Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Physics Sources of Energy Worksheet Set C. Download printable Science Class 10 Worksheets in pdf format, CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Worksheet has been prepared as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Also download free pdf Science Class 10 Assignments and practice them daily to get better marks in tests and exams for Class 10. Free chapter wise worksheets with answers have been designed by Class 10 teachers as per latest examination pattern
Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Science Worksheet for Class 10
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf in Class 10. This test paper with questions and solutions for Class 10 Science will be very useful for tests and exams and help you to score better marks
Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Worksheet Pdf
Question. A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on :
(a) A sunny day
(b) A cloudy day
(c) A hot day
(d) A windy day
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is not an example of a biomass energy source ?
(a) Wood
(b) Gobar gas
(c) Nuclear energy
(d) Coal
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statement is false ?
(a) Biomass is derived from charcoal.
(b) In the presence of oxygen, biomass undergoes decomposition to form bio gas.
(c) Wind energy converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(d) Solar radiations are converted into electricity called solar energy.
Answer : B
Question. The inhalation of fumes and obnoxious smoke from coal mines causes which type of disease ?
(a) Pulmonary disease
(b) Coronary artery disease
(c) Hepatitis
(d) Liver cancer
Answer : A
Question. Carbon monoxide is an example of ________ .
(a) Primary pollutant
(b) Secondary pollutant
(c) Biodegradable pollutant
(d) Non - Biodegradable pollutant
Answer : A
Question.Match the following
Column I Column II
(a) Rise of sea water (i) Geothermal energy
(b) Sea-wave energy (ii) Solar energy
(c) Energy form earth’s crust (iii) Tidal energy
(d) Energy obtained from sum (iv) Wane energy
Answer : (a) (iii), (b) (iv), (c) (i), (d) (ii).
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Question. If you could use any source of energy for heating your food which one would you prefer? State one reason for your choice.
Answer : I would prefer a solar cooker for heating food because solar cooker is environmental friendly and causes no pollution.
Question. Though a hot iron emits radiations, yet it is not visible in the dark, why ?
Answer : Hot iron emits infra-red rays. These rays are invisible to the eyes.
Question. Name two forms of energy in which solar energy manifests itself in oceans.
Answer : (a) Tidal energy and (b) Ocean thermal energy.
Question. Which part of Sun’s energy is responsible for drying clothes and exposure to which part could be a health hazard ?
Answer : Infra-red (IR) radiations are responsible for drying clothes and ultraviolet (UV) radiations could be a health hazard.
Question. What do you mean by the term ‘thermal power plant’ ?
Answer : Thermal power plant is the power plant where coal is burnt to produce heat energy which is converted into electrical energy.
Question. Why does acid rain happen ?
Answer : Acid rain happens because of burning of fossil fuels which release oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur in the atmosphere.
Question. ‘‘Burning fossil fuels is a cause of global warming.’’ Give reason in support of this statement.
Answer : Burning of fossil fuel produces CO2, oxides of sulphur and nitrogen. CO2 is a greenhouse gas, its excess produces greenhouse effect, increasing earth’s temperature and causes global warming.
Question. Name two constituents of biogas.
Answer : Two constituents of biogas are methane (CH4) and Hydrogen .
Short Answers Type Questions
Question. What are solar cells ? Explain the structure of solar panel. List two principal advantages associated with solar cells.
Answer : Solar cells are the devices which convert solar energy into electricity.
A simple solar cell is made up of sandwich of a siliconboron layer and a silicon-arsenic layer. Boron and arsenic are present in a very small amount. A piece of wire is soldered into the top of upper layer of cell and another piece of wire is soldered at the bottom of the lower layer to pass on the current. The solar cell is covered with a glass cover for protection.
Advantages :
(a) Solar cells have no moving parts.
(b) It requires less maintenance.
Question. While discussing about coal and petroleum a teacher told his students about PCRA’s (Petroleum Conservation Research Association) guidelines to save the fossil fuels while driving vehicles. Deepa was going to her school with her mother who was driving car. At the traffic signal, when the light was red, Deepa suggested her mother to switch off the engine. After reading the above passage, answer the following questions :
(a) Fossil fuels are natural resources, then why do we need to conserve them ?
(b) List any two ways of saving the fossil fuels.
Answer :
(a) Fossil fuels take millions of years in their formation, hence are exhaustible and need to be conserved to provide energy for a longer duration and sustainable development.
(b) Walking short distances or use of public transport.
Where possible switch off unnecessary lights.
Question. (a) Write Einstein’s mass-energy equation. Give the meaning of each symbol which occurs in it.
(b) In nuclear fission of a piece of uranium, 0.5 g of mass is lost, how much energy in MeV is obtained ?
Answer :
(a) According to Einstein, mass and energy are interchangeable and are related by the equation :
E = (Δm) c2
Here, Δm is the loss in mass in kg, c is the speed of light (3 × 108 ms–1) and E is the energy in joule (J).
(b) Here, Δm = 0.5 g = 0.5 × 10–3 kg, c = 3 × 108 ms–1 and
1 MeV = 1.6 × 10–13 J
∴ Energy released, E = (Δm) c2
= [0.5× 10−3 ×(3 ×108 )2]/ 1.6 10−13
4.5 ×1013/1.6 ×10−13 MeV
= 2.8 × 1026 MeV
Long Answers Type Questions
Question. What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumptions ?
Answer :
Environmental consequences of increasing demand for energy are as follows :
(a) Use of fossil fuels is increasing air pollution which is not good for our health.
(b) Air pollution is causing much damage to the ecosystem.
(c) Greenhouse effect has resulted in global warming which is manifesting itself in strange changes in the weather pattern around the world.
(d) Too much exploitation of fossil fuels is going to create a situation when there would be no fossil fuel.
Steps to reduce energy consumption :
(a) Use your household appliances efficiently.
(b) Use public transport instead of private modes of transport.
(c) Use bicycle whenever possible.
(d) Walk for short distance to commute.
(e) Avoid unnecessary use of modern gadgets which consume lot of energy.
(f) Get a solar water heater installed for winters.
Question. (a) What is a biogas plant ?
(b) Name five main parts of fixed dome type biogas plant.
(c) Draw a neat labelled diagram of a fixed dome type biogas plant.
Answer :
(a) The arrangement used for producing biogas from animal dung, human excreta, and domestic waste is known as biogas plant.
(b) A fixed dome type biogas plants consist of :
(i) Mixing tank : In this, slurry, animal dung and other waste materials are mixed.
(ii) Digester : It is a well like underground tank made up of bricks and cement. It has outlet and inlet valves. The roof of the digester is dome shaped. The dome acts as a storage tank of biogas. A gas outlet is fitted at the top of the dome.
(iii) Inlet chamber : It is situated on one side of the digester. It passes the slurry of cattle dung and other waste from the mixing tank to the digester.
(iv) Outlet chamber : It is on the other side of the digester. It is rectangular in shape and constructed with bricks and cement. It is connected to the overflow tank.
(v) Overflow tank : It collects the used slurry or spent slurry. This spent slurry can be used as manure.
Question. What are the merits and limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the deep inside the earth ?
Answer :
Merits of geothermal energy :
(a) It is a renewable source of energy.
(b) It involves low running cost.
(c) It does not create any pollution and help in creating clean environment.
(d) Maintenance cost of geothermal power plant is low.
(e) Geothermal power plants are unaffected by weather and night cycle day.
Limitations of geothermal energy :
(a) Geographically, there are very limited number of places where geothermal power plants are likely to operate effectively.
(b) Enhanced geothermal system can trigger earthquakes, therefore it affect land stability severly.
(c) High up front installation cost required for construction of geothermal power plant and its drilling wells, which requires advance technology.
(d) There is an abundance of greenhouse gases below the earth surface. They can might be escape through the holes drilled during constructions. It leads to global worming and acid rain.
(e) Geothermal Energy cannot be easily transported unlike other source of energy.
Case Study Based Questions
1. Answer question numbers 1(a) to 1(d) on the basis of your understanding of the following paragraph and the related studies concepts.
The Tehri dam is the highest dam in India and one of the highest in the World. The Tehri dam withholds a reservoir of capacity 4.0 km3 and surface area 52 km2. It is used for irrigation, municipal water supply and the generation of 1000 MW of hydroelectricity. The Tehri dam has been the object of protests. Environment activist Shri Sunder Lal Bahuguna led the “Anti Tehri Dam Movement” from 1980s to 2014. The protest was against the displacement of town inhabitants and environmental consequences of the weak ecosystem.The relocation of more than 1,00,000 people from the area has led to protracted legal battles over resettlement rights and ultimately resulted in the delayed completion of the project.
Question. How is hydropower harnessed ?
Answer : Hydro power plants convert the potential energy of water stored at great heights to kinetic energy of flowing water at high speed, then into electricity.
Question. Define 1 MW.
Answer : A megawatt is a unit for measuring power that is equivalent to one million watts. Megawatts are used to measure the output of a power plant or the amount of electricity (energy in per second) required by an entire city. One megawatt (MW) = 1,000 kilowatts = 1,000,000 watts.
Question. Mention two disadvantages of constructing Tehri Dam.
Answer : Major disadvantages of constructing dams are :
(i) People living in Tehri were relocated. They lost their farms and businesses.
(ii) The building of large dams can cause serious geological damage.
Question. What happens when water from great heights is made to fall on blades of turbine ?
Answer : When water from great height is made to fall on turbine it spins the motor of an electricity generator and creates a magnetic field that induces an electric current.
2. Read the following paragraph and answers the following questions :
Solar water heater consists of an insulated metallic box which is painted black from inside and outside In this box copper tubes painted black from outside and fitted in a zig-zag shape. The box and copper tubes are painted black so that they may absorb maximum radiant heat energy of the sun efficiently. The box in covered with a glass sheet lid to trap sun rays by producing greenhouse effect. The two ends of copper tubes are joined to a water storage tank as shown in figure, The solar water heater and its water storage tank are fitted on the roof of a building so that they may absorb the maximum radiant heat energy of the sun.
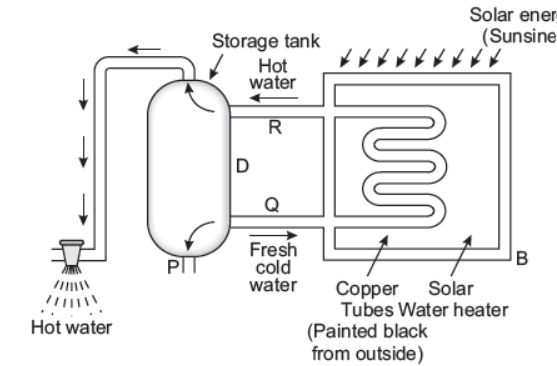
Question. Why metallic box is painted black from outside ?
Answer : Because black colour is good absorber of heat.
Question. What is meant by radiation here ?
Answer : The solar energy received is called radiation.
Question. Why copper tubes are used here ?
Answer : Because copper is good conductor of heat.
Question. What is greenhouse effect ?
Answer : The glass roof and glass walls of a greenhouse allow heat and sunlight to enter it but do not allow heat (infrared radiation) to escape on account of this greenhouse gets warmed.
3. The cost and security of energy and emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) and other pollutants from the existing means of energy production are two main problems that have led to many technological developments in alternative energy sources. Using biomass to produce energy is one such alternative that has recently become attractive worldwide as a clean and sustainable source of energy. Anaerobic digestion (AD) is one of the preferred technologies for treating organic municipal solid waste (MSW) for the production of biogas and methane, which can be used as alternative fuel to liquid petroleum gas (LPG) and natural gas.
Question. Fossil fuels are
(a) Non-renewable source of energy
(b) Renewable source of energy
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following problem is associated with a burning of coal?
(a) Carbon-dioxide emission
(b) Acid rain
(c) Ash with toxic metal supurity
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. __________ is also called a biogas
(a) Biobutanol
(b) Biodiesel
(c) Bioethanol
(d) Biomethane
Answer : D
Question. Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake because
(a) Biogas has lower calorific value.
(b) Animal dung cake has high calorific value
(c) Biogas has high calorific value and leaves no residue
(d) Biogas is used as a fuel for cooking only whereas dung cake can be used for cooking,illuminant the lanterns.
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following organism produces biogas from cow drug sherry in the biogas plant?
(a) Aerobic bacteria
(b) Anaerobic bacteria
(c) Protozoa
(d) Fungi
Answer : B
4. Energy is the primary and most universal measure of all kinds work by human beings and nature. Everything what happens the world is the expression of flow of energy in one of its forms. Energy is the major input to drive the life cycle and improve it. Energy consumption is closely related to the progress of the mankind. The conventional sources of energy are generally non-renewable sources of energy, which are being used since a long time. These sources of energy are being used extensively in such a way that their known reserves have been depleted to a great extent. The sources of energy which are being produced continuously in nature and are in exhaustible are called non-conventional energy (or) renewable sources of energy.
Question. In order to make efficient solar cooker, the cover of cooker box should be made of:
(a) Transparent plastic sheet
(b) Shining aluminium sheet
(c) Butter paper sheet
(d) Transparent glass
Answer : D
Question. The process by which energy is produced in the sun is
(a) Nuclear fission
(b) Nuclear fusion
(c) Both nuclear fusion and fission
(d) Combustion of hydrogen
Answer : B
Question. The rise of sea-water during high tide is caused by the gravitational pull of the:
(a) Sun
(b) Earth
(c) Moon
(d) Mars
Answer : C
Question. In a hydroelectric power plant more electrical power can be generated if water falls from a greater height because:
(a) Its temperature increases.
(b) Larger amount of potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
(c) The electricity content water increases with height.
(d) More water molecules dissociate into ions.
Answer : B
Question. Greenhouse effect in solar cooker is due to:
(a) Mirror
(b) Glass plate
(c) Outer cover
(d) Coating with black colour
Answer : A
Very Short Answer
Question. What happens when coal burns?
Answer : When coal burns it produces heat, so it is called fuel.
Question. What are hydro carbons?
Answer : Compounds of hydrogen and carbon are called hydrocarbon.
Question. Define source of energy?
Answer : A source of energy is one which can provide adequate amount of energy in a convenient form over a long period of time.
Question. What is a fuel?
Answer : The materials which are burnt to produce heat energy are known as fuel.
Question. Which fuel has the lowest calorific value?
Answer : Dung cakes (uple) have the lowest calorific value i.e. (6 to 8 kJ/ g).
Short Answer
Question. Why coal is most important source of energy?
Answer : Coal is one of the most important sources of energy and is being used for various proposes such as heating of housed, as fuel for boilers and steam engines and for generation of electricity by thermal plants. Burning of the coal produces heat energy.
Question. What do you mean by calorific value?
Answer : The amount of the heat produced by burning a unit mass of the fuel completely is known as its calorific value. The unit of the mass measured the calorific value of the fuel is gram, so the amount of heat produced by the burning of 1 gram of a fuel completely is called its calorific value. The common unit of measuring calorific value is kilojoules per gram (kJ/g).
Question. How fossil fuels are formed?
Answer : Fossil fuels are formed when organic matter that has been buried deep within the earth is subject to heat and pressure over millions of years. In the absence of the oxygen, the chemical effects of the pressure, heat and bacteria converted the buried remains of the plants and animals into the fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Question. What do you understand by an ignition temperature?
Answer : The minimum temperature to which a fuel must be heated so that it may catch the fire and start burning is known as the ignition temperature. The substances which have a very low ignition temperature and catch fire at a very low temperature.
Question. Why hydrogen has a highest calorific value?
Answer : Hydrogen has the highest calorific value, it is not used as a domestic fuel. It is because hydrogen is a highly combustible and it reacts explosively when it comes in contact with air. So, even though hydrogen has the highest calorific value, it is not used as a domestic fuel.
Long Answer
Question. Explain what is the good source of energy?
Answer : When we do work we needed energy, we get energy from the source of the energy and it depends on the type of work. The most common source of energy is available to us is fuels. The characteristic of the good sources of the energy are:
1. Good source of energy would do a large amount of the work per unit mass or per unit volume.
2. Good source of energy should be cheap and easily available.
3. Good source of energy is easy to store and transport.
4. Good source of the energy is safe to handle and use.
5. Good source of the energy does not cause environment pollution.
6. Good source of energy should be easily accessible and provide energy for the maximum period of time.
Question. Difference between renewable and non- renewable source of energy?
Answer : 1. The source of energy which are being produced continuously in nature and inexhaustible are called renewable source of energy whereas the source of energy which have accumulated in nature over a very long time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted are called non- renewable source of energy.
2. The renewable source of energy is also known as non- conventional sources of energy whereas the non- renewable source of energy is also known as conventional source of energy.
3. The renewable source of energy has low carbon emission and its environment friendly whereas the non- renewable source of energy has high carbon emission and it not environment friendly.
4. The renewable source of energy is present in unlimited quantity whereas the non-renewable source of energy is present in limited quantity and vanishes one day.
5. The renewable sources of energy are pollution free whereas the non- renewable sources of energy are not pollution free.
6. Solar energy. Tidal energy, wind energy etc.,, are the example of renewable source of energy whereas coal, petroleum, natural gas are the example of the non- renewable source of the energy.
Question. Explain fossil fuels and why sun is the ultimate source of fossil fuels?
Answer : A fossil fuel is a fuel formed by natural processes, such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, containing energy originating in ancient photosynthesis. Such organisms and their resulting fossil fuels typically have an age of millions of years, and sometimes more than 650 million years. Fossil fuels are found in almost every product we use daily. One major use of these products is as fuel, gasoline for cars, jet fuel, heating oil and natural gas used to generate electricity. The four types of fossil fuels are petroleum, coal, natural gas and Orimulsion. Coal is formed from ferns, plants and trees which are hardened due to pressure and heat, oil is formed from smaller organisms like algae. Intense amounts of pressure caused this complex organic matter to decompose the oil, natural gas undergoes the same process as oil. Sun is ultimate source of energy of fossil fuels, because the sun’s light energy helps plants to photosynthesize. So the fossil fuels contain the sun's power stored up inside of dead and decayed organisms that have been pressurized, heated and buried. Plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy (food) by the process of photosynthesis. Animals eat plants and use that same chemical energy for all their activities. Fossil fuels are energy rich compounds of the carbon which were originally
made by the plants with the help of the sun’s energy.
Question. What are the characteristics of the ideal fuel?
Answer : Characteristics of an ideal fuel are:
1. It should give the high calorific value, an ideal fuel is that which does not give us more heat per unit mass.
2. It should burn without giving out any smoke or harmful, gases an ideal fuel is that which does not pollute air on burning by giving out smoke or poisonous gases.
3. It should be cheap and easily available, an ideal fuel is that which is not expensive and which is available in plenty everywhere.
4. It should be easy to handle, safe to transport and convenient to store, an ideal fuel is that which does not create any safety risks during handling, during its transportation from one place to another or during its storage.
5. It should burn smoothly, an ideal fuel should have a moderate rate of combustion and burn at a steady rate.
6. It should not leave much ash behind after the burning, an ideal fuel should have low percentage of non- volatile materials which do not burn so that it may burn completely without leaving much ash.
Question. Write short note on coal and what are the uses of coal?
Answer : Coal is a complex mixture of compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and some free carbon. Small amounts of nitrogen and sulphur compounds are also present in the coal. Coal is important because it can be used as a source of the energy. Coal is a hard rock which can be burned as a solid fossil fuel. It is a sedimentary rock formed from peat, by the pressure of rocks laid down later on top. A lot of the heat is produced during the burning of coal which makes it a good fuel. Coke is a better fuel than coal because it produces more heat than an equal mass of coal and it does not produce smoke while burning. Coke is 98% carbon. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years.
Uses of coal:
1. Coal is used as a fuel for heating purposes in homes and in industry.
2. Coal is used as a fuel in thermal power plants for generating electricity.
3. Coal is used in the manufacture of fuel gases like coal gas.
4. Coal is used to make coal.
5. Coola is used in the manufacture of petrol and synthetic natural gas.
| CBSE Class 10 Biology Heredity And Evolution Set D |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Refraction of Light Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Refraction of Light Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Refraction and Refraction Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Worksheet Set E |
| CBSE Class 10 Biology Our Environment Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Biology Our Environment Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Biology Our Environment Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Biology Management of Natural Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Biology Management of Natural Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Biology Management of Natural Resources Worksheet Set C |
Chapter 14 Sources of Energy CBSE Class 10 Science Worksheet
The above practice worksheet for Chapter 14 Sources of Energy has been designed as per the current syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students studying in Class 10 can easily download in Pdf format and practice the questions and answers given in the above practice worksheet for Class 10 Science on a daily basis. All the latest practice worksheets with solutions have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Printable Worksheets for Class 10 Science students to get all the latest study material free of cost. Teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the practice sheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 10 Science which you can use to further make yourself better in Science.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Class 10 Science have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 10 CBSE Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

