Structure of Atom
Subatomic Particles:
Atomic Models:
Thomson’s Atomic Model (Plum – pudding model):-
Postulate: -Atom is a sphere of positive charge in which number of electrons are embedded.
Limitations: - Could not satisfactorily explain the results of scattering experiment carried out by Rutherford.
Rutherford’s Model:
Postulates:-
• Almost all the positive charge and mass of atom is present in its nucleus.
• Electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular orbits.
• There is strong electrostatic attraction between nucleus and electrons
Limitations: - Could not explain stability and electronic structure of atom.
Atomic Terms


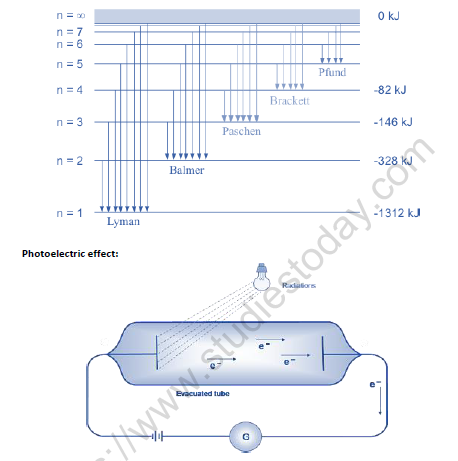
• Ejection of electrons takes place from the surface of metal when light of suitable frequency fall on it.
• Minimum frequency required for ejection of electron is called threshold frequency (vo).
• Energy of the ejected electrons is directly proportional to the frequency of radiation.
• Number of electrons ejected per second depends on the intensity of radiation.
• hv- hvo =1/2mev 2
Planck’s quantum theory:
Substances radiate or absorb energy discontinuously in the form of energy packets
The smallest packet of energy is called quantum. In case of light the quantum is known as photon.
The energy of a quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.
E = hv were v is the frequency of radiation and h is Planck’s constant having the value 6.626 × 10–27 erg sec or 6.626 × 10–34 J sec.
A body can radiate or absorb energy in whole number multiples of quantum hn, 2hν,3hν………..nhν,where n is the positive integer.
Bohr’s atomic model:
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular orbits of fixed energy.
Electron revolve only in those orbits whose angular momentum (mvr) is an integral multiple of h/2Π.
Electron absorbs energy in the form of EMR, when it jumps from lower energy level (ground state) to higher energy level (excited state) and vice-versa.
Energy absorbed or released in an electron jump, (dE) is given by dE = E2 – E1 = hν
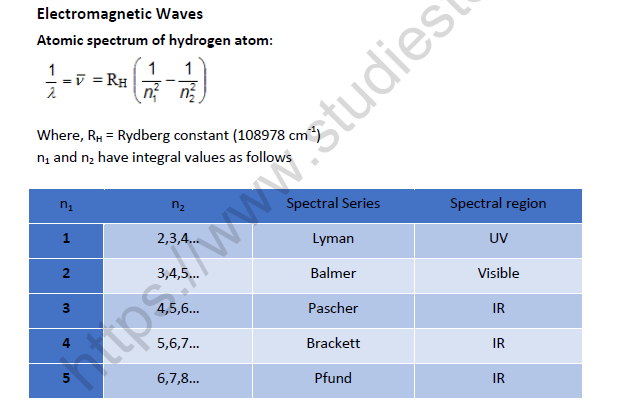
Energy of stationary state oh hydrogen atom (En) = -RH (1/n2)
For an hydrogen like species i.e. He+, Li2+ with atomic number Z
Radius of nth orbit (rn ) = 52.9 × n2/z pm
Energy of nth orbit (En) = -2.18×10-18(Z2/n2) = –13.6 ×(Z2/n2) eV = 313.6 ×(Z2/n2) kcal /mole
Velocity of electron (v) = (2.18 ×108 ) z/n cms-1
Where n = 1,2,3,4…
Please click the link below to download pdf file of NEET Chemistry Structure of Atom Revision Notes

