Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic effects of electric current Sure Shot Questions A. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 10 Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 10 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in Science and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Science prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 10 Science
Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following Pdf for Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current in Class 10. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 Science will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic effects of electric current Multiple Choice Questions
Question. A magnetic field exerts no force on
(a) a stationary electric charge
(b) a magnet
(c) an electric charge moving perpendicular to its direction
(d) an unmagnetised iron bar.
Answer. A
Question. At the centre of a magnet, the magnetism is
(a) zero
(b) same as at the poles
(c) maximum
(d) minimum.
Answer. A
Question. If a circular loop carries current I then the direction of the magnetic field at the centre with the help of magnetic lines of force will be
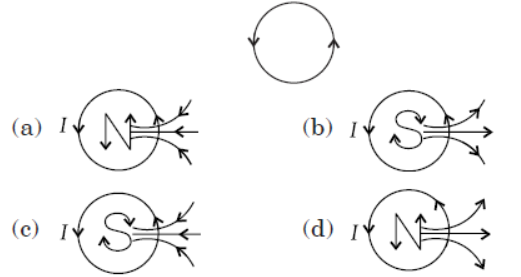
Answer. D
Question. Induced current flows through a coil
(a) for more than the period during which flux changes through it.
(b) for less than the period during which flux changes through it.
(c) only for the period during which flux changes through it.
(d) none of the above.
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following instruments works by electromagnetic induction?
(a) Dynamo.
(b) Moving coil galvanometer.
(c) Telephone receiver.
(d) Simple motor.
Answer. A
Question. An electric charge in uniform motion produces
(a) an electric field only
(b) a magnetic field only
(c) both electric and magnetic fields
(d) no such field at all
Answer. C
Question. When is the force experienced by a currentcarrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
(a) At 30°
(b) at 60°
(c) At 45°
(d) at 90°
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following properties of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field?
(a) Mass
(b) Speed
(c) Momentum
(d) Kinetic energy.
Answer. C
Question. Choose the correct alternative which matches second and third column with first column
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| Magnetic field is produced near current carrying conductor | Right hand thumb rule | Micheal Faraday |
| Electric current is generated in a conductor moving in a magnetic field | Fleming's right hand rule | Hans Oersted |
(a) I – (2) – (i), II – (2) – (ii)
(b) I – (1) – (ii), II – (2) – (ii)
(c) I – (2) – (ii), II – (1) – (i)
(d) I – (1) – (ii), II – (2) – (i)
Answer. D
Question. A soft iron bar is introduced inside a current carrying solenoid. The magnetic field inside the solenoid
(a) will increase
(b) will remain unaffected
(c) will become zero
(d) will decrease.
Answer. A
Question. A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current change once in each
(a) two revolutions
(b) one revolution
(c) half revolution
(d) one-fourth revolution.
Answer. C
Question. A circular loop is suspended in air as shown in figure. When the loop is seen from above, current flows anticlockwise and when seen from below, current flows clockwise. This loop behaves as a magnet. The N-pole of this magnet is on
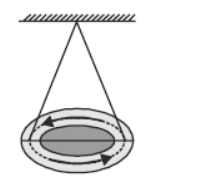
(a) the upper face
(b) lower face
(c) the lower face if current is large
(d) upper face if current is large.
Answer. A
Question. Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of field:
(a) The direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points.
(b) Magnetic field lines are closed curves.
(c) If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength.
(d) Relative strength of magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines.
Answer. C
Question. A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of paper carries a current when the key is ON. The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anticlockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the face close to
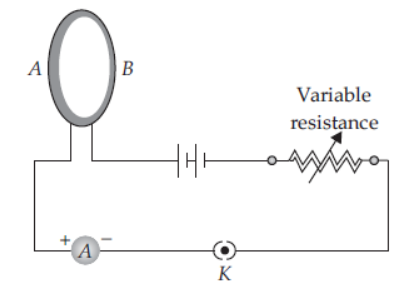
(a) A
(b) B
(c) A if the current is small, and B if the current is large
(d) B if the current is small, and A if the current is large
Answer. A
Question. For a current in a long straight solenoid,N- and S-pole are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
(a) the field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicate that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid
(b) the strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft iron, when placed inside the coil
(c) the pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet
(d) the N- and S-poles exchange positions when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
Answer. C
Question. On which of the following does not exert any force when kept in uniform magnetic field?
(a) Moving magnet
(b) Moving charge
(c) Stationary magnet
(d) Stationary charge
Answer. D
Question. An electric current passes through a straight wire. Magnetic compasses are placed at the points X and Y. Then,

(a) their needles will not deflect
(b) only one of the needles will deflect
(c) the needles will deflect in the same direction
(d) the needles will deflect in the opposite directions.
Answer. D
Question. An ionized gas contains both positive and negative ions. It is projected towards east to a region having uniform magnetic field directed into the plane of paper, then
(a) positive ions deflect towards north and negative ions deflect towards south
(b) positive ions deflect towards south and negative ions deflect towards north
(c) all ions deflect towards south
(d) all ions deflect towards north.
Answer. A
Question. The diagram given below represents magnetic field caused by a current carrying conductor which is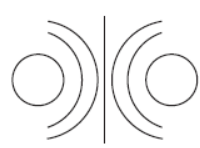
(a) a long straight wire
(b) a circular coil
(c) a solenoid
(d) a short straight wire.
Answer. B
Question. Three rings P, Q and R are dropped at the same time over identical hollow magnets as shown here.
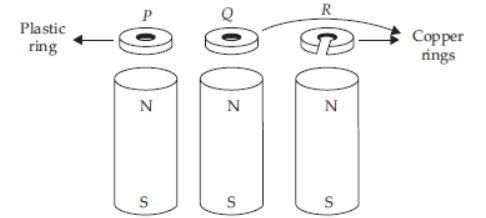
Which of the following describes the order in which the ring P, Q and R reach the bottom of the magnet?
(a) They arrive in the order, P, Q, R.
(b) They arrive in the order P, R, Q
(c) Rings P and R arrive simultaneously, followed by Q
(d) Rings Q and R arrive simultaneously, followed by P.
Answer. B
Question. The direction of magnetic field around a straight conductor carrying current can be determined by
(a) Fleming’s left hand rule
(b) Lenz’s law
(c) Right hand thumb rule
(d) Fleming’s right hand rule.
Answer. C
Question. Magnetic field is produced by the flow of current in a straight wire. This phenomenon was discovered by
(a) Coulomb
(b) Oersted
(c) Faraday
(d) Maxwell.
Answer. B
Question. An electric motor is a device which transform :
(a) mechanical anergy to electrical energy
(b) heat energy to electrical energy
(c) electrical energy to heat energy
(d) electrical energy to mechanical energy.
Answer. D
Question. For making a strong electromagnet, the material of the core should be
(a) brass
(b) laminated steel strips
(c) soft iron
(d) steel.
Answer. C
Question. The magnetic field produced due to a circular wire at its centre is
(a) at 45° to the plane of the wire
(b) at 60° to the plane of the wire
(c) in the plane of the wire
(d) perpendicular to the plane of the wire.
Answer. D
Question. Four students plotted the sketch of the patterns of magnetic field lines representing the magnetic field around a current carrying straight wire as shown in figures P, Q, R and S. Which one of the following sketches is correct?
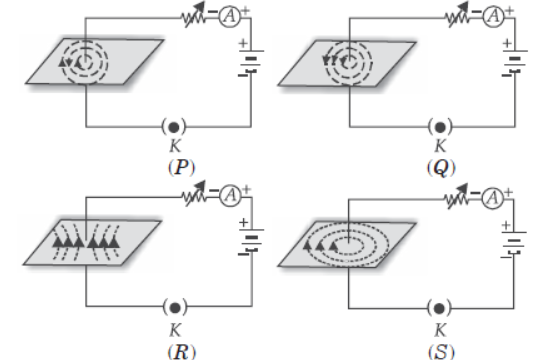
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Answer. D
Question. A positively-charged particle (alphaparticle) projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is
(a) towards south
(b) towards east
(c) downward
(d) upward
Answer. D
Question. A soft iron bar is enclosed by a coil of insulated copper wire as shown in figure. When the plug of the key is closed, the face B of the iron bar marked as
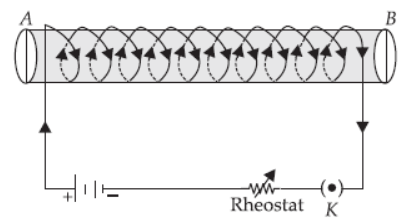
(a) N–pole
(b) S–pole
(c) N–pole if current is large
(d) S–pole if current is small.
Answer. A
Question. A horizontal wire carrying a current as shown in figure below between magnetic poles N and S. The direction of the force on the wire due to the magnet is
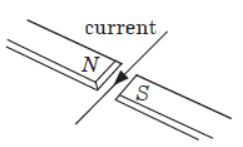
(a) in the direction of the current
(b) vertically downwards
(c) opposite to the current direction
(d) vertically upwards.
Answer. D
Question. The phenomena of electromagnetic induction is
(a) the process of charging a body
(b) the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil
(c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil
(d) the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
Answer. C
Question. If the force exerted on a current carrying wire placed in a magnetic field is zero, then the angle between wire and the direction of magnetic field is
(a) 45°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 180°
Answer. D
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic effects of electric current Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
Electric Charges moving in a magnetic field experience a force, while there is no such force on static charges. This fact was first recognized by Hendrik Antoon Lorentz, a great Dutch physicist, nearly a century ago. Thus, a charge moving in a magnetic field experience a force, except when it is moving in a direction parallel to it. The magnitude of force experienced depends on the charge, velocity (v), strength of magnetic field (B), and sine of the angle between v and B. If the direction of velocity is perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field, direction of magnetic force is given by Fleming’s left hand rule.
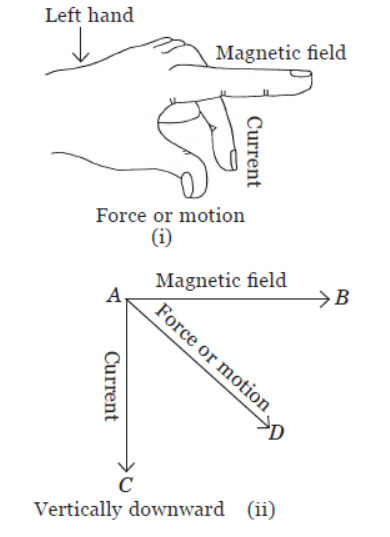
Question. If an electron is travelling horizontally towards east. A magnetic field in vertically downward direction exerts a force on the electron along
(a) east
(b) west
(c) north
(d) south.
Answer. D
Question. If a charged particle is moving along a magnetic field line. The magnetic force on the particle is
(a) along its velocity
(b) opposite to its velocity
(c) perpendicular to its velocity
(d) zero.
Answer. A
Question. A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper pointing from left to right as shown in figure. In the field an electron and a proton move as shown. The electron and the proton experience
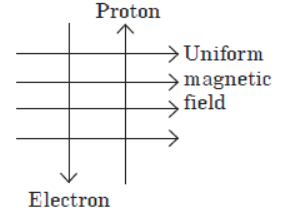
(a) forces both pointing into the plane of paper
(b) forces both pointing out of the plane of paper
(c) forces pointing into the plane of paper and out of the plane of paper, respectively
(d) force pointing opposite and along the direction of the uniform magnetic field respectively.
Answer. D
Question. An neutron beam enters a magnetic field at right angles to it as shown in the figure. Due to magnetic field, neutron beam will deflect
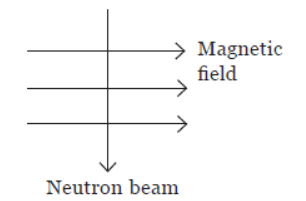
(a) to the left
(b) to the right
(c) into the page
(d) no deflection.
Answer. D
Case II : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
An electric motor is a rotating device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric motor is used as an important component in electric fans, refrigerators, mixers, washing machines, computers, MP3 players, etc.
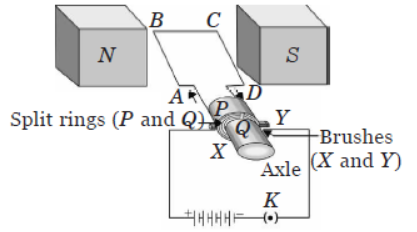
An electric motor consists of a rectangular coil ABCD of insulated copper wire. The coil is placed between the two poles of a magnetic field such that the arm AB and CD are perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. The ends of the coil are connected to the two halves P and Q of a split ring. The inner sides of these halves are insulated and attached to an axle. The external conducting edges of P and Q touch two conducting stationary brushes X and Y, respectively, as shown in the figure.
Commercial motors use an electromagnet in place of a permanent magnet.
Question. Choose incorrect statement from the following regarding split rings.
(a) Split rings are used to reverse the direction of current in coil.
(b) Split rings are also known as commutator.
(c) Split ring is a discontinuous or a broken ring.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following has no effect on the size of the turning effect on the coil of an electric motor?
(a) The amount of the current in the coil.
(b) The direction of the current in the coil.
(c) The number of turns in the coil.
(d) The strength of the magnetic field.
Answer. B
Question. When current is switched ON, an electric fan converts
(a) mechanical energy to chemical energy
(b) electrical energy to mechanical energy
(c) chemical energy to mechanical energy
(d) mechanical energy to electrical energy.
Answer. B
Question. In an electric motor, device that makes contact with the rotating rings and through them current is supplied to coil is
(a) axle
(b) brushes
(c) coil
(d) split rings.
Answer. B
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic effects of electric current Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 41-50, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Magnetic field lines show the direction (at every point) along which a small magnetised needle aligns (at the point).
Reason : Magnetic field lines certainly represent the direction of magnetic field, but not the direction of force, this is because force is always perpendicular to magnetic field B.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Magnetic field interacts with a moving charge and not with a stationary charge.
Reason : A moving charge produces a magnetic field.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : No net force acts on a rectangular coil carrying a steady current when suspended freely in a uniform magnetic field.
Reason : Forces acting on each pair of the opposite sides of the coil are equal and opposite.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : In a conductor, free electrons keep on moving but no magnetic force acts on a conductor in a magnetic field.
Reason : Force on free electron due to magnetic field always acts parallel to its direction of motion.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : The magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid is independent of its length and cross sectional area.
Reason : The magnetic field inside the solenoid is uniform.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : In electric circuits, wires carrying currents in opposite directions are often twisted together.
Reason : If the wire are not twisted together, the combination of the wires forms a current loop.
The magnetic field generated by the loop might affect adjacent circuits or components.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : The magnetic field intensity at the centre of a circular coil carrying current changes, if the current through the coil is doubled.
Reason : The magnetic field intensity is dependent on current in conductor.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : For a point on the axis of a circular coil carrying current, magnetic field is maximum at the centre of the coil.
Reason : Magnetic field is proportional to the distance of point from the circular coil.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : When two long parallel wires, hanging freely are connected in parallel to a battery, they come closer to each other.
Reason : Wires carrying current in opposite directions repel each other.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : The direction of force is given by Fleming’s left hand rule.
Reason : A magnetic field exert a force on a moving charge in the same direction as the direction of field itself.
Answer. C
Short Answer Type Question
Question. You are given the magnetic field pattern of a magnet. How will you find out from it where the magnetic field is the strongest?
Answer. Magnetic field is the strongest at the place where the magnetic field lines are closest together.
Question. How is the strength of magnetic field near a straight current-conductor
(i) related to the strength of current in the conductor?
(ii) is affected by changing the direction of flow of current in the conductor?
Answer. (i) The strength of magnetic field around a straight current conductor increases on increasing the strength of current in the conductor or vice versa.
(ii) The direction of magnetic field around a straight current carrying conductor gets reversed if the direction of current through that conductor is reversed.
Question. On what factors does the strength of magnetic field depends for a current carrying solenoid?
Answer. The strength of magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid depends on:
(i) The number of turns in the solenoid. Larger the number of turns in the solenoid, greater will be the magnetism produced.
(ii) The strength of current in the solenoid. Larger the current passed through solenoid, stronger will be the magnetic field produced.
(iii) The nature of “core material” used in making solenoid. The use of soft iron rod as core in a solenoid produces the strongest magnetism.
Question. Arun while studying the force experienced by a current carrying conductor in a magnetic Field records the following observation
1 The force experienced by the conductor is increases as the current in the conductor is decreased
2 The force experienced by the conductor is decreases as the strength of magnetic field is decreased
3 Direction of the force on the current carrying conductor is determined suing Fleming Left hand rule
Which of these observations is correct? Explain.
Answer. F = iLB
(a) So as current is decreased, Force also decreases. Observation is Incorrect
(b) Again, Force experience is decreased as strength of magnetic field is decreased. Observation is correct
(c) Observation is correct
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 MARK)
1. Name the scientist who discovered the magnetic effect of current.
2. Does a current flowing in a wire always give rise to a magnetic field around it?
3. State any two properties of magnetic field lines.
4. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
5. Name the effect of current on which an electromagnetic works.
6. What name is given to the combination of a solenoid and a soft iron core?
7. Can steel be used for making electromagnets?
8. Name the scientist who discovered that a current carrying conductor when placed in a magnetic field experiences a mechanical force.
9. When is the maximum force exerted on a current carrying conductor while it is kept in a magnetic field?
10. Does a current carrying conductor experience some force when kept parallel to the magnetic field?
11. Which rule is employed to find the direction of force on a current carrying conductor when kept in a magnetic field? State the rule and explain it by a diagram.
12. Name the transformation of energy involved in the electric motor.
13. What is the function of commutator rings in the electric motor?
14. What is the function of carbon brushes in the electric motor?
15. Name one application of electromagnetic induction.
16. What is the other name of electric generator?
17. Name the transformation of energy in an electric generator.
18. What is a turbine used for?
19. Name the different types of electric power plants for generating electricity on large scale.
20. Name the fuel used in a thermal power plant.
21. Name the fuel used in an atomic power plant.
22. What do you understand by magnetic field?
23. What do you mean by electromagnetism?
24. What is meant by magnetic effect of current?
25. Can you observe the magnetic field?
26. What do you mean by a magnetic line of force?
27. Is a magnetic line of force always a straight line?
28. What do you conclude from Oersted’s experiment?
29. Can you magnetic line of force ever intersect each other?
30. What kind of magnetic field is produced by a straight current carrying conductor?
31. What kind of magnetic field is produced by a current carrying circular field?
32. What do you mean by a solenoid?
33. State the clock rule for a current carrying solenoid.
34. How does a current carrying solenoid behave?
35. What is the nature of magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid?
36. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field inside a current carrying solenoid?
37. Name the effect of current upon which electromagnets are based?
38. Are electromagnets permanent magnets?
39. Name the material used for making the core of an electromagnet.
40. Can we use steel, instead of soft iron, for making the core of an electromagnet? Why?
41. Can we change the polarity of a permanent magnet?
42. Can we change the polarity of an electromagnet?
43. Is the strength of an electromagnet always constant?
44. Name the rule applied to know direction of the force acting on a current carrying conductor when placed in a magnetic field.
45. Name the transformations of energies takes place in an electric motor.
46. Name the two kinds of motors.
47. Which kind of motor is used in a fan?
48. Which kind of motor used in a battery-operated toy?
49. Name the experiment which formed the basis of an electric motor.
50. What forms the commutator of an electric motor?
51. State quantitatively, the effect of inserting an iron core into a current carrying solenoid.
52. Name the types of electromagnets commonly used.
53. What happens to the strength of an electromagnet when the magnitude of current decreases?
54. What will you prefer, soft iron or steel to make an electromagnet?
55. Can we produce electricity from magnetism?
56. Name the phenomenon in which an electric current could be produced in a circuit by changing the magnetic field.
57. What do you mean by electromagnetic induction?
58. What is e.m.i. or E.M.I.?
59. What do you understand by electric motor effect?
60. What is the cause of electromagnetic induction?
61. Does the AC generator have any slip ring?
62. Does the DC generator have two slip rings?
63. What is the frequency DC?
64. Name the fuel used by nuclear power station.
65. Name the device which converts electrical energy into kinetic energy.
66. What is the SI unit of induced emf?
67. State two factors on which the strength of induced current depends.
68. What is the SI unit of induced current?
69. What is electromagnetic induction?
70. What do you mean by a solenoid?
SHORT ANSWER TYPE – I QUESTIONS (2 MARKS)
1. Draw a labeled diagram of an electric motor.
2. State and explain Fleming’s right hand rule for the direction of induced current.
3. What do you mean by DC? Show by a diagram.
4. What do you mean by AC? Show by a diagram.
5. Draw a labeled to show the magnetic field pattern due to a straight wire carrying current.
6. With the help of a diagram, indicate the direction of magnetic field produced by a current carrying conductor. Name the rule employed and state it.
7. With the help of a diagram, indicate the direction of magnetic field produced due to a circular wire carrying current.
8. Indicate the direction of the magnetic field produced in a solenoid when some current is passed through it.
9. How can we increase the strength of magnetic field produced by a circular coil carrying conductor?
10. What are the factors on which the strength of magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid depends?
11. List the factors affecting the strength of an electromagnet.
12. Show that magnetic lines of force due to a bar magnet.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE – II QUESTIONS (3 MARKS)
1. Briefly describe Oersted’s experiment to demonstrate the magnetic effect of current.
2. What are magnetic field lines? Give their important properties.
3. How will your experimentally show the magnetic field produced by a straight current carrying conductor? Also state Maxwell’s right hand grip rule.
4. What kind of magnetic field is produced by a current carrying circular coil? Show it with the help of a labeled diagram.
5. What do you mean by a solenoid? With the help of a labeled, show the magneticfield due to a current carrying solenoid.
6. What do you mean by an electromagnet? With the help of diagram show the two types of electromagnets. Give two uses of electromagnets.
7. How does AC differ from DC? What are the advantages and disadvantages of AC over DC?
8. What is the basic difference between an AC generator and a DC generator?
9. Briefly explain the phenomenon of earthing using examples.
10. Describe the salient features of tree system of wiring.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (5 MARKS)
1. Why does a magnetic compass needle pointing North and South in the absence of a nearby magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is
brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines if field concept.
2. With the help of a labeled circuit diagram, illustrate the pattern of field lines of the magnetic field around a current carrying straight long conducting wire. How
is the right hand thumb rule useful to find the direction of magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor?
3. Explain with the help of a labeled diagram the distribution of magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop. Why is it that if a current carrying coil has
‘n’ turn, the field produced at any point is a times as large as that produced by a single turn?
4. (a) State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends.
(b)How does an electromagnet differ from a bar magnet or permanent magnet?
5. How will you experimentally show that a current carrying conductor experiences a force when kept in a magnetic field?
6. What is the principle of an electric motor? Briefly explain the construction and working of an electric motor using a labeled diagram. State the factors on which
the strength of a motor depends.
7. What is meant by electromagnetic inductions? How will you demonstrate this phenomenon with the help of an experiment? State the factors on which the
strength the induced current depends.
8. Briefly describe the principle, construction and working of an AC generator or dynamo.
9. (a) How are electrical installations carried out in a house? (b) What is the main function of electric fuse? Briefly explain it.
10. What safety measures do you employ in the use of electricity?
Please click the link below to download CBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic
effects of electric current Sure Shot Questions A.
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. Also download Class 10 Science Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current is free

