Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Science Heredity and evolution Sure Shot Questions A. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 10 Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 10 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in Science and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Science prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 10 Science
Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following Pdf for Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution in Class 10. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution MCQs
Question. Which of the following is a vestigial structure in python ?
(A) Teeth
(B) Scales
(C) Hind limbs
(D) Poison glands
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following can you call atavism ?
(A) Wings of bat
(B) Fins of fish
(C) Cervical fistula of man
(D) Flippers of whale
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is used for dating the bones ?
(A) C14
(B) I121
(C) K32
(D) All of these
Answer : A
Question. Evolution is the best defined by
(A) inheritance of acquired characters
(B) descent with modifications
(C) spontaneous generation
(D) struggle for existence
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is a pair of homologous organs ?
(A) Lungs of rabbit and gills of rohu
(B) Wings of bat and wings of butterfly
(C) Pectoral fin of whale and fore limb of horse
(D) Wings of grasshopper and wings of crow
Answer : C
Question. The character that proves that frogs have evolved from fishes is :
(A) The ability to swim in water
(B) The tadpole larva in frogs which resembles the fishes in many characters
(C) Similarity in the shape of the head
(D) None of these
Answer : B
Question. Analogous organs have a :
(A) Common embryonic origin but perform different functions
(B) Different embryonic origin and perform different functions
(C) Common embryonic origin and perform similar functions
(D) Different embryonic origin but perform similar functions
Answer : D
Question. The term for similarity in organ structure seen in great diversity is :
(A) Homology
(B) Identical
(C) Analogy
(D) Symmetrical
Answer : A
Question. The evidence of evolution is based on
(A) paleontology
(B) embryology
(C) anatomically
(D) all of these
Answer : D
Question. Which one is not a vestigial organ in man ?
(A) Vermiform appendix
(B) Plica semilunaris
(C) Ear muscles
(D) Epiglottis
Answer : D
Question. Which one of these is likely to have been absent in free form at the time of origin of life ?
(A) Oxygen
(B) Hydrogen
(C) Ammonia
(D) Methane
Answer : A
Question. Analogous structures are :
(A) Structurally similar
(B) Functionally similar
(C) Structurally and functionally similar
(D) Normally non-functional
Answer : B
Question. The term evolution in biology means that
(A) fossils are old
(B) life began in Sea
(C) living things constantly change
(D) none of the above
Answer : C
Question. Homologous structures have
(A) similar origin & dissimilar functions
(B) dissimilar origin but similar functions
(C) similar origin & similar functions
(D) dissimilar origin and dissimilar structures
Answer : A
Question. Who gave the term genetics ?
(A) W.Bateson
(B) Andrew Benson
(C) T. Boveri
(D) G.J. Mendel
Answer : A
Question. XX-XO type of sex determination and XX-XY type of sex determination are the examples of
(a) male heterogamety
(b) female heterogamety
(c) male homogamety
(d) both (b) and (c).
Answer. A
Question. Fossils are
(A) fovea in the retina of vertebrate eye
(B) remains of organisms presents in the rocks
(C) the fossa present in the bones
(D) foramens through which nerves pass
Answer : B
Question. Connecting link between Reptiles and Birds is
(A) Dimetrodon
(B) Dodo
(C) Archaeopteryx
(D) Sphenodon
Answer : C
Question. Fossils are dated now by
(A) stratigraphic position
(B) amount of calcium residue
(C) association with other animals
(D) radioactive carbon contents
Answer : D
Question. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) In male grasshoppers, 50% of sperms have\ no sex chromosome.
(b) Female fruitfly is heterogametic.
(c) Human male produces two types of sperms 50% having X chromosome and 50% having Y chromosomes.
(d) In turtle, sex determination is regulated by environmental factors.
Answer. B
Question. A cross between F1 generation and the recessive parent is called-
(A) Monohybrid cross
(B) Test cross
(C) Back cross
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer : B
Question. Somatic variation are due to
(A) Light
(B) Habitat
(C) Nutrition
(D) All of these
Answer : D
Question. Which of these is an inheritable variation?
(A) Somatic variation
(B) Acquired variation
(C) Germinal variation
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer : C
Question. Mutation is a
(a) change that causes evolution when inherited
(b) change which affects the parents only but never inherited
(c) change which affects the offspring of F2 generation only
(d) factor responsible for plant growth.
Answer. A
Question. Allele that cannot express itself in presence of another is
(a) codominant
(b) dominant
(c) recessive
(d) complementary.
Answer. C
Question. Some of the dominant traits studied by Mendel were
(a) round seed shape, green seed colour and axial flower position
(b) terminal flower position, green pod colour and inflated pod shape
(c) violet flower colour, green pod colour and round seed shape
(d) wrinkled seed shape, yellow pod colour and axial flower position.
Answer. C
Question. In plant, tall phenotype is dominant over dwarf phenotype, and the alleles are designated as T and t, respectively. Upon crossing one tall and one dwarf plant, total 250 plants
were obtained, out of which 124 displayed tall phenotype and rest were dwarf. Thus, the genotype of the parent plants were
(a) TT × TT
(b) TT × tt
(c) Tt × Tt
(d) Tt × tt.
Answer. D
Question. The percentage of yr gamete produced by YyRr parent will be
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 75%
(d) 12.5%.
Answer. A
Question. If a genotype consists of different types of alleles, it is called
(a) homozygous
(b) heterozygous
(c) monoallelic
(d) uniallelic.
Answer. B
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 41-50, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Mendel successfully postulated laws of heredity.
Reason : He recorded and analysed results of breeding experiments quantitatively.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : The principle of segregation given by Mendel is the principle of purity of gametes.
Reason : Gametes are pure for a character and do not mix up.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Test cross is a back cross.
Reason : In test cross, individual is crossed with recessive parent.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Pure lines are called true breeds.
Reason : True breeds are used for cross breeding.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : In a monohybrid cross, offspring of F1 generation express dominant character.
Reason : Dominance occurs only in heterozygous state.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : The traits that are obtained from parents are inherited traits.
Reason : These traits were developed in the parents during their lifetime.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : If blood group of both mother and father is ‘O’ then the blood group of children will also be O.
Reason : Blood group in humans is determined by many alleles of a gene viz. IA, IB, IO.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : In grasshoppers, females are heterogametic and males are homogametic.
Reason : In grasshoppers, male has only one sex chromosome (XO) whereas the female has sex chromosomes (XX).
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : If mother is homozygous for black hair and father has red hair then their child can inherit black hair.
Reason : Gene for black hair is recessive to gene for red hair in humans.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : A child which has inherited X chromosome from father will develop into a girl child.
Reason : Girl child inherits X chromosome from father and Y chromosome from mother
Answer. C
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why is the progeny always tall when a tall pea plant is crossed with a short pea plant?
Answer. When a tall pea plant is crossed with a short pea plant, the resultant progeny is always tall because tallness is a dominant trait while shortness is a recessive trait. Hence, dominant trait expresses itself in the progeny.
Question. How many pairs of allelic characters did Mendel study in pea plant?
Answer. Mendel studied seven pairs of allelic characters in pea plant.
Question. What do you mean by a true breeding plant?
Answer. A true breeding plant is the one that when self-fertilised, produces offspring with the same traits. They will be either homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Short Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) State one advantage of variation to a species.
(b) What are sex chromosomes? How many sex chromosomes are there in humans? Name them.
Answer. a) Variation increases the chance of the species survival in a changing environment.
(b) A sex chromosome is a type of chromosome that participates in sex determination. Humans have two sex chromosomes, X and Y.
Question. Explain in brief how Mendel interpreted his results to show that the traits may be dominant or recessive.
Answer. When Mendel crossed two pea plants with a pair of contrasting characters only one character appeared in all the members of F1 progeny, the other was not expressed.
On selfing F1, the hidden characters reappeared in just 25% of the offsprings and the other 75% shared the characters expressed in F1.
Mendel concluded that the character which expresses itself in F1 and in 75% of the individuals of F2 is dominating while the other is recessive.
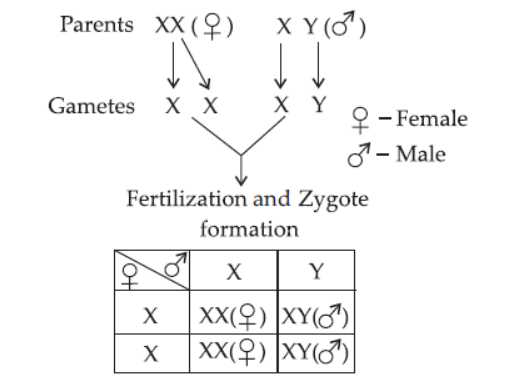
Question. Explain determination of sex among human beings, with the help of a diagram.
Answer. Diploid organisms like human beings have separate sexes. In organisms, where sex is determined genetically, a pair of chromosomes called sex chromosomes determines the sex of the individual. All other chromosomes are termed autosomes. In human beings, there are 46 chromosomes. Of these, one pair is of sex chromosomes which are of two types– X chromosome and Y chromosome.
(i) A male individual contains one X chromosome and one Y chromosome i.e., XY.
(ii) A female contains two X chromosomes i.e., XX.
The sex of the child is determined at the time of fertilisation when male and female gametes fuse to form zygote. It can be shown as follows:
Question. A blue colour flower plant denoted by BB is cross-bred with that of white colour flower plant denoted by bb.
(i) State the colour of flower you would expect in their F1 generation plants.
(ii) What must be the percentage of white flower plants in F2 generation if flowers of F1 plants are self-pollinated?
(iii) State the expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny.
Answer. (i) : The colour of the flower in F1 generation will be blue with Bb genotype.
(ii) If the flowers of F1 generations are self pollinated, then the percentage of white flowers in F2 generation must be 25%.
(iii) The expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny is 1 : 2.
The above results could be depicted by the given cross: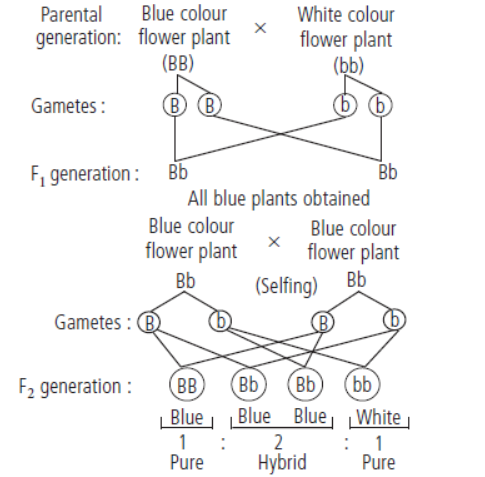
Question. Write the basic features of mechanism of inheritance. How do Mendel’s experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer. The basic features of mechanism of inheritance are as follows:
(i) Characters are controlled by genes and each gene controls one character.
(ii) Chromosomes are gene carrier and genes are basic unit of heredity.
(iii) One form of gene may be dominant on other, i.e., genes are allelic in nature.
(iv) The two forms of alleles separate at the time of gamete formation, i.e., they do not mix with each other.
(v) Two allelic forms of a gene are brought together in zygote.
Traits are inherited independently can be explained by dihybrid cross. A cross is made between a pure round yellow seeded pea plant (RRYY) with wrinkled green seeded pea plant
(rryy). Yellow colour is dominant over green and rounded seed shape over wrinkled seed shape. F1 plants are all round
and yellow seeded. F1 plants are self breed and produce F2 generation. F2 generation has four types of plants: rounded yellow, rounded green, wrinkled yellow and wrinkled green in the ratio of 9:3:3:1 respectively.
Each of the characters if considered separately shows a ratio of 3:1 as found in monohybrid cross. The F2 ratio of 9:3:3:1 shows two types of recombinants, wrinkled yellow and rounded green. They can be produced only if the alleles of the two different characters are free to recombine, i.e., separate and combine independent to each other.
Question. Plant with full green pod is said to be homozygous dominant. Plant with constricted yellow pod is said to be homozygous recessive.
Crossing of these two plants can also give rise to plants with full yellow pod. Plants with constricted green pod are also produced.
(i) What conclusion could Mendel draw from this observation?
(ii) Work out a cross upto F2 generation for such type.
Answer. (i) The plants obtained on crossing the given plants can have different combination as gametic fusion can take place in any manner (both parental combination and recombination) are possible, which proved that both the traits of the two characters are assorted independently, and hence, plants with different kind of pods are produced.
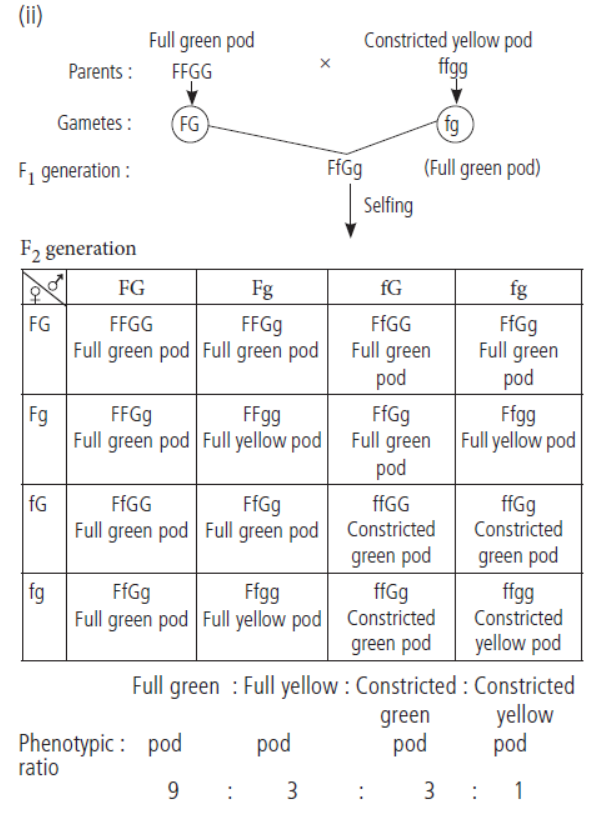
HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
1. What is heredity?
2. Name the plant on which Mendel performed his experiments?
3. Define variation?
4. Define a gene?
5. Who proposed the theory of inheritance of acquired characters.
6. State one of the evolutionary forces leading to the origin of a new species according to the synthetic theory of evolution.
7. Give an example of a vestigial organ present in human body.
8. What is the evolutionary significance of the fossil Archaeopteryx?
9. Who proposed the double helical model of DNA? Answer: Watson and Crick.
10. Who proposed the theory of natural selection? Answer: Charles Darwin.
11. What is retro virus?
12. What is a genetically modified organism (GMO)?
13. Name any two genetic diseases.
14. Write the expanded form of DNA?
15. What are the components of chromosome?
16. What is a retrovirus?
17. What is sex chromosome?
18. How is sex determined in human beings?
19. What do you understand by evolution?
20. Define homologous organs?
21. Explain Darwin’s theory of evolution?
22. Define genetics. What is the contribution of Mendel in this branch of biology?
23. Where are the genes located? What is the chemical nature of gene?
24. During which stage of cell division can chromosome be seen? Write the features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosome.
25. Who provided the evidence of DNA as a genetic material? Write the names of components of DNA?
26. What do you understand by the double helical structure of DNA? Who proposed this structure?
27. Describe the different types of chromosomes.
28. How many types of nitrogenous bases are present in DNA? Name them.
29. How do embryological studies provide evidence for evolution?
30. Define evolution. And Describe the contribution of Lamarck?
31. What are homologous organs? How do they provide evidence in support of evolution?
32. Define the following terms? (i) Vestigial organs (ii) Analogous organs.
33. What are transgenic organisms? Which property of DNA is used as a tool in genetic engineering?
34. Explain how the sex of the child is determined at the time of conception in human beings.
35. One of the examples of two analogous organs can be the wing of parrot and
a) Flippers of whale.
c) Foreleg of horse
b) Front leg of frog
d) Wing of housefly
36. Mention the ways by which variant genotypes are produced in organism?
37. In human beings blue eye colour is recessive to brown eye colour. If a brown eyed man has a blue eyed mother then find
a) What are the possible genotypes of his father?
b) What is the genotype of the man and his mother?
38. What are fossils? Of what interest are fossils to the evolutionary biologists?
39. Who isolated DNA for the first time from pus cells?
40. Why is DNA called polynucleotide?
41. Name two purine nitrogenous bases found in a DNA molecule.
42. Who put forward the double helical model of DNA?
43. What are the three chemically essential parts of nucleotides constituting a DNA?
44. Guinea pig having black colour when crossed with guinea pig having same colour produced 80 offspring, out of which 60 were black and 20 were white. Now,find out:
(a) What is the possible genotype of the guinea pigs?
(b) Which trait is dominant and which trait is recessive?
(c) What is this cross called as and what is its phenotypic ratio?
45. Distinguish between acquired and inherited traits giving one example of each.
46. Why did Mendel chosen pea plant for his experiments?
47. Cat’s paw, human hand and horse’s legs-are these organs homologous or analogous? Give reason
48. Wings of bird and wings of insect-are these organs homologous or analogous? Give one suitable season to support your answer.
49. Give one difference between eyes and eye spot. Which animal possesses eye spots?
50. Give one difference between artificial selection and natural selection.
51. What is true- humans have evolved from chimpanzees or humans and chimpanzees both have evolved from a common ancestor?
52. What is the mechanism behind the expression of a particular trait?explain briefly.
53. What will happen to the expression of a particular trait if a gene get altered?
54. What are various ways by which genes can enter a population?
55. How will new species arise in case:
(a) Two sub-populations are separated due to a huge mountain in between them?
(b) A small population of individuals gets drifted away from the main land due to sea?
56. Only advantageous variations help in the evolution of an organism giving rise to a new species. Explain with the help of an example.
57. A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed." Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
58. (a). What is genetics?
(b). Give the common name of plant on which Mendel performed his experiments. (c). What for did Mendel use the term factors and what are these factors called now. (d). What are genes? Where are the genes located?
59. 'It is a matter of chance whether a couple will give birth to a male child or a female child." Justify this statement with the help of a flow chart showing the fusion of sex chromosomes.
60. What are homologous organs? How do they provide evidence in support of evolution?
61. Who provided the evidence of DNA as a genetic material? Write the names of components of DNA? How many types of nitrogenous bases are present in DNA? Name them.
62. Name the two homologous structures in vertebrates. Why are they so called? How do such organs help in understanding an evolutionary relationship?
63. Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of a self-pollination plant species? Why or why not?
64. What are vestigial organs? Name any two vestigial organs in man and name organ which is vestigial in man but not in birds.
65. All dead organisms do not leave their fossil records, but in some cases their fossils are formed. How do these fossils records form a direct evidence of past happenings?
66. Evolution is a process in which simple life forms change into complex life forms by gradual changes. But, there is a difference between chemical and organic evolution.
Differentiate by giving three points.
67. There are a number of ways by which the genes enter a population. Explain briefly the three ways.
68. Why can the wings of a bird and the wings of a bat not be considered analogous? (Imp.)
69. How did the Mendelian 'factors' acquire a change in the terminology? Who changed it?
70. What is palaeontology? What is its importance? (Imp.)
71. The genotype of green stemmed tomato plants is denoted as GG and that of purple stemmed tomato plants is denoted as gg. When these two are crossed with each other:
(a) What colour of stem would you expect in the F1 progeny?
(b) Give the percentage of purple stemmed plants if F1 plants are self pollinated.
(c) In what ratio would you find the genotypes GG and gg in the progeny?
Draw flow chart in support of your answer.
72. How has the method of artificial selection by humans helped in the evolution of different vegetables? Explain in brief giving an example.
73. (a) Write two factors which could lead to the rise of a new species.
(b) (i) What is the scientific term of the organs shown below? (ii) How do these organs provide evidence in support of evolution?
74. (a) Name the type of sex chromosome present in human male and human female.
(b) With the help of a flow chart determine genetically in human beings the sex of the offspring if a sperm carrying Xchromosome fertilizes the egg?
75. In pea plant round seed is dominant over the wrinkled. If a cross is carried between these two plants, give answer to the following questions.
(a) Mention the genes for the traits of parents.
(b) State the trait of F1 hybrids.
(c) Write the ratio of F2 progeny obtained from this cross. What is the name of the cross? [2011]
76. Give appropriate terms for the following :
(a) The trait which can express itself in next generation.
(b) The trait an organism have due to inheritance.
(c) Origin of a new species from pre-existing one.
77. If a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf plant, then in the first generation only tall plants appear.
(a) What happens to the traits of the dwarf plant?
(b) In the second generation, the dwarf trait reappears. Why?
78. How was it established that genes are located on the chromosomes?
79. Clarify the terms 'haploid' and 'diploid'. What is the relation between the two terms?
80. Explain the law of segregation by taking an example.
81. If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same species, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
82. How does creation of variations in a species promote survival?
83. ‘Variations that confer an advantage to an individual organism only will survive in a population.’ Justify.
84. Suggest three similarities between Mendel's 'factors' and 'chromosomes'.
85. Justify logically that many genes are present on one chromosome.
Please click the link below to download CBSE Class 10 Science Heredity and evolution Sure Shot Questions A
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. Also download Class 10 Science Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution is free

