Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Science Our Environment Sure Shot Questions A. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 10 Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 10 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in Science and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Science prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 10 Science
Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following Pdf for Chapter 15 Our Environment in Class 10. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Abundance of coliform bacteria in a water body is indicative of pollution from
(A) petroleum refinery.
(B) metal smelter
(C) fertilizer factory
(D) domestic sewage.
Answer : D
Question. Prolonged exposure to the fumes released by incomplete combustion of coal may cause death of a human because of
(A) inhalation of unburnt carbon particles.
(B) continuous exposure to high temperature.
(C) increased level of carbon monoxide.
(D) increased level of carbon dioxide.
Answer : C
Question. Acid Rain is caused by :
(A) CO
(B) SO2
(C) O2
(D) All of the above
Answer : B
Question. Primary consumers form _____ trophic level.
(A) First
(B) Second
(C) Third
(D) Fourth
Answer : B
Question. Chipko andolan is associated with :
(A) Tomatoes
(B) Turtles
(C) Trees
(D) Lions
Answer : C
Question. The decomposers in an ecosystem convert
(A) Inorganic substance into organic substance
(B) Simpler substance into complex substance
(C) Solar energy into chemical energy
(D) Organic substance into inorganic substance
Answer : D
Question. In the given figure, various trophic levels are shown in the form of pyramid. At which trophic level the minimum energy is available ?
(A) Phytoplanktons
(B) Man
(C) Fish
(D) Zooplankton
Answer : B
Question. Accumulation of non-biodegradable pesticides in different trophic levels is known as :
(A) Biomagnification
(B) Bio-depostion
(C) Biological impaction
(D) None of these
Answer : A
Question. Largest Ecosystem of the world are
(A) Forest
(B) Grassland
(C) Great lakes
(D) Oceans
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following belongs to the category of primary consumers?
(a) Eagle and snake
(b) Grasshopper and cattle
(c) Snake and frog
(d) Water beetle and fish
Answer. B
Question. Which of the fallowing groups constitutes a correct food chain ?
(A) Grass → Rabbit → Snake → Eagle
(B) Grass → Goat → Fox → Lion
(C) Goat → Grass → Elephant → Snake
(D) Grass → Wheat → Frog → Goat
Answer : A
Question. Who proposed the term Ecosystem ?
(A) A.G. Tensley
(B) E.P. Odum
(C) Karl Mobius
(D) Earnest Haeckel
Answer : A
Question. Which component is formed by plants in the ecosystem ?
(A) Decomposer
(B) Consumer
(C) Producer
(D) All of above
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is a biotic components of an ecosystem ?
(A) Living organisms
(B) Temperature
(C) Soil and minerals
(D) All of the above
Answer : A
Question. Which is responsible for increase in global temperature ?
(A) Ozone layer depletion
(B) Acid rain
(C) Green house effect
(D) Lightning
Answer : C
Question. Food web helps in
(a) providing alternative pathways of food availability
(b) checking the overpopulation
(c) ecosystem stability
(d) all of these.
Answer. D
Question.Green house gas produced by incomplete decomposition by anaerobic methanogens is
(a) CH4
(b) CFCs
(c) CO2
(d) N2O
Answer. C
Question. Of the total amount of energy that passes from one trophic level to another in a food chain, about 10% is
(a) transpired
(b) burnt in respiration
(c) stored in body tissues
(d) lost as heat.
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following is true with respect to concept of Biodiversity ?
(a) Biodiversity refers to different species of floara & fauna present in an area
(b) Biodiversity refers to only the flora of given area.
(c) Biodiversity is greater in forests.
(d) Biodiversity is total no. of individuals of a species in given area.
(A) (a) & (b)
(B) (b) & (c)
(C) (a) & (c)
(D) (b) & (c)
Answer : C
Question. At which trophic level, maximum energy will be available ?
(A) T2
(B) T3
(C) T1
(D) T4
Answer : C
Question. In the following groups of materials, which group(s) contains only non biodegradable items?
I. Wood, paper, leather
II. Polythene, detergent, PVC
III. Plastic, detergent, grass
IV. Plastic, bakelite, DDT
(a) III
(b) IV
(c) I and III
(d) II and IV
Answer. D
Question. DDT is non-biodegradable chemical when it enters food chain it gets accumulated in each tropical level. This phenomenon is called as?
(A) Eutrophication
(B) Chemical Amplification
(C) Bio magnification
(D) Chemical Magnification
Answer : C
Question. Presence of ………………. is an indicator of pollution level in water
(A) Colour
(B) Coliform bacteria
(C) Rhizo bacteria
(D) Spiral bacteria
Answer : B
Question. The following diagram shows a simple version of energy flow through food web What happens to energy having the decomposers ?
(A) It is used by the decomposers it self
(B) It is reflected from the surface of earth
(C) It is lost as heat
(D) It is used in natural Biocomposting
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following is an abiotic component of an ecosystem?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Plants
(c) Fungi
(d) Humus
Answer. D
Question. In a grazing food chain, primary consumers (herbivores) represent
(a) T1 level
(b) T2 level
(c) T3 level
(d) T4 level.
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following does not help in protecting our environment?
(a) Crop rotation
(b) Treatment of sewage
(c) Deforestation
(d) Judicious use of fertilisers
Answer. C
Question. Now-a-days, which type of cups are being generally used in trains for serving tea/coffee/ soup etc. on daily basis?
(a) Washable glass cups
(b) Washable plastic cups
(c) Disposable paper cups
(d) Disposable cups made of plastic
Answer. C
Question. Shorter food chains provide
(a) more energy
(b) less energy
(c) same energy
(d) any of these.
Answer. A
Question. Maximum number of trophic levels supported in any ecosystem is?
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Three
(D) Four
Answer : D
Question. Which group of organisms together do not constitute a food chain?
I . Grass, lion, rabbit, wolf
II. Plankton, man, hawk
III. Wolf, grass, snake, tiger
IV. Frog, snake, eagle, grass, grasshopper
(a) I and III
(b) III and IV
(c) II and III
(d) I and IV
Answer. C
Question. Fish that feeds on zooplanktons is a
(a) primary consumer
(b) secondary consumer
(c) tertiary consumer
(d) decomposer.
Answer. B
Question. If there was no CO2 in the atmosphere, the earth’s temperature would be
(a) less than the present temperature
(b) same as the present temperature
(c) higher than the present temperature
(d) dependent on O2 content of air.
Answer. A
Question. As it travels along the food chains, the concentration of DDT
(a) increases
(b) remains constant
(c) decreases
(d) fluctuates randomly.
Answer. A
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Case Based Questions
Case I : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
Grazing food chains are directly dependent upon solar radiations as the primary source of energy. Green plants (or producers) form the first trophic level of the food chain. They synthesise their food by the process of photosynthesis. Herbivores or primary consumers feed upon the producers and form the second trophic level. Herbivores are eaten by carnivores of different categories. These are longer food chains.
Given below are 5 grazing food chains operating in the nature.
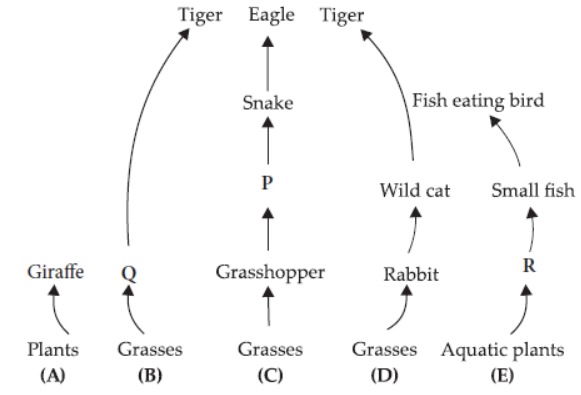
Question. Select the option that correctly identifies P,Q and R.
P Q R
(a) Frog Deer Aquatic insect
(b) Frog Elephant Phytoplankton
(c) Tadpole Deer Zooplankton
(d) Dog Elephant Algae
Answer. A
Question. According to the given food chains which of the following animals is both secondary and tertiary consumer?
(a) Rabbit
(b) Tiger
(c) Eagle
(d) Small fish
Answer. B
Question. Top consumer in which of the following food chains will have the maximum energy?
(a) Food chain A
(b) Food chain B
(c) Food chain C
(d) Food chain D
Answer. A
Question. If energy present in producers of food chain D is 20,000 KJ. Then amount of energy present in its secondary consumer will be
(a) 2000 KJ
(b) 20 KJ
(c) 2 KJ
(d) 200 KJ.
Answer. D
Question. What will be the shape of pyramid of biomass of food chain E?
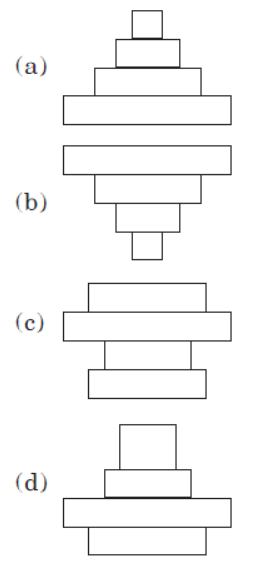
Answer. B
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Assertion And Reason Based MCQs
For question, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : There is always an interaction between neighbouring or distant ecosystems.
Reason : An ecosystem is recognised as self - regulating and self - sustaining entity.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Pyramid of biomass may be upright or inverted.
Reason : Pyramid showing total biomass produced per unit time is always upright.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Man is a social and cultured animal.
Reason : He developed socio-cultural environment and lives in it.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Ozone depletion can be reduced by limiting the use of air conditioners and refrigerators.
Reason : Air conditioner and refrigerators release chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere that destroy ozone.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Paper cups are better option than plastic cups for serving tea.
Reason : Paper cups are biodegradable and can even be disposed off by burning.
Answer. A
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the radiations that are absorbed by ozone blanket.
Answer. Ultraviolet (UV) radiations
Question.Give reason why ozone layer in the stratosphere is considered useful?
Answer. Ozone layer in the stratosphere protects the living organisms including man from harmful UV radiations of the sun by absorbing most of them.
Question. Rearrange the given members of food chain in the correct trophic level: frog, grass, snake, insect.
Answer. Grass → Insect → Frog → Snake
Question. Why are green plants called ‘producers’?
Answer. Green plants are called ‘producers’ because they prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll by the process of photosynthesis.
Question. Why are plastics non-biodegradable substances?
Answer. Plastics are non-biodegradable substance because they cannot be broken down by the action of enzymes, bacteria or decomposers.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
Answer. Differences between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable substances are:
| Biodegradable substances | Non-biodegradable substances |
| They can be broken down into simplest form by biological processes. | They cannot be broken down by biological processes. |
| They do not cause pollution. | They cause pollution. |
| They remain for less time in the environment. | They remain for a long time in the environment. |
Question. Write two causes of depletion of ozone layer.
Answer. Two causes of depletion of ozone layer are :
(a) Use of CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) in refrigerators and aerosol sprayers.
(b) Release of pollutant nitrogen monoxide by jets.
Question. Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
In the above food chain, which of the organism will have
(i) maximum available energy?
(ii) minimum available energy?
Answer. (i) Grass will have the maximum available energy.
(ii) Eagle will have the minimum available energy.
Question. Producers always occupy the first trophic level in any food chain. Why?
Answer. Producers or green plants have chlorophyll which can trap the solar energy. The first trophic level in a food chain is a producer, i.e., those organisms which can produce food with the help of sunlight and chlorophyll by a process called photosynthesis.
Question. Why are microorganisms like bacteria and fungi important in the ecosystem?
Answer. Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi are important in the ecosystem because they decompose or break down the dead remains of animals and plants. This release the locked nutrients to be recycled in the ecosystem for reuse as raw materials by the producers.
Question. What is landfilling? How is it beneficial to the environment?
Answer. Landfilling is a method of waste disposal in which solid wastes from urban areas are dumped in low lying areas and compacted by rolling with bulldozers. They are then covered with a layer of soil.
Landfilling is an effective method of solid waste disposal in urban areas and at the same time, it helps in reducing the pollution arising out of the waste.
Question. Why proposal of use of kulhads (disposable cups made of clay) in trains was set aside?
Answer. Sometime back, use of kulhads (disposable cups made of clay) was suggested as an alternative of plastic cups.
However, making of kulhads on such a large scale would have resulted in the loss of top fertile soil. Therefore, this proposal was set aside.
Question. Stability of a biotic community in an ecosystem is inversely proportional to its diversity. Do you agree with this statement?
Answer. No, I do not agree with this statement. Stability of a biotic community is directly proportional to its diversity, number of species and their interactions. Larger the number of species within a community, more stable it will be.
Question. We do not clean ponds or lakes, but an aquarium needs to be cleaned. Why?
Answer. An aquarium is an artificial or man-made ecosystem and thus, is not self-regulatory whereas, ponds and lakes are natural, self-sustaining and complete ecosystems. Therefore, ponds and lakes get cleaned by natural processes but an aquarium needs to be cleaned.
Question. What does a trophic level represent in a food chain? State the position of autotrophs and herbivores in a food chain.
Answer. The various steps representing organisms in a food chain at which the transfer of food and energy takes place are called trophic levels.
The position of producers (or autotrophs) in a food chain constitute the first trophic level. They fix up sun’s energy and make it available for consumers. The herbivores or primary consumers (which feed upon plants) constitute the second trophic level in a food chain.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Producers always occupy the first trophic level in any food chain. Why?
Answer. Only producers have the ability to trap solar energy and manufacture organic food through the process of photosynthesis.
Question. The flow of energy in the food chain is unidirectional. Why?
Answer. Energy flows from sun to plants (autotroph), plants to animals (consumer).
Question. Give any two ways in which biodegradable substance would affect the environment.
Answer. They keep the environment clean as they are easily decomposed.
They can easily go through the geochemical cycle with the help of decomposers.
Question. Name any two abiotic components of an environment.
Answer. (a) Climatic factors (light, temperature, rainfall)
(b) Edaphic factor (Soil)
Short Answer Type Question
Question. What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Answer. The organisms in specific trophic level will not be able to get the food
ii-It will cause a disturbance in food chain and therefore ecological imbalance will take place.
Question. Which gas shield the surface of earth from harmful radiation of the sun. why these radiations are supposed to be harmful for us?
Answer. Ozone gas
Harmful radiation of the sun like UV radiation may causes skin cancer, cataract, fall in immunity in infants, decline in photosynthesis rate etc
Question. Why is a lake considered to be a natural ecosystem?
Answer. In Lake living organisms grow, reproduce and interact with other biotic and abiotic components. In lake different components carry out all activities in nature by themselves without any human interference; therefore it is referred to as a natural ecosystem.
Question. In a certain study conducted on the occurrence of DDT along food chains in an ecosystem, the concentration of DDT in grass was found to be 0-5 ppm. In sheep, it was 2 ppm and in man it was 10 ppm. Name the phenomenon and define?
Answer. Bio-magnification
Bio-magnification is the increase in the level of a toxic substance with each successive rise in the trophic level of a food chain.
Question. How can we help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? List two ways.
Answer. i-Separation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes
ii-Preparation of compost / vermicomposting from biodegradable waste
iii-Recycling of waste
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Answer the followingsi-
What is ozone? How is it formed in the atmosphere?
ii- How ozone layer is useful
iii- Name the substances responsible for the depletion of ozone layer.
Answer. i- Ozone is triatomic form of oxygen, O3. Ozone is formed in the upper atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet (UV) radiations over oxygen (O2)
ii- It protects us from harmful UV radiation of sun.
iii- The important ozone depleting substances chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), methane, N2O, chlorine.
Question. In the following food chain, 100 J of energy is available to the lion. How much energy was available to the producer?
Answer. simple food chain
Plants ———> Deer ———> Lion.
As per 10 % law only 10 % of energy is transferred to next trophic level-
Energy available to deer = 100J x 10 = 1000 J
Energy available to plants = 1000 x 10 = 10,000 J.
Question. “Energy flow in a food chain is unidirectional”. Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body.
Answer. The producers convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of organic compounds. The primary consumers (herbivores) derive their nutrition from the producers. According to the energy transfer law, only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the other. So, the energy that is captured by the producers does not revert to the sun and the energy transferred to the herbivores does not come back to the producers. It just keeps on moving to the next trophic level in a unidirectional way. That is why the flow of energy in the food chain is always unidirectional. A large number of pesticides and chemicals are used to protect our crops from pests and diseases. Some of these chemicals are washed down from the soil, while some enter the water bodies. From the soil, they are absorbed by plants along with water and minerals; and from the water bodies, they are taken up by aquatic plants and animals. This is how these chemicals enter the food chain. As these chemicals cannot decompose, they accumulate progressively at each trophic level. This increase in the concentration of harmful chemicals with each step of the food chain is called biomagnification. As human beings occupy the top level in any food chain, these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies.
Question. Why bacteria and fungi are called decomposers? List any two advantages of decomposers to the environment.
Answer. Decomposers degrade breakdown the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants.
Advantages:
i- Clean environment by decomposing dead bodies of plants/ animals
ii- Replenish nutrients (Inorganic substance) into soil
iii- Helps in Nutrient recycling
Question. Explain the phenomenon of ozone depletion.What are the factors responsible for it? What are its consequences?
Answer. Ozone depletion means the thinning of ozone layer in the atmosphere. Many chemicals mainly chlorofluorocarbons are responsible for ozone depletion. These are widely used as coolants in refrigerators and air conditioners; in fire extinguishers; in aerosol sprayer and as propellants. Once released in the air, these chemicals produce `active chlorine’ (Cl and ClO radicals) in the presence of UV radiations. These radicals, through chain reaction, then destroy the ozone by converting it into oxygen. A single active chlorine can deplete one lakh ozone molecules through chain reaction. Thinning of ozone layer allows ultraviolet (UV) radiations to pass through it which then strike the earth and cause harmful effects on man, animals and plants.
(i) UV radiations increase incidences of skin cancer and herpes.
(ii) UV radiations cause damage to eyes resulting in dimming of eye sight.
(iii) Cause damage to immune system hence, lowering the body’s resistance.
(iv) Harmful UV radiations increase mortality of developing embryo in the mothers, uterus.
(v) These radiations decline the rate of photosynthesis in plants which ultimately increase the CO2 concentration leading to global warming.
Question. (a) Write two harmful effects of using plastic bags on the environment. Suggest alternatives to the usage of plastic bags.
(b) List any two practices that can be followed to dispose of the waste produced in our homes.
Answer. (a) Harmful effects of using plastic bags :
(i) These are non-biodegradable substances. They cannot be decomposed and therefore remains as pollutants in nature for many years.
(ii) The plastic bags choke drains and causes waterlogging.
(iii)The pastic release harmful chemicals in soil, water slowly over to years. Jute bags and cloth bags are the alternatives to the polyethene bags.
(b) Practices to dispose off the waste produced in our homes:
(i) Separation of biodegradable and non- biodegradable wastes.
(ii)The biodegradable waste can be converted to manure.
(iii) Non-biodegradable waste should be disposed off at suitable places from where municipal authorities can pick them up and dispose properly and scientifically.
(iv) Reuse the waste
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Chapter 15 Our Environment designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. Also download Class 10 Science Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment is free

