaline earth metal.
(ii) A and B are alkali metals.
(iii) D is an element with valency 4.
(b) If A combines with F, the formula of the resulting compound will be A+F –., i.e., AF.
(c) The electronic arrangement of G is 2, 8.
Question. The elements of the third period of the Periodic Table are given below:
Group I II III IV V VI VII
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
(a) Which atom is bigger — Na or Mg? Why?
(b) Identify the most
(i) Metallic and (ii) Non-metallic element in period 3.
Answer : (a) Na atom is bigger in size this is because as we move from Na to Cl, the atomic number goes on increasing and the nuclear charge also increases. It pulls/attract the valence electrons at the centre and thus the atomic size decreases.
(b) (i) Most metallic — Na
(ii) Most non-metallic — Cl
Question. Chlorine (atomic number 17) is more electronegative than sulphur (atomic number 16).
Explain.
Answer. Chlorine (Z = 17) is placed after sulphur (Z = 16) in the same period i.e. third period. The size of chlorine is smaller than that of sulphur and its atom needs only one electron to have noble gas electronic configuration while sulphur atom needs two electrons. Therefore, chlorine has greater attraction for electrons than sulphur. It is more electronegative than sulphur.
Question. Three elements A, B and C have atomic numbers 7, 8 and 9 respectively.
(a) What would be their positions in the modern periodic table ? (Mention group and period both)
(b) Arrange A, B and C in decreasing order of their size.
(c) Which one of the three elements is most reactive and why ?
Answer. The electronic configuration of these elements are :
(a) A ( Z = 7) 2, 5;
B (Z = 8) 2, 6;
C (Z = 9) 2, 7
Position of element A = 15th group and 2nd period
Position of element B = 16th group and 2nd period ‘
Position of element C = 17th group and 2nd period.
(b) In general, atomic size decreases along a period. Therefore, decreasing order of size is A > B > C
(c) The element C (Z = 9) is fluorine. It is the most reactive element since it needs only one electron to acquire a noble gas configuration.
Question. The atomic numbers of three elements X, Y and Z are 9, 11 and 17 respectively. Which of these two elements will show similar characteristics and why ?
Answer. The elements X and Z will show similar characteristics because they differ in their atomic numbers by 8 (9, 17). Both these are halogens and belong to group 17 (halogen family). These are fluorine (Z= 9) and chlorine (Z = 17) .
Question.
| Element (symbol) | A | B | C |
| Atomic no. | 5 | 7 | 12 |
The atomic number of three elements are given below :
Write the symbol of the element which belongs to
(i) group 13,
(ii) group 15, of the periodic table. State the period of the periodic table to which these elements belong. Give reason for your answer.
Answer. Electronic configuration of the elements A, B and C are as given :
| Element (symbol) | A | B | C |
| Atomic no. | 5 (2, 3) | 7 (2, 5) | 10(2, 8) |
Element (Symbol) A B C
Atomic number 5 (2, 3) 7 (2, 5) 10 (2, 8)
(i) Element A belongs to group 13 (Group No. = 10 + 3 = 13). It is boron (B)
(ii) Element B belongs to group 15 (Group No. = 10 + 5 = 15). It is nitrogen (N)
Both these elements belong to second period since they have two shells.
Question. Write two reasons responsible for the late discovery of noble gases.
Answer. (i) Noble gas elements were not present in earth crust as minerals like other elements and were present in air to a very small extent.
(ii) Their atoms have stable electronic configuration of their outermost shells also called valence shells. (2 in case of He and 8 for other elements). They do not combine with atoms of other elements.
That is why noble gas elements were discovered at a later stage.
Question. The elements with atomic number 3 to 10 belong to the second period. Taking into account the trends in the general periodic properties, predict.
(a) The most electronegative element
(b) The most electropositive element
(c) The element belonging to noble gas family
(d) The element which constitutes large number of organic compounds.
Answer. (a) The most electronegative element has atomic number (Z) = 9. It is fluorine (F).
(b) The most electropositive element has atomic number (Z) = 3. It is lithium (Li)
(c) The element belonging to noble gas family has atomic number (Z) = 10. It is neon (Ne)
(d) The element which constitutes large number of organic compounds has atomic number (Z) = 6. It is carbon (C).
Question.
| Element (symbol) | A | B | C | D | E |
| Atomic no. | 7 | 10 | 12 | 4 | 19 |
The atomic numbers of elements A, B, C, D and E are given below :
From the above table, answer the following questions
(a) Which two elements are chemically similar ?
(b) Which is an inert gas ?
(c) Which element belongs to 3rd period of periodic table ?
(d) Which element among these is a non-metal ?
Answer.
| Element (symbol) | A | B | C | D | E |
| Atomic no. | 7 (2,5) | 10 (2,8) | 12 (2,8,2) | 4 (2,2) | 19 (2,8,8,1) |
The electronic configuration of the elements are as follows :
Element A B C D E
Atomic no. 7(2, 5) 10 (2, 8) 12 (2, 8, 2) 4 (2, 2) 19 (2, 8, 8, 1)
(a) Elements C and D are chemically similar since they have same number of valence electrons.
(b) Element B is an inert gas element since it has complete octet.
(c) Element C belongs to third period since it has three shells.
(d) Element A is a non-metal since it has five valence electrons.
Question. Account for the following :
(a) Elements C, N, O and F are placed in the second period of the periodic table.
(b) Elements of group 17 are monovalent.
Answer. (a) All these elements have two electron shells. Therefore, these are placed in the second period.
C (Z=6) 2, 4 ;
N (Z = 7) 2, 5 ;
O (Z = 8) 2, 6 ;
F (Z = 9) 2, 7
(b) All the elements included in the group 17 have 7 valence electrons in their atoms. These atoms need only one electron to acquire the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas atom. Therefore, these are monovalent
Question. “Elements in Periodic Table show periodicity of properties”. List any four properties.
Answer. Periodicity i.e., repetition of similar properties is shown by the elements present in a group and separated by definite gaps of atomic number. For example,
1. Elements in a group have same number of valence electrons and same valency.
2. Elements present in a group show similar chemical properties.
3. The atomic sizes of the elements in a group increase regularly.
4. The m.p. and b.p. of the elements in a group increase regularly.
Question. The electronic configuration of three elements X, Y and Z are given below ;
X = 2 ; Y = 2, 6 ; Z = 2, 8, 2.
1. Which element belongs to the second period ?
2. Which element belongs to the eighteenth group ?
3. Which element belongs to the second group ?
4. What is the valency of Y ?
5. Are Y and Z metals or non-metals ?
Answer. 1. The element ‘Y’ belongs to second period.
2. The element ‘X’ belongs to eighteenth group also called zero group.
3. The element ‘Z’ belongs to second group.
4. Element ‘Y’ has valency equal to 2(8 -6 = 2).
5. The element ‘Y’ is a non-metal while element ‘Z’ is a metal.
Question. Using the part of the periodic table given below, answer the questions that follow.
(i) Na has physical properties similar to which elements and why ?
(ii) Write the electronic configuration of N and P.
(iii) State one property common to fluorine and chlorine.
Answer. (i) N a has physical properties similar to Li and K. All the three elements have one electron each in the valence shell of their atoms. These are known as alkali metals. However, the element hydrogen has different physical properties.
(ii) Electronic configuration of N (Z = 7) = 2, 5
Electronic configuration of P (Z = 15) = 2, 8, 5
(iii) Both the elements have seven electrons in the valence shells as their atoms and have valency equal to one.
Fluorine (Z = 19) 2, 7 ;
Chlorine (Z = 17) 2, 8, 7.
Question. The list of the elements present in the same period but in different groups is given :
1 2 13 14 15 16 17 18
(a) Do these groups represent modern periodic table ?
(b) Which element will belong to oxygen family ?
(c) Which element will not take part in chemical combination ?
(d) The elements belonging to which groups will form ionic bonds most readily ?
Answer. (a) Yes, these groups of elements represent modern periodic table.
(b) The element present in group 16 belongs to oxygen family.
(c) The element included in group 18 (noble gas elements) will not take part in chemical combination.
(d) The elements belonging to group 1 and group 17 will form ionic bonds most readily.
Question. Atomic radii of the elements present in second period are given :
1. Arrange them in decreasing order of their atomic radii.
2. Are these elements arranged in the pattern of a period in the periodic table ?
3. Which elements have the largest and the smallest atoms ?
4. How does the atomic radius change as you move from left to right in a period ?
Answer. 1. The decreasing order of atomic radii is :
Li (152) > Be (111) > B (88) > C(77) > N(74) > O(66)
2. No, the arrangement of the elements is not systematic. The correct arrangement is as given above.
3. The element Li has the largest atoms while the element O has the smallest atoms.
4. The atomic radii of the elements decrease in moving from left to the right.
Question. “The atomic number of Cl is 17. On the basis of this information, answer the questions that follow :
(a) Write the electronic configuration of Cl.
(b) Find its valency.
(c) To which group does it belong ?
(d) Identify the type of ion it will form.
(e) Write down the formula of the compound it forms with other elements.
Answer. (a) Electronic configuration of Cl (Z = 17) = 2, 8, 7.
(b) Valency of Cl = 8 – 7 = 1
(c) Group to which Cl belongs =17 id) Type of ion formed by Cl = Anion (Cl–).
(e) Formula of compound with other elements (M) = MClx
∴ Here x is the valency of the element.
Question. An element E has following electronic configuration :
(a) To which group of the periodic table does element E belong ?
(b) To which period of the periodic table does element E belong ?
(c) State the number of valence electrons present in element E.
(d) State the valency of the element E.
Answer. The element with atomic no. (Z) = 16 is sulphur (S).
(a) It belongs to group 16 of the periodic table,
(b) It belongs to third period since it has three shells.
(c) The element has six valence electrons.
(d) The valency of the element is 2 (8 – 6 = 2).
From the part of the periodic table given, answer the following questions.
(a) Which is the most reactive metal ?
(b) Name the family of L, Q, R, T.
(c) Name one element of group 2 and 15,
(d) Name one member of group 18 other than neon.
(e) Give the name of the element S placed below carbon in group 14.
Answer. (a) The element Z is the most reactive metal.
(b) The elements are present in group 17. The family is that of halogens.
(c) One element belonging to group 2 is calcium (Ca) while one present in to group 15 is nitrogen (N).
(d) The element argon (Ar) is also present in group 18.
(e) The element is silicon (Si)
Question. Elements magnesium and oxygen respectively belong to group 2 and group 16 of the Modern Periodic Table. If the atomic numbers of magnesium and oxygen are 12 and 8 respectively,draw their electronic configuration and show the process of formation of their compound by transfer of electrons.
Answer. Atomic number of magnesium = 12
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
Valency of magnesium (Mg) = 2
Similarly, for oxygen (O) atomic number = 8
Electronic configuration = 2, 6
Valency of oxygen = 8 – 6 = 2
Formation of their compound will be as follows :
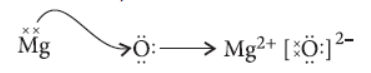
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. State the modern periodic law for classification of elements. How many groups andperiods are there in the modern periodic table?
Q2. An element 'M' has atomic number 11.
(i) Write its electronic configuration.
(ii) State the group to which 'M' belongs.
(iii) Is 'M' a metal or a non-metal?
(iv) Write the formula of its chloride.
Q3. Name two elements that show chemical properties similar to bromine .Give reason. Q4. An atom has electronic configuration 2, 8,2. (i) What is the atomic no. of this element? (ii) Is it a metal or non-metal?
Q1. The elements Li(Z = 3), Na (Z = 11)and K (Z = 19) belong to group 1
(i) Predict the periods they belong.
(ii)Which one of them is least reactive?
(iii) Which one of them has the largest atomic radius? Give reason to justify.
Q2. F, Cl and Br are the elements each having seven valence electrons. Pick the elemen
(i) with the largest atomic radius
(ii) which is most reactive. Justify your answer.
Q3. Nitrogen(Z = 7) and Phosphorus(Z = 15) belong to same group-15 of the periodic table. Write the electronic configuration of these two elements. Which of these two is more electronegative? Why? Long AnswerType Questions (5marks)
Q1.(i) How does atomic size vary along the group? Give reason.
(ii) Why are metals electropositive in nature?
(iii) What are metalloids? Give an example.
Q2. Name- (i) Two elements that have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(ii) Two elements that have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(iii) Two elements with filled outermost shell.
(iv)Two elements thatbelong to halogen family.
(v) An element which is tetravalent and forms the basis of organic chemistry.
Please click the link below to download CBSE Class 10 Science-Periodic Classification Of Elements.
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. Also download Class 10 Science Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements is free

