Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Science Heredity And Evolution. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 10 Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 10 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in Science and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Science prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 10 Science
Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following Pdf for Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution in Class 10. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution
HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
FLOW CHART
DEFINITIONS:- 1) GENE- Each character of an individual is determined by two factors.
2) GENOTYPE- Genes inherited from both the parents, may or may not be expressed are called genotype.
3)PHENOTYPE-Expressed structural and functional traits as a result of genes as well as environment
4)FOSSIL- Dead remain of plant and animal.
DOWN
1. An individual having two different alleles for the same trait.
4. Reductional division which required for gamete formation.
ACROSS
2. A functional unit of trait.
5. Organs having different basic structure but similar appearance and function.
6. Sudden changes in the genetic form of organisms which are passed on to the next generation.
7. Remains or impressions of dead organisms that lived in past
UP
3. Theory of inheritance of acquired character is given by
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution MCQs
Question. When a red flowered homozygous pea plant is crossed with a white flowered plant what colour is produced in F1 generation in mirabilis jalapa.
(A) Red
(B) White
(C) Pink
(D) Red and white
Answer : C
Question. The ratio of phenotype in F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is
(A) 3 : 1
(B) 1 : 2 : 1
(C) 2 : 1
(D) 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Answer : D
Question. A cross between AaBB X aa BB yields a genotypic ratio of
(A) 1 AaBB: 1 aaBB
(B) 1 AaBB : 3 aaBB
(C) 3Aa BB : 1 aa BB
(D) All AaBb
Answer : A
Question. In monohybrid cross, what is the ratio of homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive individuals in F2 – generation ?
(A) 1 : 2 : 1
(B) 2 : 1 / 1 : 2
(C) 3 : 1 / 1 : 3
(D) 1 : 1
Answer : D
Question. Plants having similar genotypes produced by plant breeding are called
(A) clone
(B) haploid
(C) autopolyploid
(D) genome
Answer : A
Question. Mendel conducted his hybridization experiments on
(A) chick pea
(B) garden pea
(C) pigeon pea
(D) wild pea
Answer : B
Question. Which one carries extra nuclear genetic material ?
(A) Plastids
(B) Ribosomes
(C) Chromosomes
(D) Golgi – complex
Answer : A
Question. Disease resistant varieties can be produced by
(A) crossing a plant with wild variety
(B) treating with colchicine
(C) crossing with hormones
(D) treating with low temperature
Answer : A
Question. The factors which represent the contrasting pairs of characters are called
(A) Dominant
(B) Recessive
(C) Determinants
(D) Alleles
Answer : D
Question. The main aim of plant breeding is
(A) to produce improved varieties
(B) to make soil fertile
(C) to control pollution
(D) to become more progressive
Answer : A
Question. Allele is the
(A) alternate trait of a gene pair
(B) total number of genes for a trait
(C) total number of chromosomes of a haploid set
(D) total number of genes present on a chromosome
Answer : A
Question. Two allelic genes are located on
(A) the heterologous chromosome
(B) two homologous chromosomes
(C) two non – homologous chromosomes
(D) any two chromosomes
Answer : B
Question. Mendel’s law of segregation is based on separation of alleles during
(A) gamete formation
(B) seed formation
(C) pollination
(D) embryonic development
Answer : A
Question. Recessive mutations are expressed
(a) always since it is a mutation
(b) in heterozygous condition
(c) neither in homozygous nor in heterozygous condition
(d) in homozygous condition.
Answer. D
Question. Heterozygous tall plants were crossed with dwarf plants, what will be the ratio of dwarf plants in the progeny
(A) 50%
(B) 25%
(C) 75%
(D) 100%
Answer : A
Question. A pure tall plant can be differentiated from a hybrid tall plant
(A) by measuring length of plant
(B) by spraying gibberellins
(C) if all plants are tall after self – pollination
(D) if all plants are dwarf after self – pollination
Answer : C
Question. The reason why some mutations, which are harmful, do not get eliminated from gene pool is that
(a) they are recessive and carried by heterozygous individuals
(b) they are dominant and show up more frequently
(c) genetic drift occur because of a small population
(d) they have future survival value.
Answer. A
Question. In Drosophila, red eye character is dominant over white eye character. When a homozygous red-eyed individual is crossed with a homozygous white-eyed individual, and individuals of F1 generation are intercrossed, 12 individuals are produced. White-eyed individuals of these will be
(a) three
(b) six
(c) nine
(d) twelve.
Answer. A
Question. A true breeding tall and smooth-seeded pea plant was crossed with a true breeding dwarf and wrinkled-seeded plant. All the F1 plants were tall and demonstrate
(a) principle of assortment of characters
(b) that recombination of characters appears in F2 generation
(c) that P tall plants were heterozygous
(d) that tallness was dominant over dwarfness
Answer. D
Question. The information source for making proteins in the cell is the
(a) chromosome
(b) DNA
(c) enzyme
(d) nucleus.
Answer. B
Question. A plant bearing purple flowers (RR) was cross pollinated with a plant bearing white flowers (rr). What would be the ratio of the plants bearing white flowers and purple flowers respectively in F2 generation when the F1 progeny were self pollinated?
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 1 : 1
(d) 2 : 1
Answer. A
Question. What will be the percentage of purple stemmed plants in the F2 generation, when the F1 generation resulted due to cross breeding of green stemmed (GG) tomato plants with purple stemmed (gg) tomato plants, are self pollinated?
(a) 10%
(b) 25%
(c) 75%
(d) 50%
Answer. B
Question. In human beings, the statistical probability of having a male child is
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 75%
(d) 60%.
Answer. B
Question. Mendel formulated the law of purity of gametes on the basis of
(A) dihybrid cross
(B) monohybrid cross
(C) back cross
(D) test cross
Answer : B
Question. Back cross is a cross between
(A) F1 × F1
(B) F1 × Recessive
(C) F1 × Dominant
(D) F1 × any parent
Answer : D
Question. Segregation of alleles takes place during
(a) meiosis
(b) cleavage
(c) fertilisation
(d) crossing over.
Answer. A
Question. The genotypic ratio in F2 generation of monohybrid cross will be
(a) 1 : 2 : 1
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 1 : 1
(d) 1 : 2.
Answer. A
Question. Mendel studied seven contrasting characters for his breeding experiment with Pisum sativum.Which of the following characters did he not use?
(a) Pod colour
(b) Pod shape
(c) Leaf shape
(d) Plant height
Answer. C
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Case Based MCQs
Case : Read the following and answer the following questions.
Refer to the given table regarding results of F2 generation of Mendelian cross.
| Plants with round and yellow coloured seeds (P) | 315 |
| Plants with round and green coloured seeds (Q) | 108 |
| Plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds (R) | 101 |
| Plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds (S) | 32 |
Question. Which of the following would be the phenotype of F1 generation regarding given data of F2 generation?
(a) Plants with round and yellow coloured seeds.
(b) Plants with round and green coloured seeds.
(c) Plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds.
(d) Plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds.
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following would be the genotype of parental generation regarding given result of F2 generation?
(a) YYRR and yyrr
(b) YYRR and YYRR
(c) YYRR and YyRr
(d) YyRr and YyRr
Answer. A
Question. If plant with wrinkled and green coloured seeds (S) is crossed with plant having wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds (R), what will be the probable phenotype of offsprings?
(a) All plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds.
(b) 50% plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds and 50% plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds.
(c) All plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following will result when plant YyRr is self-pollinated?
(a) 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio of phenotypes only
(b) 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio of genotypes only
(c) 1 : 1 : 1 : 1 ratio of phenotypes only
(d) 1 : 1 : 1 : 1 ratio of phenotypes and genotypes
Answer. A
Question. The percentage of yR gamete produced by YyRR parent will be
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 75%
(d) 12.5%
Answer. B
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name one trait which is inherited and one trait which is acquired.
Answer. Inherited trait – Eye colour in humans Acquired traits – Reduction in body weight of an animals due to starvation.
Question. All the variations in a species do not have equal chances of survival. Why?
Answer. All the variations do not have equal chances of survival in the environment in which they live. Depending on the nature of variations, different individuals would have different kinds of advantages. The organisms which are most adapted to the environment will survive.
Question.Sex chromosomes of human males are dissimilar. Justify.
Answer. Human males have XY sex chromosomes, where X chromosome is morphologically distinct from Y chromosome. Y chromosome is smaller than X chromosome. Hence, they are dissimilar or heteromorphic.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Short Answer Type Questions
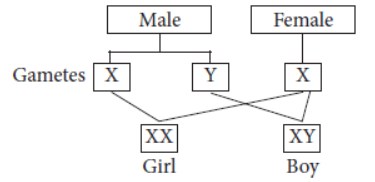
Question. “It is a matter of chance whether a couple will have a male or a female child.” Justify this statement by drawing a flow chart.
Answer. Sex is determined at the time of fertilisation when male and female gametes fuse to form zygote. Male produces two types of gametes, i.e., having X or Y chromosome and female produces one type of gametes all containing X chromosomes. If a sperm (male gamete) carrying X chromosome fertilises an egg or ovum (female gamete) carrying X chromosome, then the offspring will be a girl (female). This is because the offspring will have XX combination of sex chromosomes. If a sperm (male gamete) carrying Y chromosome fertilises an egg or ovum (female gamete) which has X chromosome, then the offspring will be a boy (male). This is because the offspring will have XY combination of sex chromosomes.
Therefore, there is 50% chance of a male child and 50% chance of a female child.
Question. The genotype of green stemmed tomato plants is denoted as GG and that of purple stemmed tomato plants as gg. When these two are crossed :
(i) What colour of stem would you expect in their F1 progeny ?
(ii) Give the percentage of purple-stemmed plants if F1 plants are self pollinated.
(iii) In what ratio would you find the genotypes GG and Gg in the F2 progeny?
Answer. (i) In F1 progeny all tomato plants will be green stemmed with genotype Gg.
(ii) 25% of plants will be purple stemmed in F2 generation which are produced due to self pollination of F1 plants.
(iii) In F2 progeny ratio of GG to Gg will be 1 : 2 and will be green stemmed.
Question. How do germ cells make a single set of genes from two normal copies of genes?
Answer. There is a pair of genes for a particular trait. The genes controlling a particular trait separate from each other during gamete formation. Germs cells make a single set of genes from two normal copies by a process called meiosis or reduction division. Hence gamete is always pure as far as contrasting characters are considered and will possess only one gene set. When male and female gametes fuse during fertilisation, paired condition is restored.
Question. “Different species use very different strategies for determining the sex of their new born.” Justify this statement.
Answer. In some animals, environmental factors such as association with families, egg size and incubation temperature determine the sex of the individuals. For example, in lizards the temperature at which fertilised eggs are kept, determines whether the developing animal in fertilised egg is male or female. In some animals, like snail, individual can change sex. However, in some animals, sex of individuals determined genetically by specific chromosomes. For example in humans, if a child inherits X-chromosome from the father, will be a girl and one who inherits a Y-chromosome from the father will be a boy.
Question. How do proteins control the expression of characters? Explain it by taking an example of tallness in plants as a characteristic.
Answer. Plants have hormones that can trigger growth. Plant height can depend on the amount of a particular plant hormone. The amount of the plant hormone produced will depend on the efficiency of the process for making it. An enzyme (chemically protein molecules) that is important for this process, if works efficiently, a lot of hormone will be produced, and the plant will be tall. If the gene for that enzyme has an alteration that makes the enzyme less efficient, the amount of hormone will be less, and the plant will be short. Thus, enzymes which are protein in nature control the expression of characters.
Question. Give reasons for the appearance of new combinations of characters in the F2 progeny.
Answer. A breeding experiment dealing with two characters at the same time is called a dihybrid cross. In such a cross only one parental combination appears in F1 generation. However, in F2 generation raised by self pollination, four combinations of traits appear. These include two parental types and two new combinations. A typical dihybrid cross in pea plant is depicted as follows :
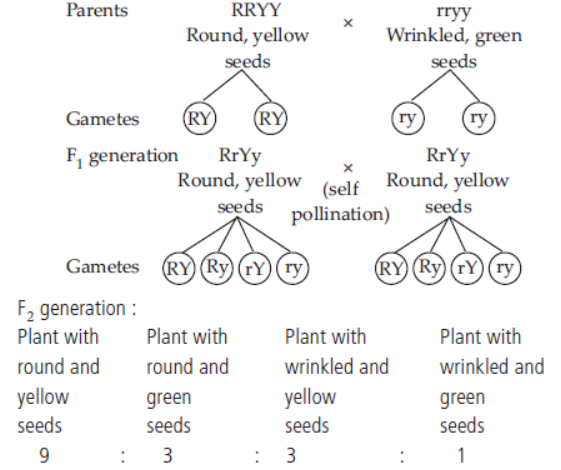
New combination of characters appear in F2 generation because the inheritance of factors controlling a particular trait in an organism are independent of each other. This is called law of independent assortment. At the time of reproduction, two pairs of factors of each of the two traits in a dihybrid cross segregate independently during gamete formation and randomly form combinations in F2 generation.
Question. In the following crosses write the characteristics of the progeny.
| Cross | Progeny |
| RRYY x RRYY Round, Round, yellow yellow | --- |
| RrYy x RrYy Round, Round, yellow yellow | --- |
Answer. (a) When two plants with round yellow seeds are crossed, the progeny produced will also possess round yellow seeds.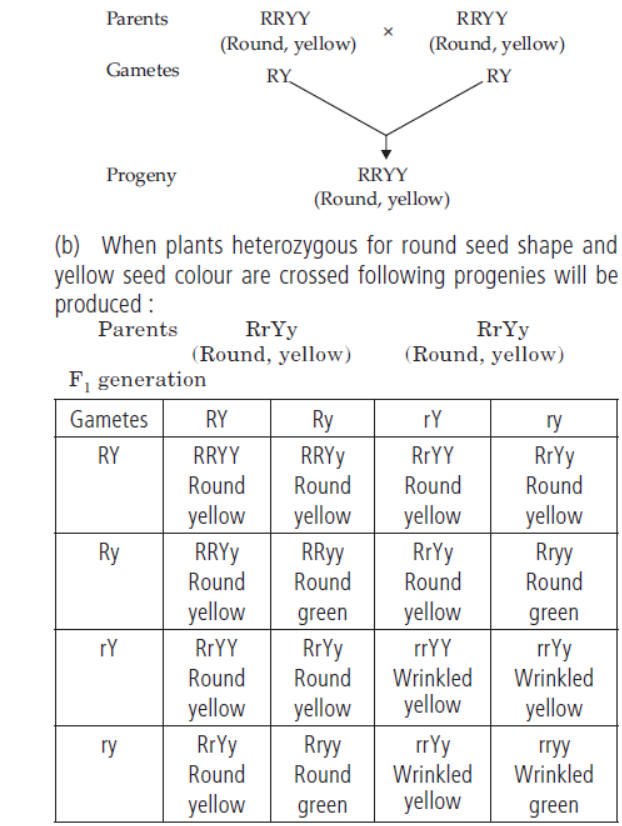
The progeny produced will posses round yellow, round green, wrinkled yellow, and wrinkled green seeds in the ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
Question. After self-pollination in pea plants with round, yellow seeds, following types of seeds were obtained by Mendel:
| Seeds | Number |
| Round, yellow | 630 |
| Round, green | 216 |
| Wrinkled, yellow | 202 |
| Wrinkled, green | 64 |
Analyse the result and describe the mechanism of inheritance which explains these results.
Answer. In Mendel’s dihybrid cross, with yellow round and green wrinkled seeds 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio was obtained showing four phenotypes. Yellow colour was originally present with round seeds but in F2 generation it was assorted independently of round seed character and expressed with wrinkled seeds.Same is the case with green colour. Thus, it shows independent assortment of characters.
Question. A man having blood group O marries a woman having blood group B and they have a daughter. What will be the blood group of the daughter?
Answer. 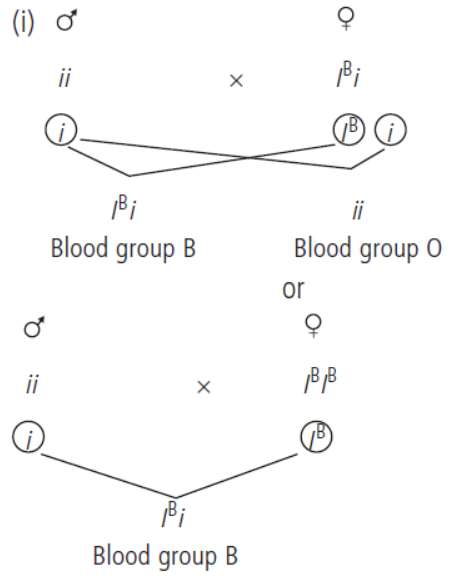
The blood group of the daughter be either B or O depending upon the blood group of mother.
Question. Explain with an example, how genes control the characteristics (or traits).
Answer. The genes control the characteristics by making a specific protein. Genes are the segment of DNA that contains information to form RNA which ultimately forms protein. Each gene contains two alleles and this instruct the cell to make protein for expression of traits. For example, if the plant has genes for violet flower, then it will make protein which will give violet colour to flowers.
Please click the link below to download pdf file of CBSE Class 10 Science-Heredity And Evolution.
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. Also download Class 10 Science Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution is free

